-
你真的了解C语言 if - else 、bool(布尔值)、浮点数损失吗 ?
你真的了解C语言 if - else 、bool(布尔值)、浮点数损失吗 ?

每博一文案
我们路上遇见很多人 但不是所有人都会去同一个地方,有的人陪我们走过一段岁月, 也有人会陪我们走过岁岁年年,该是我们的跑也跑不掉,不该我们的求也求不得得失。 皆是缘来去一匆匆,花字向阳开,人中向前走。 有些人遇见了是种幸运,而有些人错过了才是幸运。 有些事我有经历过了,才会深刻地记住,时光,不会证明很多东西, 但会让我们看透很多东西。 人生很短,不妨尽心一点,从此去爱这山。 这水,这世间万物,和自己别再拘泥于,过往,余生不求深刻,只求简单 一念当下即是自在。 岁月深长,万物有期。 把圈子变小,把语速放缓,把心放宽,把生活打理简单,用心做好手边事, 该有的总会有,越努力,生活的你,有属于自己的风雨灿烂, 也愿余生守住所有的情绪,好好生活。 ———————————— 一禅心灵庙语- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
if
- if 的执行方式
- 先执行 ( ) 括号中的表达式,得到真假的结果:i ++、i –
- 条件的判断功能:== 、!=
- 进行分支的判断 :else 、else if( )
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int flag = 3; if (3 == flag) { printf("1\n"); } else if (2 == flag) { printf("2\n"); if (1) { printf("HelloWorld\n"); } } else { printf("else\n"); } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- else 总是和最近没有被匹配的 if 相匹配起来
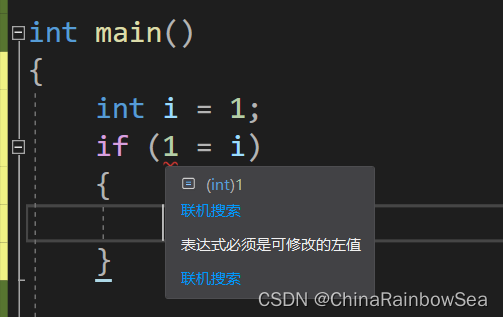
- 使用 if 判断数值的时候,我们可以把 数值放在等于号的左边,这样的好处就是:当我们把 ==(等号)不小心写成了 =(赋值)的时候,会给我们报错 (表达式必须是可修改的左值) ,是因为赋值是 (从左往右) 赋值的,左边必须是变量,从而提醒我们修改过来,防止出现大问题
- 如果判断一个函数返回值的真假,而该函数的返回值,也只是两种结果:真假 的话,建议直接写,直接调用,不要附加上什么,func( ) == 0、func( )== 1,之类的。
#include<stdio.h> int func() { return 1; } int main() { if (func) { prinntf("推荐使用这种判断方式\n"); } if (1 == func) { printf("不推荐使用这种判断方式\n"); } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
bool(布尔)变量
- 许多人都是认为C语言是没有布尔值的,这句话说的是对的也是错的,因为在不同的标准中有不同的说法
- bool(布尔值),在c89 、C90 的C语言标准中是没有布尔值类型的
- bool(布尔值),是在c99 ,c11 的C语言标准中引入的新特性:在头文件 #include<stdbool.h> 库中
- 下面是:c99 中布尔值的源码:
// // stdbool.h // // Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. // // The C Standard Library <stdbool.h> header. // #ifndef _STDBOOL #define _STDBOOL #define __bool_true_false_are_defined 1 #ifndef __cplusplus #define bool _Bool #define false 0 #define true 1 #endif /* __cplusplus */ #endif /* _STDBOOL */- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 从源码中我们可以看到,其布尔值中 false 是 定义的宏 为 0 、ture 是定义的宏为 1
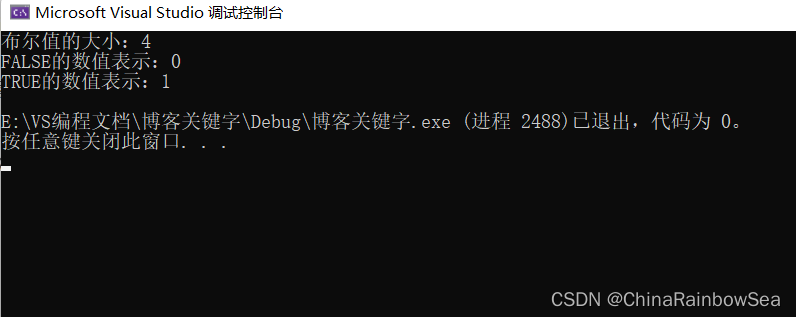
- 在c90,c11 的标准中布尔值的所占空间的大小为 1个字节 ,如下:
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdbool.h> // 布尔值的使用需要导入该头文件 int main() { bool x = false; printf("布尔值的大小:%d\n", sizeof(x)); printf("false的数值表示:%d\n", false); printf("true的数值表示:%d\n", true); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
运行结果:

- 在C语言中还有套微软的执行标准中也是引入了布尔值的,是为 int 类型的
- 源码如下:
typedef unsigned long DWORD; typedef int BOOL; // 这里******** typedef unsigned char BYTE; typedef unsigned short WORD; typedef float FLOAT; typedef FLOAT *PFLOAT; typedef BOOL near *PBOOL; typedef BOOL far *LPBOOL; typedef BYTE near *PBYTE; typedef BYTE far *LPBYTE; typedef int near *PINT; typedef int far *LPINT; typedef WORD near *PWORD; typedef WORD far *LPWORD; typedef long far *LPLONG; typedef DWORD near *PDWORD; typedef DWORD far *LPDWORD; typedef void far *LPVOID; typedef CONST void far *LPCVOID; typedef int INT; typedef unsigned int UINT; typedef unsigned int *PUINT;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 微软的执行标准中布尔值的大小为 4个字节 ,同样 FALSE 的数值表示 为 0 ,TRUE 的数值表示 1
int main() { BOOL x = FALSE; printf("布尔值的大小:%d\n", sizeof(x)); printf("FALSE的数值表示:%d\n", FALSE); printf("TRUE的数值表示:%d\n", TRUE); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
运行结果
- 好了,如果我们真的需要在 C 中使用 布尔值的话,建议使用 C99 中的执行标准,因为兼容性强,而微软中的是,Microsoft自己搞的一套BOOL值 ,只适用于微软它本身,不适用于其他
浮点数损失
- 浮点数在内存中的存储,并不是我们简单想的完整存储的,在十进制转化二进制,是有可能存在精度上的损失的
- 注意这里的损失 ,不是一味的减少,还有可能增多,浮点数本身存储的时候,在计算不尽的时候,会有 “四舍五入”或者 其他的策略的
- 如下:
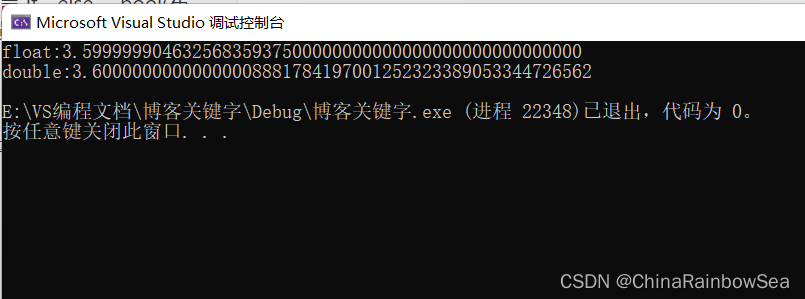
#include<stdio.h> int main() { float x = 3.6f; // 这里注意;float类型加上后缀 f,因为 c中 小数默认是 double 类型的 double y = 3.6; printf("float:%.50f\n", x); printf("double:%.50f\n", y); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
运行结果
-
从上面 运行的结果 的我们可以发现其中 float 中的精度的丢失更大,double 的精度更高
-
因为精度损失问题,两个浮点数,绝对不能直接使用==进行相等比较判断的 。如下
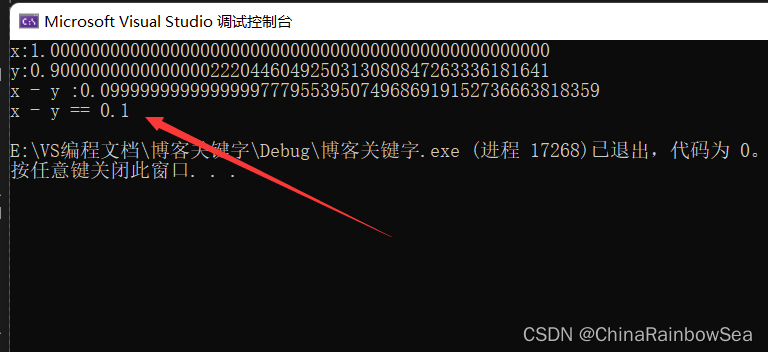
#include<stdio.h> int main() { double x = 1.0; double y = 0.9; printf("x:%.50f\n", x); printf("y:%.50f\n", y); printf("x - y :%.50f", x - y); if ((x - y) == 0.1) { printf("x - y == 0.1 \n"); } else { printf("x - y != 0.1 \n"); } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
运行结果
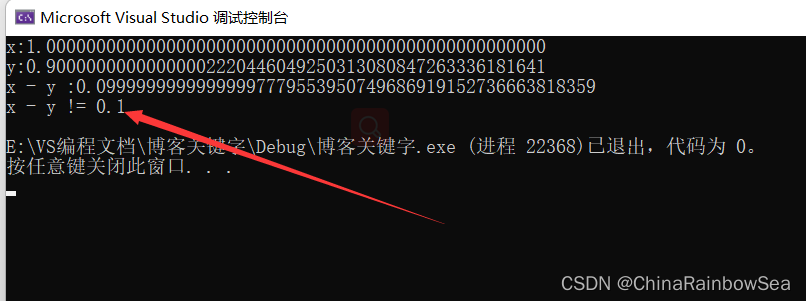
- 从 运行的结果 上看我们会发现只要存在一些较小的误差,计算机也是会不匹配的,从而导致不相等
- 如果我们一定要使用 浮点数进行比较判断呢,也是有办法的
- 我们可以规定一个误差范围,只要结果上的误差是在该范围之内的,我们就可以认定为是符合的,相等的
- 我们可以使用 宏 来规定该误差范围,代码如下:
if ( x - y ) > (- 精度) && ( x- y ) < ( 精度 ) 绝对值 因为存在差值上的正负
{
}
if ( fabs (x - y )) < 精度 ) // fabs 求浮点数的绝对值,需要导入头文件 #include <math.h>
{
}
#define EPS 0.0000000001 // 注意定义宏不要加分号 ; int main() { double x = 1.0; double y = 0.9; printf("x:%.50f\n", x); printf("y:%.50f\n", y); printf("x - y :%.50f\n", x - y); if ((x - y) - 1.0 < EPS) { printf("x - y == 0.1 \n"); } else { printf("x - y != 0.1 \n"); } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
运行结果。与上面的结果不同,这里是 x - y == 0.1 的

- 其中,我们的 C语言 中自带了这样一种,精度误差的范围,在头文件 #include<float.h> 中的 DBL_EPSILON
- 源码如下:
//-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ // // Constants // //-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ #define DBL_DECIMAL_DIG 17 // # of decimal digits of rounding precision #define DBL_DIG 15 // # of decimal digits of precision #define DBL_EPSILON 2.2204460492503131e-016 // smallest such that 1.0+DBL_EPSILON != 1.0 #define DBL_HAS_SUBNORM 1 // type does support subnormal numbers #define DBL_MANT_DIG 53 // # of bits in mantissa #define DBL_MAX 1.7976931348623158e+308 // max value #define DBL_MAX_10_EXP 308 // max decimal exponent #define DBL_MAX_EXP 1024 // max binary exponent #define DBL_MIN 2.2250738585072014e-308 // min positive value #define DBL_MIN_10_EXP (-307) // min decimal exponent #define DBL_MIN_EXP (-1021) // min binary exponent #define _DBL_RADIX 2 // exponent radix #define DBL_TRUE_MIN 4.9406564584124654e-324 // min positive value- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 运用 头文件 #include<float.h> 中的 DBL_EPSILON
#include<stdio.h> #include<float.h> // 精度范围 #include<math.h> // 浮点数绝对值 int main() { double x = 1.0; double y = 0.9; printf("x:%.50f\n", x); printf("y:%.50f\n", y); printf("x - y :%.50f\n", x - y); if ( (fabs(x-y) - 0.1 ) < DBL_EPSILON) // fabs 计算浮点数的绝对值,DEL_EPSILON 精度差 { printf("x - y == 0.1 \n"); } else { printf("x - y != 0.1 \n"); } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
运行结果
最后:
限于自身水平,其中存在的错误,希望大家给予指教,韩信点兵 —— 多多益善,谢谢大家,后会有期,江湖再见!
-
相关阅读:
Python 三维网格体素化
《羊了个羊》微信小游戏为什么火了?
彻底搞懂Mybatis
巧用 CSS 构建渐变彩色二维码
【Python脚本进阶】2.2、构建一个SSH僵尸网络(上):SSH交互脚本
Python基本语法元素
【JSP 基础】
gulimall基础篇回顾Day-14
DAY57
kube-prometheus 系列1 项目介绍
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_61635597/article/details/125516867
