-
【Kafka】MirrorMaker 一次错误的配置引发的血案
前言
最近
Mirror Maker需要增加同步几个topic到下游Kafka集群。修改配置后,重启Mirror Maker服务后一直无法正常消费。报(Re-join group)的错误。这里整理并记录一下。一、报错现象
Mirror Maker一直在卡在了这,然后上游Kafka服务没有明显的日志输出。过段时间后,MM服务就自动退出了。- 伴随着服务所在节点
cpu使用率升高,使用率大概在500%。
pool-16-thread-13 org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.AbstractCoordinator (Re-)joining group- 1
二、问题分析
一开始,观察到服务没有别的异常输出,只是在频繁的打印
(Re-) join group,由于无法登录服务器,所以无法打印服务的jstack信息,只是根据CPU的异常使用率,怀疑是与锁/GC 有关,只能根据现有的工具来排查问题。1. 调大
JVM既然怀疑是与 锁 / GC 有关,那么先从GC 入手,调大
JVM Heap大小。然后观察服务情况。重启服务后,发现问题没有解决,依然是服务无法正常消费数据,然后服务CPU 使用率高。
那么只可能是与锁有关了,但是无法打印服务的堆栈信息,只能求助
CDH原厂专家了。2. 重要的配置
num.streams专家介入后,很快发现我们的
num.streams和num.produces这两个参数设置的很不合理。我们生产上的配置:
num.streams设置了 700num.producers设置了400
经过介绍,
num.producers这个配置,即使配置了也不会生效,默认是1,所以这个配合就算改了还好,但是确实是过大了。影响最大的是
num.streams这个配置,这个配置是:-
每个线程实例化并使用一个消费者。
MM线程和消费者之间的1:1映射。 -
每个线程共享同一个生产者。线程和生产者之间的N:1映射。
这里我们一共起了 3 个
MM实例,每个实例700个线程,也就是 700 个消费者,总共 2100 个消费者,但是我们需要消费的topic全部的分区数加起来预估可能也才 200 个左右。误区
综上,很明显我们消费者是远远大于分区数的。这里我们陷入了误区,因为一开始服务是能正常使用的,只是我们多订阅了几个
topic,然后重启服务,就不可用了,一开始没往这个地方想,而且即使消费者数量多了,最多导致很多的线程空载,不会实际消费数据,应该也无所谓。三、解决方案
这里的解决方案也很简单, 降低
num.streams为 50。核心思想:
降低消费者的数量,减少 stop-the-world Rebalaning 次数。四、问题原理
负载平衡和调度是每个分布式系统的核心,
Apache Kafka也不例外。Kafka 客户端使用组管理 API 来形成协作客户端进程组。这些客户端形成组的能力由 Kafka 代理促进,该代理充当参与组的客户端的协调器。客户端之间的实际负载分配发生在它们之间,这样就不会给
Kafka服务带来压力,每当需要在客户端之间分配负载时,就会开始新一轮的再平衡,在此期间所有进程都会释放它们的资源。在此阶段结束时,重申组成员身份并选举组领导,每个客户端都被分配一组新资源。简而言之,这也称为stop-the-world rebalancing,这个短语可以追溯到垃圾收集文献。stop-the-world Rebalancing带来的挑战
- 放大和缩小:毫不奇怪,在重新平衡的同时停止世界的影响与参与进程之间平衡的资源数量有关。例如,在空的 Connect 集群中启动 10 个 Connect 任务与在运行 100 个现有 Connect 任务的集群中启动相同数量的任务是不同的。
- 异构负载下的多租户:这里的主要示例是 Kafka Connect。当另一个连接器(可能来自另一个用户)被添加到集群中时,停止连接器任务的副作用不仅是不可取的,而且还会大规模破坏。
- Kubernetes 进程死亡:无论是在云中还是在本地,故障都是不寻常的。当一个节点发生故障时,另一个节点会迅速替换它,尤其是在使用 Kubernetes 这样的编排器时。理想情况下,一组 Kafka 客户端能够在不执行完全重新平衡的情况下吸收这种暂时的资源损失。一旦节点返回,之前分配的资源将立即分配给它。
- 滚动弹跳:间歇性中断不仅是由于环境因素而偶然发生的。作为计划升级的一部分,它们也可以被有意安排。但是,应避免完全重新分配资源,因为缩减只是暂时的。
这里引用了
https://www.confluent.io/blog/incremental-cooperative-rebalancing-in-kafka/的测试数据。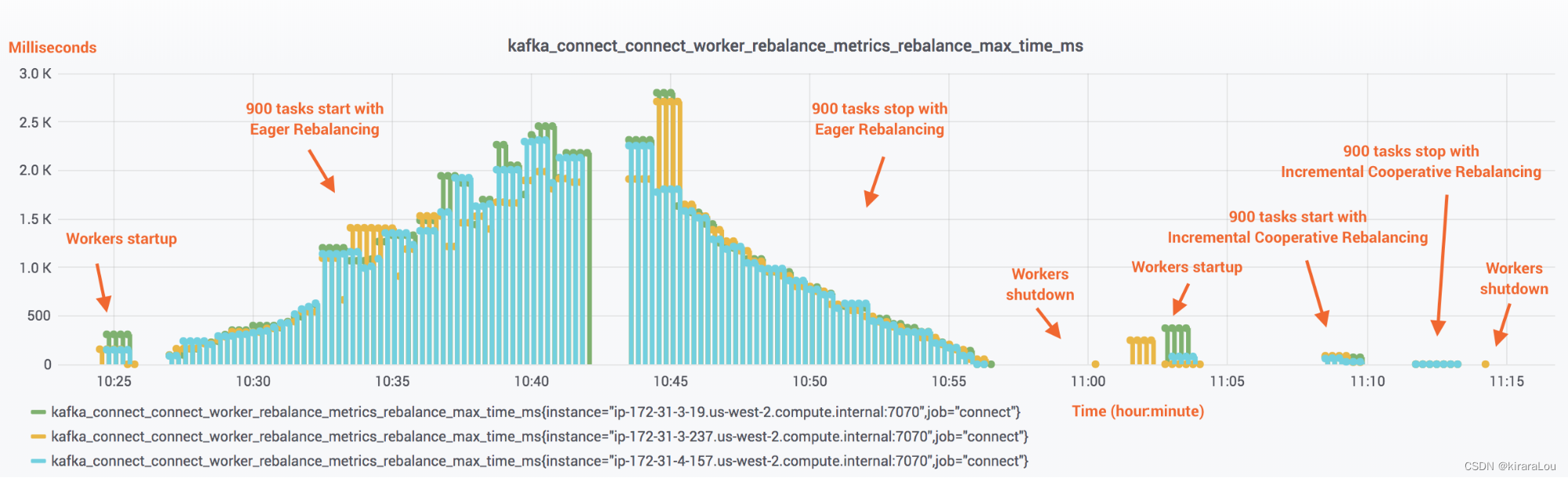
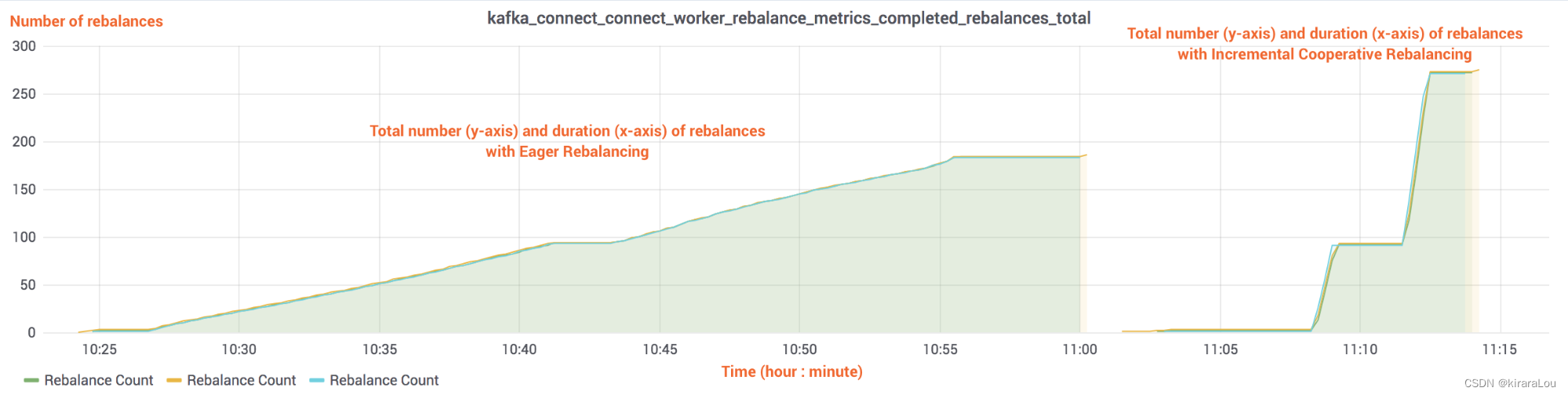
可以看到,当连接器及其任务启动或停止时 stop-the-world)的成本与集群中当前运行的任务数量成正比。从上文得知,我们的消费者数量过大,就会导致
频繁的进行Rebalancer,然后就会出现频繁的(Re-) join group。而且由于客户端代码的实现很多地方都是synchronized,更加重了锁竞争,导致CPU使用率过高的问题。五、相关代码
直接相关
RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> sendJoinGroupRequest() { if (coordinatorUnknown()) return RequestFuture.coordinatorNotAvailable(); // send a join group request to the coordinator log.info("(Re-)joining group"); JoinGroupRequest.Builder requestBuilder = new JoinGroupRequest.Builder( new JoinGroupRequestData() .setGroupId(rebalanceConfig.groupId) .setSessionTimeoutMs(this.rebalanceConfig.sessionTimeoutMs) .setMemberId(this.generation.memberId) .setGroupInstanceId(this.rebalanceConfig.groupInstanceId.orElse(null)) .setProtocolType(protocolType()) .setProtocols(metadata()) .setRebalanceTimeoutMs(this.rebalanceConfig.rebalanceTimeoutMs) ); log.debug("Sending JoinGroup ({}) to coordinator {}", requestBuilder, this.coordinator); // Note that we override the request timeout using the rebalance timeout since that is the // maximum time that it may block on the coordinator. We add an extra 5 seconds for small delays. int joinGroupTimeoutMs = Math.max(rebalanceConfig.rebalanceTimeoutMs, rebalanceConfig.rebalanceTimeoutMs + 5000); return client.send(coordinator, requestBuilder, joinGroupTimeoutMs) .compose(new JoinGroupResponseHandler()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
初始化加入组
private synchronized RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> initiateJoinGroup() { if (joinFuture == null) { // fence off the heartbeat thread explicitly so that it cannot interfere with the join group. // Note that this must come after the call to onJoinPrepare since we must be able to continue // sending heartbeats if that callback takes some time. disableHeartbeatThread(); state = MemberState.REBALANCING; // a rebalance can be triggered consecutively if the previous one failed, // in this case we would not update the start time. if (lastRebalanceStartMs == -1L) lastRebalanceStartMs = time.milliseconds(); joinFuture = sendJoinGroupRequest(); joinFuture.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<ByteBuffer>() { @Override public void onSuccess(ByteBuffer value) { synchronized (AbstractCoordinator.this) { } else { log.info("Generation data was cleared by heartbeat thread. Rejoin failed."); recordRebalanceFailure(); } } } @Override public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) { synchronized (AbstractCoordinator.this) { recordRebalanceFailure(); } } private void recordRebalanceFailure() { state = MemberState.UNJOINED; sensors.failedRebalanceSensor.record(); } }); } return joinFuture; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
相关调用
/** * Ensure the group is active (i.e., joined and synced) * * @param timer Timer bounding how long this method can block * @throws KafkaException if the callback throws exception * @return true iff the group is active */ boolean ensureActiveGroup(final Timer timer) { // always ensure that the coordinator is ready because we may have been disconnected // when sending heartbeats and does not necessarily require us to rejoin the group. if (!ensureCoordinatorReady(timer)) { return false; } startHeartbeatThreadIfNeeded(); return joinGroupIfNeeded(timer); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
客户端最开始调用
public void poll(long now, long remainingMs) { invokeCompletedOffsetCommitCallbacks(); if (subscriptions.partitionsAutoAssigned()) { ... if (needRejoin()) { ... ensureActiveGroup(); ... } } else { ... } } pollHeartbeat(now); maybeAutoCommitOffsetsAsync(now); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
六、总结
MM是一个 kafka conect。MM一个线程对应一个消费者,这个线程会在开始时订阅需要消费的全部topic ,由内部的客户端来实现负载均衡。也就是会进行多次的rebalancer和(re-) join group.MM最好通过水平横向扩展实例来提高性能,因为num.producers配置是写死的。Kafka消费者数量与 rebalancer时间 和 次数有绝对的影响,不要调到过高。MM内部的消费线程是CountDownLatch实现的。在关闭MM服务时,也会出现频繁重平衡问题,因为关闭一个线程,就会触发重平衡。所以这个参数切记调小。
参考
- http://luojinping.com/2017/11/12/%E8%A7%A3%E5%86%B3-Kafka-Consumer-%E5%8D%A1%E9%A1%BF%E7%9A%84%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98/
- https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/KAFKA-9140
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/incremental-cooperative-rebalancing-in-kafka/
- https://www.cnblogs.com/keepal/p/14729336.html
-
相关阅读:
Rust的协程机制:原理与简单示例
EMCC 删除配置错误的数据库信息 以及修改度量METRICS
Redis-分布式锁
用Redis实现延迟队列,我研究了两种方案,发现并不简单
windows10下安装Mujoco 详细安装教程 + 附安装包
性能测试工具:如何录制脚本?
第2章 模拟器/真机对后端数据的获取之前端实现
0x61c88647斐波那契数列
Java—封装、继承、多态
精准测试之分布式调用链底层逻辑
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Mrerlou/article/details/125496643