-
MyBatis-Plus 入门与实践
MyBatis-Plus 入门与实践
尚硅谷的课程笔记
一、 MyBatis-Plus 简介
1. 简介
Mybatis-Plus(简称 MP)是一个MyBatis的增强工具,在MyBatis的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。MyBatis-Plus提供了通用的mapper和service,可以在不编写任何SQL语句的情况下、快速的实现对单表的CRUD、批量、逻辑删除、分页等操作。
愿景:我们的愿景是成为 MyBatis 最好的搭档,就像魂斗罗中的 1P、2P,基友搭配,效率翻倍。


2. 特性

注意:MyBatis只能生成mapper接口,映射文件,实体类!3. 支持数据库

4. 框架结构
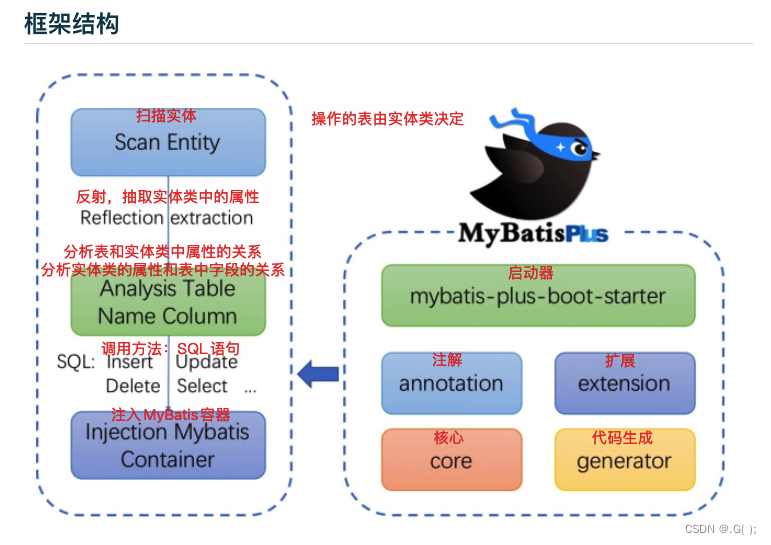
5. 代码及文档地址
MyBatis-Plus官网:https://baomidou.com/

代码发布地址:
Github:https://github.com/baomidou/mybatis-plus
Gitee:https://gitee.com/baomidou/mybatis-plus
文档发布地址:https://baomidou.com/pages/24112f/二、 入门案例
1. 开发环境
IDE:idea 2021.3.3
JDK:JDK8+
构建工具:maven 3.5.4
MySQL版本:MySQL 8.0.162. 创建数据库表
a>创建表
CREATE DATABASE `mybatis_plus` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 */; use `mybatis_plus`; CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID', /*mybatis-plus使用的是雪花算法,ID比较长,因此需要使用bigint*/ `name` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄', `email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
b>添加数据
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@qq.com'), (2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@163.com'), (3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@outlook.com'), (4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@162.com'), (5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@gmail.com');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3. 创建Spring Boot工程
a> 先查看Maven地址,idea每一个初始化maven项目会初始化一个maven仓库我感觉有些繁琐,都使用自己的吧
Win版idea:Configure -> Settings
macOS版idea:IntelliJ IDEA -> Preferences…

b> 初始化工程
使用Spring Initializr 快速初始化一个Spring Boot工程




c>引入依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--mybatis-plus 启动器--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <!--lombok 用于简化实体类开发--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <!--mysql驱动 springboot自带的mysql--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
d>idea中安装lombok插件,必要时需要重启idea!
e> 文件结构

application.properties和application.yml选一个配置就好!application.properties 通过
.分隔
application.yml 通过:分隔,格式要求高4、编写代码
4.1 设置数据源(Spring Boot默认)和sql驱动类:
4.1.1
application.properties文件的配置spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver- 1
- 2
设置sql驱动类:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=
4.1.2
application.yml文件的配置application.yml文件中,如果配置拥有相同的配置前缀,可以不写,按上下级结构配置:spring: # 配置数据源信息 datasource: # 配置数据源类型 type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource # 配置连接数据库的各个信息 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false username: root password: *****- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.1.3 注意:
1、驱动类
driver-class-name
spring boot 2.0(内置jdbc5驱动),驱动类使用:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring boot 2.1及以上(内置jdbc8驱动),驱动类使用:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
否则运行测试用例的时候会有 WARN 信息
2、连接地址url
MySQL5.7版本的url:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
MySQL8.0以上版本的url:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
否则运行测试用例报告如下错误:
java.sql.SQLException: The server time zone value ‘Öйú±ê׼ʱ¼ä’ is unrecognized or represents more4.2 启动类
数据库表和实体类要形成映射关系!
建立启动类:
package com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo; public class User { private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
快捷键:
Windows:alt + insert
macOS:command+N
创建有参构造和无参构造


添加get和set方法:


因为使用了Lombok 用于简化实体类开发,因此我们可以直接在类上添加@NoArgsConstructor即可生成无参构造

可以点击右侧Maven菜单栏的中的clean清除掉生成的target文件夹package com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo; import lombok.*; @NoArgsConstructor //无参构造 @AllArgsConstructor //有参构造 @Getter //get方法 @Setter //set方法 @EqualsAndHashCode //equal和hashCode方法 public class User { private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
生成target文件夹里的User类:
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by FernFlower decompiler) // package com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo; public class User { private Long id; private String name; private Integer age; private String email; public User() { } public User(final Long id, final String name, final Integer age, final String email) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.email = email; } public Long getId() { return this.id; } public String getName() { return this.name; } public Integer getAge() { return this.age; } public String getEmail() { return this.email; } public void setId(final Long id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(final String name) { this.name = name; } public void setAge(final Integer age) { this.age = age; } public void setEmail(final String email) { this.email = email; } public boolean equals(final Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (!(o instanceof User)) { return false; } else { User other = (User)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } else { label59: { Object this$id = this.getId(); Object other$id = other.getId(); if (this$id == null) { if (other$id == null) { break label59; } } else if (this$id.equals(other$id)) { break label59; } return false; } Object this$age = this.getAge(); Object other$age = other.getAge(); if (this$age == null) { if (other$age != null) { return false; } } else if (!this$age.equals(other$age)) { return false; } Object this$name = this.getName(); Object other$name = other.getName(); if (this$name == null) { if (other$name != null) { return false; } } else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) { return false; } Object this$email = this.getEmail(); Object other$email = other.getEmail(); if (this$email == null) { if (other$email != null) { return false; } } else if (!this$email.equals(other$email)) { return false; } return true; } } } protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) { return other instanceof User; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = true; int result = 1; Object $id = this.getId(); int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode()); Object $age = this.getAge(); result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode()); Object $name = this.getName(); result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); Object $email = this.getEmail(); result = result * 59 + ($email == null ? 43 : $email.hashCode()); return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
以上方法比较麻烦,可以使用
@Data进行简化package com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo; import lombok.*; @Data //代替使用其他的Lombok注释 无参构造、get和set方法、equal和hashCode方法、toString方法 public class User { private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
生成的所有方法:

4.3 添加mapper

MyBati-Plus为我们提供了通用的mapper和Service,我们只需要少量的配置即可完成单表的增删改查(CRUD)操作。
BaseMapper是MyBatis-Plus提供的模板mapper,其中包含了基本的增删改查CRUD方法,泛型为所操作的实体类类型package com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
使用SpringBoot中使用MyBatis功能时需要设置mapper接口所在的包和映射文件所在的包,在启动类
MybatisplusApplication上加注解:package com.guo.mybatisplus; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication //由于扫描指定包下的mapper接口 @MapperScan("com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper") public class MybatisplusApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MybatisplusApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
4.4 测试
启动类
MybatisplusApplication上加注解@MapperScan("com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper"),SpringBoot启动时会将所有指定包下的mapper接口动态生成的代理类交给IOC容器来管理,测试类就可以自动装配UserMapper接口了。package com.guo.mybatisplus; import com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import java.util.List; @SpringBootTest public class MyBatisPlusTest { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; //这里可能爆红,但是运行没问题 @Test public void testSelectList(){ //selectList()根据MyBatisPlus内置的条件构造器查询一个list集合,null表示没有条件,即查询所有 List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(null); list.forEach(System.out::println); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
还需要注意测试类中
UserMapper可能会爆红,其实运行时没问题,但是如果非要去掉爆红可以在UserMapper上添加@Repository,将类或接口变成持久层组件!package com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
测试结果:

文件结构:
4.5 添加日志
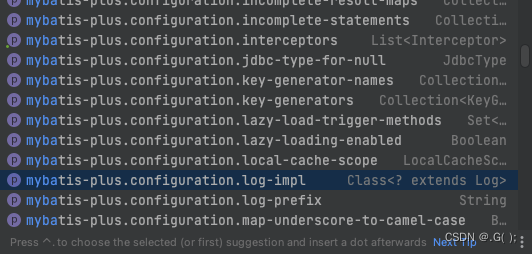
在
application.yml中配置日志输出:配置项是:mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl
# 配置MyBatis日志 mybatis-plus: configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
SQL语句根据实体类自动生成!属性是根据实体类里的顺序来查找的!
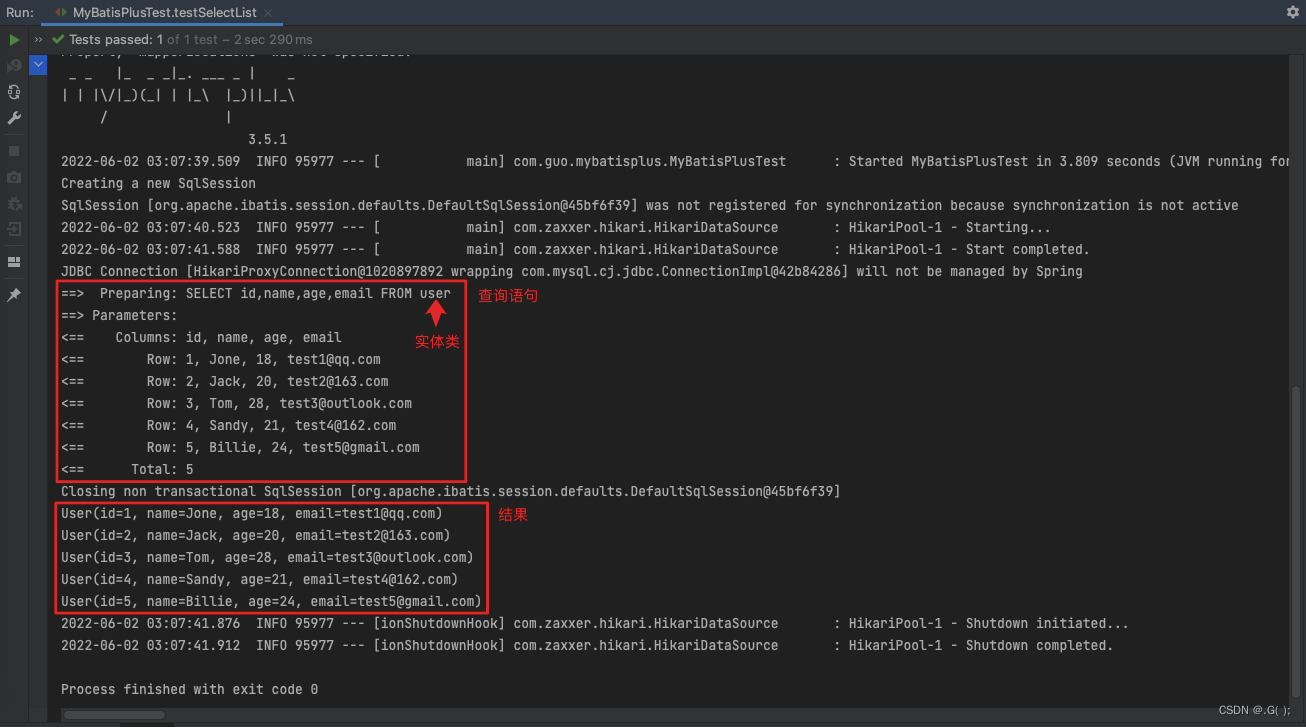
这里体现出来MyBatis-Plus的优越性,不用写出SQL语句,就可以完成单表的查询!

三、基本CRUD
3.1 BaseMapper
MyBatis-Plus中的基本CRUD在内置的BaseMapper中都已得到了实现,我们可以直接使用,接口如下:
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by FernFlower decompiler) // package com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.Wrapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.metadata.IPage; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.CollectionUtils; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.ExceptionUtils; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; public interface BaseMapper<T> extends Mapper<T> { /** * 插入一条记录 * @param entity 实体对象 */ int insert(T entity); /** * 根据 ID 删除 * @param id 主键ID */ int deleteById(Serializable id); /** * 根据实体(ID)删除 * @param entity 实体对象 * @since 3.4.4 */ int deleteById(T entity); /** * 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录 * @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象 */ int deleteByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap); /** * 根据 entity 条件,删除记录 * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句) */ int delete(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); /** * 删除(根据ID 批量删除) * @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty) */ int deleteBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<?> idList); /** * 根据 ID 修改 * @param entity 实体对象 */ int updateById(@Param("et") T entity); /** * 根据 whereEntity 条件,更新记录 * @param entity 实体对象 (set 条件值,可以为 null) * @param updateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句) */ int update(@Param("et") T entity, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> updateWrapper); /** * 根据 ID 查询 * @param id 主键ID */ T selectById(Serializable id); /** * 查询(根据ID 批量查询) * @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty) */ List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList); /** * 查询(根据 columnMap 条件) * @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象 */ List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap); /** * 根据 entity 条件,查询一条记录 * <p>查询一条记录,例如 qw.last("limit 1") 限制取一条记录, 注意:多条数据会报异常</p> * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ default T selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) { List<T> ts = this.selectList(queryWrapper); if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(ts)) { if (ts.size() != 1) { throw ExceptionUtils.mpe("One record is expected, but the query result is multiple records", new Object[0]); } else { return ts.get(0); } } else { return null; } } /** * 根据 Wrapper 条件,判断是否存在记录 * * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类 * @return */ default boolean exists(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) { Long count = this.selectCount(queryWrapper); return null != count && count > 0L; } /** * 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询总记录数 * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ Long selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); /** * 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录 * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); /** * 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录 * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); /** * 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录 * <p>注意: 只返回第一个字段的值</p> * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); /** * 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页)实体对象 * @param page 分页查询条件(可以为 RowBounds.DEFAULT) * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ <P extends IPage<T>> P selectPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); /** * 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页) Map集合 * @param page 分页查询条件 * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类 */ <P extends IPage<Map<String, Object>>> P selectMapsPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
3.2 插入
@Test public void testInsert(){ //实现新增用户信息 //INSERT INTO user ( id, name, age, email ) VALUES ( ?, ?, ?, ? ) User user = new User(); user.setName("张三"); user.setAge(23); user.setEmail("zhangsan@163.com"); int result = userMapper.insert(user); //result 受影响的行数 System.out.println("result:"+result); System.out.println("id:"+user.getId());//获取一下id }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
最终执行的结果,所获取的id为1533642894998966273(这可能每个人运行都不一样!)
这是因为MyBatis-Plus在实现插入数据时,会默认基于雪花算法的策略生成id
id实体类定义时是Long类型,数据库字段定义时是BigInt类型

3.3 删除
@Test public void testDeleteById(){ int result = userMapper.deleteById(1533642894998966273L); //加L表示 Long类型 System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

@Test public void testDeleteByMap(){ //根据map集合中所设置的条件,删除用户信息 //DELETE FROM user WHERE name = ? AND age = ? Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name","张三"); // 条件 map.put("age",23); // 条件 int result = userMapper.deleteByMap(map); System.out.println("result:"+ result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

@Test public void testDeleteBatchIds(){ //通过多个id实现批量删除 //DELETE FROM user WHERE id IN ( ? , ? , ? ) List<Long> list = Arrays.asList(1L,2L,3L);//将数据直接转换为集合 int result = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(list); System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

原来:

删除后:

3.4 更新
@Test public void testUpdateById(){ //修改用户信息 //UPDATE user SET name=?, email=? WHERE id=? User user = new User(); user.setId(4L); user.setName("李四"); user.setEmail("lisi@162.com"); int result = userMapper.updateById(user); System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
可以看到,通过
setId找到了id=4的那条数据,因为只有setName和setEmail方法,因此只改了名字和邮箱,年龄age字段没有修改!
修改后

3.5 查询
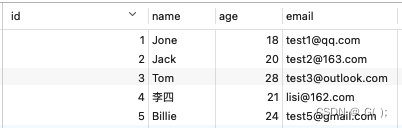
a>根据id查询用户信息
@Test public void testSelectById(){ //通过id查询用户信息 //SELECT id,name,age,email FROM user WHERE id=? User user = userMapper.selectById(4L); System.out.println("user:"+user); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

b>根据多个id查询多个用户信息
@Test public void testSelectBatichIds(){ //根据多个id查询多个用户信息 // SELECT id,name,age,email FROM user WHERE id IN ( ? , ? , ? ) List<Long> list = Arrays.asList(1L,2L,3L); List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(list); users.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

c>通过map条件查询用户信息
@Test public void testSelectByMap(){ //根据map集合中的条件查询用户信息 //SELECT id,name,age,email FROM user WHERE name = ? AND age = ? Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name","Jack"); map.put("age",20); List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map); users.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

d>查询所有数据
@Test public void testSelectList(){ // 查询所有数据信息 // SELECT id,name,age,email FROM user //selectList()根据MyBatisPlus内置的条件构造器查询一个list集合,null表示没有条件,即查询所有 List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(null);// queryWrapper条件构造器,可以写null list.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

通过观察BaseMapper中的方法,大多方法中都有Wrapper类型的形参,此为条件构造器,可针对于SQL语句设置不同的条件,若没有条件,则可以为该形参赋值null,即查询(删除/修改)所有数据
3.6 自定义功能
和mybatis一样,设置映射文件可以在
application.yml中配置,具体配置是mapper-locations,但是此默认路径是:类路径下的mapper下的任意目录下的所有xml文件(可以在mapper下继续加文件夹)都是映射文件!因此这配置可以不写,当然这里支持自定义!
创建xml:名字要和接口名字对应上 UserMapper.xml对应UserMapper接口

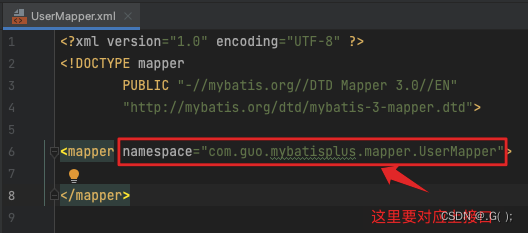
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper"> <!--Map<String,Object> selectMapById(Long id);--> <select id="selectMapById" resultType="map"> select id,name,age,email from user where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
UserMapper.java
package com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.Map; @Repository public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { /** * 根据id查询用户信息为map集合 * @param id * @return */ Map<String,Object> selectMapById(Long id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
MyBatisPlusTest.java
@Test public void testSelectByMyself(){ //自定义用法 //select id,name,age,email from user where id = ? Map<String,Object> map = userMapper.selectMapById(1L); System.out.println(map); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

3.6.1 通用Service (需特别注意!)
说明:
通用 Service CRUD 封装IService接口,进一步封装 CRUD 采用 get 查询单行 remove 删除 list 查询集合 page 分页 前缀命名方式区分 Mapper 层避免混淆,
泛型 T 为任意实体对象
建议如果存在自定义通用 Service 方法的可能,请创建自己的 IBaseService 继承Mybatis-Plus 提供的基类
官网地址:官网:Service CRUD 接口3.6.1.1 IService
MyBatis-Plus中有一个接口 IService和其实现类 ServiceImpl,封装了常见的业务层逻辑,详情查看源码IService和ServiceImpl

3.6.1.1 创建Service接口和实现类
虽然可以使用现成的
IService接口和ServiceImpl实现类,但是当实际进行开发过程中,难免会遇到更多的开发要求,此时现成的IService接口和ServiceImpl实现类就不好使了,不如自己创建Service接口同时继承IService接口和ServiceImpl实现类。3.6.1.1.1 UserService (Service接口)
package com.guo.mybatisplus.service; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; /** * UserService继承IService模板提供的基础功能 */ public interface UserService extends IService<User> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
3.6.1.1.2 UserServiceImpl (实现类)
package com.guo.mybatisplus.service.impl; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl; import com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import com.guo.mybatisplus.service.UserService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * ServiceImpl实现了IService,提供了IService中基础功能的实现 * 若ServiceImpl无法满足业务需求,则可以使用自定的UserService定义方法,并在实现类中实现 */ @Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
文件结构:

3.6.1.1.3 测试查询记录数(测试类)
创建测试类:MyBatisPlusService.java
@Test public void testGetCount(){ //查询总记录数 //SELECT COUNT( * ) FROM user long count = userService.count(); System.out.println("总记录数:"+count); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

3.6.1.1.4 测试批量添加(测试类)
@Test public void testInsertMore(){ //批量添加 //INSERT INTO user ( id, name, age, email ) VALUES ( ?, ?, ?, ? ) List<User> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1;i<=10;i++){ User user = new User(); user.setName("user"+i); user.setAge(20+i); user.setEmail("user"+i+"@163.com"); list.add(user); } boolean b = userService.saveBatch(list); //boolean 操作是否成功 System.out.println("结果:"+b); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
此功能也是通过单个SQL语句循环执行添加操作的!

四、常用注解
4.1 @TableName
经过以上的测试,在使用MyBatis-Plus实现基本的CRUD时,我们并没有指定要操作的表,只是在Mapper接口继承BaseMapper时,设置了泛型User,而操作的表为user表,由此得出结论,MyBatis-Plus在确定操作的表时,由BaseMapper的泛型决定,即实体类型决定,且默认操作的表名和实体类型的类名一致
4.1.1 问题
若实体类类型的类名和要操作的表的表名不一致,会出现什么问题?我们将表
user更名为t_user,测试查询功能程序抛出异常,Table 'mybatis_plus.user' doesn't exist,因为现在的表名为t_user,而默认操作的表名和实体类型的类名一致,即user表
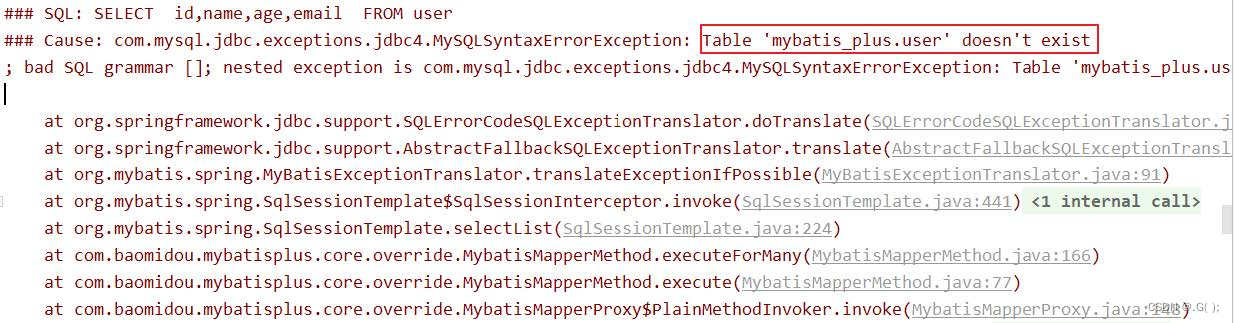
4.1.2 通过@TableName解决问题
在实体类类型上添加@TableName(“t_user”),标识实体类对应的表,即可成功执行SQL语句
@Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("t_user") public class User { private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
4.1.3 通过全局配置解决问题
在开发的过程中,我们经常遇到以上的问题,即实体类所对应的表都有固定的前缀,例如
t_或tbl_此时,可以使用MyBatis-Plus提供的全局配置,为实体类所对应的表名设置默认的前缀,那么就不需要在每个实体类上通过@TableName标识实体类对应的表# 配置MyBatis-Plus的全局配置 global-config: db-config: # 配置MyBatis-Plus操作表的统一前缀 table-prefix: t_- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4.2 @TableId
经过以上的测试,MyBatis-Plus在实现CRUD时,会默认将id作为主键列,并在插入数据时,默认基于雪花算法的策略生成id
4.2.1 问题
若实体类和表中表示主键的不是id,而是其他字段,例如uid,MyBatis-Plus会自动识别uid为主键列吗?我们实体类中的属性id改为uid,将表中的字段id也改为uid,测试添加功能

4.2.2 通过@TableId解决问题
在实体类中uid属性上通过@TableId将其标识为主键,即可成功执行SQL语句
@Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("user") public class User { //设置主键:将这个属性所对应的字段指定为主键 //@TableId 注解的value属性用于指定主键的字段 @TableId(value = "id") //这里的value是数据库的字段名 private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
4.2.3 @TableId的value属性
若实体类中主键对应的属性为
id,而表中表示主键的字段为uid,此时若只在属性id上添加注解@TableId,则抛出异常Unknown column 'id' in 'field list',即MyBatis-Plus仍然会将id作为表的主键操作,而表中表示主键的是字段uid此时需要通过@TableId注解的value属性,指定表中的主键字段,@TableId("uid")或@TableId(value="uid")

4.2.4 @TableId的type属性
type属性用来定义主键策略
@Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("user") public class User { //设置主键:将这个属性所对应的字段指定为主键 //@TableId 注解的value属性用于指定主键的字段 //@TableId 注解的type属性设置主键生成策略 @TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.ASSIGN_ID) //这里的value是数据库的字段名 type是主键策略 private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
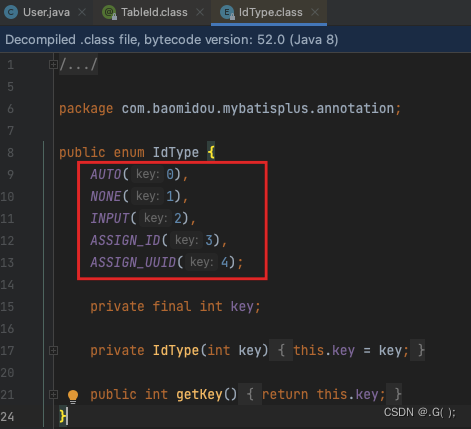
常用的主键生成策略:
值 描述 IdType.ASSIGN_ID(默认) 基于雪花算法的策略生成数据id,与数据库id是否设置自增无关 IdType.AUTO 使用数据库的自增策略,注意:该类型请确保数据库设置了id自增,否则无效!设置自增后,如果后续需要添加数据时就不需要给主键赋值了,如果设置了那么这条数据的主键就不自增了 IdType.ASSIGN_UUID 通用唯一识别码(Universally Unique Identifier) 
可以进入方法看一下:

配置全局主键策略:
# 配置MyBatis日志 mybatis-plus: configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 配置MyBatis-Plus的全局配置 global-config: db-config: # 配置MyBatis-Plus操作表的默认前缀 table-prefix: t_ # 配置MyBatis-Plus的主键策略 这里设置了uuid id-type: assign_uuid- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
可设置的值:

4.2.5 雪花算法
-
背景
需要选择合适的方案去应对数据规模的增长,以应对逐渐增长的访问压力和数据量。数据库的扩展方式主要包括:业务分库、主从复制,数据库分表。 -
数据库分表
将不同业务数据分散存储到不同的数据库服务器,能够支撑百万甚至千万用户规模的业务,但如果业务继续发展,同一业务的单表数据也会达到单台数据库服务器的处理瓶颈。例如,淘宝的几亿用户数据,如果全部存放在一台数据库服务器的一张表中,肯定是无法满足性能要求的,此时就需要对单表数据进行拆分。
单表数据拆分有两种方式:垂直分表和水平分表。示意图如下:

-
垂直分表
垂直分表适合将表中某些不常用且占了大量空间的列拆分出去。
例如,前面示意图中的 nickname 和 description 字段,假设我们是一个婚恋网站,用户在筛选其他用户的时候,主要是用 age 和 sex 两个字段进行查询,而 nickname 和 description 两个字段主要用于展示,一般不会在业务查询中用到。description 本身又比较长,因此我们可以将这两个字段独立到另外一张表中,这样在查询 age 和 sex 时,就能带来一定的性能提升。 -
水平分表
水平分表适合表行数特别大的表,有的公司要求单表行数超过 5000 万就必须进行分表,这个数字可以作为参考,但并不是绝对标准,关键还是要看表的访问性能。对于一些比较复杂的表,可能超过 1000万就要分表了;而对于一些简单的表,即使存储数据超过 1 亿行,也可以不分表。但不管怎样,当看到表的数据量达到千万级别时,作为架构师就要警觉起来,因为这很可能是架构的性能瓶颈或者隐患。
水平分表相比垂直分表,会引入更多的复杂性,例如要求全局唯一的数据id该如何处理
主键自增
①以最常见的用户 ID 为例,可以按照 1000000 的范围大小进行分段,1 ~ 999999 放到表 1中,
1000000 ~ 1999999 放到表2中,以此类推。
②复杂点:分段大小的选取。分段太小会导致切分后子表数量过多,增加维护复杂度;分段太大可能会导致单表依然存在性能问题,一般建议分段大小在 100 万至 2000 万之间,具体需要根据业务选取合适的分段大小。
③优点:可以随着数据的增加平滑地扩充新的表。例如,现在的用户是 100 万,如果增加到 1000 万,只需要增加新的表就可以了,原有的数据不需要动。
④缺点:分布不均匀。假如按照 1000 万来进行分表,有可能某个分段实际存储的数据量只有 1 条,而另外一个分段实际存储的数据量有 1000 万条。取模
①同样以用户 ID 为例,假如我们一开始就规划了 10 个数据库表,可以简单地用 user_id % 10 的值来表示数据所属的数据库表编号,ID 为 985 的用户放到编号为 5 的子表中,ID 为 10086 的用户放到编号为 6 的子表中。
②复杂点:初始表数量的确定。表数量太多维护比较麻烦,表数量太少又可能导致单表性能存在问题。
③优点:表分布比较均匀。
④缺点:扩充新的表很麻烦,所有数据都要重分布。雪花算法
雪花算法是由Twitter公布的分布式主键生成算法,它能够保证不同表的主键的不重复性,以及相同表的主键的有序性。
①核心思想:
长度共64bit(一个long型)。首先是一个符号位,1bit标识,由于long基本类型在Java中是带符号的,最高位是符号位,正数是0,负数是1,所以id一般是正数,最高位是0。41bit时间截(毫秒级),存储的是时间截的差值(当前时间截 - 开始时间截),结果约等于69.73年。10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心,5个bit的机器ID,可以部署在1024个节点)。12bit作为毫秒内的流水号(意味着每个节点在每毫秒可以产生 4096 个 ID)。
②优点:整体上按照时间自增排序,并且整个分布式系统内不会产生ID碰撞,并且效率较高。
4.3 @TableField
经过以上的测试,我们可以发现,MyBatis-Plus在执行SQL语句时,要保证实体类中的属性名和表中的字段名一致,如果实体类中的属性名和字段名不一致的情况,会出现什么问题呢?
4.3.1 情况1
若实体类中的属性使用的是驼峰命名风格,而表中的字段使用的是下划线命名风格
例如实体类属性userName,表中字段user_name,此时MyBatis-Plus会自动将下划线命名风格转化为驼峰命名风格相当于在MyBatis中配置。4.3.2 情况2
若实体类中的属性和表中的字段不满足情况1
例如实体类属性name,表中字段username,此时需要在实体类属性上使用@TableField("username")设置属性所对应的字段名。@Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("user") public class User { //设置主键:将这个属性所对应的字段指定为主键 //@TableId 注解的value属性用于指定主键的字段 //@TableId 注解的type属性设置主键生成策略 @TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.ASSIGN_UUID) //这里的value是数据库的字段名 private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid //指定属性所对应的字段名 除主键属性使用 @TableField("user_name") private String name; private Integer age; private String email; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
4.4 @TableLogic
4.4.1 逻辑删除
- 物理删除:真实删除,将对应数据从数据库中删除,之后查询不到此条被删除的数据
- 逻辑删除:假删除,将对应数据中代表是否被删除字段的状态修改为“被删除状态”,之后在数据库中仍旧能看到此条数据记录
- 使用场景:可以进行数据恢复
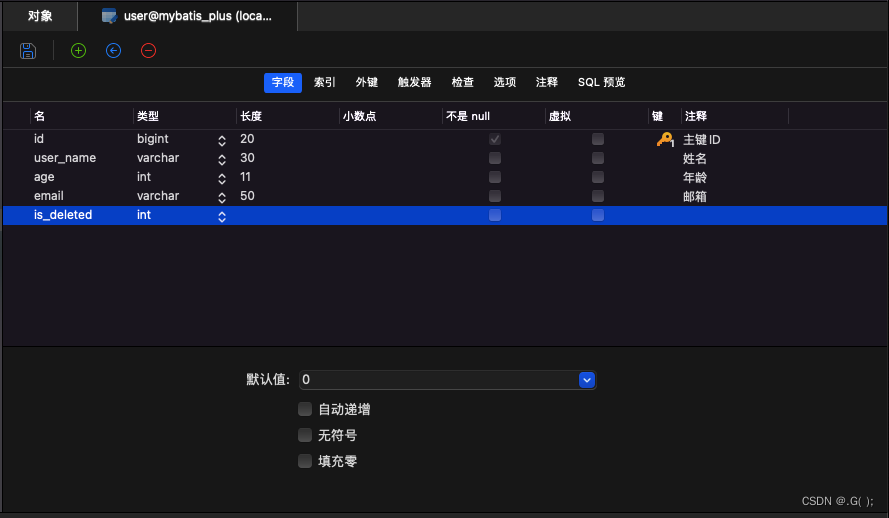
4.4.2 实现逻辑删除
step1:数据库中创建逻辑删除状态列,设置默认值为0
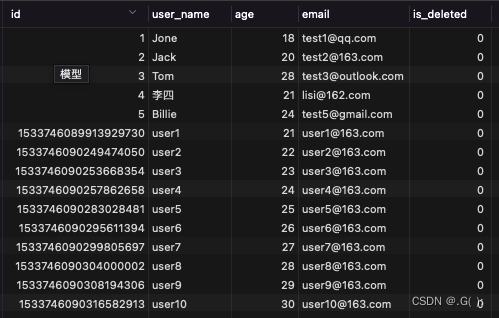
step2:实体类中添加逻辑删除属性
@Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("user") public class User { //设置主键:将这个属性所对应的字段指定为主键 //@TableId 注解的value属性用于指定主键的字段 //@TableId 注解的type属性设置主键生成策略 @TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.ASSIGN_UUID) //这里的value是数据库的字段名 private Long id; //数据库表id是bigid //指定属性所对应的字段名 @TableField("user_name") private String name; private Integer age; private String email; //逻辑删除字段 @TableLogic private Integer isDeleted; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
step3:测试
测试删除功能,真正执行的是修改
UPDATE user SET is_deleted=1 WHERE id=? AND is_deleted=0因为有
@TableLogic原来的Delete改成了Update


测试查询功能,被逻辑删除的数据默认不会被查询
SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0查询的时候已经看不到
is_deleted = 1的数据了

五、条件构造器和常用接口
5.1 wapper介绍

- Wrapper : 条件构造抽象类,最顶端父类
- AbstractWrapper : 用于查询条件封装,生成 sql 的 where 条件
- QueryWrapper : 查询条件封装
- UpdateWrapper : Update 条件封装
- AbstractLambdaWrapper : 使用Lambda 语法
- LambdaQueryWrapper :用于Lambda语法使用的查询Wrapper
- LambdaUpdateWrapper :用于Lambda语法更新封装Wrapper
- AbstractWrapper : 用于查询条件封装,生成 sql 的 where 条件
需要注意的是,删除
Delete的Wrapper是在queryWrapper中:

5.2 QueryWrapper
创建MyBatisPlusWrapperTest.java

5.2.0 可组装的值(重要)
值 含义 eq equal 等于 ne not equal 不等于 gt greater than 大于 lt less than 小于 ge greater than or equal 大于等于 le less than or equal 小于等于 in in 包含(数组) isNull 等于 null between 在2个条件之间(包括边界值) like 模糊查询 5.2.1 例1:组装查询条件
新写一个测试方法,调用
selectList可以看到里面存在queryWrapper参数:

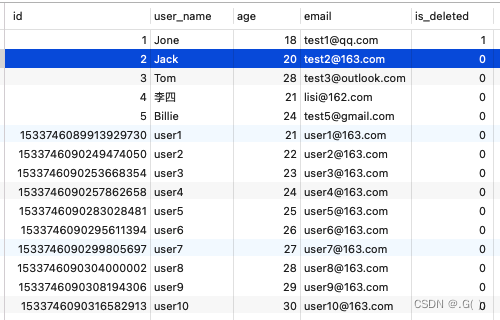
@Test public void test1(){ //查询用户名包含a,年龄在20到30之间,邮箱信息不为null的用户信息 //SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND age BETWEEN ? AND ? AND email IS NOT NULL) QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.like("user_name","a") .between("age",20,30) .isNotNull("email");//column 是数据库字段名 List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper); list.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
column是数据库字段名:

运行结果:

数据库里数据:
5.2.2 例2:组装排序条件
@Test public void test2(){ //查询用户信息,按照年龄的降序排序,若年龄相同,则按照id升序排序 // SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 ORDER BY age DESC,id ASC QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.orderByDesc("age") //降序排列 .orderByAsc("id");//升序排列 List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper); list.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

5.2.3 例3:组装删除条件 (需要注意的是,删除
Delete的Wrapper是在queryWrapper中:)在数据库里新增一条数据:
email为null

@Test public void test3(){ //删除邮箱地址为null的用户信息 //UPDATE user SET is_deleted=1 WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (email IS NULL) QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.isNull("email"); int result = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper); System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
因为有逻辑删除
@TableLogic因此SQL语句不是Delete而是Update

数据库中的数据没有真正被删除,而是
is_deleted的值被改成了1
5.2.4 例4:条件的优先级

update方法有两个参数: User(实体类)和updateWrapper。
这里有两种用法:
- 通过实体类对象设置修改的内容,通过
queryWrapper设置修改条件 - 实体类对象设置为
null,通过updateWrapper既可以设置修改条件,也可以设置修改的字段
5.2.4.1 第一种用法:通过实体类对象设置修改的内容,通过
queryWrapper设置修改条件@Test public void test4(){ // 将(年龄大于20或邮箱为null)并且用户名中包含有a的用户信息修改 // UPDATE user SET user_name=?,email=? WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? OR email IS NULL) QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //设置条件 queryWrapper.gt("age",19) //gt greater than 大于 .like("user_name","a") //因为 是并且关系 因此 直接写 .or()// or 或 .isNull("email"); User user = new User(); user.setName("小a"); // 修改的内容 user.setEmail("xiaoA@163.com"); // 修改的内容 int result = userMapper.update(user,queryWrapper); //第一个参数是实体内容,第二个参数是查询条件 System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
数据库原数据:

运行结果:

运行后的数据库数据:

改变优先级:
数据库原数据:

@Test public void test42(){ // 将用户名中包含有a并且(年龄大于20或邮箱为null)的用户信息修改 优先级发生变化 (年龄大于20或邮箱为null)优先判断 //lambda表达式内的逻辑优先运算 //UPDATE user SET user_name=?, email=? WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND (age > ? OR email IS NULL)) QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //设置条件 queryWrapper.like("user_name","a") .and(i ->i.gt("age",19) // i -> lambda表达式内的逻辑优先运算 .or().isNull("email")); User user = new User(); user.setName("小a2"); // 修改的内容 user.setEmail("xiaoA2@163.com"); // 修改的内容 int result = userMapper.update(user,queryWrapper); //第一个参数是实体内容,第二个参数是查询条件 System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
.and方法可以添加lambda表达式
运行结果:
运行后数据:

5.2.5 例5:组装select子句
@Test public void test5(){ //查询用户的用户名,年龄,邮箱信息 //SELECT user_name,age,email FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //设置条件 queryWrapper.select("user_name","age","email"); //按照设置只查询部分字段 List<Map<String,Object>> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper); maps.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
.select方法里面可以添加数据库字段

5.2.6 例6:实现子查询
@Test public void test6(){ //查询id小于等于100的用户信息 //SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (id IN (select id from user where id <=100)) QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //设置条件 queryWrapper.inSql("id","select id from user where id <=100");//column 是数据库字段名 String inValue 是in 比较的数据————SQL语句 List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper); list.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
.inSql方法:两个参数,一个是数据库的字段,一个是in 比较数据SQL语句

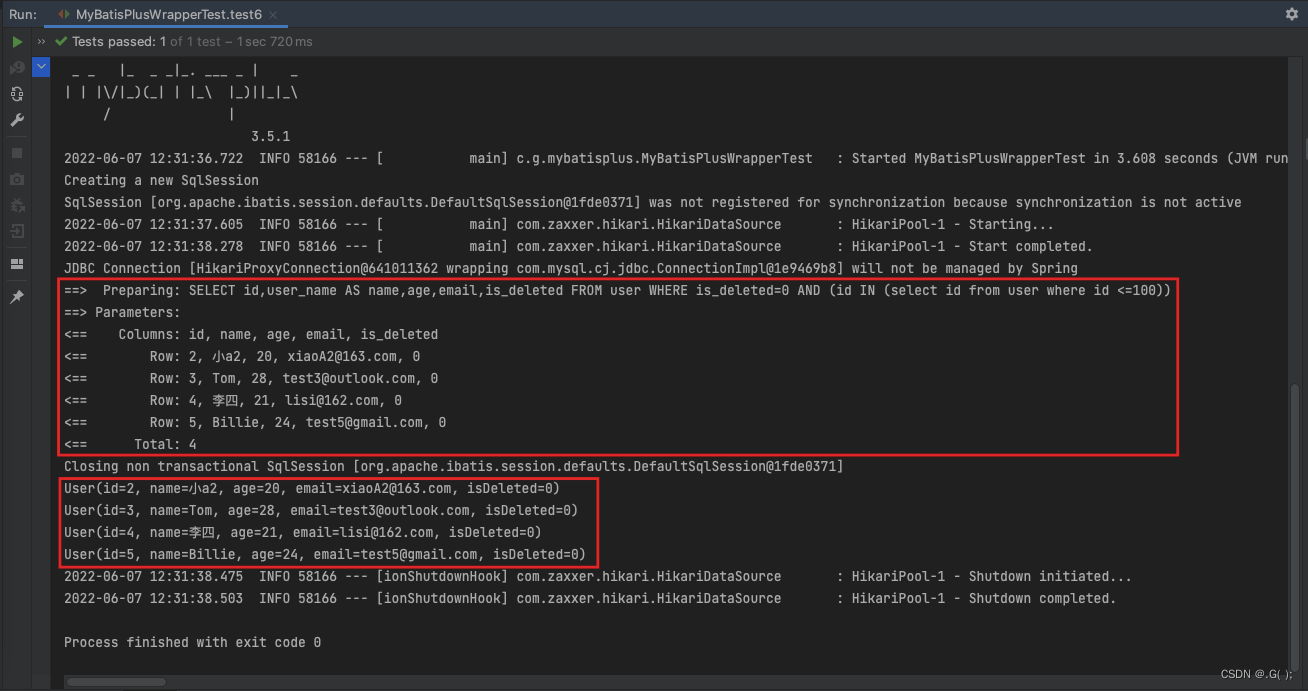
5.3 UpdateWrapper (update方法的第二种用法:实体类对象设置为
null,通过updateWrapper既可以设置修改条件,也可以设置修改的字段)UpdateWrapper更简单!
UpdateWrapper中有一个set方法,里面有两个参数:第一个参数对应的是字段名,第二个参数对应的是值:
数据库原数据:

@Test public void test7(){ // 将用户名中包含有a并且(年龄大于20或邮箱为null)的用户信息修改 //UPDATE user SET user_name=?,email=? WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND (age > ? OR email IS NULL)) UpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>(); updateWrapper.like("user_name","a") .and(i -> i.gt("age",19).or().isNull("email")); updateWrapper.set("user_name","updateWrapper修改").set("email","abc@163.com"); int result = userMapper.update(null,updateWrapper); System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

数据库修改后的数据:

5.4 condition
在真正开发的过程中,组装条件是常见的功能,而这些条件数据来源于用户输入,是可选的,因此我们在组装这些条件时,必须先判断用户是否选择了这些条件,若选择则需要组装该条件,若没有选择则一定不能组装,以免影响SQL执行的结果
5.4.1 思路一:
@Test public void test8() { //定义查询条件,有可能为null(用户未输入或未选择) String username = "a"; Integer ageBegin = 10; Integer ageEnd = 24; QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //StringUtils.isNotBlank()判断某字符串是否不为空字符串且长度不为0且不由空白符(whitespace)构成 if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(username)){ queryWrapper.like("user_name",username); //如果不为空 则为"a"的模糊查询 } if(ageBegin != null){ queryWrapper.ge("age", ageBegin); //ge greater than or equal 大于等于 } if(ageEnd != null){ queryWrapper.le("age", ageEnd); // less than or equal 小于等于 } //SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND age >= ? AND age <= ?) List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper); users.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
StringUtils选择MyBatis-Plus中的包:


5.4.2 思路二:
queryWrapper里面的方法:比如.le参数有boolean condition判断条件,其他方法也有boolean condition判断条件,满足条件即组装,不满足就不组装:

@Test public void test9(){ //定义查询条件,有可能为null(用户未输入或未选择) String username = "a"; Integer ageBegin = 10; Integer ageEnd = 24; QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //StringUtils.isNotBlank()判断某字符串是否不为空且长度不为0且不由空白符(whitespace)构成 queryWrapper.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(username), "user_name", username) .ge(ageBegin != null, "age", ageBegin) // greater than or equal 大于等于 .le(ageEnd != null, "age", ageEnd); // less than or equal 小于等于 //SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND age >= ? AND age <= ?) List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper); users.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

5.5 LambdaQueryWrapper
使用
LambdaQueryWrapper后里面有一些方法就可以使用函数接口了,这也是为了防止字段名写错!通过函数访问到实体类属性所对应的字段名:
直接访问字段:

@Test public void test10(){ //LambdaQueryWrapper String username = "a"; Integer ageBegin = 10; Integer ageEnd = 24; LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(username),User::getName,username) .ge(ageBegin != null,User::getAge,ageBegin) .le(ageEnd != null,User::getAge,ageEnd); // SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND age >= ? AND age <= ?) //selectList方法放的参数是最顶级的抽象类————Wrapper,各子类都可以进行赋值 List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper); users.forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16

5.6 LambdaUpdateWrapper
数据库原数据:

@Test public void test11(){ // 将用户名中包含有a并且(年龄大于20或邮箱为null)的用户信息修改 //LambdaUpdateWrapper 参数写的是函数接口 //UPDATE user SET user_name=?,email=? WHERE is_deleted=0 AND (user_name LIKE ? AND (age > ? OR email IS NULL)) LambdaUpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>(); updateWrapper.like(User::getName,"a") .and(i -> i.gt(User::getAge,19).or().isNull(User::getEmail)); updateWrapper.set(User::getName,"LambdaUpdateWrapper修改").set(User::getEmail,"abc改@163.com"); int result = userMapper.update(null,updateWrapper); System.out.println("result:"+result); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
运行结果:

运行后的数据:

六、插件
6.1 分页插件
MyBatis Plus自带分页插件,只要简单的配置即可实现分页功能
a>添加配置类

package com.guo.mybatisplus.config; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //扫描mapper接口所在的包 @MapperScan("com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper")//可以写在MyBatisplusApplication中 public class MyBatisPlusConfig { @Bean public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){ MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor(); //添加分页插件 interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL)); return interceptor; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
测试类:

可以按住Ctrl/command+点击进入方法中:选中
IpageCtrl/control+H发现Page是继承IPage

b>测试
@SpringBootTest public class MyBatisPlusPluginsTest { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test public void test1(){ // SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 LIMIT ?,? Page<User> page = new Page<User>(2,3);//这里有 limit 后面两个参数 当前也起始索引index pageSize每页显示的条数 userMapper.selectPage(page,null);//selectPage方法有两个参数,第一个分页对象,第二个参数Wrapper条件构造器 System.out.println(page); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
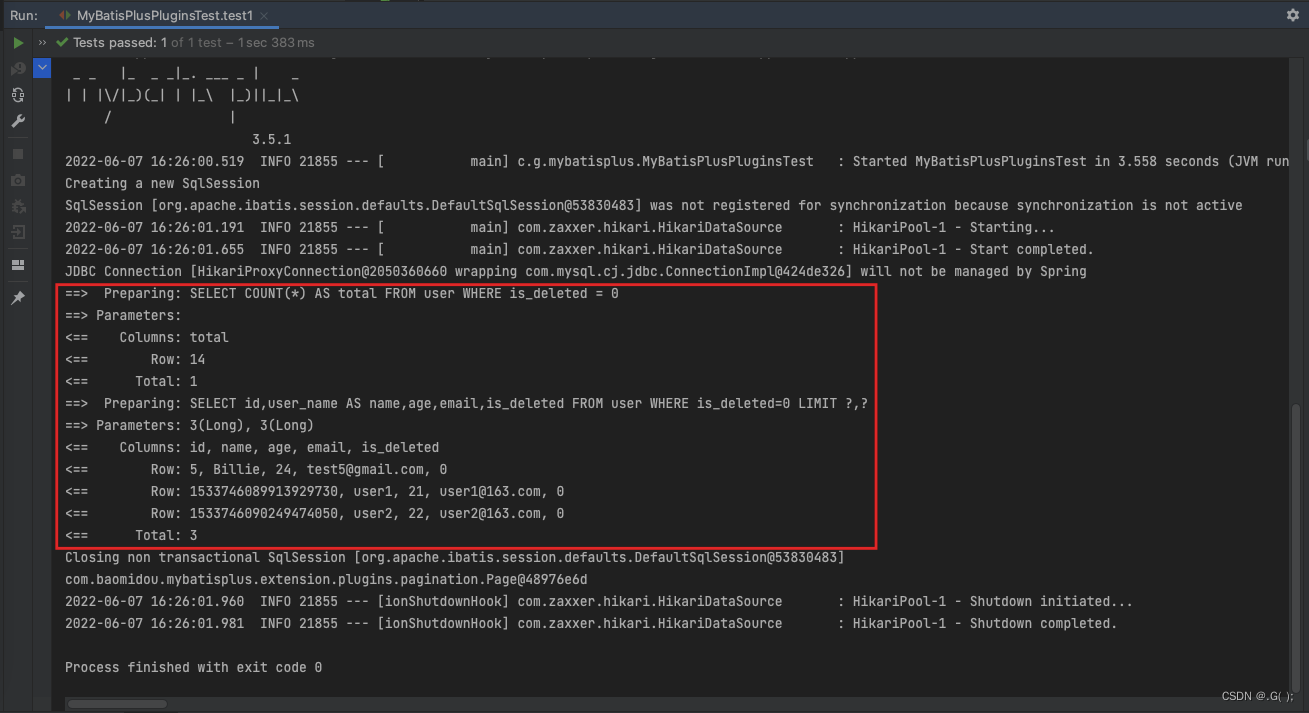
@Test public void test1(){ // SELECT id,user_name AS name,age,email,is_deleted FROM user WHERE is_deleted=0 LIMIT ?,? Page<User> page = new Page<User>(2,3);//这里有 limit 后面两个参数 当前也起始索引index pageSize每页显示的条数 userMapper.selectPage(page,null);//selectPage方法有两个参数,第一个分页对象,第二个参数Wrapper条件构造器 System.out.println("page:"+page); System.out.println("当前页信息:getRecords():"+page.getRecords()); //获取当前页数据信息 System.out.println("当前页页码:getCurrent():"+page.getCurrent()); // 获取当前页页码 System.out.println("每页显示的条数:getSize():"+page.getSize());// 获得当前页条数 System.out.println("总页数:getPages():"+page.getPages());//获取总页数,不包含逻辑删除的数据 System.out.println("总记录数:getTotal():"+page.getTotal());//获取总记录数 System.out.println("是否有上一页:hasNext():"+page.hasNext());//判断有没有下一页 System.out.println("是否有下一页:hasPrevious():"+page.hasPrevious());//判断有没有上一页 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

6.2 xml自定义分页
a>UserMapper中定义接口方法
/** * 根据年龄查询用户信息,分页显示 * @param page MyBatis-Plus所提供的分页对象,xml中可以从里面进行取值,传递参数 Page 即自动分页,必须放在第一个参数位置 * @param age 年龄 * @return */ Page<User> selectPageVo(@Param("page")Page<User> page,@Param("age") Integer age);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
b>UserMapper.xml中编写SQL
注意在
applicaion.yml配置一下类型别名对应的包:
<!--SQL片段,记录基础字段--> <sql id="BaseColumns">id,user_name,age,email</sql> <!--Page<User> selectPageVo(@Param("page")Page<User> page,@Param("age") Integer age);--> <select id="selectPageVo" resultType="User"> SELECT <include refid="BaseColumns"></include> FROM user WHERE age > #{age} </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
c>测试
@Test public void testVo(){ Page<User> page = new Page<User>(1,3); userMapper.selectPageVo(page,20); System.out.println("page:"+page); System.out.println("当前页信息:getRecords():"+page.getRecords()); //获取当前页数据信息 System.out.println("当前页页码:getCurrent():"+page.getCurrent()); // 获取当前页页码 System.out.println("每页显示的条数:getSize():"+page.getSize());// 获得当前页条数 System.out.println("总页数:getPages():"+page.getPages());//获取总页数,不包含逻辑删除的数据 System.out.println("总记录数:getTotal():"+page.getTotal());//获取总记录数 System.out.println("是否有上一页:hasNext():"+page.hasNext());//判断有没有下一页 System.out.println("是否有下一页:hasPrevious():"+page.hasPrevious());//判断有没有上一页 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
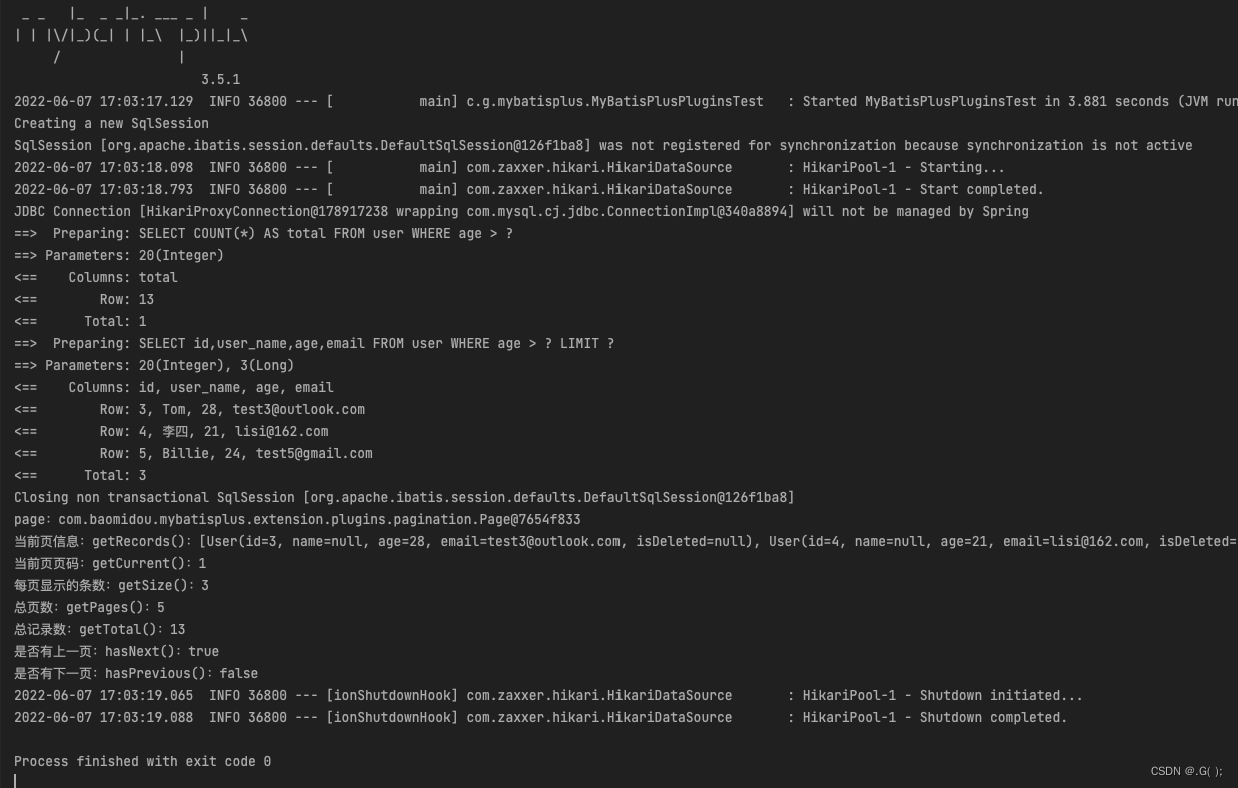
d>顺序

6.3 乐观锁
a>场景
一件商品,成本价是80元,售价是100元。老板先是通知小李,说你去把商品价格增加50元。小李正在玩游戏,耽搁了一个小时。正好一个小时后,老板觉得商品价格增加到150元,价格太高,可能会影响销量。又通知小王,你把商品价格降低30元。
此时,小李和小王同时操作商品后台系统。小李操作的时候,系统先取出商品价格100元;小王也在操作,取出的商品价格也是100元。小李将价格加了50元,并将100+50=150元存入了数据库;小王将商品减了30元,并将100-30=70元存入了数据库。是的,如果没有锁,小李的操作就完全被小王的覆盖了。
现在商品价格是70元,比成本价低10元。几分钟后,这个商品很快出售了1千多件商品,老板亏1万多。b>乐观锁与悲观锁
如果是悲观锁,小李取出数据后,小王只能等小李操作完之后,才能对价格进行操作,也会保证最终的价格是120元。
上面的故事,如果是乐观锁,一般通过表里设置版本号来实现,小王保存价格前,会检查下价格是否被人修改过了(查询版本号)。如果被修改过了,则重新取出的被修改后的价格,150元,这样他会将120元存入数据库。c>模拟修改冲突
数据库中增加商品表
CREATE TABLE t_product ( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID', NAME VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品名称', price INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '价格', VERSION INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '乐观锁版本号', PRIMARY KEY (id) );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
添加数据
INSERT INTO t_product (id, NAME, price) VALUES (1, '外星人笔记本', 100);- 1

添加实体类
package com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName; import lombok.Data; @Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("t_product") public class Product { private Long id; private String name; private Integer price; private Integer version; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
添加mapper
package com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.Product; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository //需要持久层组件 保证test测试类中不报错 public interface ProductMapper extends BaseMapper<Product> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
测试
@Test public void testProduct1(){ //1、小李 Product p1 = productMapper.selectById(1L); System.out.println("小李取出的价格:" + p1.getPrice()); //2、小王 Product p2 = productMapper.selectById(1L); System.out.println("小王取出的价格:" + p2.getPrice()); //3、小李将价格加了50元,存入了数据库 p1.setPrice(p1.getPrice() + 50);// 100 + 50 int result1 = productMapper.updateById(p1); System.out.println("小李修改结果:" + result1); //4、小王将商品减了30元,存入了数据库 p2.setPrice(p2.getPrice() - 30);// 100 -30 int result2 = productMapper.updateById(p2); System.out.println("小王修改结果:" + result2); //最后的结果 老板查询 Product p3 = productMapper.selectById(1L); //价格覆盖,最后的结果:70 System.out.println("最后的结果:" + p3.getPrice()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27

最终老板查数据为:70

d>乐观锁实现流程
数据库中添加version字段
取出记录时,获取当前versionSELECT id,`name`,price,`version` FROM product WHERE id=1- 1
更新时,version + 1,如果where语句中的version版本不对,则更新失败
UPDATE product SET price=price+50, `version`=`version` + 1 WHERE id=1 AND `version`=1- 1
e>Mybatis-Plus实现乐观锁
修改实体类
package com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.Version; import lombok.Data; @Data @TableName("t_product") public class Product { private Long id; private String name; private Integer price; @Version //表示乐观锁版本号字段 private Integer version;//版本号加上 @Version 注解 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
添加乐观锁插件配置 (MyBatisPlusConfig.java)
package com.guo.mybatisplus.config; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //扫描mapper接口所在的包 @MapperScan("com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper") //可以写在MyBatisplusApplication中 public class MyBatisPlusConfig { @Bean public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){ MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor(); //添加分页插件 interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL)); //添加乐观锁插件 interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor()); return interceptor; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
复原数据 价格为100

测试
最后价格应该是150,小王修改失败,原因:小李改完版本号变了,小王再修改时版本号对不上,应该无法修改了!
测试修改冲突
小李查询商品信息:
SELECT id,name,price,version FROM t_product WHERE id=?
小王查询商品信息:
SELECT id,name,price,version FROM t_product WHERE id=?
小李修改商品价格,自动将version+1
UPDATE t_product SET name=?, price=?, version=? WHERE id=? AND version=?Parameters: 外星人笔记本(String), 150(Integer), 1(Integer), 1(Long), 0(Integer)
小王修改商品价格,此时version已更新,条件不成立,修改失败
UPDATE t_product SET name=?, price=?, version=? WHERE id=? AND version=?Parameters: 外星人笔记本(String), 70(Integer), 1(Integer), 1(Long), 0(Integer)
最终,小王修改失败,查询价格:150
SELECT id,name,price,version FROM t_product WHERE id=?
最后数据库的值:

优化流程
此时数据库里的数据:版本号已经是1

//testProduct简单优化后 @Test public void testProductUpdate(){ //1、小李 Product p1 = productMapper.selectById(1L); System.out.println("小李取出的价格:" + p1.getPrice()); //2、小王 Product p2 = productMapper.selectById(1L); System.out.println("小王取出的价格:" + p2.getPrice()); //3、小李将价格加了50元,存入了数据库 p1.setPrice(p1.getPrice() + 50);// 100 + 50 int result1 = productMapper.updateById(p1); System.out.println("小李修改结果:" + result1); //4、小王将商品减了30元,存入了数据库 p2.setPrice(p2.getPrice() - 30);// 100 -30 int result2 = productMapper.updateById(p2); System.out.println("小王修改结果:" + result2); //改良 if(result2 == 0){ //操作失败,重新获得版本号 Product productNew = productMapper.selectById(1L); productNew.setPrice(productNew.getPrice() - 30); int resultNew = productMapper.updateById(productNew); System.out.println("如果出现问题,最后小王的修改结果:" + resultNew); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29

最终数据库中的数据:版本号变为3

注意:本方法只是简单的解决了遇到的数据问题,如果在真实项目中如果遇到类似问题还是直接爆红提醒就好,直接在方法中写if不是很专业!七、通用枚举
表中的有些字段值是固定的,例如性别(男或女),此时我们可以使用MyBatis-Plus的通用枚举来实现
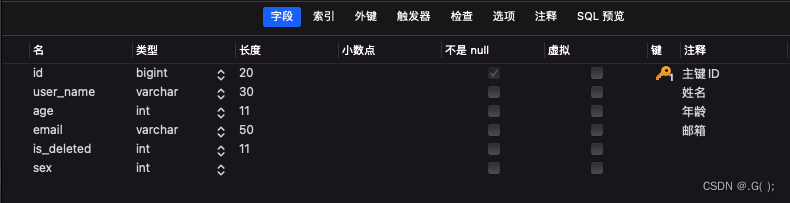
a>数据库表添加字段sex
b>创建通用枚举类型
创建一个枚举类:

package com.guo.mybatisplus.enums; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.EnumValue; import lombok.Getter; @Getter public enum SexEnum { MALE(1, "男"), FEMALE(2, "女"); @EnumValue //将注解所标识的值存储到数据库中 private Integer sex; private String sexName; SexEnum(Integer sex, String sexName) { this.sex = sex; this.sexName = sexName; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
// User.java实体类里也要加 private SexEnum sex;- 1
- 2
c>配置扫描通用枚举
# 配置MyBatis日志 mybatis-plus: configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 配置MyBatis-Plus的全局配置 global-config: db-config: # 配置MyBatis-Plus操作表的默认前缀 table-prefix: # 配置MyBatis-Plus的主键策略 这里设置了uuid id-type: assign_uuid #配置类型别名所对应的包 type-aliases-package: com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo # 扫描通用枚举包 type-enums-package: com.guo.mybatisplus.enums- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
d>测试
package com.guo.mybatisplus; import com.guo.mybatisplus.enums.SexEnum; import com.guo.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest public class MyBatisPlusEnumTest { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test public void test(){ User user = new User(); user.setId(7L);//这里我固定设值了,如果是自增不需要设置 user.setName("admin"); user.setAge(33); user.setSex(SexEnum.MALE); int result = userMapper.insert(user); System.out.println("result:"+result); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

e> 顺序

注意:当表中的有些字段值是固定的,例如性别(男或女),此时我们可以使用MyBatis-Plus的通用枚举来实现,需要注意设定枚举类型@EnumValue同时在application.yml文件中设置type-enums-package: com.guo.mybatisplus.enums八、代码生成器
MyBatis是通过数据库表,逆向工程生成实体类和Mapper接口以及映射文件!
Mybatis-Plus中也是通过数据库表,逆向工程生成控制层、业务层、持久层、Mapper接口以及映射文件都能生成8.1 引入依赖
<!--代码生成器依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <!--freemarker模版--> <dependency> <groupId>org.freemarker</groupId> <artifactId>freemarker</artifactId> <version>2.3.31</version> </dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
8.2 快速生成
package com.guo.mybatisplus; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.FastAutoGenerator; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.OutputFile; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.engine.FreemarkerTemplateEngine; import java.util.Collections; public class FastAutoGeneratorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { FastAutoGenerator.create("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false", "username:root", "password:****") .globalConfig(builder -> { //全局配置 builder.author("guo") // 设置作者 .enableSwagger() // 开启 swagger 模式 .fileOverride() // 覆盖已生成文件 .outputDir("/.../.../.../.../..."); // 指定输出目录 }) .packageConfig(builder -> { builder.parent("com.guo.mybatisplus") // 设置父包名 .moduleName("mybatisplusAuto") // 设置父包模块名 生成的内容都在com.guo.mybatisplus.mybatisplusAuto包下 .pathInfo(Collections.singletonMap(OutputFile.mapperXml, "/.../.../.../.../...")); // 设置mapperXml生成路径 }) .strategyConfig(builder -> { //策略配置 根据哪个表,逆向生成 builder.addInclude("t_user") // 设置需要生成的表名 .addTablePrefix("t_", "c_"); // 设置过滤表前缀 }) .templateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine()) // 使用Freemarker引擎模板,默认的是Velocity引擎模板 .execute(); //执行 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
自动生成器官网:https://baomidou.com/pages/779a6e/#%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8

自动弹出生成位置的文件夹:展开后发现控制层、业务层、持久层、Mapper接口以及映射文件都已经自动生成

映射文件里面根据需要可以自定义写SQL:

九、多数据源
适用于多种场景:纯粹多库、 读写分离(有的数据库只完成读功能、有的数据库只完成写功能)、 一主多从、 混合模式等
目前我们就来模拟一个纯粹多库的一个场景,其他场景类似
场景说明:
我们创建两个库,分别为:mybatis_plus(以前的库不动)与mybatis_plus_1(新建),将mybatis_plus库的product表移动到mybatis_plus_1库,这样每个库一张表,通过一个测试用例分别获取用户数据与商品数据,如果获取到说明多库模拟成功9.1 创建数据库及表
创建数据库mybatis_plus_1和表product
CREATE DATABASE `mybatis_plus_1` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 */; use `mybatis_plus_1`; CREATE TABLE product ( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID', name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品名称', price INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '价格', version INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '乐观锁版本号', PRIMARY KEY (id) );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
添加测试数据
INSERT INTO product (id, NAME, price) VALUES (1, '外星人笔记本', 100);- 1
删除mybatis_plus库product表
use mybatis_plus; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS product;- 1
- 2
9.2 创建新项目(看自己)
配置好项目名字和包名后,点击Next
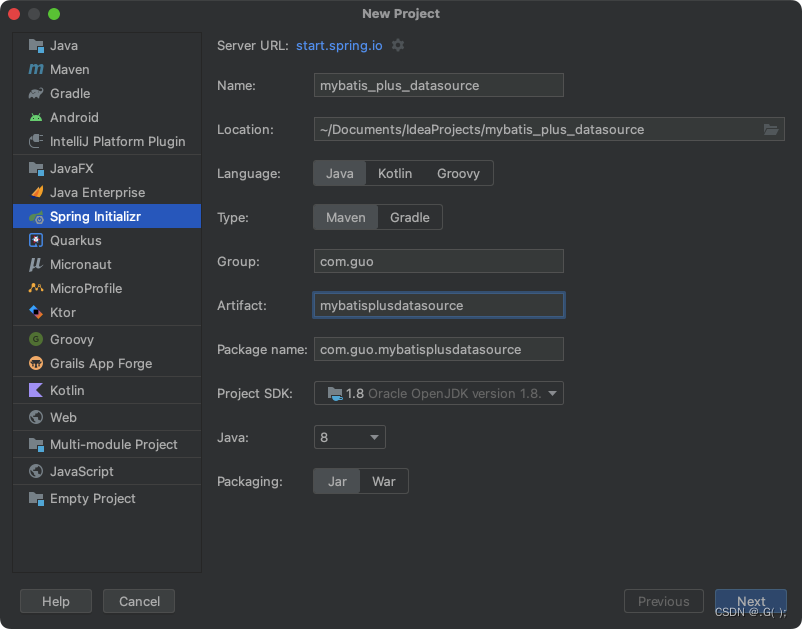
这里可以啥也不设置:点击Finish

有些文件可以删除,具体可用文件如图所示:

9.3 引入依赖(还有前面提到的相关MyBatisPlus依赖)
<!--多数据源--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.5.0</version> </dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
9.4 配置多数据源
说明:注释掉之前的数据库连接,添加新配置
spring: # 配置数据源信息 datasource: dynamic: # 设置默认的数据源或者数据源组,默认值即为master 要与下面的datasource下的master对应,名称要一样 primary: master # 严格匹配数据源,默认false.true未匹配到指定数据源时抛异常,会报错,false使用默认master数据源 strict: false datasource: master: # 与上面primary名字相同 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: **** slave_1: # 从数据源 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: ****- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
9.5 创建用户Mapper
9.5.1 实体类 User
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.*; import lombok.Data; @Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("user") public class User { //设置主键:将这个属性所对应的字段指定为主键 //@TableId 注解的value属性用于指定主键的字段 //@TableId 注解的type属性设置主键生成策略 @TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.ASSIGN_ID) //这里的value是数据库的字段名 private Integer id; //指定属性所对应的字段名 @TableField("user_name") private String userName; private Integer age; private String email; //逻辑删除字段 @TableLogic private Integer isDeleted; private Integer sex; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
9.5.2 UserMapper
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
9.6 创建商品Mapper
9.6.1 实体类 Product
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName; import lombok.Data; @Data //设置实体类对应的表名 @TableName("product") public class Product { //设置主键:将这个属性所对应的字段指定为主键 //@TableId 注解的value属性用于指定主键的字段 //@TableId 注解的type属性设置主键生成策略 @TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.ASSIGN_ID) //这里的value是数据库的字段名 private Integer id; private String name; private Integer price; private Integer version; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
9.6.2 ProductMapper
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo.Product; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface ProductMapper extends BaseMapper<Product> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
9.7 启动类 MyBatisPlusDatasourceApplication.java
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.mapper") //Copy Reference mapper包 public class MybatisPlusDatasourceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MybatisPlusDatasourceApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
9.8 创建用户Service
9.8.1 UserService 接口
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo.User; public interface UserService extends IService<User> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
9.8.2 UserServiceImpl 实现类
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service.impl; import com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.annotation.DS; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.mapper.UserMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo.User; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service.UserService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * ServiceImpl实现了IService,提供了IService中基础功能的实现 * 若ServiceImpl无法满足业务需求,则可以使用自定的UserService定义方法,并在实现类中实现 */ @Service //指定业务层组建 @DS("master") //指定所操作的数据源 public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
9.9 创建商品Service
9.9.1 ProductService 接口
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo.Product; public interface ProductService extends IService<Product> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
9.9.2 ProductServiceImpl 实现类
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service.impl; import com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.annotation.DS; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.mapper.ProductMapper; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.pojo.Product; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service.ProductService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * ServiceImpl实现了IService,提供了IService中基础功能的实现 * 若ServiceImpl无法满足业务需求,则可以使用自定的ProductService定义方法,并在实现类中实现 */ @Service //指定业务层组建 @DS("slave_1") //指定所操作的数据源 public class ProductServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ProductMapper, Product> implements ProductService{ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
9.10 测试 MybatisPlusDatasourceApplicationTests.java
package com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service.ProductService; import com.guo.mybatisplusdatasource.service.UserService; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest class MybatisPlusDatasourceApplicationTests { @Test void contextLoads() { } @Autowired private UserService userService; @Autowired private ProductService productService; @Test public void testDynamicDataSource(){ System.out.println("查找id为1的数据:"+userService.getById(1L)); //通用service的查询都是get开头 数据已经逻辑删除 搜索不到 System.out.println("查找id为2的数据:"+userService.getById(2L)); //通用service的查询都是get开头 System.out.println("查找id为1的数据:"+productService.getById(1L));//通用service的查询都是get开头 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

结果:
1、都能顺利获取对象,则测试成功
2、如果我们实现读写分离,将写操作方法加上主库数据源,读操作方法加上从库数据源,自动切换,也能实现读写分离。
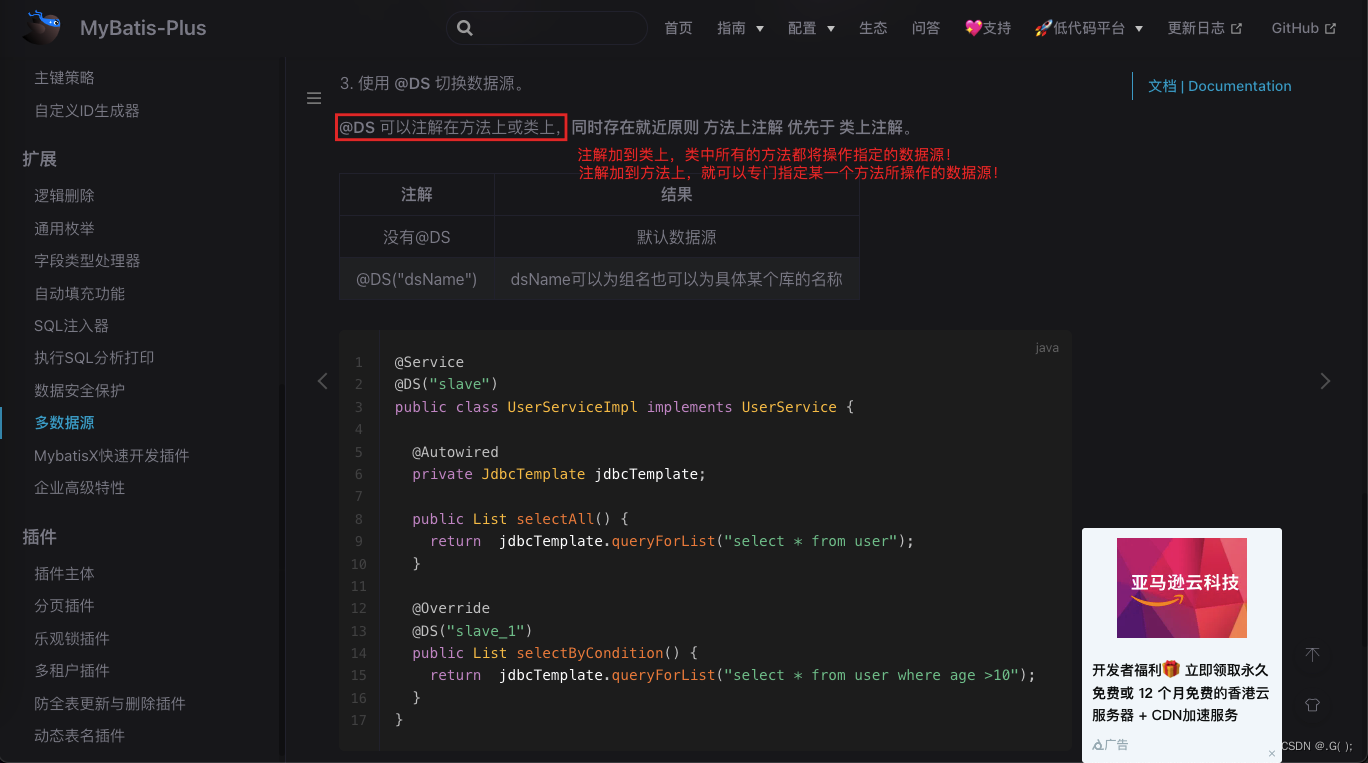
@DS设置好就行!注意:如果主数据库的User表实现的是写操作,从数据库的User表实现的是写读操作,Service和Mapper都是以User开头,因此官网中提到了:@DS 可以注解在方法上或类上,如果注解加到类上,类中所有的方法都将操作指定的数据源!如果注解加载到方法上,就可以专门指定某一个方法所操作的数据源!
十、MyBatisX插件
MyBatis-Plus为我们提供了强大的mapper和service模板,能够大大的提高开发效率但是在真正开发过程中,MyBatis-Plus并不能为我们解决所有问题,例如一些复杂的SQL,多表联查,我们就需要自己去编写代码和SQL语句,我们该如何快速的解决这个问题呢,这个时候可以使用MyBatisX插件
MyBatisX一款基于 IDEA 的快速开发插件,为效率而生。
MyBatisX插件用法:MyBatisX插件用法:https://baomidou.com/pages/ba5b24/10.1 安装方法:
Windows:打开 IDEA,进入 File -> Settings -> Plugins,输入
mybatisx搜索并安装。
macOS:打开 IDEA,进入 IntelliJ IDEA -> Preferences… -> Plugins,输入mybatisx搜索并安装。

如果不行,搜不出来东西!!!idea官网下载离线安装:IDEA插件:http://plugins.jetbrains.com/
搜索MyBatisX,点进去下载即可!

本地离线安装:


10.2 简单使用
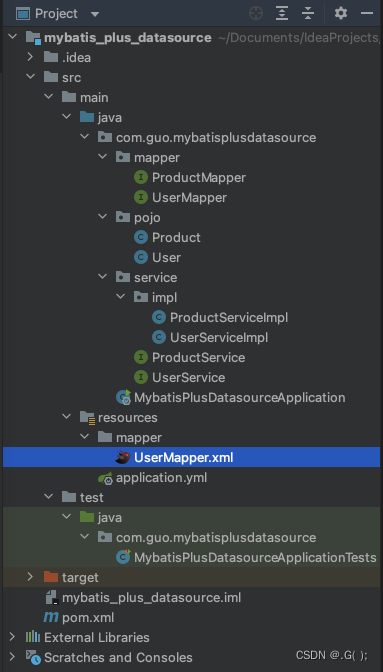
MyBatisX可以帮助我们快速对应mapper接口和映射文件! 比如我们在以后的开发过程中:一个mapper接口对应一个映射文件操作的是一张表,而当开发庞大的项目中mapper接口和映射文件有好几十个甚至好几百个时,众多的mapper接口找到相对应的映射文件是很麻烦的,因此我们需要MyBatisX快速定位mapper接口所对应的映射文件以及映射文件所对应的mapper接口!


以上文件结构:
10.3 MyBatisX代码快速生成
10.3.1 新建一个项目
配置好项目名字和包名后,点击Next

这里可以啥也不设置:点击Finish
10.3.2 引入依赖 注意要刷新Maven
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--mybatis-plus 启动器--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <!--lombok 用于简化实体类开发--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <!--mysql驱动 springboot自带的mysql--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
10.3.3 application.yml
spring: # 配置数据源信息 datasource: # 配置数据源类型 type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource # 配置连接数据库的各个信息 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false username: root password: ****- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
10.3.4 连接数据库


10.3.5 使用MyBatisX生成器
选中表,右键选择
MyBatisX-Generator
开始配置:

点击module path选择Module

继续配置,配置完成后点击Finish

自动生成文件:

10.3.6 使用MyBatisX快速生成CRUD
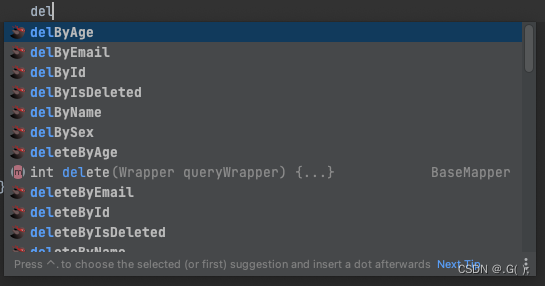
直接在
UserMapper接口中写方法,而且MyBatisX会有提示:
可以叠加写:

按住alt/option+enter再选择[MyBatisX]Generate Mybatis Sql自动在映射文件中生成SQL语句:

可以写多种方法:

映射文件中会自动生成SQL语句:

以上就是所有MyBatis-Plus的内容,希望可以有所收获! -
相关阅读:
【汇编】[bx+idata]的寻址方式、SI和DI寄存器
14.6 Socket 应用结构体传输
Ae:内容识别填充面板
日语等级J.TEST的自测卷
Linux权限管理
利用OGG实现PostgreSQL实时同步
MyBatis 第一个程序
微信小程序模板消息推送
Rust生命周期简介
数据结构 二叉树
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45048331/article/details/125478431
