-
ESP32/8266使用painlessMesh库实现mesh
ESP32/8266使用painlessMesh库实现mesh
测试了esp的mesh通信,使用的平台是PIO,基于Arduino。
最终实现的结果是设置相同的ssid和pwd之后,可以互相传输数据,但存在我呢提:通信速率不高、存在终端的问题- 使用VScode 的PIO平台,搜索painlessMesh的lib进行下载。
可以发现代码的原理还是很简单的,用的库也是简单,猜测其原理就是AP+不连接的通信
- 发射端代码:也不叫发射端,两个代码完全可以一样
#include "painlessMesh.h" #define MESH_PREFIX "esp8266" #define MESH_PASSWORD "12345678" #define MESH_PORT 5555 Scheduler userScheduler; // to control your personal task painlessMesh mesh; // User stub void sendMessage() ; // Prototype so PlatformIO doesn't complain Task taskSendMessage( TASK_SECOND * 1 , TASK_FOREVER, &sendMessage ); char c[] = {'1', '2','3','4','5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '0'}; int i =0; void sendMessage() { String msg = "Hello from node "; // msg += mesh.getNodeId(); msg += c[(i++)%10]; mesh.sendBroadcast( msg ); // taskSendMessage.setInterval( random( TASK_SECOND * 1, TASK_SECOND * 5 )); taskSendMessage.setInterval(100); } // Needed for painless library void receivedCallback( uint32_t from, String &msg ) { Serial.printf("startHere: Received from %u msg=%s\n", from, msg.c_str()); } void newConnectionCallback(uint32_t nodeId) { Serial.printf("--> startHere: New Connection, nodeId = %u\n", nodeId); } void changedConnectionCallback() { Serial.printf("Changed connections\n"); } void nodeTimeAdjustedCallback(int32_t offset) { Serial.printf("Adjusted time %u. Offset = %d\n", mesh.getNodeTime(),offset); } void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); //mesh.setDebugMsgTypes( ERROR | MESH_STATUS | CONNECTION | SYNC | COMMUNICATION | GENERAL | MSG_TYPES | REMOTE ); // all types on mesh.setDebugMsgTypes( ERROR | STARTUP ); // set before init() so that you can see startup messages mesh.init( MESH_PREFIX, MESH_PASSWORD, &userScheduler, MESH_PORT ); mesh.onReceive(&receivedCallback); mesh.onNewConnection(&newConnectionCallback); mesh.onChangedConnections(&changedConnectionCallback); mesh.onNodeTimeAdjusted(&nodeTimeAdjustedCallback); userScheduler.addTask( taskSendMessage ); taskSendMessage.enable(); } void loop() { // it will run the user scheduler as well mesh.update(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 接收端代码
#include "painlessMesh.h" #define MESH_PREFIX "esp8266" #define MESH_PASSWORD "12345678" #define MESH_PORT 5555 Scheduler userScheduler; // to control your personal task painlessMesh mesh; // User stub void sendMessage() ; // Prototype so PlatformIO doesn't complain Task taskSendMessage( TASK_SECOND * 1 , TASK_FOREVER, &sendMessage ); void sendMessage() { String msg = "Hello from node "; msg += mesh.getNodeId(); mesh.sendBroadcast( msg ); taskSendMessage.setInterval( random( TASK_SECOND * 1, TASK_SECOND * 5 )); } // Needed for painless library void receivedCallback( uint32_t from, String &msg ) { Serial.printf("startHere: Received from %u msg=%s\n", from, msg.c_str()); } void newConnectionCallback(uint32_t nodeId) { Serial.printf("--> startHere: New Connection, nodeId = %u\n", nodeId); } void changedConnectionCallback() { Serial.printf("Changed connections\n"); } void nodeTimeAdjustedCallback(int32_t offset) { Serial.printf("Adjusted time %u. Offset = %d\n", mesh.getNodeTime(),offset); } void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); //mesh.setDebugMsgTypes( ERROR | MESH_STATUS | CONNECTION | SYNC | COMMUNICATION | GENERAL | MSG_TYPES | REMOTE ); // all types on mesh.setDebugMsgTypes( ERROR | STARTUP ); // set before init() so that you can see startup messages mesh.init( MESH_PREFIX, MESH_PASSWORD, &userScheduler, MESH_PORT ); mesh.onReceive(&receivedCallback); mesh.onNewConnection(&newConnectionCallback); mesh.onChangedConnections(&changedConnectionCallback); mesh.onNodeTimeAdjusted(&nodeTimeAdjustedCallback); userScheduler.addTask( taskSendMessage ); taskSendMessage.enable(); } void loop() { // it will run the user scheduler as well mesh.update(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 一些bug
最气人的是,esp8266、esp32各种报错,这里的最重要的问题就是,使用好的usb线。换了线之后,一切都正常了。
通信的时候,即使设置成休眠100ms的通信方式,根本达不到10Hz的通信频率,并且偶尔会出现通信中断的问题。
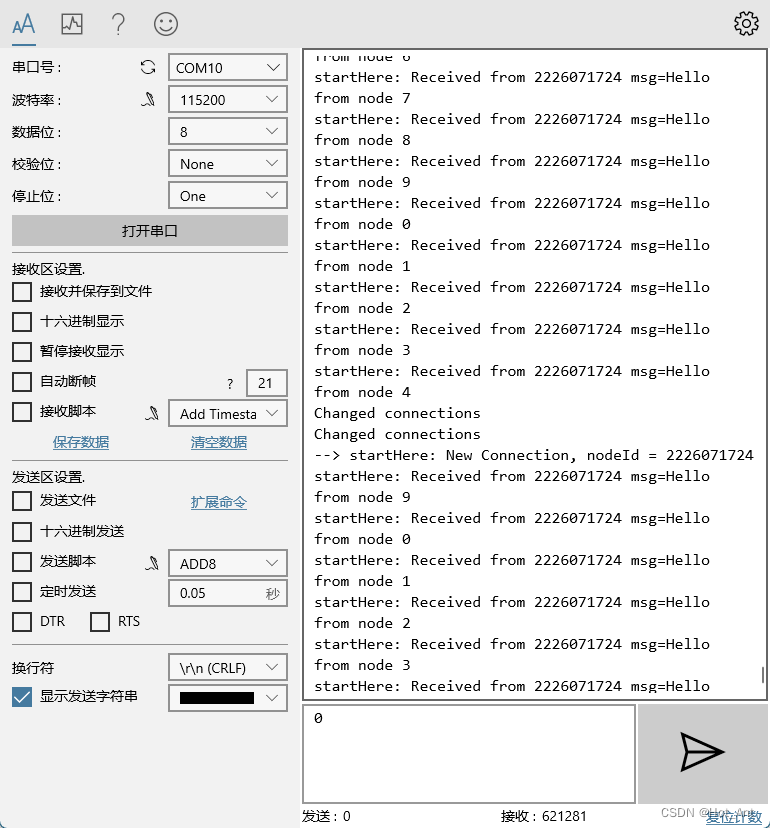
图中会出现改变里连接的问题,不清楚是发射端的问题,还是接收端的问题。即使放的很近也是。当然放在远处也是差不多的(10m测试仍通信正常)。
既然是mesh,当然是多个也可以。三个的时候仍然正常通信,接收的频率也是差不多的,看来接收限制会不是很高。但是出现了接收着就卡住了。
多个的时候,接收端一个近一个远可以同时接收两个,但是两个都很远的时候,会出现同一时刻只能接收到一个。
还是会存在着,接收着就卡住了,哎~
-
相关阅读:
代码随想录算法训练营 单调栈part03
实验一 熟悉OpenCV环境和基本操作
redis下载与安装(Linux环境下)
uniapp 微信小程序仿抖音评论区功能,支持展开收起
方法递归详解
[C++ 网络协议] 套接字和标准I/O
Loader自定义组件sourceComponent 和source区别
【毕业设计】基于stm32的迷你示波器 - 单片机 嵌入式 物联网
《谷粒商城》开发记录 12:购物车和订单
基于JAVA学校运动会信息管理系统计算机毕业设计源码+系统+mysql数据库+lw文档+部署
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Hot_Ant/article/details/125473716
