-
操作系统实验(4)—— 处理机调度算法模拟实现与比较
处理机调度算法模拟实现与比较
1. 实验目的
分析处理器实施进程调度的前提条件,理解并掌握各类处理器调度算法的设计原理和实现机制。
2. 实验内容
分析和探索处理器实施进程调度的前提条件,理解并掌握处理器调度算法的设计原理和实现机制,随机发生和模拟进程创建及相关事件,编程实现基于特定处理器调度算法(三种以上,譬如先来先服务调度算法、短进程优先调度算法、高优先权优先调度算法、高响应比优先调度算法、时间片轮转调度算法、多级反馈队列调度算法、等等)的系统调度处理过程,并加以测试验证。
3. 实验要求
本实验课题主要功能设计要求包括:
- 选取和设计实现三种以上的处理器调度算法;
- 针对特定的处理器调度算法,分析处理器实施进程调度的前提条件和要求(譬如进程创建时刻、运行时间长短、各【集中计算运行/输入输出操作】时间段长短、优先级),并随机发生和模拟处理对应的进程创建及相关事件;
- 编程实现处理器调度机制,针对特定的处理器调度算法和随机事件序列,给出相应的调度处理过程,主要涵盖进程相关事件、处理器调度操作或处理措施以及各状态进程列表;
- 测试验证处理器调度机制的有效性及有关处理器调度算法设计方案的正确性。
4. 实验过程
4.1 程序框架设计
4.1.1 主要数据结构
定义结构体数组pinfo,包含进程相关的各种信息。
typedef struct { int process_order; // 进程到达的顺序。数值越低,说明到达的越早。 而且这个值必须是唯一的。 int process_arrival_time; // 到达时间 int process_priority; // 优先权。数值越小,证明优先权越高。而且这个值必须是唯一的。 int how_much_left; // 还剩余多少个时间可以完成这个进程 int waiting_time; // 等待CPU的时间 int response_time; // CPU的响应时间 int turnaround_time; // 周转时间 = 进程完成时间 - 进程到达时间 int has_run_at_least_once; // 标志该进程是否至少运行了一次,用来计算响应时间 int has_terminated; // 标志进程是否结束 int time_slice_left; // 时间片轮转算法中记录当前时间片的剩余时间 int process_number; // 进程数 } pinfo; // 进程信息- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
4.1.2 主要处理函数
allocate_mem_for_process_list子程序为进程列表分配内存空间
pinfo **allocate_mem_for_process_list(int length, int only_outer) { pinfo **pinfos = malloc(sizeof(pinfo *) * length); if (!only_outer) { for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { pinfos[i] = (pinfo *) malloc(sizeof(pinfo)); } } return pinfos; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
deallocate_mem_for_process_list子程序回收进程列表的内存空间
void deallocate_mem_for_process_list(pinfo **pinfos, int length, int only_outer) { if (!only_outer) { for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { free(pinfos[i]); } } free(pinfos); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
take_input子程序,用户交互程序,通过用户的输入选择不同的算法
void take_input(pinfo ***pinfos_out, int *pinfos_len, int *algorithm, int *preemptive, int *quantum) { int nprocs; char algo[5]; char preempt[4]; pinfo **pinfos = NULL; // 选择不同类型的进程调度算法 printf("请输入要选择的算法(fcfs/sjf/pri/rr): "); scanf("%s", algo); if (strcmp(algo, "fcfs") == 0) { *algorithm = FCFS_SCHED; // FCFS } else if (strcmp(algo, "sjf") == 0) { *algorithm = SJF_SCHED; // SJF } else if (strcmp(algo, "pri") == 0) { *algorithm = PRI_SCHED; // PRI } else if (strcmp(algo, "rr") == 0) { *algorithm = RR_SCHED; // RR } else { exit(1); } // 如果是SJF或者PRI, 选择是否采取抢占式算法 if (*algorithm == SJF_SCHED || *algorithm == PRI_SCHED) { printf("是否选择抢占式算法 (yes/no)? "); scanf("%s", preempt); } if (strcmp(preempt, "yes") == 0) { *preemptive = PREEMT; } else if (strcmp(preempt, "no") == 0) { *preemptive = NO_PREEMT; } //如果是RR算法,则需要输入时间片的大小 if (*algorithm == RR_SCHED) { printf("请输入时间片的大小: "); scanf("%d", quantum); } //请输入进程数 printf("请输入进程数: "); scanf("%d", &nprocs); *pinfos_len = nprocs; //为进程列表分配内存空间 pinfos = allocate_mem_for_process_list(nprocs, 0); for (int i = 0; i < nprocs; ++i) { printf("\n"); //初始化进程列表信息 pinfos[i]->process_priority = 0; pinfos[i]->waiting_time = 0; pinfos[i]->response_time = 0; pinfos[i]->turnaround_time = 0; pinfos[i]->has_run_at_least_once = 0; pinfos[i]->has_terminated = 0; pinfos[i]->process_number = i; //如果是PRI算法,需要输入进程的优先权 if (*algorithm == PRI_SCHED) { printf("请输入进程 P%d 的优先权: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->process_priority); } // 如果是FCFSh或者RR算法,需要输入进程的到达次序 if ((*algorithm == FCFS_SCHED) || (*algorithm == RR_SCHED)) { printf("请输入进程 P%d 的到达次序: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->process_order); } // 所有算法都需要输入进程的到达时间 printf("请输入进程 P%d 的到达时间: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->process_arrival_time); printf("请输入进程 P%d 的需要服务时间: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->how_much_left); } // 如果是RR算法,需要初始化时间片的剩余时间=原时间片的大小 if (*algorithm == RR_SCHED) { for (int i = 0; i < *pinfos_len; ++i) { pinfos[i]->time_slice_left = *quantum; } } *pinfos_out = pinfos; printf("\n"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
display_output打印输出信息
void display_output(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int context_switches) { printf("\n"); for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { printf("\n进程 P%d 的响应时间: %d\n", i, pinfos[i]->response_time); printf("进程 P%d 的等待时间: %d\n", i, pinfos[i]->waiting_time); printf("进程 P%d 的周转时间: %d\n", i, pinfos[i]->turnaround_time); } printf("\n进程切换(状态转换)次数: %d\n", context_switches); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
has_process_arrived判断进程是否到达
int has_process_arrived(pinfo **pinfos, int process, int time) { if (process == NO_PROCESS) return 1; return pinfos[process]->process_arrival_time <= time; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
has_process_finished判断进程是否结束
int has_process_finished(pinfo **pinfos, int process) { if (process == NO_PROCESS) // 如果当前没有进程 return 1; return pinfos[process]->has_terminated; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
is_process_available_to_run判断进程是否可以运行
int is_process_available_to_run(pinfo **pinfos, int process, int time) { return has_process_arrived(pinfos, process, time) && !has_process_finished(pinfos, process);// 已经开始,但是还未结束 }- 1
- 2
- 3
next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order按照order的次序,找到下一个未完成但是已经到达的进程。
int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0; // 已经检查过的进程个数 int min_order = MAX_ORDER_OR_PRIORITY; // 保存最小的order的值 int min_process = NO_PROCESS; // 保存order最小的进程(即待调度的进程) while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { // 遍历所有的进程 current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; // 因为是列表,所以循环遍历 if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) // 当前进程正在运行 if (pinfos[current_process]->process_order < min_order) { // 寻找最小的order进程 min_process = current_process; min_order = pinfos[current_process]->process_order; } ++processes_checked; } return min_process; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority按照priority的次序,找到下一个未完成但是已经到达的进程
int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0;// 已经检查过的进程个数 int min_priority = MAX_ORDER_OR_PRIORITY;// 保存最小的priority的值 int min_process = NO_PROCESS;//保存priority最小的进程(即待调度的进程) while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { // 遍历所有的进程 current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; // 因为是列表,所以循环遍历 if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) // 当前进程正在运行 if (pinfos[current_process]->process_priority < min_priority) {// 寻找最小的priority进程 min_process = current_process; min_priority = pinfos[current_process]->process_priority; } ++processes_checked; } return min_process; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining按照最短剩余时间的次序,找到下一个未完成但是已经到达的进程
int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0;// 已经检查过的进程个数 int min_process_time = MAX_BURST_TIME;// 保存最小剩余时间的值 int min_process = NO_PROCESS;//保存剩余时间最小的进程(即待调度的进程) while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) {// 遍历所有的进程 current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len;// 因为是列表,所以循环遍历 if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time))// 当前进程正在运行 if (pinfos[current_process]->how_much_left < min_process_time) { // 寻找最小的priority进程 min_process = current_process; min_process_time = pinfos[current_process]->how_much_left; } ++processes_checked; } return min_process; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order_for_rr对于RR算法,按照order, 找到下一个已到达但未完成的进程
int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order_for_rr(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0; while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) return current_process; ++processes_checked; } return NO_PROCESS; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
order_comparator比较两个进程的order,如果第一个进程大于第二个进程则返回正数,否则返回负数
int order_comparator(const void *x, const void *y) { pinfo *x_ptr = *(pinfo **) x; pinfo *y_ptr = *(pinfo **) y; int x_order = x_ptr->process_order; int y_order = y_ptr->process_order; return (x_order - y_order); // 返回值是两个进程order的差值 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
sort_by_order按照order进行排序
void sort_by_order(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len) { qsort((void **) pinfos, pinfos_len, sizeof(pinfo *), order_comparator); // 调用qsort函数,对各个进程按照order的大小进行排序 }- 1
- 2
- 3
next_process_to_run选择下一个进程去调度
int next_process_to_run(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int algorithm, int preemptive, int time, int quantum, int *context_switches) { switch (algorithm) { // 根据algorithm参数选择不同的调度算法 case FCFS_SCHED: return fcfs(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); case SJF_SCHED: switch (preemptive) { case NO_PREEMT: return sjf_nonpreempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); case PREEMT: return sjf_preempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); default: return NO_PROCESS; } case PRI_SCHED: switch (preemptive) { case NO_PREEMT: return pri_nonpreempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); case PREEMT: return pri_preempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); default: return NO_PROCESS; } case RR_SCHED: return rr(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, quantum, time, context_switches); default: return NO_PROCESS; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 运行进程并更新状态
void run_process_and_update_structs(int process_to_run, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int *time) { if (process_to_run != NO_PROCESS) { --pinfos[process_to_run]->how_much_left; // 还需服务时间减去1 pinfos[process_to_run]->has_run_at_least_once = 1; // 标志曾经被服务过 if (pinfos[process_to_run]->how_much_left <= 0) { // 如果当前所需时间为负,则说明运行结束 pinfos[process_to_run]->has_terminated = 1; // 终止标志置为1 pinfos[process_to_run]->turnaround_time = *time - pinfos[process_to_run]->process_arrival_time + 1;// 计算周转时间=当前时间-到达时间 } } for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) {//遍历进程列表 if (i == process_to_run) continue; //如果是正在运行的进程则不作处理 if (has_process_arrived(pinfos, i, *time) && (!pinfos[i]->has_run_at_least_once)) { // 如果是已经到达的进程,且并没有被处理机运行过 ++pinfos[i]->response_time; // 则响应时间+1 } if (has_process_arrived(pinfos, i, *time) && (!pinfos[i]->has_terminated)) { // 如果是已经到达,但是并未结束的进程 ++pinfos[i]->waiting_time; // 则等待时间+1 } } ++*time;// 整体时间向前推进一个单位 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
all_processes_have_finished判断所有的进程是否都运行结束
int all_processes_have_finished(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len) { for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { // 循环遍历所有的进程,查看是否有未结束的进程 if (!pinfos[i]->has_terminated) // 如果有则返回0 return 0; } return 1; // 返回1说明所有的进程都运行结束 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 主函数
int main() { pinfo **pinfos = NULL; int pinfos_len, time = 0, next_process = NO_PROCESS, algorithm, preemptive, context_switches = 0, previous_process, quantum; take_input(&pinfos, &pinfos_len, &algorithm, &preemptive, &quantum); // 读取用户的输入 while (!all_processes_have_finished(pinfos, pinfos_len)) { // 如果不是所有进程都执行结束,则继续运行 previous_process = next_process; next_process = next_process_to_run(next_process, pinfos, pinfos_len, algorithm, preemptive, time, quantum,&context_switches);// 得到下一个要运行的进程 if (next_process == NO_PROCESS && previous_process != NO_PROCESS && algorithm != RR_SCHED) { printf("【状态转换】从一个具体的进程到无进程\n"); ++context_switches; } else if (next_process != NO_PROCESS && previous_process == NO_PROCESS && algorithm != RR_SCHED) { printf("【状态转换】从无进程到创建一个具体的进程\n"); ++context_switches; } else if (next_process != NO_PROCESS && previous_process != NO_PROCESS && next_process != previous_process && algorithm != RR_SCHED) { printf("【状态转换】从一个进程切换到另一个进程\n"); ++context_switches; } if (next_process == NO_PROCESS) printf("从时间点 = %d 到时间点 = %d. 无进程\n", time, time + 1); else printf("F从时间点 = %d 到时间点 = %d. 运行进程 P%d\n", time, time + 1, next_process); run_process_and_update_structs(next_process, pinfos, pinfos_len, &time); // 运行该进程并且更新状态信息 } display_output(pinfos, pinfos_len, context_switches); // 输出性能分析的相关结果 deallocate_mem_for_process_list(pinfos, pinfos_len, 0); // 回收内存空间 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
4.2 FCFS算法
4.2.1 原理介绍
FCFS 先来先服务 (First come first sever)
-
算法思想:主要从“公平”的角度考虑
-
算法规则 : 按照作业/进程到达的先后顺序进行服务。
-
属于非抢占式的算法。
-
优点:公平、算法实现简单; 缺点:排在长作业(进程)后面的短作业需要等待很长时间,带权周转时间很大,对短作业来说用户体验不好。即,FCFS算法对长作业有利,对短作业不利
4.2.2 代码实现
Fcfs算法主要通过
has_process_finished函数的返回值判断上一个时间段正在运行的进程有没有结束,如果上一个时间段正在运行的进程没有结束,则继续运行该进程;否则按照order找到下一个已到达但是为结束的进程。其具体实现函数是fcfs如下// fcfs算法流程 int fcfs(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { if (!has_process_finished(pinfos, last_process_running)) return last_process_running; // 如果上一个时间段正在运行的进程没有结束,则继续运行该进程 else return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); // 否则按照order找到下一个已到达但是没有结束的进程 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
4.2.3 测试结果
- 初始化运行状态
进程 到达时间 运行时间 P0 0 7 P1 2 4 P2 4 1 P3 5 4 
-
输出状态转换过程
根据先来先服务的算法,按照到达时间的先后顺序执行P0->P1->P2->P3
时间段 进程 [0,7) P0 [7,11) P1 [11,12) P2 [12,15) P3

-
性能分析
计算得到各个进程的响应时间,等待时间和周转时间。

4.3 SJF算法
4.3.1 原理介绍
SJF 短作业优先 (Shortest Job First)
- 算法思想: 追求最少的平均等待时间,最少的平均周转时间、最少的平均平均带权周转时间
- 算法规则:最短的作业/进程优先得到服务(所谓“最短”,是指要求服务时间最短)
- SJF是非抢占式的算法。但是也有抢占式的版本――最短剩余时间优先算法(SRTN, Shortest Remaining Time Next)
- 优点:“最短的”平均等待时间、平均周转时间。缺点:不公平。对短作业有利,对长作业不利。可能产生饥饿现象。另外,作业/进程的运行时间是由用户提供的,并不一定真实,不一定能做到真正的短作业优先。如果源源不断地有短作业/进程到来,可能使长作业/进程长时间得不到服务,产生“饥饿”现象。如果一直得不到服务,则称为“饿死”
4.3.2 代码实现
sjf_nonpreempt非抢占式sjf算法
int sjf_nonpreempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { if (!has_process_finished(pinfos, last_process_running)) return last_process_running; // 如果上一个时间段正在运行的进程没有结束,则继续运行该进程 else return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); // 否则按照最短服务时间时间找到下一个已到达但是没有结束的进程 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
sjf_preempt抢占式sjf算法
int sjf_preempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); // 按照最短服务时间时间找到下一个已到达但是没有结束的进程 }- 1
- 2
- 3
4.3.3 测试结果
- 初始化运行状态
进程 到达时间 运行时间 P0 0 7 P1 2 4 P2 4 1 P3 5 4 -
非抢占式sjf算法
- 初始化进程信息

- 进程运行过程
- 在0时刻,只有P0到达,因此0~7时刻,P0运行
- 在7时刻,进程P1、P2、P3都已经到达了,此时按照最短服务时间,选择P2运行
- 在8时刻,P2运行完成,但是由于P3和P1要求服务时间相等,然后按照在列表前后的顺序,选择P3运行。
- 在12时刻,P3运行完成,最后运行P1

-
性能分析
计算得到各个进程的响应时间,等待时间、周转时间以及状态转换次数。

-
抢占式sjf算法
- 初始化进程信息

-
进程的运行过程
- 在0时刻,只有P0到达,因此先运行P0
- 在2时刻,P1到达,P1的要求运行时间要小于P0,因此抢占CPU开始运行P1
- 在4时刻,P2到达,P2的要求运行时间要小于P1,因此抢占CPU开始运行P2
- 在5时刻,P2运行结束,选择剩下进程中运行时间最小的P1
- 在7时刻,P1运行完成,选择剩下进程中运行时间最小的P3
- 在11时刻,P3运行完成,选择剩下进程中运行时间最小的P0

- 计算得到各个进程的响应时间,等待时间、周转时间以及状态转换次数。

4.4 PRI算法
4.4.1 原理介绍
- 算法思想:随着计算机的发展,特别是实时操作系统的出现,越来越多的应用场景需要根据任务的紧急程度来决定处理顺序调度时选择优先级最高的作业/进程
- 算法规则:既可用于作业调度,也可用于进程调度。甚至,还会用于在之后会学习的I/o调度中
- 抢占式、非抢占式都有
- 优点:用优先级区分紧急程度、重要程度,适用于实时操作系统。可灵活地调整对各种作业/进程的偏好程度。缺点:若源源不断地有高优先级进程到来,则可能导致饥饿4.4.2 代码实现
4.4.2 代码实现
pri_nonpreempt非抢占式pri算法
int pri_nonpreempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { if (!has_process_finished(pinfos, last_process_running))// 如果上一个时间段正在运行的进程没有结束,则继续运行该进程 return last_process_running; else return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time);// 否则按照最高优先权找到下一个已到达但是没有结束的进程 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
pri_preempt抢占式pri算法
int pri_preempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); // 按照最高优先权找到下一个已到达但是没有结束的进程 }- 1
- 2
- 3
4.4.3 测试结果
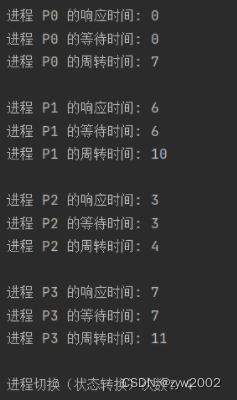
进程 到达时间 运行时间 优先级 P0 0 7 3 P1 2 4 2 P2 4 1 1 P3 5 4 4 -
非抢占式pri
-
初始化进程信息

-
状态转换
- 时刻0,P0到达,先运行P0
- 时刻7,P0运行结束,此时P1,P2,P3都已经到达,选择优先权最高的P2进程运行
- 时刻8,P2运行结束,在剩下的进程中选择优先权最高的P1进程运行
- 时刻12,P1运行结束,运行最后一个进程P3
-

-
性能分析
-
抢占式pri
- 初始化进程信息

-
状态转换
- 时刻0,只有P0到达,因此执行P0
- 时刻2,P1也到达。由于P1的优先级高于P0,因此抢占CPU运行P1
- 时刻4,P2也到达,由于P2的优先级高于P1,因此抢占CPU运行P2
- 时刻5,P2运行结束,执行当前优先级中最高的P1
- 时刻7,P1运行结束,执行当前优先级中最高的P0
- 时刻12,P0运行结束,执行当前优先级中最高的P3

-
性能分析

4.5 RR算法
4.5.1 原理介绍
- 算法思想:公平地、轮流地为各个进程服务,让每个进程在一定时间间隔内都可以得到响应
- 算法规则:按照各进程到达就绪队列的顺序,轮流让各个进程执行一个时间片(如100ms)。若进程未在一个时间片内执行完,则剥夺处理机,将进程重新放到就绪队列队尾重新排队。用于进程调度(只有作业放入内存建立了相应的进程后,才能被分配处理机时间片)
- 若进程未能在时间片内运行完,将被强行剥夺处理机使用权,因此时间片轮转调度算法属于抢占式的算法。由时钟装置发出时钟中断来通知CPU时间片己到
- 优点:公平;响应快,适用于分时操作系统; 缺点:由于高频率的进程切换,因此有一定开销;不区分任务的紧急程度。不会导致饥饿。
4.5.2 代码实现
rr用来实现时间片轮转算法// 时间片轮转算法 int rr(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int quantum, int time, int *context_switches) { pinfo **sorted_pinfos = allocate_mem_for_process_list(pinfos_len, 1); for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) sorted_pinfos[i] = pinfos[i]; sort_by_order(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len); // 按照到达的先后次序进行排列 if (last_process_running != NO_PROCESS) { // 如果上一个时间片有进程 if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, last_process_running, time)) {// 判断该进程是否能够运行 if (--pinfos[last_process_running]->time_slice_left) {// 时间片未用完,则继续运行该进程 deallocate_mem_for_process_list(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, 1); return last_process_running; } else { pinfos[last_process_running]->time_slice_left = quantum; // 时间片用完导致进程切换 ++*context_switches; printf("【状态转换】由于时间片用完导致进程切换!\n"); } } else if (pinfos[last_process_running]->time_slice_left) { // 进程任务结束,导致进程切换 ++*context_switches; printf("【状态转换】由于进程任务结束导致进程切换,但是时间片仍然有剩余\n"); } } int last_process_running_in_sorted_pinfos = -1; for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { // 循环遍历进程队列 if (sorted_pinfos[i]->process_number == last_process_running) { last_process_running_in_sorted_pinfos = i; // 找到上一个运行的进程 break; } } int to_return = next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order_for_rr(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running_in_sorted_pinfos, time);// 按照order排序,返回下一个未完成但是已到达的进程 if (to_return == NO_PROCESS) { // 如果当前返回没有进程 deallocate_mem_for_process_list(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, 1); // 说明所有进程都运行完毕,释放内存空间 return to_return; } else { to_return = sorted_pinfos[to_return]->process_number; if (last_process_running == NO_PROCESS) {// 上一次没有进程,则说明处于开始状态,需要创建进程。 ++*context_switches; printf("【状态转换】从没有进程到开始创建进程\n"); } deallocate_mem_for_process_list(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, 1); // 释放内存空间 return to_return; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
4.5.3 测试结果
- 初始化进程信息,设定时间片的大小为2

-
进程切换
根据进程到达的先后顺序进行循环的切换,顺序分别是P0->P1->P2->P3->P0… 当有进程运行完成后,则会从该循环队列中移除。每个进程运行的时间为2的时间片,当该时间片用完后,会剥夺该CPU资源,留给下一个进程运行。当一个时间片为用完但是进程已经结束时,则会自动放弃CPU的资源,立即给下一个进程使用

- 性能分析

5. 心得体会
通过这次实验,加深了我对于不同种处理机调度算法的理解,包括不同算法的原理,特点,优缺点等。通过实际的测试用例,让我对不同调度算法的工作流程和规则更加熟悉。同时,也提升了自己的编程能力,受益匪浅。
6. 源代码附录
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define FCFS_SCHED 0 // first come, first served algorithm 先来先服务 #define SJF_SCHED 1 // shortest job first algorithm 短作业优先 #define PRI_SCHED 2 // priority based algorithm 高优先权调度算法 #define RR_SCHED 3 // round-robin algorithm 时间片轮转算法 #define PREEMT 0 // 抢占式标志 #define NO_PREEMT 1 // 非抢占式标志 #define NO_PROCESS 99 // 无进程 #define MAX_BURST_TIME 99999 // 最大时间 #define MAX_ORDER_OR_PRIORITY 99999 // 最大优先权 typedef struct { int process_order; // 进程到达的顺序。数值越低,说明到达的越早。 而且这个值必须是唯一的。 int process_arrival_time; // 到达时间 int process_priority; // 优先权。数值越小,证明优先权越高。而且这个值必须是唯一的。 int how_much_left; // 还剩余多少个时间可以完成这个进程 int waiting_time; // 等待CPU的时间 int response_time; // CPU的响应时间 int turnaround_time; // 周转时间 = 进程完成时间 - 进程到达时间 int has_run_at_least_once; // 标志该进程是否至少运行了一次,用来计算响应时间 int has_terminated; // 标志进程是否结束 int time_slice_left; // 时间片轮转算法中记录当前时间片的剩余时间 int process_number; // 进程数 } pinfo; // 进程信息 // 为进程列表分配内存空间 pinfo **allocate_mem_for_process_list(int length, int only_outer) { pinfo **pinfos = malloc(sizeof(pinfo *) * length); if (!only_outer) { for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { pinfos[i] = (pinfo *) malloc(sizeof(pinfo)); } } return pinfos; } //回收进程列表的内存空间 void deallocate_mem_for_process_list(pinfo **pinfos, int length, int only_outer) { if (!only_outer) { for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { free(pinfos[i]); } } free(pinfos); } // 用户交互程序,通过用户的输入选择不同的算法 void take_input(pinfo ***pinfos_out, int *pinfos_len, int *algorithm, int *preemptive, int *quantum) { int nprocs; char algo[5]; char preempt[4]; pinfo **pinfos = NULL; // 选择不同类型的进程调度算法 printf("请输入要选择的算法(fcfs/sjf/pri/rr): "); scanf("%s", algo); if (strcmp(algo, "fcfs") == 0) { *algorithm = FCFS_SCHED; // FCFS } else if (strcmp(algo, "sjf") == 0) { *algorithm = SJF_SCHED; // SJF } else if (strcmp(algo, "pri") == 0) { *algorithm = PRI_SCHED; // PRI } else if (strcmp(algo, "rr") == 0) { *algorithm = RR_SCHED; // RR } else { exit(1); } // 如果是SJF或者PRI, 选择是否采取抢占式算法 if (*algorithm == SJF_SCHED || *algorithm == PRI_SCHED) { printf("是否选择抢占式算法 (yes/no)? "); scanf("%s", preempt); } if (strcmp(preempt, "yes") == 0) { *preemptive = PREEMT; } else if (strcmp(preempt, "no") == 0) { *preemptive = NO_PREEMT; } //如果是RR算法,则需要输入时间片的大小 if (*algorithm == RR_SCHED) { printf("请输入时间片的大小: "); scanf("%d", quantum); } //请输入进程数 printf("请输入进程数: "); scanf("%d", &nprocs); *pinfos_len = nprocs; //为进程列表分配内存空间 pinfos = allocate_mem_for_process_list(nprocs, 0); for (int i = 0; i < nprocs; ++i) { printf("\n"); //初始化进程列表信息 pinfos[i]->process_priority = 0; pinfos[i]->waiting_time = 0; pinfos[i]->response_time = 0; pinfos[i]->turnaround_time = 0; pinfos[i]->has_run_at_least_once = 0; pinfos[i]->has_terminated = 0; pinfos[i]->process_number = i; //如果是PRI算法,需要输入进程的优先权 if (*algorithm == PRI_SCHED) { printf("请输入进程 P%d 的优先权: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->process_priority); } // 如果是FCFSh或者RR算法,需要输入进程的到达次序 if ((*algorithm == FCFS_SCHED) || (*algorithm == RR_SCHED)) { printf("请输入进程 P%d 的到达次序: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->process_order); } // 所有算法都需要输入进程的到达时间 printf("请输入进程 P%d 的到达时间: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->process_arrival_time); printf("请输入进程 P%d 的需要服务时间: ", i); scanf("%d", &pinfos[i]->how_much_left); } // 如果是RR算法,需要初始化时间片的剩余时间=原时间片的大小 if (*algorithm == RR_SCHED) { for (int i = 0; i < *pinfos_len; ++i) { pinfos[i]->time_slice_left = *quantum; } } *pinfos_out = pinfos; printf("\n"); } // 打印输出信息 void display_output(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int context_switches) { printf("\n"); for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { printf("\n进程 P%d 的响应时间: %d\n", i, pinfos[i]->response_time); printf("进程 P%d 的等待时间: %d\n", i, pinfos[i]->waiting_time); printf("进程 P%d 的周转时间: %d\n", i, pinfos[i]->turnaround_time); } printf("\n进程切换(状态转换)次数: %d\n", context_switches); } // 判断进程是否到达 int has_process_arrived(pinfo **pinfos, int process, int time) { if (process == NO_PROCESS) return 1; return pinfos[process]->process_arrival_time <= time; } // 判断进程是否结束 int has_process_finished(pinfo **pinfos, int process) { if (process == NO_PROCESS) return 1; return pinfos[process]->has_terminated; } // 判断进程是否可以运行 int is_process_available_to_run(pinfo **pinfos, int process, int time) { return has_process_arrived(pinfos, process, time) && !has_process_finished(pinfos, process);// 已经开始,但是还未结束 } // 按照order的次序,找到下一个未完成但是已经到达的进程。 int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0; int min_order = MAX_ORDER_OR_PRIORITY; int min_process = NO_PROCESS; while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) if (pinfos[current_process]->process_order < min_order) { min_process = current_process; min_order = pinfos[current_process]->process_order; } ++processes_checked; } return min_process; } // 按照priority的次序,找到下一个未完成但是已经到达的进程 int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0; int min_priority = MAX_ORDER_OR_PRIORITY; int min_process = NO_PROCESS; while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) if (pinfos[current_process]->process_priority < min_priority) { min_process = current_process; min_priority = pinfos[current_process]->process_priority; } ++processes_checked; } return min_process; } // 按照最短剩余时间的次序,找到下一个未完成但是已经到达的进程 int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0; int min_process_time = MAX_BURST_TIME; int min_process = NO_PROCESS; while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) if (pinfos[current_process]->how_much_left < min_process_time) { min_process = current_process; min_process_time = pinfos[current_process]->how_much_left; } ++processes_checked; } return min_process; } // 对于RR算法,按照order, 找到下一个已到达但未完成的进程 int next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order_for_rr(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int current_process, int time) { int processes_checked = 0; while (processes_checked < pinfos_len) { current_process = (current_process + 1) % pinfos_len; if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, current_process, time)) return current_process; ++processes_checked; } return NO_PROCESS; } // 比较两个进程的order,如果第一个进程大于第二个进程则返回正数,否则返回负数 int order_comparator(const void *x, const void *y) { pinfo *x_ptr = *(pinfo **) x; pinfo *y_ptr = *(pinfo **) y; int x_order = x_ptr->process_order; int y_order = y_ptr->process_order; return (x_order - y_order); } // 按照order进行排序 void sort_by_order(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len) { qsort((void **) pinfos, pinfos_len, sizeof(pinfo *), order_comparator); } // fcfs算法流程 int fcfs(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { if (!has_process_finished(pinfos, last_process_running)) return last_process_running; else return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); } // 非抢占式sjf算法 int sjf_nonpreempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { if (!has_process_finished(pinfos, last_process_running)) return last_process_running; else return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); } // 抢占式sjf算法 int sjf_preempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_shortest_time_remaining(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); } // 非抢占式pri算法 int pri_nonpreempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { if (!has_process_finished(pinfos, last_process_running)) return last_process_running; else return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); } // 抢占式pri算法 int pri_preempt(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int time) { return next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_priority(pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running, time); } // 时间片轮转算法 int rr(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int quantum, int time, int *context_switches) { pinfo **sorted_pinfos = allocate_mem_for_process_list(pinfos_len, 1); for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) sorted_pinfos[i] = pinfos[i]; sort_by_order(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len); if (last_process_running != NO_PROCESS) { if (is_process_available_to_run(pinfos, last_process_running, time)) { if (--pinfos[last_process_running]->time_slice_left) { deallocate_mem_for_process_list(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, 1); return last_process_running; } else { pinfos[last_process_running]->time_slice_left = quantum; ++*context_switches; printf("【状态转换】由于时间片用完导致进程切换!\n"); } } else if (pinfos[last_process_running]->time_slice_left) { ++*context_switches; printf("【状态转换】由于进程任务结束导致进程切换,但是时间片仍然有剩余\n"); } } int last_process_running_in_sorted_pinfos = -1; for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { if (sorted_pinfos[i]->process_number == last_process_running) { last_process_running_in_sorted_pinfos = i; break; } } int to_return = next_unfinished_arrived_process_by_order_for_rr(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, last_process_running_in_sorted_pinfos, time); if (to_return == NO_PROCESS) { deallocate_mem_for_process_list(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, 1); return to_return; } else { to_return = sorted_pinfos[to_return]->process_number; if (last_process_running == NO_PROCESS) { ++*context_switches; printf("【状态转换】从没有进程到开始创建进程\n"); } deallocate_mem_for_process_list(sorted_pinfos, pinfos_len, 1); return to_return; } } // 选择下一个进程去调度 int next_process_to_run(int last_process_running, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int algorithm, int preemptive, int time, int quantum, int *context_switches) { switch (algorithm) { case FCFS_SCHED: return fcfs(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); case SJF_SCHED: switch (preemptive) { case NO_PREEMT: return sjf_nonpreempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); case PREEMT: return sjf_preempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); default: return NO_PROCESS; } case PRI_SCHED: switch (preemptive) { case NO_PREEMT: return pri_nonpreempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); case PREEMT: return pri_preempt(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, time); default: return NO_PROCESS; } case RR_SCHED: return rr(last_process_running, pinfos, pinfos_len, quantum, time, context_switches); default: return NO_PROCESS; } } // 运行进程并更新状态 void run_process_and_update_structs(int process_to_run, pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len, int *time) { if (process_to_run != NO_PROCESS) { --pinfos[process_to_run]->how_much_left; pinfos[process_to_run]->has_run_at_least_once = 1; if (pinfos[process_to_run]->how_much_left <= 0) { pinfos[process_to_run]->has_terminated = 1; pinfos[process_to_run]->turnaround_time = *time - pinfos[process_to_run]->process_arrival_time + 1; } } for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { if (i == process_to_run) continue; if (has_process_arrived(pinfos, i, *time) && (!pinfos[i]->has_run_at_least_once)) { ++pinfos[i]->response_time; } if (has_process_arrived(pinfos, i, *time) && (!pinfos[i]->has_terminated)) { ++pinfos[i]->waiting_time; } } ++*time; } // 判断是否所有的进程都结束运行 int all_processes_have_finished(pinfo **pinfos, int pinfos_len) { for (int i = 0; i < pinfos_len; ++i) { if (!pinfos[i]->has_terminated) return 0; } return 1; } int main() { pinfo **pinfos = NULL; int pinfos_len, time = 0, next_process = NO_PROCESS, algorithm, preemptive, context_switches = 0, previous_process, quantum; take_input(&pinfos, &pinfos_len, &algorithm, &preemptive, &quantum); while (!all_processes_have_finished(pinfos, pinfos_len)) { previous_process = next_process; next_process = next_process_to_run(next_process, pinfos, pinfos_len, algorithm, preemptive, time, quantum,&context_switches); if (next_process == NO_PROCESS && previous_process != NO_PROCESS && algorithm != RR_SCHED) { printf("【状态转换】从一个具体的进程到无进程\n"); ++context_switches; } else if (next_process != NO_PROCESS && previous_process == NO_PROCESS && algorithm != RR_SCHED) { printf("【状态转换】从无进程到创建一个具体的进程\n"); ++context_switches; } else if (next_process != NO_PROCESS && previous_process != NO_PROCESS && next_process != previous_process && algorithm != RR_SCHED) { printf("【状态转换】从一个进程切换到另一个进程\n"); ++context_switches; } if (next_process == NO_PROCESS) printf("从时间点 = %d 到时间点 = %d. 无进程\n", time, time + 1); else printf("F从时间点 = %d 到时间点 = %d. 运行进程 P%d\n", time, time + 1, next_process); run_process_and_update_structs(next_process, pinfos, pinfos_len, &time); } display_output(pinfos, pinfos_len, context_switches); deallocate_mem_for_process_list(pinfos, pinfos_len, 0); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
-
相关阅读:
ACCESS_MASK不明确的符号
这一篇让你搞定 Flutter 的数据表格
leetcode刷题(第四十八天) 198.打家劫舍 ; 213.打家劫舍II ; 337.打家劫舍III
Python自动化测试之request库(五)
Android Studio实现内容丰富的安卓博客发布平台
【AI】PyTorch入门(四):对数据样本进行转换
2023年9款好用的在线流程图软件推荐!
用OCC+VS+Qt创建并显示一个几何
【Mybatis】mybatis使用与理解
从力扣[203]理解递归思想
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zyw2002/article/details/125444496