-
人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.23

ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

工具库:PyTorch Lightning + Hydra深度学习项目模板
tags: [pytorch,lightning,深度学习,模板]
‘PyTorch Lightning + Hydra Template - PyTorch Lightning + Hydra + Optuna + Weights&Biases. A very general, feature-rich template for rapid and scalable Machine Learning experimentation process’ by Łukasz Zalewski
GitHub: https://github.com/hobogalaxy/lightning-hydra-template


工具:MockingBird——AI中文拟声: 5秒内克隆您的声音并生成任意语音内容
tags: [语音,声音克隆]
‘Clone a voice in 5 seconds to generate arbitrary speech in real-time’ by Vega
GitHub: https://github.com/babysor/MockingBird

工具平台:square-core——问答在线研究平台
tags: [问答系统,在线平台]
‘square-core - SQuARE: Software for question answering research.’ by
UKP-SQuARE
GitHub: https://github.com/UKP-SQuARE/square-core


工具库:PosePipe: 用于临床研究的开源人体姿态估计管道
tags: [姿态预估,姿态检测]
‘PosePipe: Open-Source Human Pose Estimation Pipeline for Clinical Research’ by peabody124
GitHub: https://github.com/peabody124/PosePipeline

工具:PicoShare——极简的、易于托管的图像/文件共享服务
tags: [文件托管]
‘PicoShare - A minimalist, easy-to-host service for sharing images and other files’ by Michael Lynch
GitHub: https://github.com/mtlynch/picoshare

2.博文&分享

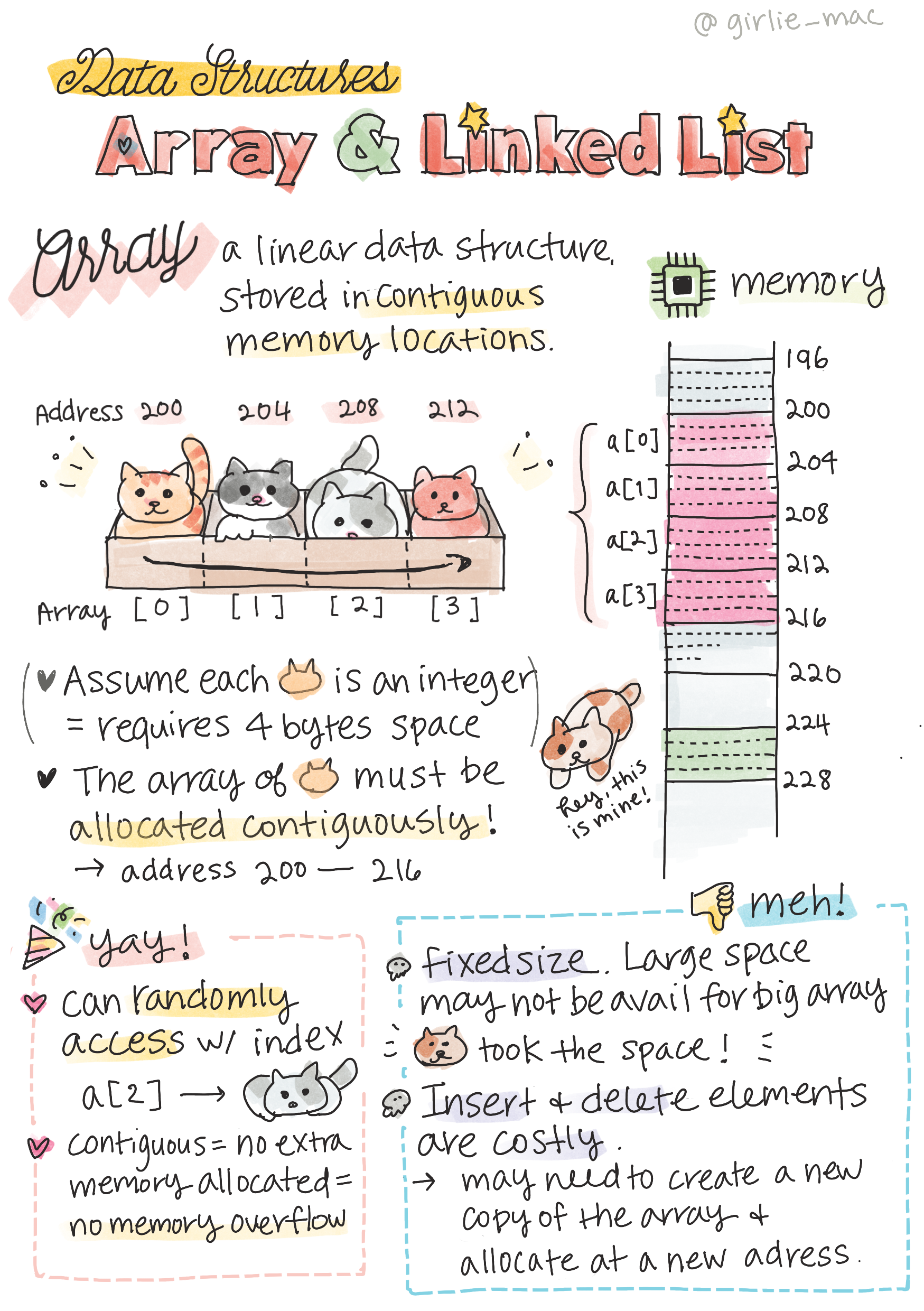
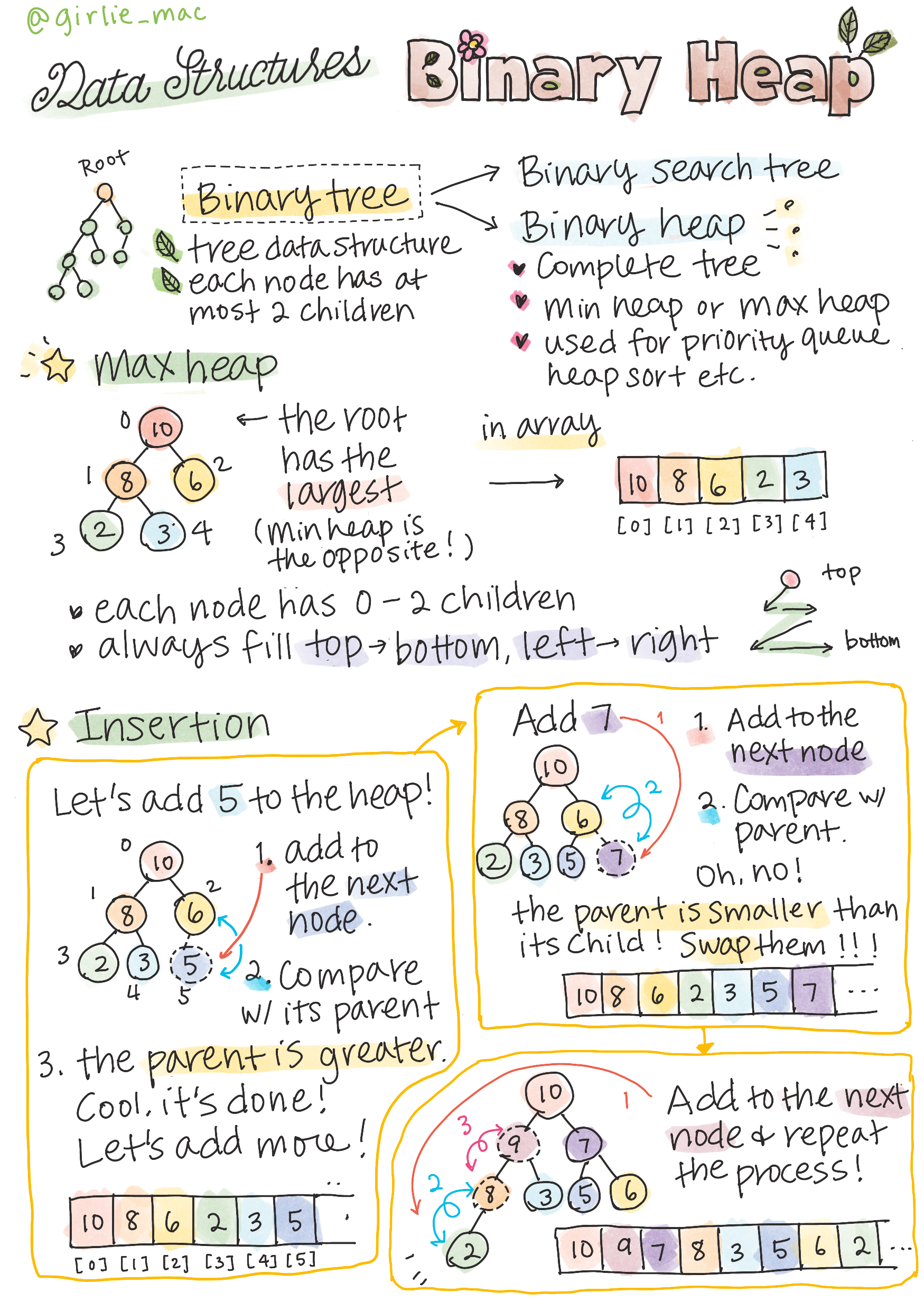
分享:图解算法数据结构
tags: [数据结构,图解]
GitHub: https://github.com/girliemac/a-picture-is-worth-a-1000-words/tree/main/algorithms


分享:wtfpython——一些有趣且鲜为人知的 Python 特性
tags: [python,特性]
这个项目收集了Python 中那些难以理解和反人类直觉的例子以及鲜为人知的功能特性, 并尝试讨论这些现象背后真正的原理!
GitHub: https://github.com/satwikkansal/wtfpython


3.数据&资源

书籍:《实用 Python 项目》
tags: [python,项目]
Link: https://practicalpython.yasoob.me/


书籍:《Spark权威指南》中文翻译
tags: [spark,大数据,指南]
Link: https://snaildove.github.io/2020/02/10/summary_of_Translation(SparkTheDefinitiveGuide)_online/

4.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:LAVENDER: Unifying Video-Language Understanding as Masked Language Modeling**
论文标题:LAVENDER: Unifying Video-Language Understanding as Masked Language Modeling
论文时间:14 Jun 2022
所属领域:自然语言处理
对应任务:Language Modelling,Masked Language Modeling,Question Answering,Text to Video Retrieval,Video Captioning,Video Question Answering,Video Retrieval,语言建模,蒙面语言建模,问答,文字转视频检索,视频字幕/看图说话,视频问答,视频检索
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.07160
代码实现:https://github.com/microsoft/lavender
论文作者:Linjie Li, Zhe Gan, Kevin Lin, Chung-Ching Lin, Zicheng Liu, Ce Liu, Lijuan Wang
论文简介:In this work, we explore a unified VidL framework LAVENDER, where Masked Language Modeling (MLM) is used as the common interface for all pre-training and downstream tasks./在这项工作中,我们探索了一个统一的 VidL 框架 LAVENDER,其中使用掩码语言建模 (MLM) 作为所有预训练和下游任务的通用接口。
论文摘要:Unified vision-language frameworks have greatly advanced in recent years, most of which adopt an encoder-decoder architecture to unify image-text tasks as sequence-to-sequence generation. However, existing video-language (VidL) models still require task-specific designs in model architecture and training objectives for each task. In this work, we explore a unified VidL framework LAVENDER, where Masked Language Modeling (MLM) is used as the common interface for all pre-training and downstream tasks. Such unification leads to a simplified model architecture, where only a lightweight MLM head, instead of a decoder with much more parameters, is needed on top of the multimodal encoder. Surprisingly, experimental results show that this unified framework achieves competitive performance on 14 VidL benchmarks, covering video question answering, text-to-video retrieval and video captioning. Extensive analyses further demonstrate the advantage of LAVENDER over existing VidL methods in: (i) supporting all downstream tasks with just a single set of parameter values when multi-task finetuned; (ii) few-shot generalization on various downstream tasks; and (iii) enabling zero-shot evaluation on video question answering tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/microsoft/LAVENDER.
近年来,统一的视觉语言框架取得了长足的进步,其中大多数采用编码器-解码器架构将图像-文本任务统一为序列到序列的生成。然而,现有的视频语言 (VidL) 模型仍然需要在模型架构和每个任务的训练目标中进行特定于任务的设计。在这项工作中,我们探索了一个统一的 VidL 框架 LAVENDER,其中掩码语言建模 (MLM) 用作所有预训练和下游任务的通用接口。这种统一导致了简化的模型架构,在多模式编码器之上只需要一个轻量级的 MLM 头,而不是具有更多参数的解码器。令人惊讶的是,实验结果表明,这个统一的框架在 14 个 VidL 基准上实现了具有竞争力的性能,涵盖视频问答、文本到视频检索和视频字幕/看图说话。广泛的分析进一步证明了 LAVENDER 优于现有 VidL 方法的优势在于:(i)在多任务微调时仅使用一组参数值支持所有下游任务; (ii) 对各种下游任务的小样本泛化; (iii) 对视频问答任务进行零样本评估。代码可在 https://github.com/microsoft/LAVENDER]() 获得。



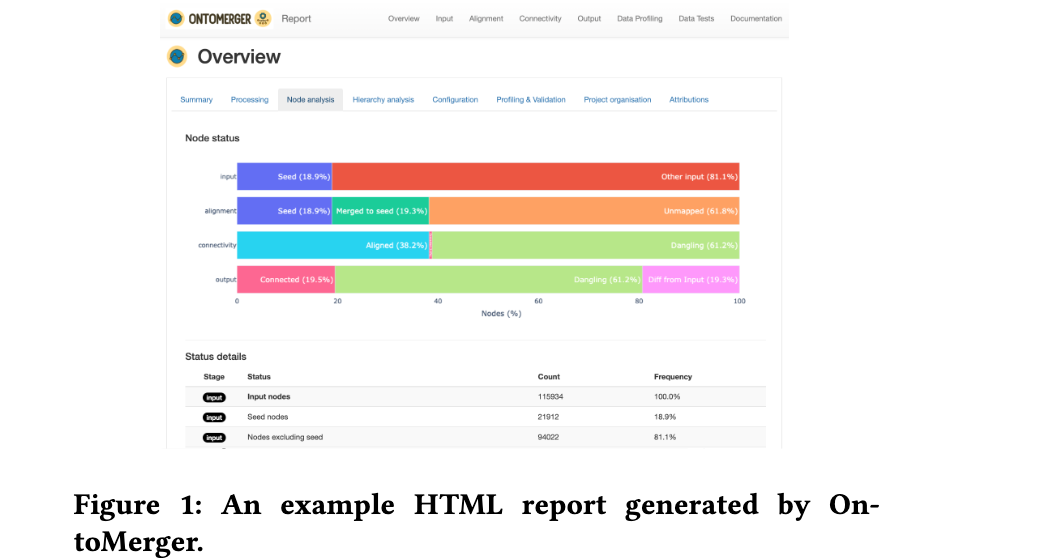
论文:OntoMerger: An Ontology Integration Library for Deduplicating and Connecting Knowledge Graph Nodes**
论文标题:OntoMerger: An Ontology Integration Library for Deduplicating and Connecting Knowledge Graph Nodes
论文时间:5 Jun 2022
所属领域:知识库
对应任务:知识图谱
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02238
代码实现:https://github.com/astrazeneca/onto_merger
论文作者:David Geleta, Andriy Nikolov, Mark ODonoghue, Benedek Rozemberczki, Anna Gogleva, Valentina Tamma, Terry R. Payne
论文简介:Duplication of nodes is a common problem encountered when building knowledge graphs (KGs) from heterogeneous datasets, where it is crucial to be able to merge nodes having the same meaning./节点重复是从异构数据集构建知识图(KG)时遇到的常见问题,其中能够合并具有相同含义的节点至关重要。
论文摘要:Duplication of nodes is a common problem encountered when building knowledge graphs (KGs) from heterogeneous datasets, where it is crucial to be able to merge nodes having the same meaning. OntoMerger is a Python ontology integration library whose functionality is to deduplicate KG nodes. Our approach takes a set of KG nodes, mappings and disconnected hierarchies and generates a set of merged nodes together with a connected hierarchy. In addition, the library provides analytic and data testing functionalities that can be used to fine-tune the inputs, further reducing duplication, and to increase connectivity of the output graph. OntoMerger can be applied to a wide variety of ontologies and KGs. In this paper we introduce OntoMerger and illustrate its functionality on a real-world biomedical KG.
节点重复是从异构数据集中构建知识图(KG)时遇到的常见问题,其中能够合并具有相同含义的节点至关重要。 OntoMerger 是一个 Python 本体集成库,其功能是去重 KG 节点。我们的方法采用一组 KG 节点、映射和断开的层次结构,并生成一组合并的节点以及连接的层次结构。此外,该库还提供分析和数据测试功能,可用于微调输入,进一步减少重复,并增加输出图的连通性。 OntoMerger 可以应用于各种本体和 KG。在本文中,我们介绍了 OntoMerger 并在真实世界的生物医学 KG 上说明了它的功能。


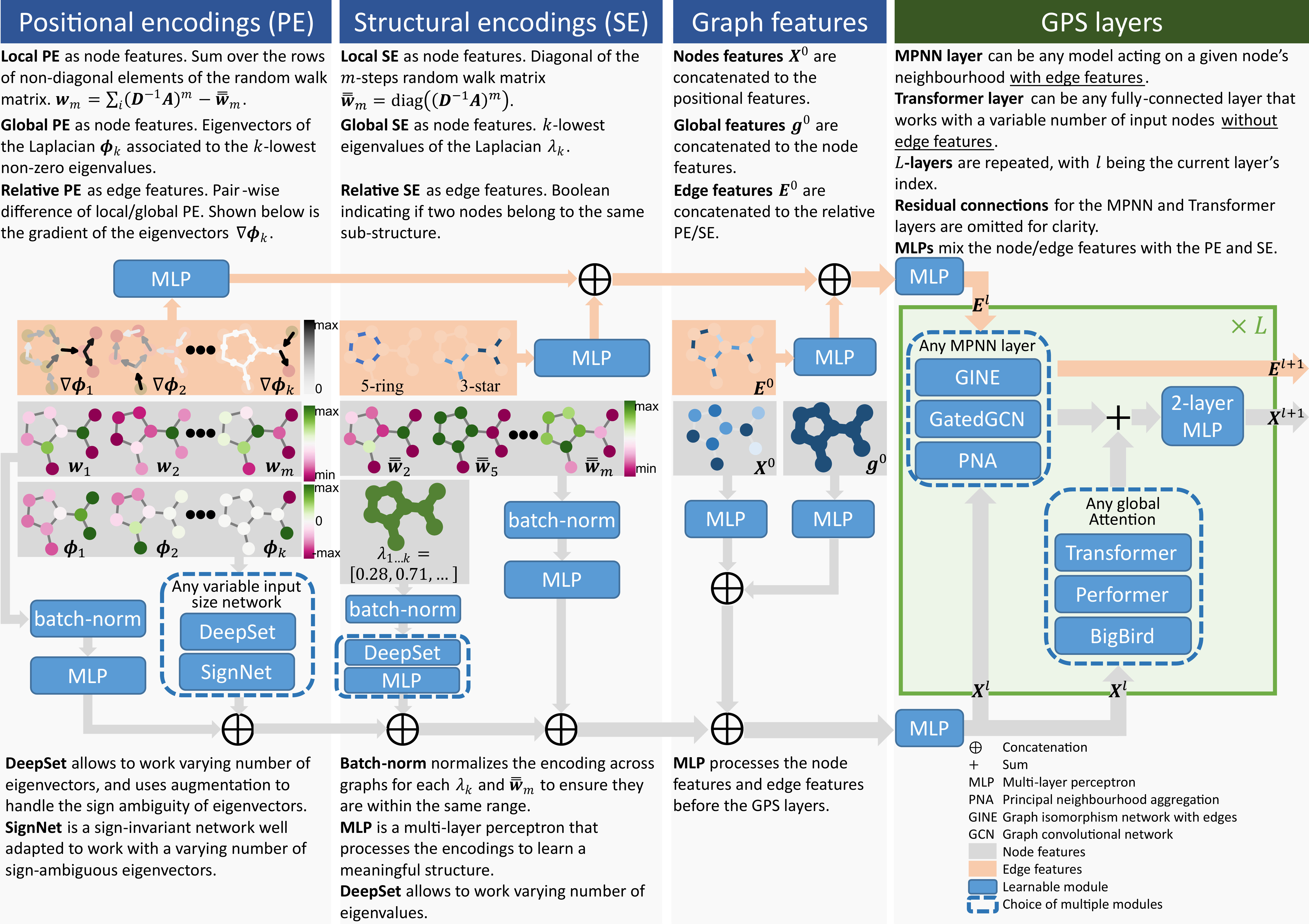
论文:Recipe for a General, Powerful, Scalable Graph Transformer
论文标题:Recipe for a General, Powerful, Scalable Graph Transformer
论文时间:25 May 2022
所属领域:图算法
对应任务:Graph Classification,Graph Property Prediction,Graph Regression,Graph Representation Learning,Node Classification,Representation Learning,图分类,图属性预测,图回归,图表示学习,节点分类,表示学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12454
代码实现:https://github.com/rampasek/GraphGPS
论文作者:Ladislav Rampášek, Mikhail Galkin, Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Anh Tuan Luu, Guy Wolf, Dominique Beaini
论文简介:We propose a recipe on how to build a general, powerful, scalable (GPS) graph Transformer with linear complexity and state-of-the-art results on a diverse set of benchmarks./我们提出了一个关于如何构建一个通用的、强大的、可扩展的 (GPS) 图Transformer的方法,该Transformer具有线性复杂性和在各种基准上的最新结果。
论文摘要:We propose a recipe on how to build a general, powerful, scalable (GPS) graph Transformer with linear complexity and state-of-the-art results on a diverse set of benchmarks. Graph Transformers (GTs) have gained popularity in the field of graph representation learning with a variety of recent publications but they lack a common foundation about what constitutes a good positional or structural encoding, and what differentiates them. In this paper, we summarize the different types of encodings with a clearer definition and categorize them as being local, global or relative. Further, GTs remain constrained to small graphs with few hundred nodes, and we propose the first architecture with a complexity linear to the number of nodes and edges O(N+E) by decoupling the local real-edge aggregation from the fully-connected Transformer. We argue that this decoupling does not negatively affect the expressivity, with our architecture being a universal function approximator for graphs. Our GPS recipe consists of choosing 3 main ingredients: (i) positional/structural encoding, (ii) local message-passing mechanism, and (iii) global attention mechanism. We build and open-source a modular framework GraphGPS that supports multiple types of encodings and that provides efficiency and scalability both in small and large graphs. We test our architecture on 11 benchmarks and show very competitive results on all of them, show-casing the empirical benefits gained by the modularity and the combination of different strategies.
我们提出了如何构建一个通用的、强大的、可扩展的 (GPS) 图 Transformer 的方法,它具有线性复杂性和在各种基准上的最新结果。 Graph Transformers (GTs) 在图表示学习领域已经获得了广泛的欢迎,最近发表了各种出版物,但它们缺乏关于什么构成良好的位置或结构编码以及它们之间的区别的共同基础。在本文中,我们用更清晰的定义总结了不同类型的编码,并将它们分类为局部的、全局的或相对的。此外,GT 仍然受限于具有几百个节点的小图,我们通过将局部实边聚合与全连接 Transformer 解耦,提出了第一个复杂度与节点和边数 O(N+E) 成线性关系的架构。我们认为这种解耦不会对表达性产生负面影响,因为我们的架构是图的通用函数逼近器。我们的 GPS 配方包括选择 3 个主要成分:(i) 位置/结构编码,(ii) 本地消息传递机制,以及 (iii) 全局注意力机制。我们构建并开源了一个模块化框架 GraphGPS,它支持多种类型的编码,并在小型和大型图形中提供效率和可扩展性。我们在 11 个基准上测试了我们的架构,并在所有这些基准上展示了非常有竞争力的结果,展示了模块化和不同策略组合所获得的经验优势。


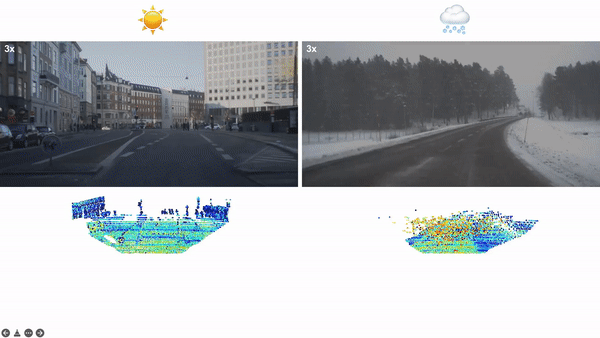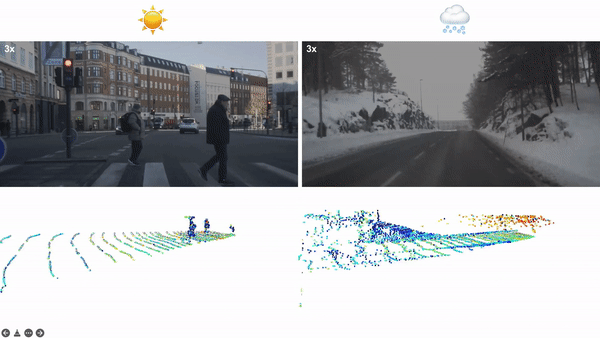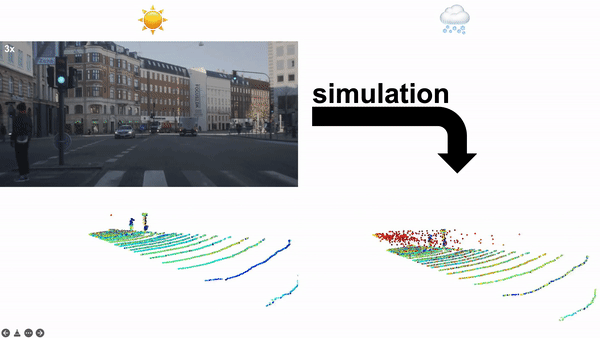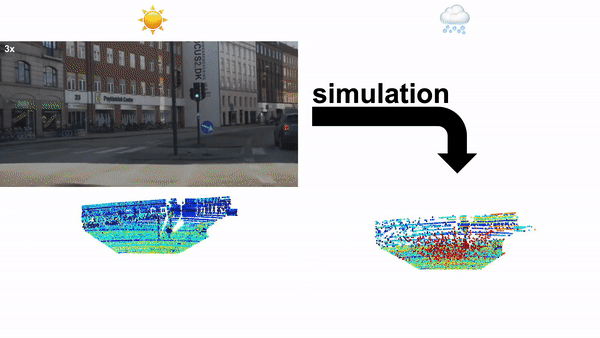
论文:LiDAR Snowfall Simulation for Robust 3D Object Detection**
论文标题:LiDAR Snowfall Simulation for Robust 3D Object Detection
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Object Detection,Autonomous Driving,object-detection,Object Detection,Physical Simulations,3D物体检测,自动驾驶,物体检测,物理模拟
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.15118
代码实现:https://github.com/syscv/lidar_snow_sim
论文作者:Martin Hahner, Christos Sakaridis, Mario Bijelic, Felix Heide, Fisher Yu, Dengxin Dai, Luc van Gool
论文简介:Due to the difficulty of collecting and annotating training data in this setting, we propose a physically based method to simulate the effect of snowfall on real clear-weather LiDAR point clouds./由于在此设置中收集和注释训练数据的困难,我们提出了一种基于物理的方法来模拟降雪对真实天气晴天 LiDAR 点云的影响。
论文摘要:3D object detection is a central task for applications such as autonomous driving, in which the system needs to localize and classify surrounding traffic agents, even in the presence of adverse weather. In this paper, we address the problem of LiDAR-based 3D object detection under snowfall. Due to the difficulty of collecting and annotating training data in this setting, we propose a physically based method to simulate the effect of snowfall on real clear-weather LiDAR point clouds. Our method samples snow particles in 2D space for each LiDAR line and uses the induced geometry to modify the measurement for each LiDAR beam accordingly. Moreover, as snowfall often causes wetness on the ground, we also simulate ground wetness on LiDAR point clouds. We use our simulation to generate partially synthetic snowy LiDAR data and leverage these data for training 3D object detection models that are robust to snowfall. We conduct an extensive evaluation using several state-of-the-art 3D object detection methods and show that our simulation consistently yields significant performance gains on the real snowy STF dataset compared to clear-weather baselines and competing simulation approaches, while not sacrificing performance in clear weather. Our code is available at www.github.com/SysCV/LiDAR_snow_sim.
3D 物体检测是自动驾驶等应用的核心任务,其中系统需要对周围的交通主体进行定位和分类,即使在恶劣天气的情况下也是如此。在本文中,我们解决了降雪下基于 LiDAR 的 3D 目标检测问题。由于在此设置中收集和注释训练数据的困难,我们提出了一种基于物理的方法来模拟降雪对真实晴天 LiDAR 点云的影响。我们的方法在二维空间中为每条 LiDAR 线采样雪粒,并使用诱导几何来修改测量值相应地对每个 LiDAR 光束进行更换。此外,由于降雪经常导致地面潮湿,我们还在 LiDAR 点云上模拟了地面湿度。我们使用我们的模拟生成部分合成的下雪 LiDAR 数据,并利用这些数据来训练对降雪具有鲁棒性的 3D 对象检测模型。我们使用几种最先进的 3D 对象检测方法进行了广泛的评估,并表明与晴天基线和竞争模拟方法相比,我们的模拟始终在真实的雪 STF 数据集上产生显着的性能提升,同时不牺牲性能天气晴朗。我们的代码可在 www.github.com/SysCV/LiDAR_snow_sim 获得。


论文:SelfRecon: Self Reconstruction Your Digital Avatar from Monocular Video
论文标题:SelfRecon: Self Reconstruction Your Digital Avatar from Monocular Video
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:神经渲染
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12792
代码实现:https://github.com/jby1993/selfreconcode
论文作者:Boyi Jiang, Yang Hong, Hujun Bao, Juyong Zhang
论文简介:Meanwhile, the explicit mesh is updated periodically to adjust its topology changes, and a consistency loss is designed to match both representations./同时,显式网格会定期更新以调整其拓扑变化,并设计一致性损失来匹配两种表示。
论文摘要:We propose SelfRecon, a clothed human body reconstruction method that combines implicit and explicit representations to recover space-time coherent geometries from a monocular self-rotating human video. Explicit methods require a predefined template mesh for a given sequence, while the template is hard to acquire for a specific subject. Meanwhile, the fixed topology limits the reconstruction accuracy and clothing types. Implicit representation supports arbitrary topology and can represent high-fidelity geometry shapes due to its continuous nature. However, it is difficult to integrate multi-frame information to produce a consistent registration sequence for downstream applications. We propose to combine the advantages of both representations. We utilize differential mask loss of the explicit mesh to obtain the coherent overall shape, while the details on the implicit surface are refined with the differentiable neural rendering. Meanwhile, the explicit mesh is updated periodically to adjust its topology changes, and a consistency loss is designed to match both representations. Compared with existing methods, SelfRecon can produce high-fidelity surfaces for arbitrary clothed humans with self-supervised optimization. Extensive experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness on real captured monocular videos. The source code is available at https://github.com/jby1993/SelfReconCode
我们提出了 SelfRecon,一种结合隐式和显式表示的穿衣人重建方法,从单目自旋转人体视频中恢复时空相干几何图形。显式方法需要为给定序列预定义模板网格,而对于特定主题很难获取模板。同时,固定的拓扑结构限制了重建精度和服装类型。隐式表示支持任意拓扑,并且由于其连续性,可以表示高保真几何形状。然而,很难整合多帧信息来为下游应用程序生成一致的注册序列。我们建议结合两种表示的优点。我们利用显式网格的微分掩模损失来获得连贯的整体形状,而隐式表面上的细节则通过可微分的神经渲染进行细化。同时,显式网格会定期更新以调整其拓扑变化,并设计了一致性损失来匹配两种表示。与现有方法相比,SelfRecon 可以通过自我监督优化为任意穿着衣服的人生成高保真表面。广泛的实验结果证明了它对真实捕获的单目视频的有效性。源代码位于 https://github.com/jby1993/SelfReconCode




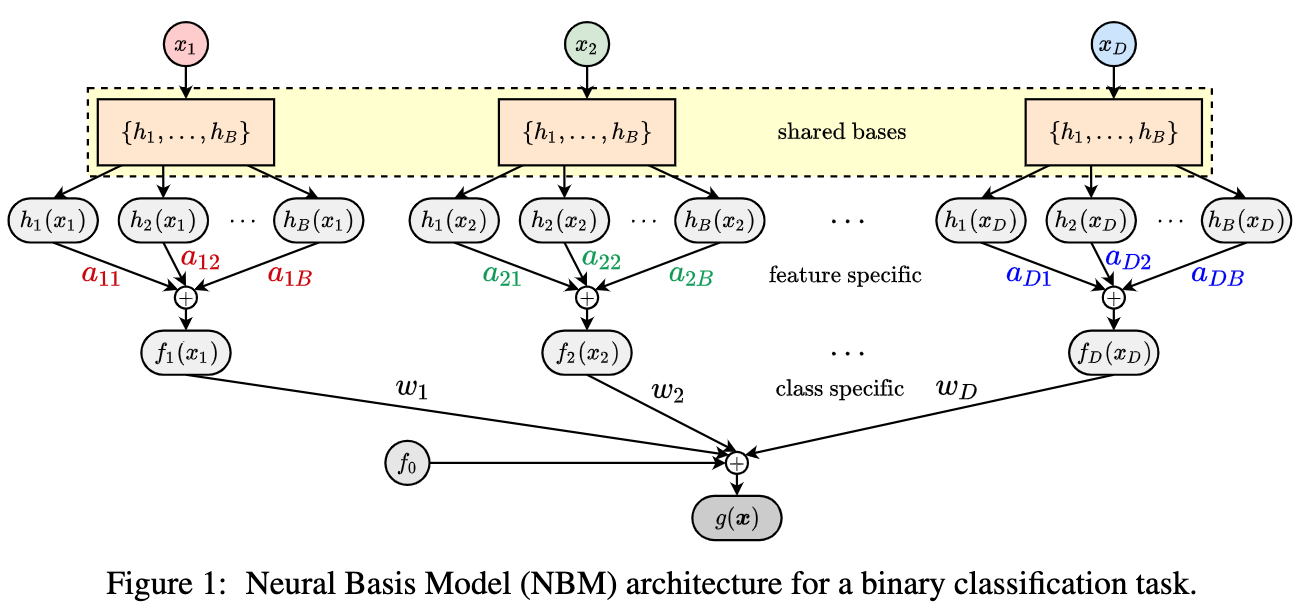
论文:Neural Basis Models for Interpretability
论文标题:Neural Basis Models for Interpretability
论文时间:27 May 2022
所属领域:机器学习
对应任务:Additive models,Interpretable Machine Learning,加法模型,可解释的机器学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14120
代码实现:https://github.com/facebookresearch/nbm-spam
论文作者:Filip Radenovic, Abhimanyu Dubey, Dhruv Mahajan
论文简介:However, these models are typically black-box deep neural networks, explained post-hoc via methods with known faithfulness limitations./然而,这些模型通常是黑盒深度神经网络,通过具有已知信度限制的方法进行事后解释。
论文摘要:Due to the widespread use of complex machine learning models in real-world applications, it is becoming critical to explain model predictions. However, these models are typically black-box deep neural networks, explained post-hoc via methods with known faithfulness limitations. Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) are an inherently interpretable class of models that address this limitation by learning a non-linear shape function for each feature separately, followed by a linear model on top. However, these models are typically difficult to train, require numerous parameters, and are difficult to scale. We propose an entirely new subfamily of GAMs that utilizes basis decomposition of shape functions. A small number of basis functions are shared among all features, and are learned jointly for a given task, thus making our model scale much better to large-scale data with high-dimensional features, especially when features are sparse. We propose an architecture denoted as the Neural Basis Model (NBM) which uses a single neural network to learn these bases. On a variety of tabular and image datasets, we demonstrate that for interpretable machine learning, NBMs are the state-of-the-art in accuracy, model size, and, throughput and can easily model all higher-order feature interactions. Source code is available at https://github.com/facebookresearch/nbm-spam
由于复杂机器学习模型在实际应用中的广泛使用,解释模型预测变得至关重要。然而,这些模型通常是黑盒深度神经网络,通过具有已知信度限制的方法进行事后解释。广义加法模型 (GAM) 是一类固有的可解释模型,它通过分别学习每个特征的非线性形状函数,然后在顶部学习线性模型来解决这一限制。然而,这些模型通常难以训练、需要大量参数并且难以扩展。我们提出了一个全新的 GAM 子家族,它利用形状函数的基分解。少量的基函数在所有特征之间共享,并针对给定任务共同学习,从而使我们的模型对具有高维特征的大规模数据具有更好的扩展性,尤其是在特征稀疏的情况下。我们提出了一种称为神经基础模型(NBM)的架构,它使用单个神经网络来学习这些基础。在各种表格和图像数据集上,我们证明对于可解释的机器学习,NBM 在准确性、模型大小和吞吐量方面是最先进的,并且可以轻松地对所有高阶特征交互进行建模。源代码可在 https://github.com/facebookresearch/nbm-spam 获得。

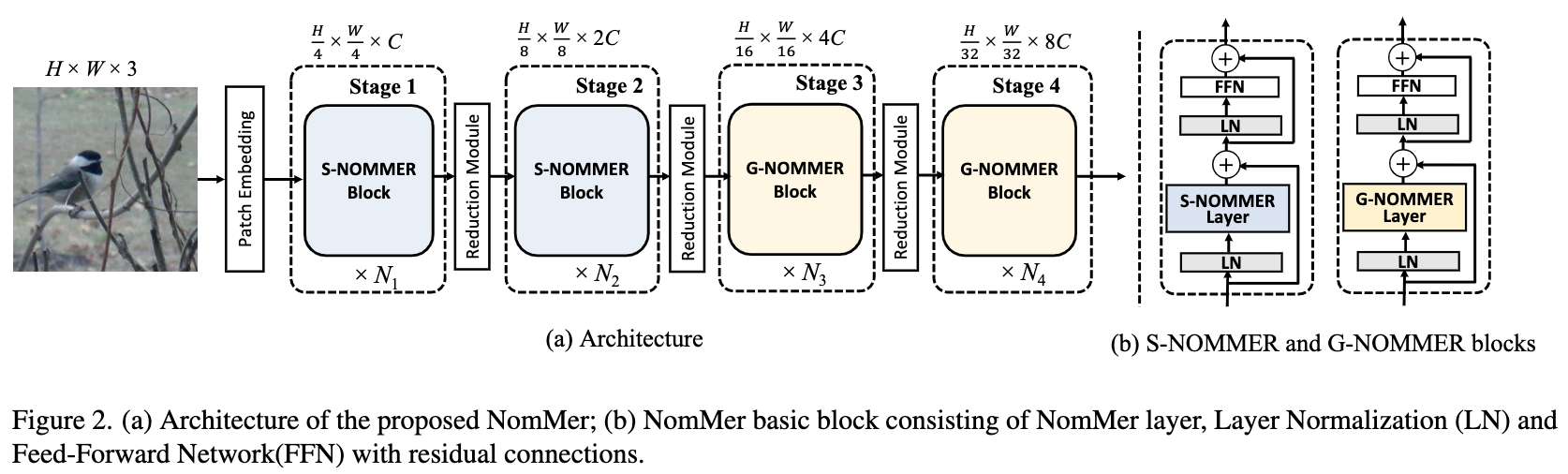
论文:NomMer: Nominate Synergistic Context in Vision Transformer for Visual Recognition
论文标题:NomMer: Nominate Synergistic Context in Vision Transformer for Visual Recognition
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:object-detection,Object Detection,Semantic Segmentation,物体检测,物体检测,语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.12994
代码实现:https://github.com/tencentyouturesearch/visualrecognition-nommer
论文作者:Hao liu, Xinghua Jiang, Xin Li, Zhimin Bao, Deqiang Jiang, Bo Ren
论文简介:For the sake of trade-off between efficiency and performance, a group of works merely perform SA operation within local patches, whereas the global contextual information is abandoned, which would be indispensable for visual recognition tasks./为了效率和性能之间的权衡,一组作品仅在局部块内执行 SA 操作,而放弃了全局上下文信息,这对于视觉识别任务来说是必不可少的。
论文摘要:Recently, Vision Transformers (ViT), with the self-attention (SA) as the de facto ingredients, have demonstrated great potential in the computer vision community. For the sake of trade-off between efficiency and performance, a group of works merely perform SA operation within local patches, whereas the global contextual information is abandoned, which would be indispensable for visual recognition tasks. To solve the issue, the subsequent global-local ViTs take a stab at marrying local SA with global one in parallel or alternative way in the model. Nevertheless, the exhaustively combined local and global context may exist redundancy for various visual data, and the receptive field within each layer is fixed. Alternatively, a more graceful way is that global and local context can adaptively contribute per se to accommodate different visual data. To achieve this goal, we in this paper propose a novel ViT architecture, termed NomMer, which can dynamically Nominate the synergistic global-local context in vision transforMer. By investigating the working pattern of our proposed NomMer, we further explore what context information is focused. Beneficial from this “dynamic nomination” mechanism, without bells and whistles, the NomMer can not only achieve 84.5% Top-1 classification accuracy on ImageNet with only 73M parameters, but also show promising performance on dense prediction tasks, i.e., object detection and semantic segmentation. The code and models will be made publicly available at https://github.com/TencentYoutuResearch/VisualRecognition-NomMer
最近,以自注意 (SA) 作为事实成分的视觉Transformers (ViT) 在计算机视觉领域表现出了巨大的潜力。为了在效率和性能之间进行权衡,一组作品仅在局部块内执行 SA 操作,而放弃了全局上下文信息,这对于视觉识别任务来说是必不可少的。为了解决这个问题,随后的全局-局部 ViT 尝试在模型中以并行或替代方式将局部 SA 与全局 SA 结合起来。然而,详尽组合的局部和全局上下文可能存在各种视觉数据的冗余,并且每一层内的感受野是固定的。或者,一种更优雅的方式是全局和局部上下文本身可以自适应地贡献以适应不同的视觉数据。为了实现这一目标,我们在本文中提出了一种新的 ViT 架构,称为 NomMer,它可以动态地提名视觉Transformer中的协同全局-局部上下文。通过研究我们提出的 NomMer 的工作模式,我们进一步探索了关注哪些上下文信息。得益于这种“动态提名”机制,NomMer 不仅可以在只有 73M 参数的 ImageNet 上实现 84.5% 的 Top-1 分类准确率,而且在密集预测任务(即对象检测和语义)上表现出可观的性能分割。代码和模型将在 https://github.com/TencentYoutuResearch/VisualRecognition-NomMer 公开


论文:Distance-Sensitive Offline Reinforcement Learning
论文标题:Distance-Sensitive Offline Reinforcement Learning
论文时间:23 May 2022
所属领域:强化学习
对应任务:Offline RL,reinforcement-learning,离线强化学习,强化学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.11027
代码实现:https://github.com/Facebear-ljx/DOGE
论文作者:Jianxiong Li, Xianyuan Zhan, Haoran Xu, Xiangyu Zhu, Jingjing Liu, Ya-Qin Zhang
论文简介:In offline reinforcement learning (RL), one detrimental issue to policy learning is the error accumulation of deep Q function in out-of-distribution (OOD) areas./在离线强化学习 (RL) 中,策略学习的一个不利问题是深度 Q 函数在分布外 (OOD) 区域的误差累积。
论文摘要:In offline reinforcement learning (RL), one detrimental issue to policy learning is the error accumulation of deep Q function in out-of-distribution (OOD) areas. Unfortunately, existing offline RL methods are often over-conservative, inevitably hurting generalization performance outside data distribution. In our study, one interesting observation is that deep Q functions approximate well inside the convex hull of training data. Inspired by this, we propose a new method, DOGE (Distance-sensitive Offline RL with better GEneralization). DOGE marries dataset geometry with deep function approximators in offline RL, and enables exploitation in generalizable OOD areas rather than strictly constraining policy within data distribution. Specifically, DOGE trains a state-conditioned distance function that can be readily plugged into standard actor-critic methods as a policy constraint. Simple yet elegant, our algorithm enjoys better generalization compared to state-of-the-art methods on D4RL benchmarks. Theoretical analysis demonstrates the superiority of our approach to existing methods that are solely based on data distribution or support constraints.
在离线强化学习 (RL) 中,策略学习的一个不利问题是深度 Q 函数在分布外 (OOD) 区域的误差累积。不幸的是,现有的离线 RL 方法通常过于保守,不可避免地会损害数据分布之外的泛化性能。在我们的研究中,一个有趣的观察是深度 Q 函数在训练数据的凸包内很好地近似。受此启发,我们提出了一种新方法 DOGE(具有更好 GEneralization 的距离敏感离线 RL)。 DOGE 将数据集几何与离线 RL 中的深度函数逼近器结合起来,并能够在可泛化的 OOD 区域中进行利用,而不是在数据分布中严格限制策略。具体来说,DOGE 训练了一个状态条件距离函数,该函数可以很容易地插入标准的actor-critic 方法作为策略约束。与 D4RL 基准上的最新方法相比,我们的算法简单而优雅,具有更好的泛化性。理论分析证明了我们的方法优于仅基于数据分布或支持约束的现有方法。




我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

-
相关阅读:
CentOS7开机启动 jar包
HTTP协议(超级详细)
【高质量C/C++】4.表达式和基本语句
MyBatis 如何实现缓存(一级缓存和二级缓存)呢?
uniapp 小程序 堆叠轮播图 左滑 右滑 自动翻页 点击停止自动翻页
这里是php查询数据库更具时间范围和id
hive 问题解决 Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings
CH06_第一组重构(下)
详解如何保证消息队列不丢失消息(以kafka为例)
9. 微积分 - 导数
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ShowMeAI/article/details/125415520