-
【常见算法】第三篇:回溯算法
一、概念
回溯法
- 回溯算法实际上一个类似枚举的搜索尝试过程,主要是在搜索尝试过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。
- 回溯法是一种选优搜索法,按选优条件向前搜索,以达到目标。但当探索到某一步时,发现原先选择并不优或达不到目标,就退回一步重新选择,这种走不通就退回再走的技术为回溯法,而满足回溯条件的某个状态的点称为“回溯点”。也可以称为剪枝点,所谓的剪枝,指的是把不会找到目标,或者不必要的路径裁剪掉。
- 许多复杂的,规模较大的问题都可以使用回溯法,有“通用解题方法”的美称。
- 在包含问题的所有解的解空间树中,按照深度优先搜索的策略,从根结点出发深度探索解空间树。当探索到某一结点时,要先判断该结点是否包含问题的解,如果包含,就从该结点出发继续探索下去,如果该结点不包含问题的解,则逐层向其祖先结点回溯。(其实回溯法就是对隐式图的深度优先搜索算法)。
- 若用回溯法求问题的所有解时,要回溯到根,且根结点的所有可行的子树都要已被搜索遍才结束。
- 而若使用回溯法求任一个解时,只要搜索到问题的一个解就可以结束。
- 除过深度优先搜索,常用的还有广度优先搜索。
二、深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)------ 一条道走到黑
2.1 放牌
假如有编号为1-3的3张扑克牌和编号为1~3的3个盒子,现在需要将3张牌分别放到3个盒子中去,且每个盒子只能放一张牌,一共有多少种不同的放法
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; void DFS(vector<int>& book, vector<int>& box, int index, int n) { if (index == n + 1) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { cout << box[i] << " "; } cout << endl; return; } for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (book[i] == 0) { box[index] = i; book[i] = 1;//设置成已用 //深度优先遍历 DFS(book, box, index+1, n); //回收 book[i] = 0; } } } int main() { int n = 0; cin >> n; vector<int> book(n + 1, 0);//标记是否被用,0--未用, 1--已用 vector<int> box(n + 1, 0);//放入牌的盒子 DFS(book, box, 1, n); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
2.2 员工的重要性

/* // Definition for Employee. class Employee { public: int id; int importance; vector<int> subordinates; }; */ class Solution { public: int DFS(map<int, Employee*>& info, int id) { int curImportance = info[id]->importance; for(auto& e : info[id]->subordinates) { curImportance += DFS(info, e); } return curImportance; } int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) { if(employees.empty()) { return 0; } //将id的员工的地址保存在map里面 map<int, Employee*> info; for(auto& e : employees) { info[e->id] = e; } return DFS(info, id); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
2.3 图像渲染

class Solution { int nextP[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; public: void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& image, int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>&book, int curX, int curY, int oldColor, int newColor) { //修改当前位置颜色 image[curX][curY] = newColor; book[curX][curY] = 1; for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newX = curX + nextP[i][0]; int newY = curY + nextP[i][1]; if(newX < 0 || newY < 0 || newX >= row || newY >= col) continue; if(image[newX][newY] == oldColor && book[newX][newY] == 0) DFS(image, row, col, book, newX, newY, oldColor, newColor); } } vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int color) { if(image.empty()) return image; int row = image.size(); int col = image[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> book(row, vector<int>(col, 0)); int oldColor = image[sr][sc]; int newColor = color; DFS(image, row, col, book, sr, sc, oldColor, newColor); return image; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
2.4 被围绕的区域
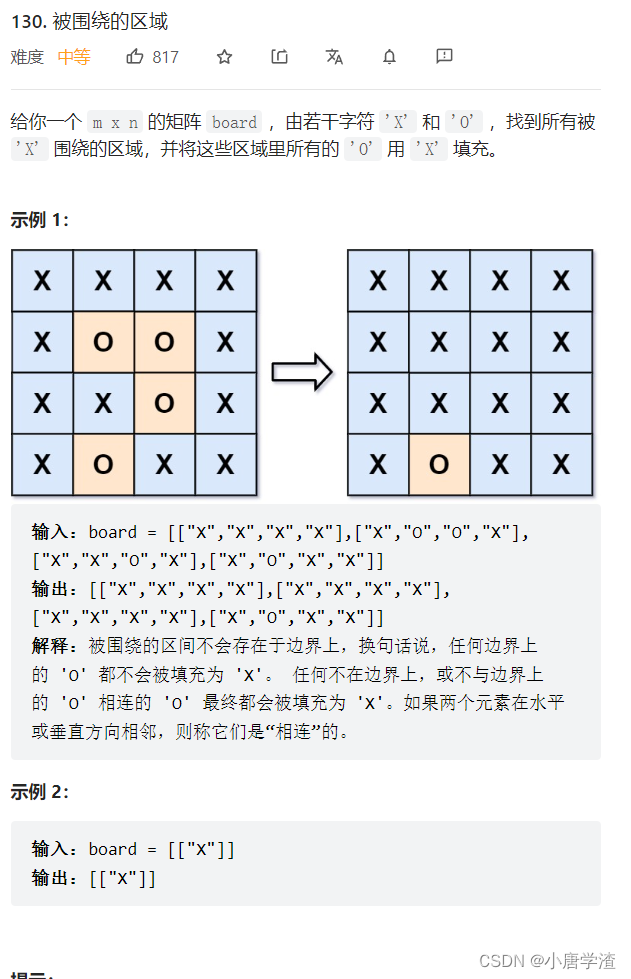
本题的意思被包围的区间不会存在于边界上,所以边界上的o以及与o联通的都不算做包围,只要把边界上的o以及与之联通的o进行特殊处理,剩下的o替换成x即可。故问题转化为,如何寻找和边界联通的o,我们需要考虑如下情况。
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O O X
从每一个边缘的o开始,只要和边缘的o联通,则它就没有被包围。
1.首先寻找边上的每一个o,如果没有,表示所有的o都被包围
2.对于边上的每一个o进行dfs进行扩散,先把边上的每一个o用特殊符号标记,比如*,#等,
3.把和它相邻的o都替换为特殊符号,每一个新的位置都做相同的dfs操作
4.所有扩散结束之后,把特殊符号的位置(和边界连通)还原为o,原来为o的位置(和边界不连通)替换为x即可。这里一定要注意这里是大’O’和大’X’class Solution { public: int nextP[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} }; void DFS(vector<vector<char>>& board, int row, int col, int curX, int curY) { //将当前位置修改成为'A' board[curX][curY] = 'A'; //上下左右分别遍历,将所有和边界相连的O字符变为A字符 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newX = curX + nextP[i][0]; int newY = curY + nextP[i][1]; //下表越界了 if(newX < 0 || newX >= row || newY < 0 || newY >= col) continue; if(board[newX][newY] == 'O') DFS(board, row, col, newX, newY); } } void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) { if(board.empty()) return; int row = board.size(); int col = board[0].size(); for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { if(board[i][0] == 'O') DFS(board, row, col, i, 0); if(board[i][col-1] == 'O') DFS(board, row, col, i, col-1 ); } for(int i = 1; i < col - 1; ++i) { if(board[0][i] == 'O') DFS(board, row, col, 0, i); if(board[row-1][i] == 'O') DFS(board, row, col, row-1, i); } for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) { if(board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X'; if(board[i][j] == 'A') board[i][j] = 'O'; } } } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
2.5 岛屿数量

class Solution { public: int nextP[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} }; void DFS(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int row, int col, int curX, int curY) { //将当前位置置为0 grid[curX][curY] = '0'; //遍历上下左右将所有与当前位置相连的1字符置为0字符 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newX = curX + nextP[i][0]; int newY = curY + nextP[i][1]; if(newX < 0 || newX >= row || newY < 0 || newY >= col ) continue; if(grid[newX][newY] == '1') DFS(grid, row, col, newX, newY); } } int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) { if(grid.empty()) return 0; int row = grid.size(); int col = grid[0].size(); int count = 0; for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) { if(grid[i][j] == '1') { DFS(grid, row, col, i, j); ++count; } } } return count; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
2.6 电话号码的字母组合

class Solution { public: map<char, string> mapstr = { {'2', "abc"}, {'3', "def"}, {'4', "ghi"}, {'5', "jkl"}, {'6', "mno"}, {'7', "pqrs"}, {'8', "tuv"}, {'9', "wxyz"} }; void DFS(vector<string>& ret, string& digits, string curStr, int digitsIndex) { if(digitsIndex == digits.size()) { ret.push_back(curStr); return; } string str = mapstr[digits[digitsIndex]]; for(auto ch : str) { DFS(ret, digits, curStr + ch, digitsIndex+1); } } vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) { vector<string> ret; if(digits.empty()) return ret; DFS(ret, digits, "", 0); return ret; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
2.7 组合总和

class Solution { public: void DFS(vector<int>& candidates, vector<vector<int>>& vv, vector<int> v, int curSum, int prevPosition, int target) { if(curSum >= target) { if(curSum == target) vv.push_back(v); return; } for(int i = prevPosition; i < candidates.size(); ++i) { if(candidates[i] > target) continue; v.push_back(candidates[i]); DFS(candidates, vv, v, curSum + candidates[i], i, target); v.pop_back(); } } vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) { vector<vector<int>> vv; vector<int> v; if(candidates.empty()) return vv; int curSum = 0; DFS(candidates, vv, v, curSum, 0, target); return vv; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
2.8 活字印刷

class Solution { public: void DFS(string& tiles, string curStr, vector<int>& book, unordered_set<string>& ret) { if(!curStr.empty()) { ret.insert(curStr); } for(int i = 0; i < tiles.size(); ++i) { if(book[i] == 0) { book[i] = 1; DFS(tiles, curStr + tiles[i], book, ret); book[i] = 0; } } } int numTilePossibilities(string tiles) { if(tiles.empty()) { return 0; } int size = tiles.size(); vector<int> book(size, 0);//标记位 unordered_set<string> ret;//存储每个字符串 string curStr; DFS(tiles, curStr, book, ret); return ret.size(); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
2.9 N皇后
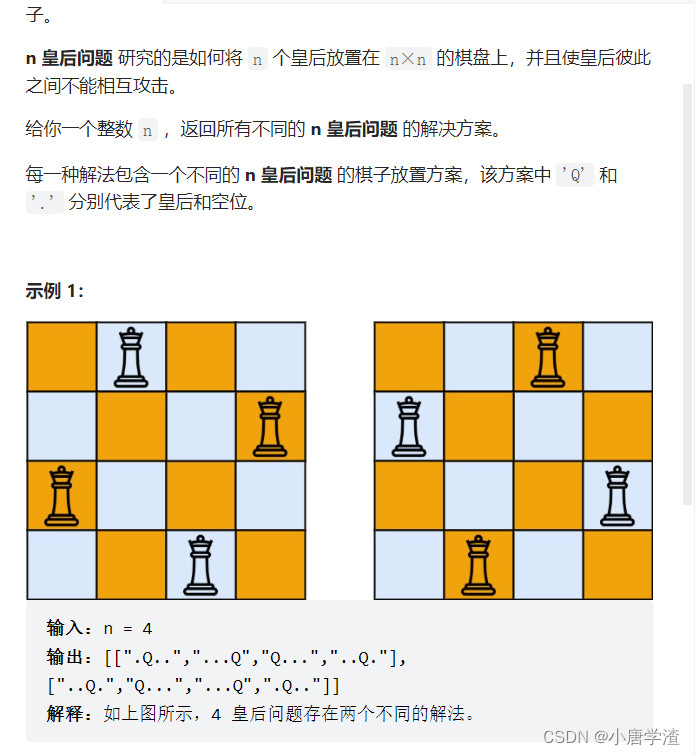
class Solution { public: bool isValuePos(vector<pair<int, int>>& curRet, int row, int col) { for(pair<int, int> pos : curRet) { if(pos.second == col || pos.first + pos.second == row + col || pos.second - pos.first == col - row) return false; } return true; } void DFS(vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& AllRet, vector<pair<int, int>>& curRet, int curRow, int n) { if(curRow == n) { AllRet.push_back(curRet); return; } for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { //判断当前位置是否有效 if(isValuePos(curRet, curRow, i)) { curRet.push_back(make_pair(curRow, i)); //递归下一行 DFS(AllRet, curRet, curRow + 1, n); //递归到最后一行后回溯 curRet.pop_back(); } } } vector<vector<string>> Transfer(vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& AllRet, int n) { vector<vector<string>> allMat; //所有方案 for(auto curRet : AllRet) { //一种方案 vector<string> curMat(n, string(n, '.')); for(auto pos : curRet) { curMat[pos.first][pos.second] = 'Q'; } allMat.push_back(curMat); } return allMat; } vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) { vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> AllRet; vector<pair<int,int>> curRow; DFS(AllRet, curRow, 0, n); return Transfer(AllRet, n); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
三、广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search) ------ 一石激起千层浪
3.1 迷宫
假设有一个迷宫,里面有障碍物,迷宫用二维矩阵表示,标记为0的地方表示可以通过,标记为1的地方表示障碍物,不能通过。现在给一个迷宫出口,让你判断是否可以从入口进来之后,走出迷宫,每次可以向任意方向走
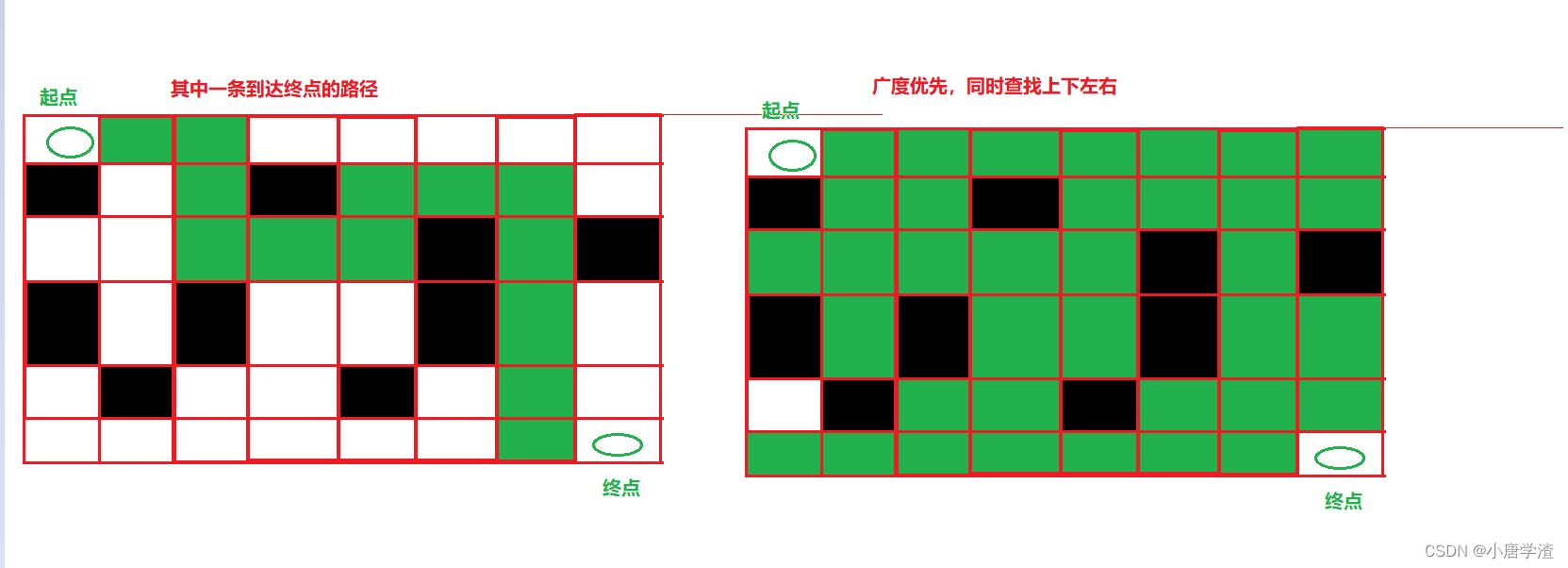
#include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct node { node(int x, int y) :_x(x) ,_y(y) {} int _x; int _y; }; bool BFS(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int sx, int sy, int ex, int ey) { int row = graph.size(); int col = graph[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> book(row, vector<int>(col, 0));//标记位置是否已走 0--未走 1--已走 int next[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} }; queue<node> q; //将其实位置入队 q.push(node(sx, sy)); book[sx][sy] = 1; int flag = 0; while (!q.empty()) { node cur = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int nextX = cur._x + next[i][0]; int nextY = cur._y + next[i][1]; if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= row || nextY < 0 || nextY >= col) continue; //判断是否入队 if (graph[nextX][nextY] == 0 && book[nextX][nextY] == 0) { q.push(node(nextX, nextY)); book[nextX][nextY] = 1; } //当前点是终点 if (nextX == ex && nextY == ey) { flag = 1; break; } } if (flag == 1) { break; } } return flag; } int main() { int m = 0;//行 int n = 0;//列 cin >> m >> n; vector<vector<int>> graph(m, vector<int>(n, 0)); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { cin >> graph[i][j]; } } int sx = 0;//其实位置 int sy = 0; int ex = m - 1;//结束位置 int ey = n - 1; cout << BFS(graph, sx, sy, ex, ey) << endl; return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
3.2 N叉树的层序遍历
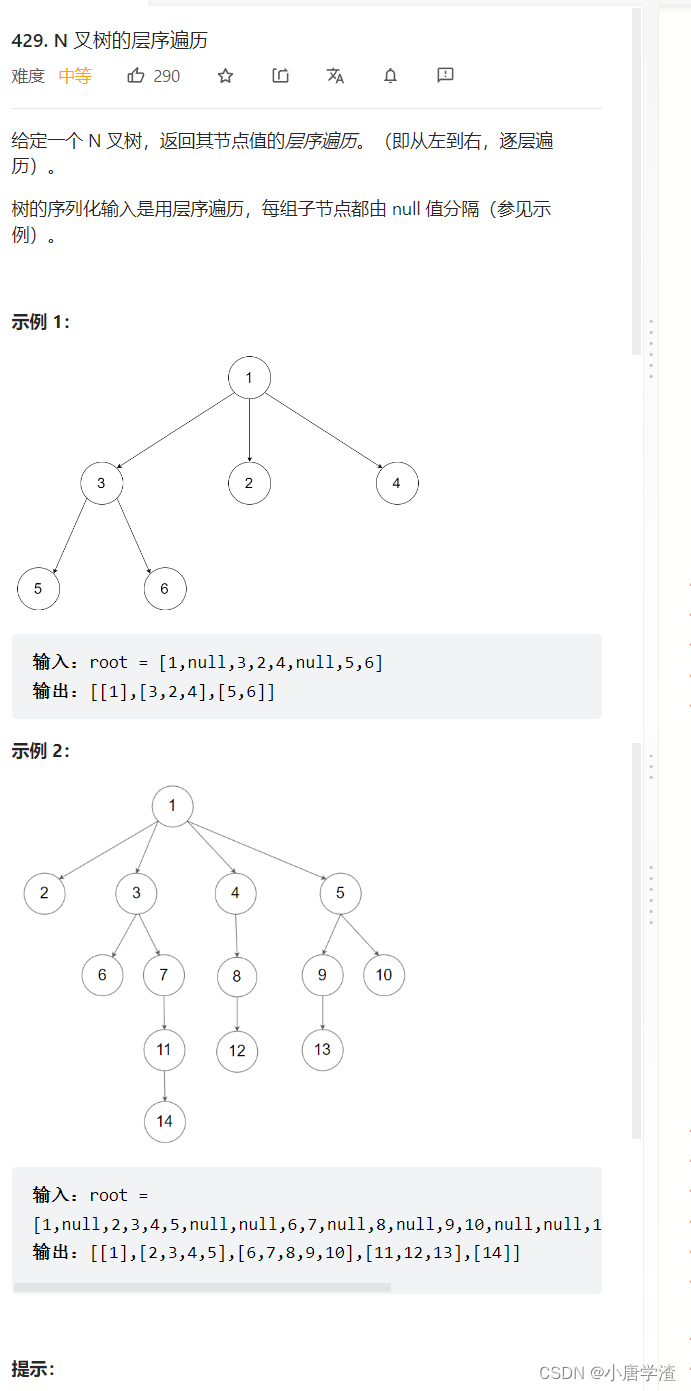
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val) { val = _val; } Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) { queue<Node*> q; if(root) q.push(root); vector<vector<int>> ret; while(!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); vector<int> rowV; while(size--) { Node* front = q.front(); q.pop(); rowV.push_back(front->val); //将结点的孩子全部入队 for(auto* e : front->children) { q.push(e); } } ret.push_back(rowV); } return ret; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
3.3 腐烂的橘子

class Solution { public: struct Node{ Node(int x, int y) :_x(x) ,_y(y) {} int _x; int _y; }; int next[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} }; int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { if(grid.empty()) return 0; int row = grid.size(); int col = grid[0].size(); queue<Node> q; for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) { //将所有腐烂的橘子入队 if(grid[i][j] == 2) { q.push(Node(i, j)); } } } int count = 0; while(!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); int flag = false; while(size--) { Node front = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newX = front._x + next[i][0]; int newY = front._y + next[i][1]; if(newX < 0 || newX >= row || newY < 0 || newY >= col) continue; if(grid[newX][newY] == 1) { flag = true; q.push(Node(newX, newY)); grid[newX][newY] = 2; } }//end of for }//end of while if(flag) ++count; } for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) { if(grid[i][j] == 1) return -1; } } return count; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
3.4 单词接龙

class Solution { public: int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) { //用hash表查找更快 unordered_set<string> dict(wordList.begin(), wordList.end()); unordered_set<string> book;//标记单词是否用过 queue<string> q; int step = 1;//步数 q.push(beginWord); book.insert(beginWord); while(!q.empty()) {//while 1 int size = q.size(); while(size--) {//while 2 string curStr = q.front(); q.pop(); if(curStr == endWord) return step; //替换单词的每个字符 for(int i = 0; i < curStr.size(); ++i) {//for 1 string temp = curStr; for(char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ++ch) { temp[i] = ch; //替换后的单词是否能在词典中找到, 并且没有被使用过 if(dict.find(temp) != dict.end() && book.find(temp) == book.end()) { q.push(temp); book.insert(temp); } } }//end of for 1 }//end of while 2 ++step; }//end of while 1 return 0; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
3.5 打开转盘锁

class Solution { public: int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) { //方便查找 unordered_set<string> deadendsMap(deadends.begin(), deadends.end()); unordered_set<string> book;//标记当前密码是否已经出现过 queue<string> q; if(deadendsMap.find("0000") != deadendsMap.end()) return -1; q.push("0000"); book.insert("0000"); int step = 0; while(!q.empty()) {//while 1 int size = q.size(); while(size--) {//while 1 string curStr = q.front(); q.pop(); if(curStr == target) return step; //改变每一位的数字 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { //每一位数字向上旋转也可以向下旋转 string tmpStr1 = curStr; string tmpStr2 = curStr; tmpStr1[i] = tmpStr1[i] == '9' ? '0' : tmpStr1[i] + 1; tmpStr2[i] = tmpStr2[i] == '0' ? '9' : tmpStr2[i] - 1; if(deadendsMap.find(tmpStr1) == deadendsMap.end() && book.find(tmpStr1) == book.end()) { q.push(tmpStr1); book.insert(tmpStr1); } if(deadendsMap.find(tmpStr2) == deadendsMap.end() && book.find(tmpStr2) == book.end()) { q.push(tmpStr2); book.insert(tmpStr2); } } }//end of while 2 ++step; }//end of while 1 return -1; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
-
相关阅读:
【Python脚本进阶】2.5、编写自己的0day概念验证代码(终)
Arduino驱动DFPlayer Mini MP3模块
EasyPlayer如何获取点播视频流的时间戳?
boa交叉编译(移植到arm)
Java面试题汇总(一)
53、基于51单片机蓄电池充电器过充过放保护LCD液晶屏显示系统设计(程序+原理图+PCB源文件+参考论文+参考PPT+元器件清单等)
基础复习——数据库SQLite——SQL的基本语法——数据库管理器SQLiteDatabase——数据库帮助器SQLiteOpenHelper...
在“美国死海”边的科研盛会 ACM CCS‘24 截稿日期逼近 行动要快
发布文章到wordpress
1.1 git常规操作
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52809807/article/details/125376398