-
文件操作File类的用法和输入流和输出流的用法
系列文章目录
进程调度的基本过程
学不懂多线程?代码加实例详解帮你深入理解多线程(1)
学不懂多线程?代码加实例详解帮你深入理解多线程(2)
前言
🌴 文件操作可分为对metadata的操作和对文件内部数据内容的操作两部分;
1. 对于metadata的操作
🌴 对于metadata的操作比较常用的有以下几种:
Modifier and Type Method Description String getName() Returns the name of the file or directory denoted by this abstract pathname. String getPath() Converts this abstract pathname into a pathname string. long length() Returns the length of the file denoted by this abstract pathname. long lastModified() Returns the time that the file denoted by this abstract pathname was last modified. boolean mkdir() Creates the directory named by this abstract pathname. boolean mkdirs() Creates the directory named by this abstract pathname, including any necessary but nonexistent parent directories. boolean createNewFile() Atomically creates a new, empty file named by this abstract pathname if and only if a file with this name does not yet exist. boolean renameTo(File dest) Renames the file denoted by this abstract pathname. 1.1 mkdir()
🌴 mkdir()是一个创建文件夹的方法;
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class cnd { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/2"); if(!f.exists()){ f.mkdir(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
🌴 创建前:
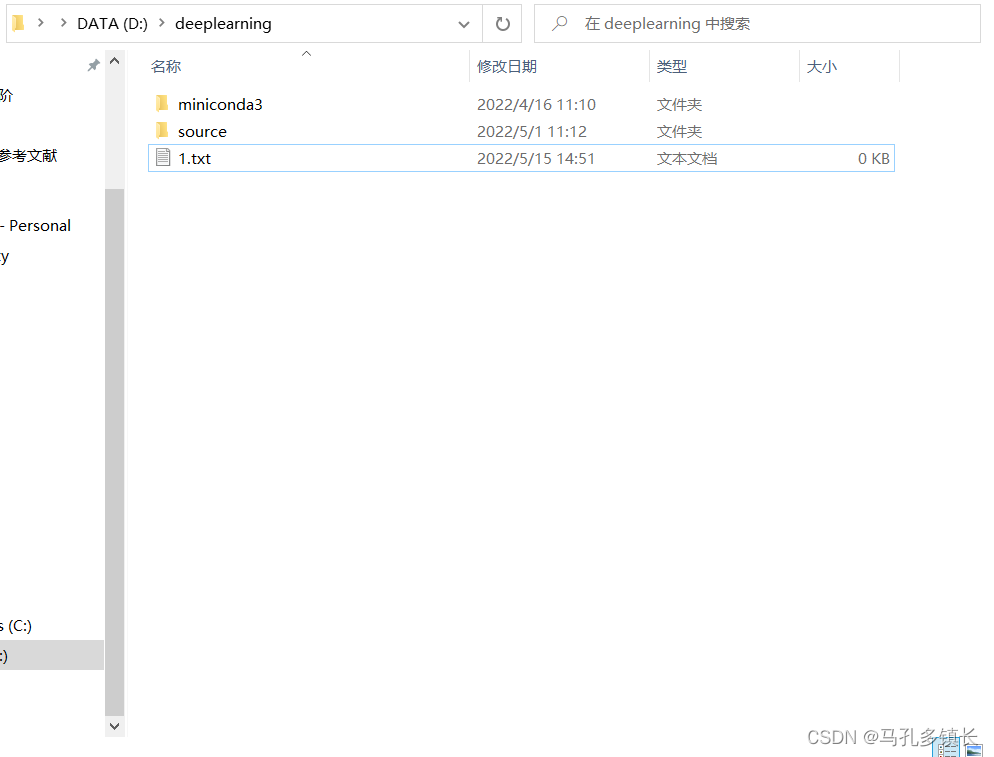
🌴 创建后: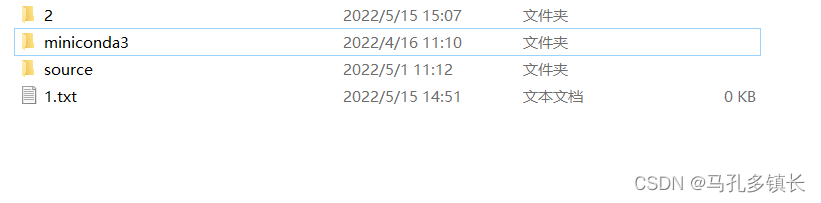
🌴 mkdirs()方法可以创建多级文件夹;🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; public class cnds { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1/2/3/4"); f.mkdirs(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
🌴 创建前:

🌴 创建后:

1.2 createNewFile()
🌴 我们可以使用newFile()方法创建文件;
🌴 代码如下:import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class cnf { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); if(!f.exists()){ f.createNewFile(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
🌴 运行结果为:

1.3 文件重命名
🌴 我们使用renameTo()方法可以对文件进行重命名;
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; public class rname { public static void main(String[] args) { //重命名 File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); f.renameTo(new File("D:/deeplearning/1_rename.txt")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
🌴 代码运行前:
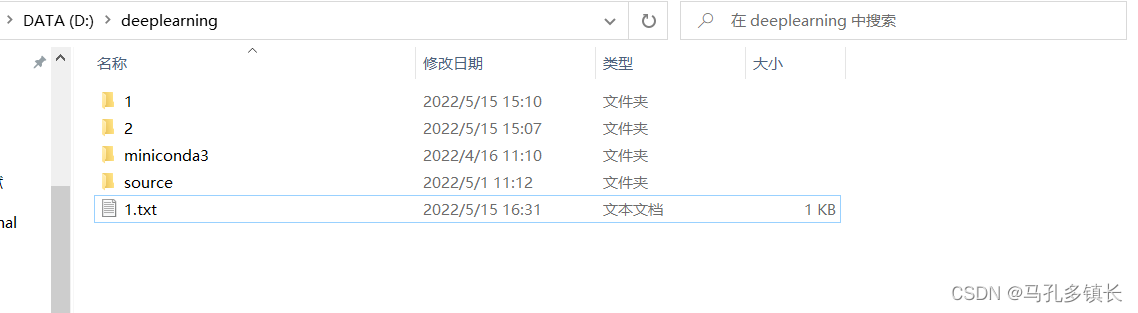
🌴 代码运行后:
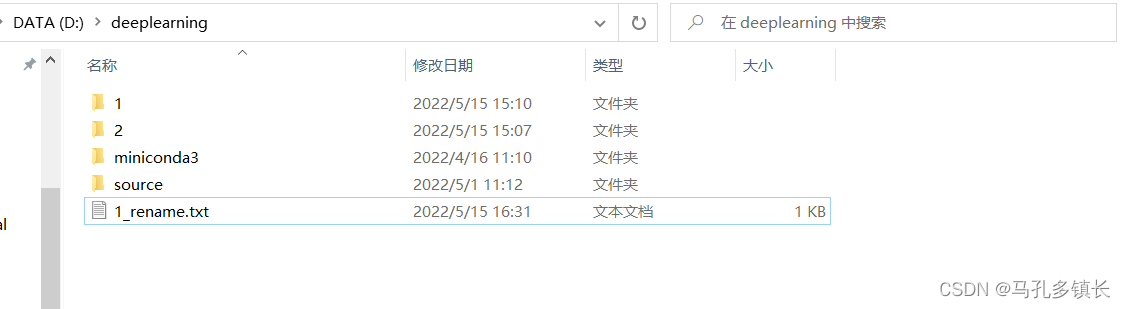
1.4 使用重命名方法进行文件移动
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; public class rname { public static void main(String[] args) { //移动 File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1_rename.txt"); f.renameTo(new File("D:/deeplearning/1/2/3/1_rename.txt")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
🌴
🌴
🌴public class getFileInfo { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); System.out.println("path:"+f.getPath()); System.out.println("name:"+f.getName()); System.out.println("length:"+f.length()); System.out.println("last modified:"+f.lastModified()); System.out.println("isFile:"+f.isFile()); System.out.println("isDirectory:"+f.isDirectory()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
🌴 代码运行前:
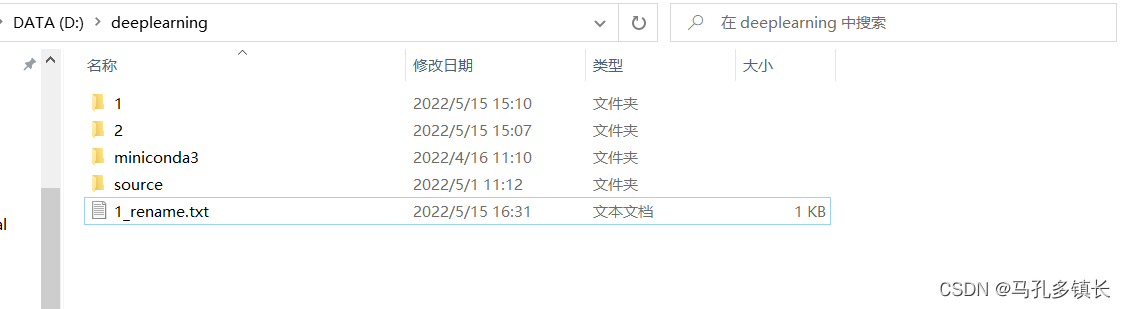
🌴 代码运行后:
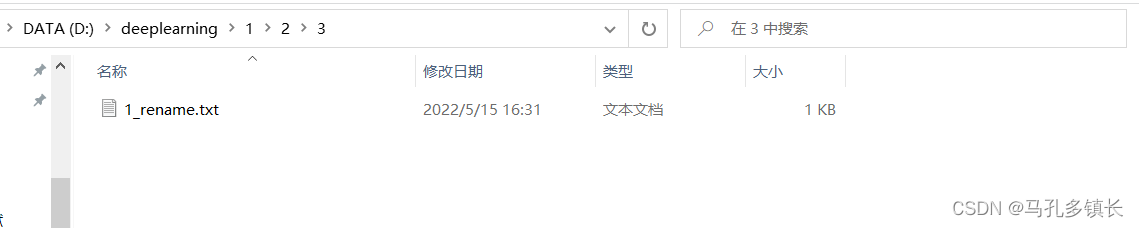
1.5 删除操作
🌴 使用delete()方法可以删除文件或者文件夹,需要注意的是delete()方法只能一级一级删除且只能删除空文件夹;
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; public class rname { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1/2/3/1_rename.txt"); f.delete(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
🌴 代码运行前:
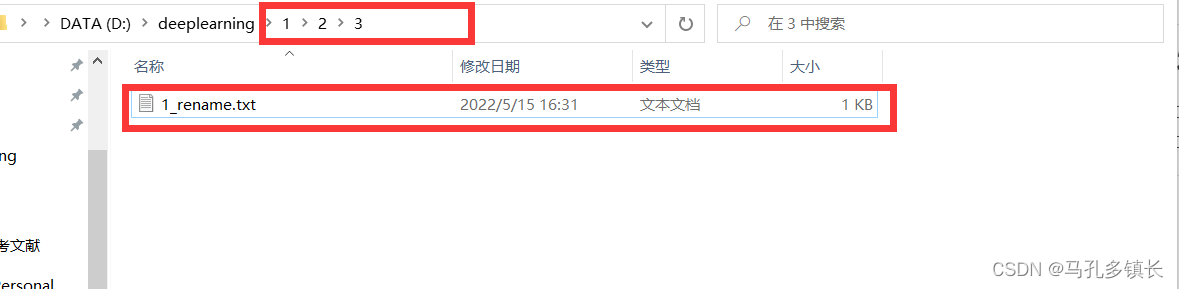
🌴 代码运行后:
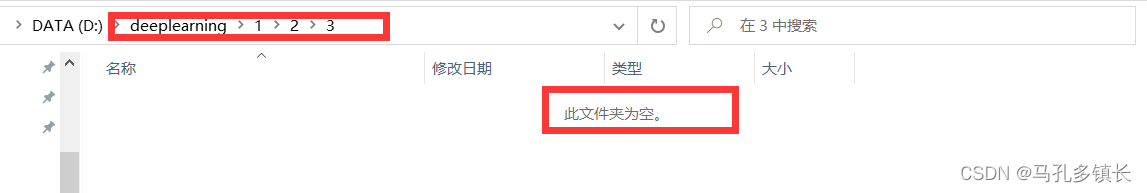
🌴 也可以使用delete()删除文件夹;
🌴 代码如下:import java.io.File; public class rname { public static void main(String[] args) { //删除文件夹 File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1/2/3"); f.delete(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
🌴 代码运行前:
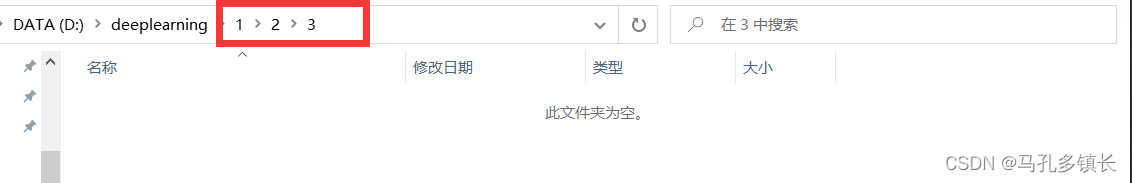
🌴 代码运行后:
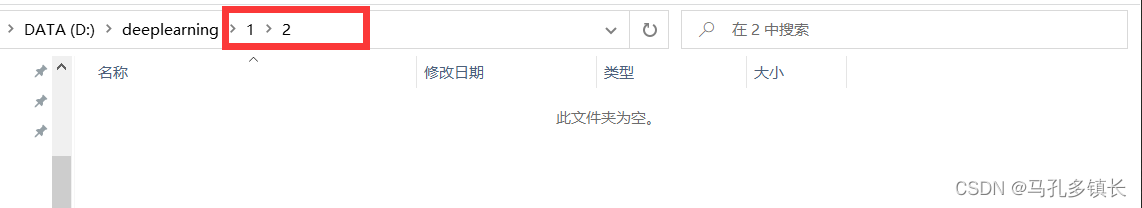
1.6 File中的其他方法
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; import java.util.Date; public class getFileInfo { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("D:/deeplearning/1.txt");//传入文件路径 System.out.println("path:"+f.getPath());//获取文件路径 System.out.println("name:"+f.getName());//获取目标文件名称 System.out.println("length:"+f.length());//获取内容字节数 System.out.println("last modified:"+new Date(f.lastModified()));//上次修改时间 System.out.println("isFile:"+f.isFile());//是否是文件 System.out.println("isDirectory:"+f.isDirectory());//是否是文件夹 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
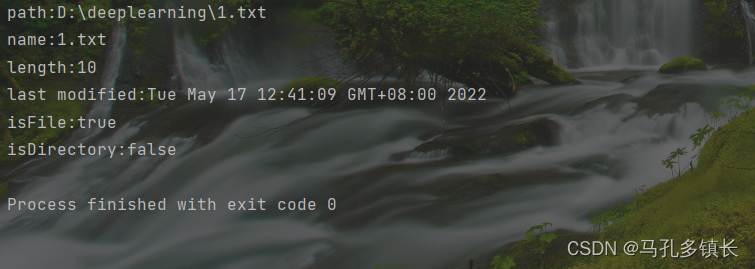
🌴 文件路径对应的文件是:
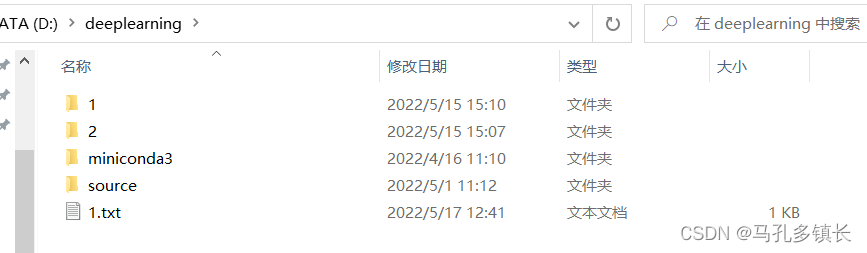
🌴 文件内有十个字节大小的数据
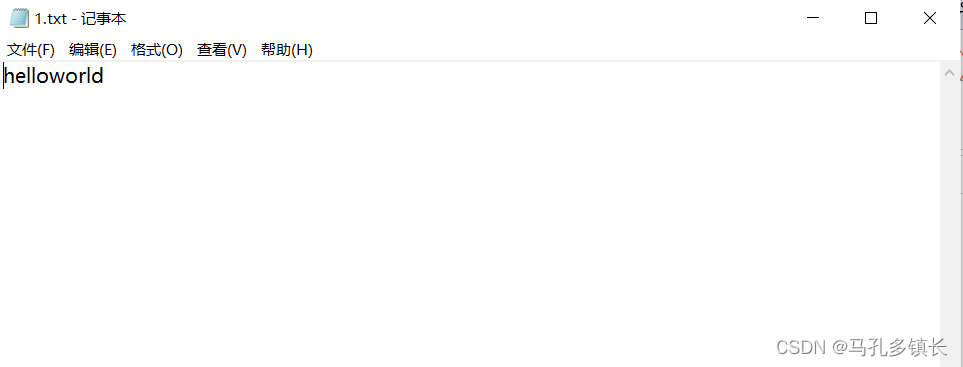
🌴 输出结果为:
1.7 遍历所有文件和目录
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.File; public class 获取所有文件和目录 { public static void main(String[] args) { File f =new File("D:/deeplearning"); list(f); } private static void list(File f){ System.out.println(f); if(f.isDirectory()){ File[] children = f.listFiles(); for(File child:children){ list(child);//使用递归的方法遍历每一个文件夹 } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
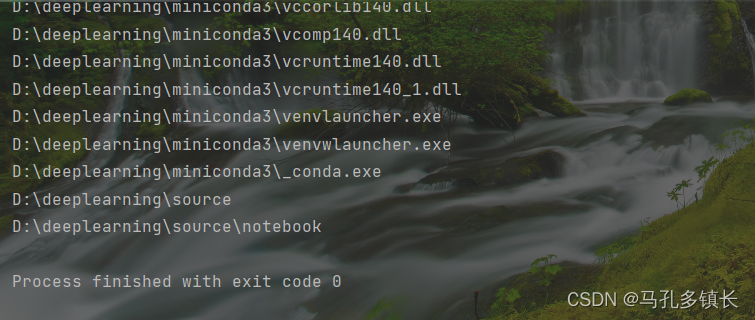
🌴 输出结果为:
2. 对于文件内容的读写操作
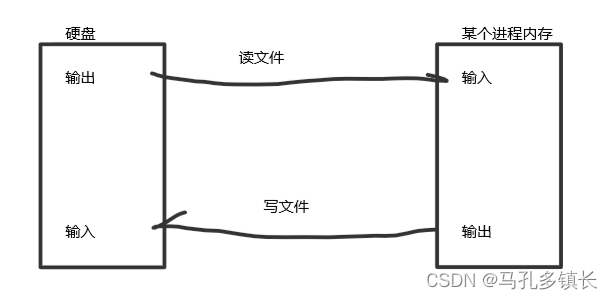
🌴 在Java中,使用数据流来传输数据,站在某个进程的内存的角度来看,从硬盘里读取数据使用的是输入流(InputStream),从进程内存中往硬盘里写数据使用的是输出流(OutputStream);
2.1 InputStream
🌴 InputStream 只是一个抽象类,要使用还需要具体的实现类;
2.1.1 FileInputStream
🌴 FileInputStream 用于读取原始字节流,例如图像数据;
Modifier and Type Method Description int read() Reads a byte of data from this input stream. int read(byte[] b) Reads up to b.length bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes. int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) Reads up to len bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes. 2.1.2 使用字节流读取文本
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class 使用字节流读取文本 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); int b; while((b=fis.read())!=-1){//不停地读取,直到返回给len一个-1 System.out.println((char)b); } fis.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
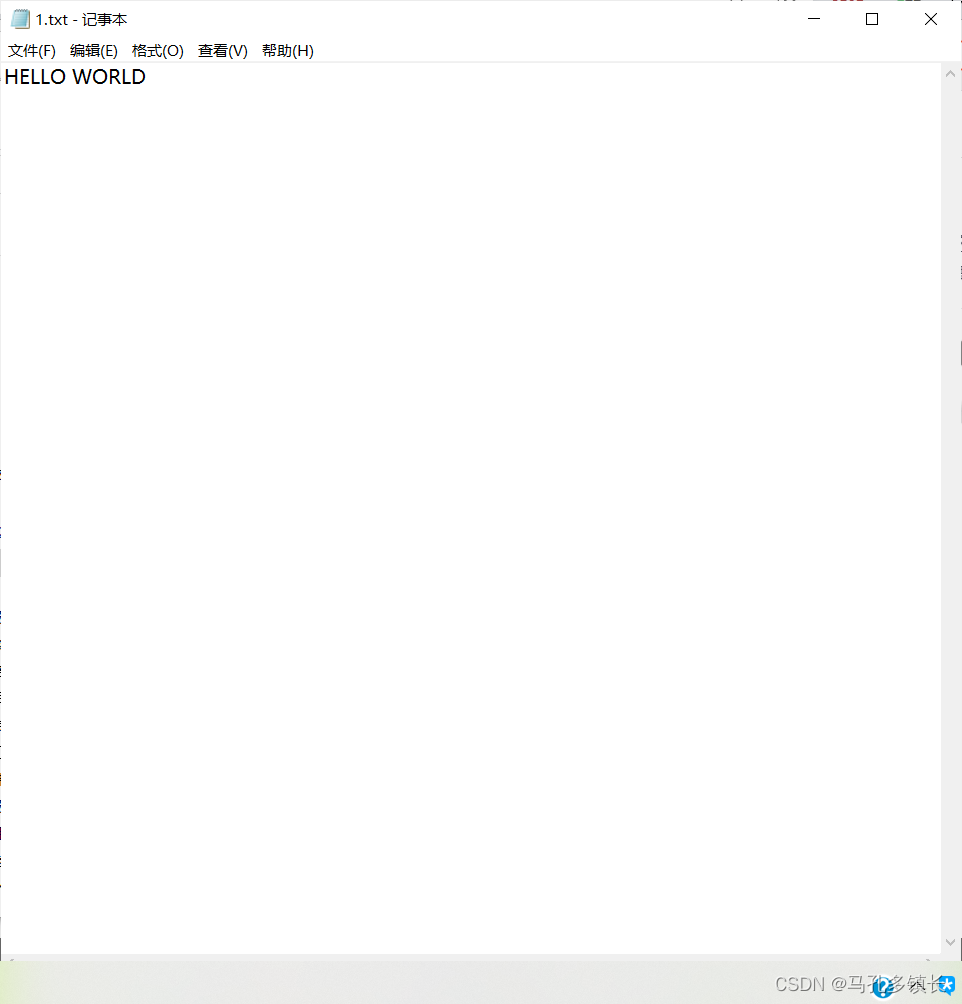
🌴 1.txt文本中的内容为:
🌴 输出结果为:

2.1.3 使用字节流数组读取文本
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class 使用字节数组流读取文本 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];//每次读1024个字节 int len;//每次读取的长度返回给len while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){//不停地读取,直到返回给len一个-1 String s=new String(bytes,0,len,"GBK");//0,len的作用是防止读空字符串 System.out.println(s); } fis.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
🌴 输出结果为:

2.2 OutputStream
🌴 与InputStream一样,OutputStream只是一个抽象类,要使用还需要具体的实现类;
Modifier and Type Method Description void write(byte[] b) Writes b.length bytes from the specified byte array to this output stream. void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) Writes len bytes from the specified byte array starting at offset off to this output stream. abstract void write(int b) Writes the specified byte to this output stream. 2.2.1 字符串转换为数组写入文本
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class 字符串转为数组写入文本 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/deeplearning/1.txt");//写入的目标文件 byte[] bytes = new byte[100]; String s = "HELLO"; bytes=s.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); fos.write(bytes); fos.flush(); fos.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
🌴 执行结果为:
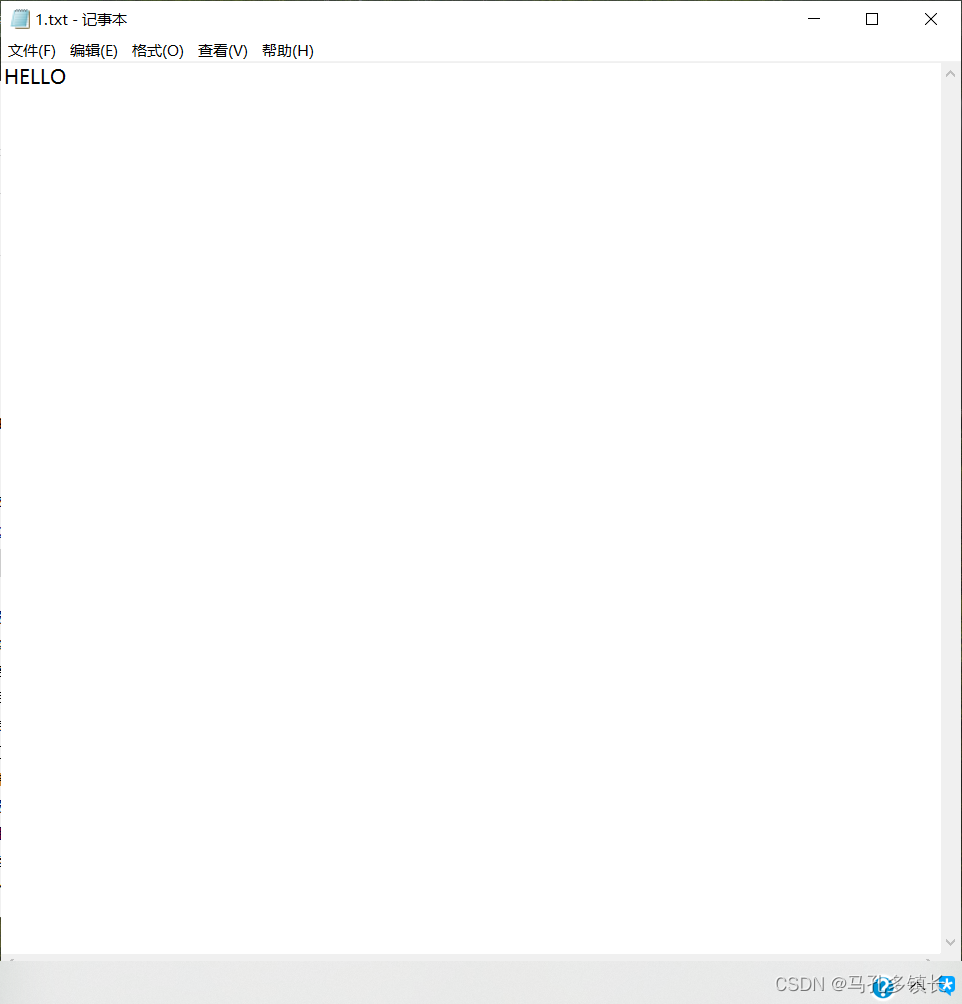
2.2.2 使用输出流进行单个字符写入
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class 使用输出流进行字符写入 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); fos.write('N'); fos.write('I'); fos.write('H'); fos.write('A'); fos.write('O'); fos.flush(); fos.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
🌴 执行结果为:
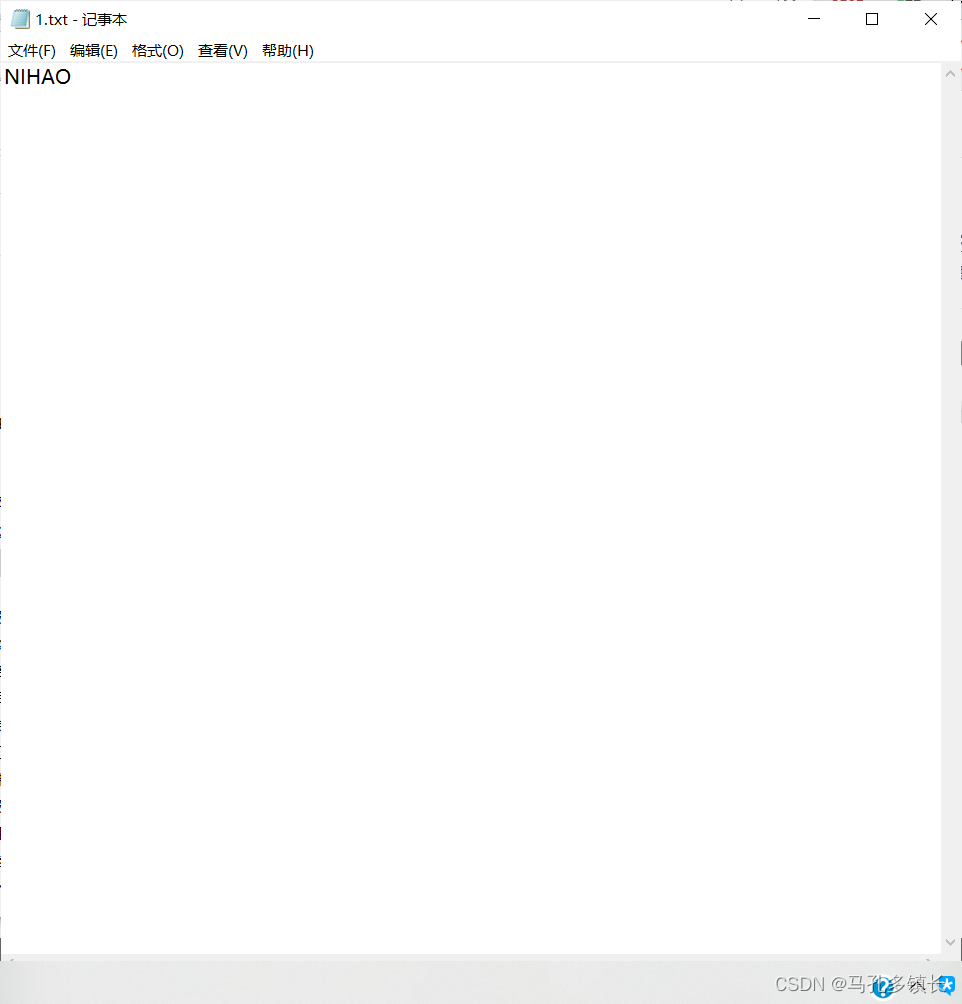
2.2.3 将字符数组写入文本
🌴 代码如下:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class 使用字节流数组进行字符写入 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); byte[] bytes = new byte[]{ 'W','O','R', 'L','D' }; fos.write(bytes); fos.flush(); fos.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
🌴 执行结果为:
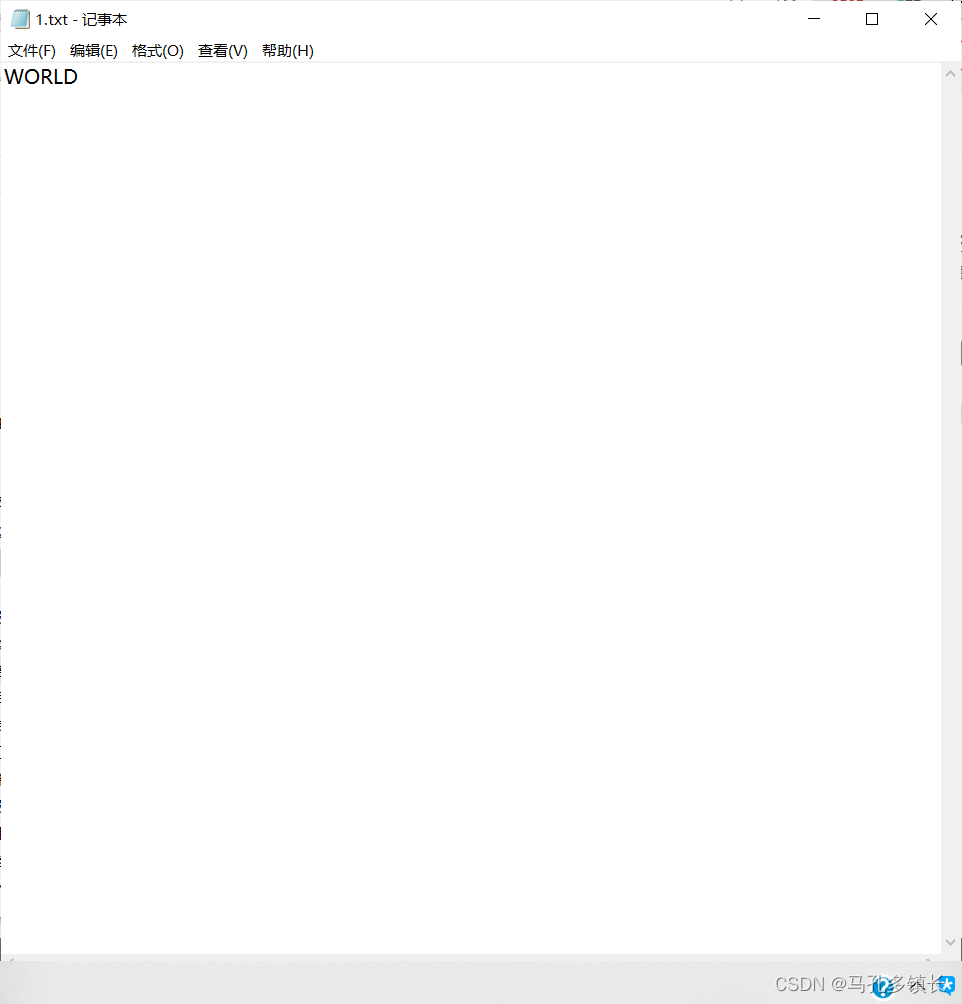
2.2.4 使用printwriter方法写入文本
🌴 代码如下:
public class 使用printwriter方法写入文本 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/deeplearning/1.txt"); OutputStreamWriter foswriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"utf-8"); PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(foswriter); writer.println("H"); writer.flush(); writer.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
🌴 执行结果为:
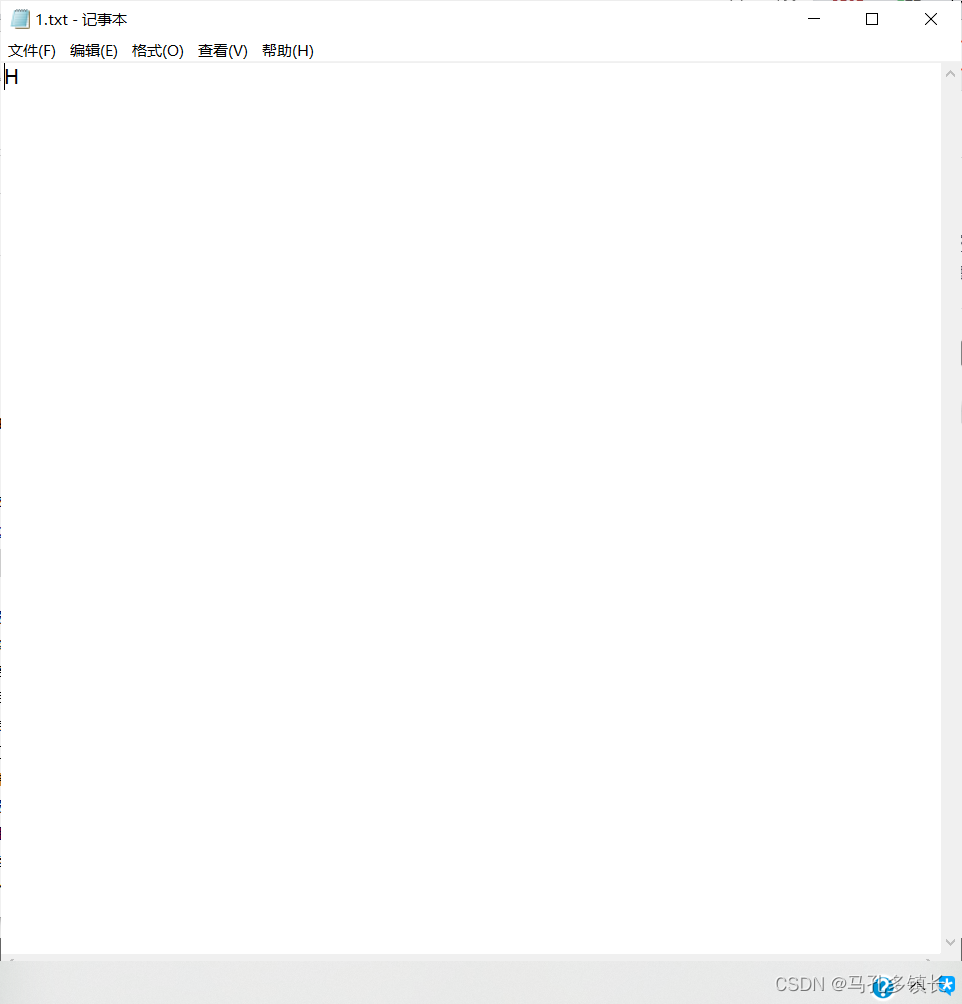
总结
🌴 只有多加练习,才能更牢固地掌握,加油!
-
相关阅读:
企业虚拟化KVM的三种安装方式(1、完全文本2、模板镜像+配置文件3、gustos图形方式部署安装虚拟机)
String类相关面试题
Android源码——ComponentCallbacks源码解析
通过示例详细了解ES6导入导出模块
Google Earth Engine(GEE)——ccdc分类,采用的是随机森林分类器
JDK8升级JDK11最全实践干货来了
维基百科是如何定义联合办公空间的?
APM Profile 在系统可观测体系中的应用
【C++ map、set】
一次c++监听Linux文件目录的实践
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_60266328/article/details/124784564