-
<Rust>egui部件学习:如何在窗口及部件显示中文字符?
前言
本专栏是关于Rust的GUI库egui的部件讲解及应用实例分析,主要讲解egui的源代码、部件属性、如何应用。环境配置
系统:windows
平台:visual studio code
语言:rust
库:egui、eframe概述
本文是本专栏的第一篇博文,主要讲述如何使用egui库来显示一个窗口以及如何在窗口显示中文字符。egui是基于rust的一个GUI库,可以创建窗口并添加部件、布局,其github地址:
https://github.com/emilk/egui事实上,类似于iced,egui都提供了示例程序,本专栏的博文都是建立在官方示例程序以及源代码的基础上,进行的实例讲解。
即,本专栏的文章并非只是简单的翻译egui的官方示例与文档,而是针对于官方代码进行的实际使用,会在官方的代码上进行修改,包括解决一些问题。部件属性
在使用egui前,需要添加其依赖:
egui="0.28.1" eframe="0.28.1"将上面的库添加到你的项目的toml文件中,然后编译一下。
然后我们来看一个简单的示例,我们以官方提供的例子中的第一个confirm_exit例子来进行说明。这个例子很简单,就是生成一个窗口,并且在关闭窗口时弹出一个提示窗口,选择yes关闭,选择no,不关闭。
官方代码如下:
#![cfg_attr(not(debug_assertions), windows_subsystem = "windows")] // hide console window on Windows in release #![allow(rustdoc::missing_crate_level_docs)] // it's an example use eframe::egui; fn main() -> eframe::Result { env_logger::init(); // Log to stderr (if you run with `RUST_LOG=debug`). let options = eframe::NativeOptions { viewport: egui::ViewportBuilder::default().with_inner_size([320.0, 240.0]), ..Default::default() }; eframe::run_native( "Confirm exit", options, Box::new(|_cc| Ok(Box::<MyApp>::default())), ) } #[derive(Default)] struct MyApp { show_confirmation_dialog: bool, allowed_to_close: bool, } impl eframe::App for MyApp { fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) { egui::CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| { ui.heading("Try to close the window"); }); if ctx.input(|i| i.viewport().close_requested()) { if self.allowed_to_close { // do nothing - we will close } else { ctx.send_viewport_cmd(egui::ViewportCommand::CancelClose); self.show_confirmation_dialog = true; } } if self.show_confirmation_dialog { egui::Window::new("Do you want to quit?") .collapsible(false) .resizable(false) .show(ctx, |ui| { ui.horizontal(|ui| { if ui.button("No").clicked() { self.show_confirmation_dialog = false; self.allowed_to_close = false; } if ui.button("Yes").clicked() { self.show_confirmation_dialog = false; self.allowed_to_close = true; ui.ctx().send_viewport_cmd(egui::ViewportCommand::Close); } }); }); } } }运行之后显示如下:
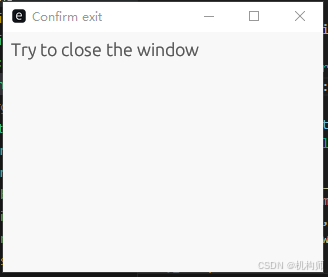
点击关闭按钮,弹出提示窗口:

点击yes按钮,直接关闭,点击no按钮,提示窗口消失,窗口不关闭。本文暂且不关注窗口如何显示以及如何添加部件,这将在以后的文章中说明。
现在,我们来修改上面的代码,将上面代码中涉及的text文本的内容都修改为中文,再来看看效果。
修改后的代码:
#![cfg_attr(not(debug_assertions), windows_subsystem = "windows")] // hide console window on Windows in release #![allow(rustdoc::missing_crate_level_docs)] // it's an example use eframe::egui; fn main() -> eframe::Result { env_logger::init(); // Log to stderr (if you run with `RUST_LOG=debug`). let options = eframe::NativeOptions { viewport: egui::ViewportBuilder::default().with_inner_size([320.0, 240.0]), ..Default::default() }; eframe::run_native( "egui测试窗口", options, Box::new(|_cc| Ok(Box::<MyApp>::default())), ) } #[derive(Default)] struct MyApp { show_confirmation_dialog: bool, allowed_to_close: bool, } impl eframe::App for MyApp { fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) { egui::CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| { ui.heading("尝试关闭窗口"); }); if ctx.input(|i| i.viewport().close_requested()) { if self.allowed_to_close { // do nothing - we will close } else { ctx.send_viewport_cmd(egui::ViewportCommand::CancelClose); self.show_confirmation_dialog = true; } } if self.show_confirmation_dialog { egui::Window::new("你想要关闭吗?") .collapsible(false) .resizable(false) .show(ctx, |ui| { ui.horizontal(|ui| { if ui.button("否").clicked() { self.show_confirmation_dialog = false; self.allowed_to_close = false; } if ui.button("是").clicked() { self.show_confirmation_dialog = false; self.allowed_to_close = true; ui.ctx().send_viewport_cmd(egui::ViewportCommand::Close); } }); }); } } }再来运行看下:

点击关闭按钮:

可以看到,无论是窗口直接显示的文本还是按钮的文本,都显示乱码,这是因为egui自带的字体不支持中文导致的。所以,和iced库一样,我们只要想办法将字体替换为自定义的字体(支持中文字符)即可。
支持中文字符的字体有很多,可以去网上自行下载,一般来说,最常用的应该是simsun.ttf,当然,也可以去egui作者提供的一个字体网站下载字体:
https://github.com/notofonts/noto-cjk/tree/main/Sans#downloading-noto-sans-cjk下面我们来看下,如何替换字体,这里依然参考官方提供的示例custom_font。这里就不贴具体代码了,自定义字体的方法,是在efram的一个属性AppCreator中:
/// This is how your app is created. /// /// You can use the [`CreationContext`] to setup egui, restore state, setup OpenGL things, etc. pub type AppCreator = Box<dyn FnOnce(&CreationContext<'_>) -> Result<Box<dyn App>, DynError>>;其实就是设置CreationContext,其下的ctx:
/// You can use this to customize the look of egui, e.g to call [`egui::Context::set_fonts`], /// [`egui::Context::set_visuals`] etc. pub egui_ctx: egui::Context,context实现了set_fonts函数:
/// Tell `egui` which fonts to use. /// /// The default `egui` fonts only support latin and cyrillic alphabets, /// but you can call this to install additional fonts that support e.g. korean characters. /// /// The new fonts will become active at the start of the next frame. pub fn set_fonts(&self, font_definitions: FontDefinitions) { crate::profile_function!(); let pixels_per_point = self.pixels_per_point(); let mut update_fonts = true; self.read(|ctx| { if let Some(current_fonts) = ctx.fonts.get(&pixels_per_point.into()) { // NOTE: this comparison is expensive since it checks TTF data for equality if current_fonts.lock().fonts.definitions() == &font_definitions { update_fonts = false; // no need to update } } }); if update_fonts { self.memory_mut(|mem| mem.new_font_definitions = Some(font_definitions)); } }而set_fonts的参数是FontDefinitions,我们设置其font_data即可。
pub struct FontDefinitions { /// List of font names and their definitions. /// /// `epaint` has built-in-default for these, but you can override them if you like. pub font_data: BTreeMap<String, FontData>, /// Which fonts (names) to use for each [`FontFamily`]. /// /// The list should be a list of keys into [`Self::font_data`]. /// When looking for a character glyph `epaint` will start with /// the first font and then move to the second, and so on. /// So the first font is the primary, and then comes a list of fallbacks in order of priority. pub families: BTreeMap<FontFamily, Vec<String>>, }font_data实现了from_static函数:
pub fn from_static(font: &'static [u8]) -> Self { Self { font: std::borrow::Cow::Borrowed(font), index: 0, tweak: Default::default(), } }我们为from_static传入自定义字体的字节数组即可,可以适应include_byets来获取数组:
const ICON_BYTES:&[u8]=include_bytes!("../font/simsun.ttf");如上,我们下载simsun.ttf字体文件,放到项目文件夹中,然后获取其静态字节数组。
// Start with the default fonts (we will be adding to them rather than replacing them). let mut fonts = egui::FontDefinitions::default(); // Install my own font (maybe supporting non-latin characters). // .ttf and .otf files supported. fonts.font_data.insert( "my_font".to_owned(), egui::FontData::from_static( ICON_BYTES, ), );这是官方提供的示例代码,我们只是修改其中的字体的内容。
使用自定义字体后,我们再来运行一下程序看看:

点击关闭按钮后:

好了,以上就是使用egui显示窗口时,如何显示中文的解决办法,基本上是基于官方给的示例。
本文并没有修改太多,因为主要是说明如何显示中文的问题。对于一些初学者来说,可能即使看官方示例和说明,也不知道如何解决这个问题,如果我这边的解释能帮助你,那就不枉了。后续的文章里,中文字符显示的函数将会被独立出来,单独作为一个mod,然后在main中调用,这样也方便管理。
完整代码:
#![cfg_attr(not(debug_assertions), windows_subsystem = "windows")] // hide console window on Windows in release #![allow(rustdoc::missing_crate_level_docs)] // it's an example use eframe::egui; const MY_FONTS_BYTES:&[u8]=include_bytes!("../font/simsun.ttf"); fn main() -> eframe::Result { env_logger::init(); // Log to stderr (if you run with `RUST_LOG=debug`). let options = eframe::NativeOptions { viewport: egui::ViewportBuilder::default().with_inner_size([320.0, 240.0]), ..Default::default() }; eframe::run_native( "egui测试窗口", options, //Box::new(|_cc| Ok(Box::::default())), Box::new(|cc| Ok(Box::new(MyApp::new(cc)))), ) } /// /// 设置自定义字体 /// fn setup_custom_fonts(ctx: &egui::Context) { // Start with the default fonts (we will be adding to them rather than replacing them). let mut fonts = egui::FontDefinitions::default(); // Install my own font (maybe supporting non-latin characters). // .ttf and .otf files supported. fonts.font_data.insert( "my_font".to_owned(), egui::FontData::from_static( MY_FONTS_BYTES, ), ); // Put my font first (highest priority) for proportional text: fonts .families .entry(egui::FontFamily::Proportional) .or_default() .insert(0, "my_font".to_owned()); // Put my font as last fallback for monospace: fonts .families .entry(egui::FontFamily::Monospace) .or_default() .push("my_font".to_owned()); // Tell egui to use these fonts: ctx.set_fonts(fonts); } #[derive(Default)] struct MyApp { show_confirmation_dialog: bool, allowed_to_close: bool, } impl MyApp{ fn new(cc: &eframe::CreationContext<'_>) -> Self { setup_custom_fonts(&cc.egui_ctx); Self { show_confirmation_dialog:false, allowed_to_close:false, } } } impl eframe::App for MyApp { fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) { egui::CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| { ui.heading("尝试关闭窗口"); }); if ctx.input(|i| i.viewport().close_requested()) { if self.allowed_to_close { // do nothing - we will close } else { ctx.send_viewport_cmd(egui::ViewportCommand::CancelClose); self.show_confirmation_dialog = true; } } if self.show_confirmation_dialog { egui::Window::new("你想要关闭吗?") .collapsible(false) .resizable(false) .show(ctx, |ui| { ui.horizontal(|ui| { if ui.button("否").clicked() { self.show_confirmation_dialog = false; self.allowed_to_close = false; } if ui.button("是").clicked() { self.show_confirmation_dialog = false; self.allowed_to_close = true; ui.ctx().send_viewport_cmd(egui::ViewportCommand::Close); } }); }); } } } -
相关阅读:
Spring Security进行权限控制
【Kafka】Java整合Kafka
训练和测试的loss不下降,并且精度超低
【ESP-IDF篇】搭建ESP-IDF软件开发环境,包括手动命令行和VSCode两种方式
webpack配置之source-map的使用
VSCode 远程反复输入密码不能链接问题解决
爱奇艺极速版刷视频
文件、异常、模块
人人自媒体的时候,Ai绘画还值得踏入吗?
王道数据结构第五章二叉树的遍历第13题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/normer123456/article/details/140430756