-
Meta Llama 3 RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization)
Meta Llama 3 RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization)
flyfish
先看LayerNorm和BatchNorm
展示计算的方向
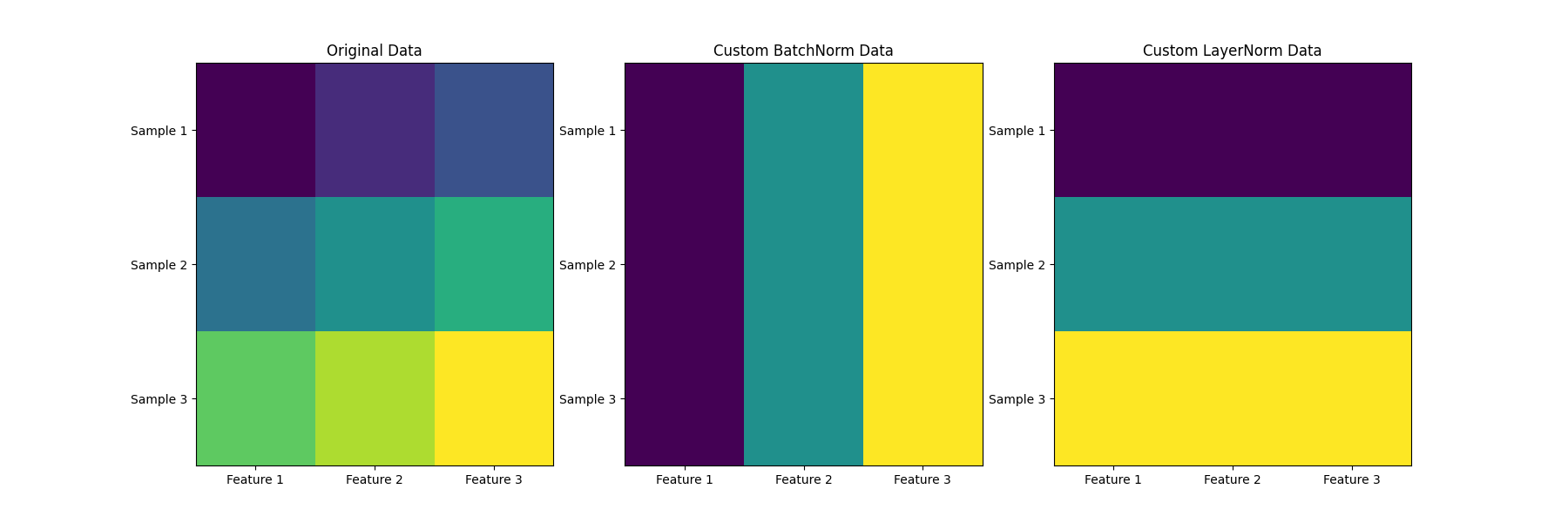
- axis=0 代表第一个轴,逐列处理数据。
- axis=1 代表第二个轴,逐行处理数据。在二维数组中,axis=-1 等同于 axis=1。
- axis=-1 代表最后一个轴。在二维数组中,axis=-1 等同于 axis=1,即最后一个轴。
在二维的情况 下,BatchNorm是按列算,LayerNorm按行算
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torch import torch.nn as nn class CustomLayerNorm: def __init__(self, eps=1e-5): self.eps = eps def __call__(self, x): mean = np.mean(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True) std = np.std(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True) normalized = (x - mean) / (std + self.eps) return normalized class CustomBatchNorm: def __init__(self, eps=1e-5): self.eps = eps def __call__(self, x): mean = np.mean(x, axis=0) std = np.std(x, axis=0) normalized = (x - mean) / (std + self.eps) return normalized # Original Data data = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0], [7.0, 8.0, 9.0]]) # Apply Custom LayerNorm custom_layer_norm = CustomLayerNorm() custom_layer_norm_data = custom_layer_norm(data) # Apply Custom BatchNorm custom_batch_norm = CustomBatchNorm() custom_batch_norm_data = custom_batch_norm(data) # Apply PyTorch LayerNorm data_tensor = torch.tensor(data, dtype=torch.float32) layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(data_tensor.size()[1:]) pytorch_layer_norm_data = layer_norm(data_tensor).detach().numpy() # Compare Custom and PyTorch LayerNorm print("Original Data:\n", data) print("Custom LayerNorm Data:\n", custom_layer_norm_data) print("PyTorch LayerNorm Data:\n", pytorch_layer_norm_data)Original Data: [[1. 2. 3.] [4. 5. 6.] [7. 8. 9.]] Custom LayerNorm Data: [[-1.22472987 0. 1.22472987] [-1.22472987 0. 1.22472987] [-1.22472987 0. 1.22472987]] PyTorch LayerNorm Data: [[-1.2247356 0. 1.2247356] [-1.2247356 0. 1.2247356] [-1.2247356 0. 1.2247356]]举个例子计算 LayerNorm
具体步骤如下:
- 计算每行的均值:
- 对每一行,计算其均值。
- 第1行: mean = (1 + 2 + 3) / 3 = 2
- 第2行: mean = (4 + 5 + 6) / 3 = 5
- 第3行: mean = (7 + 8 + 9) / 3 = 8
- 计算每行的标准差:
- 对每一行,计算其标准差。
- 第1行: s t d = s q r t ( ( ( 1 − 2 ) 2 + ( 2 − 2 ) 2 + ( 3 − 2 ) 2 ) / 3 ) = s q r t ( ( 1 + 0 + 1 ) / 3 ) = s q r t ( 2 / 3 ) ≈ 0.8165 std = sqrt(((1-2)^2 + (2-2)^2 + (3-2)^2) / 3) = sqrt((1 + 0 + 1) / 3) = sqrt(2 / 3) ≈ 0.8165 std=sqrt(((1−2)2+(2−2)2+(3−2)2)/3)=sqrt((1+0+1)/3)=sqrt(2/3)≈0.8165
- 第2行: s t d = s q r t ( ( ( 4 − 5 ) 2 + ( 5 − 5 ) 2 + ( 6 − 5 ) 2 ) / 3 ) = s q r t ( ( 1 + 0 + 1 ) / 3 ) = s q r t ( 2 / 3 ) ≈ 0.8165 std = sqrt(((4-5)^2 + (5-5)^2 + (6-5)^2) / 3) = sqrt((1 + 0 + 1) / 3) = sqrt(2 / 3) ≈ 0.8165 std=sqrt(((4−5)2+(5−5)2+(6−5)2)/3)=sqrt((1+0+1)/3)=sqrt(2/3)≈0.8165
- 第3行: s t d = s q r t ( ( ( 7 − 8 ) 2 + ( 8 − 8 ) 2 + ( 9 − 8 ) 2 ) / 3 ) = s q r t ( ( 1 + 0 + 1 ) / 3 ) = s q r t ( 2 / 3 ) ≈ 0.8165 std = sqrt(((7-8)^2 + (8-8)^2 + (9-8)^2) / 3) = sqrt((1 + 0 + 1) / 3) = sqrt(2 / 3) ≈ 0.8165 std=sqrt(((7−8)2+(8−8)2+(9−8)2)/3)=sqrt((1+0+1)/3)=sqrt(2/3)≈0.8165
- 标准化每一行:
- 对每一行,使用均值和标准差进行标准化。公式为: ( x − m e a n ) / ( s t d + e p s ) (x - mean) / (std + eps) (x−mean)/(std+eps)。其中 eps 是一个小常数,防止除零,通常取值为 1e-5。
- 计算结果如下:
标准化公式: n o r m a l i z e d = ( x − m e a n ) / ( s t d + e p s ) normalized = (x - mean) / (std + eps) normalized=(x−mean)/(std+eps)
第1行: [(1-2)/(0.8165+1e-5), (2-2)/(0.8165+1e-5), (3-2)/(0.8165+1e-5)] = [-1.2247, 0, 1.2247] 第2行: [(4-5)/(0.8165+1e-5), (5-5)/(0.8165+1e-5), (6-5)/(0.8165+1e-5)] = [-1.2247, 0, 1.2247] 第3行: [(7-8)/(0.8165+1e-5), (8-8)/(0.8165+1e-5), (9-8)/(0.8165+1e-5)] = [-1.2247, 0, 1.2247]最终标准化结果矩阵为:
[[-1.2247, 0, 1.2247] [-1.2247, 0, 1.2247] [-1.2247, 0, 1.2247]]RMSNorm 的整个计算过程
Meta Llama 3 使用了RMSNorm
假设我们有以下 2D 输入张量 X X X(为了简单起见,我们假设这个张量有 2 行 3 列):
[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 ] [123456] [142536]
RMSNorm 的计算过程如下:- 计算每行的均方根 (RMS):
首先,对于每一行,我们计算该行元素的平方和的均值,然后取其平方根。
对于第 1 行:
RMS row1 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 3 = 1 + 4 + 9 3 = 4.67 ≈ 2.16 \text{RMS}_{\text{row1}} = \sqrt{\frac{1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2}{3}} = \sqrt{\frac{1 + 4 + 9}{3}} = \sqrt{4.67} \approx 2.16 RMSrow1=312+22+32=31+4+9=4.67≈2.16
对于第 2 行:
RMS row2 = 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 3 = 16 + 25 + 36 3 = 25.67 ≈ 5.07 \text{RMS}_{\text{row2}} = \sqrt{\frac{4^2 + 5^2 + 6^2}{3}} = \sqrt{\frac{16 + 25 + 36}{3}} = \sqrt{25.67} \approx 5.07 RMSrow2=342+52+62=316+25+36=25.67≈5.07 - 使用均方根对输入进行归一化:
将每行的元素除以该行的 RMS 值。这里的 epsilon 用于防止除以零的问题,我们假设 ϵ = 1 e − 6 \epsilon = 1e-6 ϵ=1e−6。
对于第 1 行: Normed row1 = [ 1 2.16 + ϵ 2 2.16 + ϵ 3 2.16 + ϵ ] ≈ [ 0.462 0.925 1.387 ] \text{Normed}_{\text{row1}} = [12.16+ϵ22.16+ϵ32.16+ϵ] \approx [0.4620.9251.387] Normedrow1=[2.16+ϵ12.16+ϵ22.16+ϵ3]≈[0.4620.9251.387]
对于第 2 行: Normed row2 = [ 4 5.07 + ϵ 5 5.07 + ϵ 6 5.07 + ϵ ] ≈ [ 0.789 0.986 1.183 ] \text{Normed}_{\text{row2}} = [45.07+ϵ55.07+ϵ65.07+ϵ] \approx [0.7890.9861.183] Normedrow2=[5.07+ϵ45.07+ϵ55.07+ϵ6]≈[0.7890.9861.183] - 应用可学习的缩放参数:
假设权重参数 weight \text{weight} weight 为一个向量 [ 1 , 1 , 1 ] [1, 1, 1] [1,1,1],表示每个元素的缩放因子。对于第 1 行: Output row1 = [ 0.462 ⋅ 1 0.925 ⋅ 1 1.387 ⋅ 1 ] = [ 0.462 0.925 1.387 ] \text{Output}_{\text{row1}} = [0.462⋅10.925⋅11.387⋅1] = [0.4620.9251.387] Outputrow1=[0.462⋅10.925⋅11.387⋅1]=[0.4620.9251.387]对于第 2 行: Output row2 = [ 0.789 ⋅ 1 0.986 ⋅ 1 1.183 ⋅ 1 ] = [ 0.789 0.986 1.183 ] \text{Output}_{\text{row2}} = [0.789⋅10.986⋅11.183⋅1] = [0.7890.9861.183] Outputrow2=[0.789⋅10.986⋅11.183⋅1]=[0.7890.9861.183]
实际代码实现
以下是使用 PyTorch 实现上述步骤的代码示例:
import torch import torch.nn as nn class RMSNorm(nn.Module): def __init__(self, dim: int, eps: float = 1e-6): super().__init__() self.eps = eps self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(dim)) def _norm(self, x): return x * torch.rsqrt(x.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True) + self.eps) def forward(self, x): output = self._norm(x.float()).type_as(x) return output * self.weight # 示例数据 data = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]]) # 实例化 RMSNorm 层 rms_norm = RMSNorm(dim=data.size(-1)) # 计算归一化后的输出 normalized_data = rms_norm(data) print("Original Data:\n", data) print("RMSNorm Normalized Data:\n", normalized_data)结果
运行上述代码后,我们将得到归一化后的数据:
tensor([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]]) RMSNorm Normalized Data: tensor([[0.4629, 0.9258, 1.3887], [0.7895, 0.9869, 1.1843]], grad_fn=) -
相关阅读:
MyBatis与Spring框架整合实现对数据库的增删改查
Linux系统权限和用户相关操作
肠道微生物群与过敏性鼻炎
Java类加载器
用pip_search代替pip search
你必须学UML之理论篇
我不允许你还不知道这本助你斩获高薪offer的神书
【网络技术】TCP详解
3.yolov5训练前的图片处理详解(python)
代码都是对的,但结果就不对,leetcode上的
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/flyfish1986/article/details/139488600