-
PyTorch 张量数据类型
-
【数据类型】Python 与 PyTorch 常见数据类型对应:
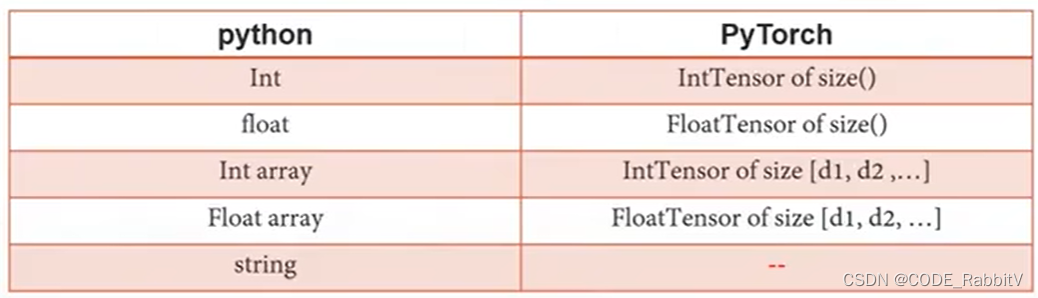
用a.type()获取数据类型,用isinstance(a, 目标类型)进行类型合法化检测>>> import torch >>> a = torch.randn(2,3) >>> a tensor([[-1.7818, -0.2472, -2.0684], [ 0.0117, 1.4698, -0.9359]]) >>> a.type() ## 获取数据类型 'torch.FloatTensor' >>> isinstance(a, torch.FloatTensor) ## 类型合法化检测 True >>> -
【什么是张量】标量与张量:用
a.dim(),a.shape或者a.size()查看 dim 为 0 是标量,否则是张量>>> import torch >>> >>> a = torch.tensor(1) >>> a tensor(1) >>> a.dim() >>> 0 ## 标量 >>> a = torch.Tensor([1]) >>> a tensor([1.]) >>> a.dim() >>> 1 ## 张量 -
【生成张量】常见方法如下:
- 常见随机方法:
torch.randn(shape),torch.rand(shape),torch.randint(min, max, shape),torch.rand_like(a),torch.normal(mean, std)… 具体示例如下 - Dim 1 / rank 1: 以 size 2 为例
>>> a = torch.randn(2) ## 随机, >>> a: tensor([1.4785, 0.6089]) >>> a = torch.Tensor(2) ## 接收维度, unintialized 不推荐 >>> a: tensor([5.4086e+26, 4.5907e-41]) >>> a = torch.Tensor([1,2]) ## 同 torch.tensor([1,2]) 接收具体数据 >>> a: tensor([1, 2]) >>> a = torch.from_numpy(np_data) ## 数据维持不变,类型一一对应 >>> a = torch.full([2],7) ## 全部填充为一样的值 >>> a: tensor([7, 7]) >>> a = torch.arange(0,10) ## arange >>> a: tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) >>> a = torch.linspace(0,10, steps=4) ## >>> a: tensor([ 0.0000, 3.3333, 6.6667, 10.0000]) >>> a = torch.logspace(0,10, steps=4) >>> a: tensor([1.0000e+00, 2.1544e+03, 4.6416e+06, 1.0000e+10]) - Dim 2 / rank 2: 以 size [2,3] 为例
…>>> a = torch.randn(2, 3) ## 随机 >>> a: tensor([[ 2.0631, -1.7011, 0.6375], [-1.2104, -1.3341, -0.8187]]) >>> a = torch.Tensor(2, 3) ## 接收维度, unintialized 不推荐 >>> a: tensor([[-0.2438, -0.9554, -0.4694], [ 0.8636, 1.6497, -0.8862]]) >>> a = torch.Tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) ## 同 torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) 接收具体数据 >>> a: tensor([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]]) >>> a = torch.from_numpy(np_data) ## 数据维持不变,类型一一对应 >>> a = torch.full([2,3],7) ## 全部填充为一样的值 >>> a: tensor([[7, 7, 7], [7, 7, 7]])
- 常见随机方法:
-
-
相关阅读:
通过汇编理解cortex-m3:第0章
Spring事务几种失效原因
Apache Doris 发展历程、技术特性及云原生时代的未来规划
每日一练--IT冷知识&C/C++--第三天
竞赛开源项目汇总
CLEARTEXT communication to XX not permitted by network security policy 报错
代码随想录算法训练营 day56|583. 两个字符串的删除操作、72. 编辑距离
苹果秋季发布会官宣,新款Mac将搭载M3芯片,来势迅猛!
解决uniapp手机真机调试时找不到手机问题
2023年十款开源测试开发工具推荐(自动化、性能、造数据、流量复制)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/CODE_RabbitV/article/details/139592278