-
OpenCV实现霍夫变换
返回:OpenCV系列文章目录(持续更新中......)
上一篇:OpenCV 如何实现边缘检测器
下一篇 :OpenCV 实现霍夫圆变换
在本教程中,您将学习如何:
- 使用 OpenCV 函数 HoughLines()和 HoughLinesP()检测图像中的线条。
- 注:由于输入法问题按Q替代
 进行角度说明。
进行角度说明。
理论
注意
下面的解释属于 Bradski 和 Kaehler 的 Learning OpenCV 一书。
Hough 线变换
- Hough 线变换是用于检测直线的变换。
- 要应用变换,首先需要边缘检测预处理。
它是如何工作的?
- 如您所知,图像空间中的一条线可以用两个变量表示。例如:
- 在笛卡尔坐标系中:参数:(m,b)
- 在极坐标系中: 参数:(r,Q)
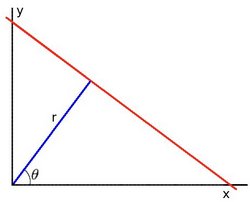
对于 Hough 变换,我们将在 Polar 系统中表示线。因此,直线方程可以写成:
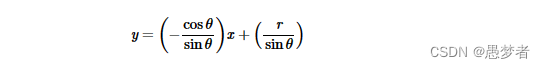
排列项:
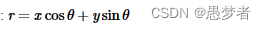
-
一般来说,对于每个点 \((x_{0}, y_{0})\),我们可以将通过该点的线族定义为:

这意味着每对 \(r_{\theta},\theta)\) 表示经过 \((x_{0}, y_{0})\) 的每条线。
- 如果对于给定的(x0,有),我们绘制穿过它的线族,我们得到一个正弦曲线。例如,对于 (x0=8)和(y0=6,我们得到以下图(在平面plane Q~r中):
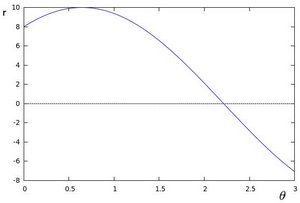
我们只考虑(r<0)和
 这样的点。
这样的点。- 我们可以对图像中的所有点执行上述相同的操作。如果两个不同点的曲线在平面 Q~r中相交,则表示两个点属于同一条直线。例如,按照上面的例子,再画两个点的图:X1=4,y1=9 和x2=12,y2=3,我们得到:
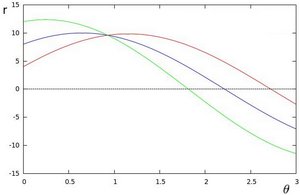
这三个图在一个点(0.925,9.6)相交,这些坐标是参数(Q,r)或(x0,y0)和(x1,y1)所在的线。
- 以上所有内容是什么意思?这意味着通常可以通过查找曲线之间的交点数来检测一条线。相交的曲线越多,意味着该相交所表示的直线具有更多的点。通常,我们可以定义检测一条线所需的最小交叉点数的阈值。
- 这就是 Hough Line Transform 的作用。它跟踪图像中每个点的曲线之间的交点。如果交点数高于某个阈值,则将其声明为具有交点参数(Q,r0)的线。
标准和概率 Hough 线变换
OpenCV 实现了两种类型的 Hough 线变换:
a. 标准 Hough 变换
- 它几乎包含我们在上一节中解释的内容。结果,它给你一个夫妻向量 (Q,r0)
- 在 OpenCV 中,它是使用函数 HoughLines()实现的
b. 概率霍夫线变换
- 更高效地实现 Hough 线变换。它给出检测到的行的极值(x0,y0,x1,y1)
- 在 OpenCV 中,它是使用函数 HoughLinesP()实现的
这个程序是做什么的?
- 加载图像
- 应用标准 Hough 线变换和概率线变换。
- 在三个窗口中显示原始图像和检测到的线条。
C++代码
们将要解释的示例代码可以从这里下载。可以在此处找到一个稍微花哨的版本(它显示了 Hough 标准和概率,带有用于更改阈值的跟踪栏)。
- #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
- using namespace cv;
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char** argv)
- {
- // Declare the output variables
- Mat dst, cdst, cdstP;
- const char* default_file = "sudoku.png";
- const char* filename = argc >=2 ? argv[1] : default_file;
- // Loads an image
- Mat src = imread( samples::findFile( filename ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
- // Check if image is loaded fine
- if(src.empty()){
- printf(" Error opening image\n");
- printf(" Program Arguments: [image_name -- default %s] \n", default_file);
- return -1;
- }
- // Edge detection
- Canny(src, dst, 50, 200, 3);
- // Copy edges to the images that will display the results in BGR
- cvtColor(dst, cdst, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
- cdstP = cdst.clone();
- // Standard Hough Line Transform
- vector
lines; // will hold the results of the detection - HoughLines(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 150, 0, 0 ); // runs the actual detection
- // Draw the lines
- for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
- {
- float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
- Point pt1, pt2;
- double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
- double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
- pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000*(-b));
- pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000*(a));
- pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000*(-b));
- pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000*(a));
- line( cdst, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, LINE_AA);
- }
- // Probabilistic Line Transform
- vector
linesP; // will hold the results of the detection - HoughLinesP(dst, linesP, 1, CV_PI/180, 50, 50, 10 ); // runs the actual detection
- // Draw the lines
- for( size_t i = 0; i < linesP.size(); i++ )
- {
- Vec4i l = linesP[i];
- line( cdstP, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0,0,255), 3, LINE_AA);
- }
- // Show results
- imshow("Source", src);
- imshow("Detected Lines (in red) - Standard Hough Line Transform", cdst);
- imshow("Detected Lines (in red) - Probabilistic Line Transform", cdstP);
- // Wait and Exit
- waitKey();
- return 0;
- }
代码片段解释
- const char* default_file = "sudoku.png";
- const char* filename = argc >=2 ? argv[1] : default_file;
- // Loads an image
- Mat src = imread( samples::findFile( filename ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
- // Check if image is loaded fine
- if(src.empty()){
- printf(" Error opening image\n");
- printf(" Program Arguments: [image_name -- default %s] \n", default_file);
- return -1;
- }
使用 Canny 检测器检测图像的边缘:
- // Edge detection
- Canny(src, dst, 50, 200, 3);
现在我们将应用 Hough 线变换。我们将解释如何使用可用于此目的的两个 OpenCV 函数。
标准 Hough 线变换:
首先,应用转换:
- // Standard Hough Line Transform
- vector
lines; // will hold the results of the detection - HoughLines(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 150, 0, 0 ); // runs the actual detection
- 使用以下参数:
- dst:边缘检测器的输出。它应该是灰度图像(尽管实际上它是二进制图像)
- lines:将存储检测到的线的参数的向量(r,Q)
- rho :参数的分辨率,单位为r像素。我们使用 1 个像素。
- theta:参数的分辨率,单位为Q弧度。我们使用 1 度 (CV_PI/180)
- threshold:要“检测*”一条线的最小交叉点数
- srn 和 stn:默认参数为零。有关详细信息,请查看 OpenCV 参考。
然后通过绘制线条来显示结果。
- // Draw the lines
- for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
- {
- float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
- Point pt1, pt2;
- double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
- double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
- pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000*(-b));
- pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000*(a));
- pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000*(-b));
- pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000*(a));
- line( cdst, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, LINE_AA);
- }
概率 Hough 线变换
首先,应用转换:
- // Probabilistic Line Transform
- vector
linesP; // will hold the results of the detection - HoughLinesP(dst, linesP, 1, CV_PI/180, 50, 50, 10 ); // runs the actual detection
- 带有参数:
- dst:边缘检测器的输出。它应该是灰度图像(尽管实际上它是二进制图像)
- lines:将存储检测到的线的参数的向量(xstart,ystart,xend,yend)
- rho :参数的分辨率,单位为r像素。我们使用 1 个像素。
- theta:参数的分辨率,单位为Q弧度。我们使用 1 度 (CV_PI/180)
- threshold:要“检测*”一条线的最小交叉点数
- minLineLength:可以形成一条线的最小点数。小于此点数的线将被忽略。
- maxLineGap:在同一条直线上要考虑的两点之间的最大间隙。
然后通过绘制线条来显示结果。
- // Draw the lines
- for( size_t i = 0; i < linesP.size(); i++ )
- {
- Vec4i l = linesP[i];
- line( cdstP, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0,0,255), 3, LINE_AA);
- }
显示原始图像和检测到的线:
- // Show results
- imshow("Source", src);
- imshow("Detected Lines (in red) - Standard Hough Line Transform", cdst);
- imshow("Detected Lines (in red) - Probabilistic Line Transform", cdstP);
等到用户退出程序
- // Wait and Exit
- waitKey();
- return 0;
结果
注意
下面的结果是使用我们在代码部分提到的稍微花哨的版本获得的。它仍然实现与上述相同的内容,只是为阈值添加了跟踪栏。使用输入图像,例如数独图像。我们通过使用标准 Hough 线变换得到以下结果:

通过使用概率 Hough 线变换:
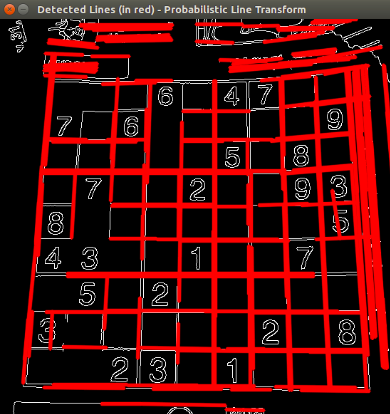
您可能会发现,在更改阈值时,检测到的行数会发生变化。解释是显而易见的:如果建立更高的阈值,则检测到的行将减少(因为您将需要更多的点来声明检测到的行)。
参考文献:
1、《Hough Line Transform》-----Ana Huamán
-
相关阅读:
深入Django项目实战与最佳实践
拉格朗日粒子扩散FLEXPART模式
【PCL】教程global_hypothesis_verification 通过验证模型假设来实现 3D 对象识别与位姿估计...
RabbitMQ实现秒杀场景示例
Postman接口自动化
小程序容器技术加持下,企业自主打造小程序生态
如何解决 Critical dependency: the request of a dependency is an expression ?
【云原生】Docker网络模式详解
Vue2组件间通讯
用户授权设置全局变量为undefined?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_78348935/article/details/138174597

