-
【浅尝C++】STL第三弹=>list常用接口使用示例/list底层结构探索/list模拟实现代码详解

🏠专栏介绍:浅尝C++专栏是用于记录C++语法基础、STL及内存剖析等。
🎯每日格言:每日努力一点点,技术变化看得见。
list介绍
- list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
- list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
- list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
- 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
- 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)
list常用接口使用示例
下面仅给出list部分常用接口及使用示例,更多关于list接口的介绍请参阅->list参考文档
构造类函数
接口声明 接口描述 list(size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) 用n个值为val的元素构造list list() 构造空的list list(const list& x) 拷贝构造函数 list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) 用[first,last)区间元素构造list 下面给出上述接口的示例代码↓↓↓
#include#include #include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
迭代器
接口声明 接口描述 begin + end 返回第一个元素的迭代器/返回最后一个元素的下一位置的迭代器 rebegin + rend 返回最后一个元素的下一位置/返回第一个元素的位置 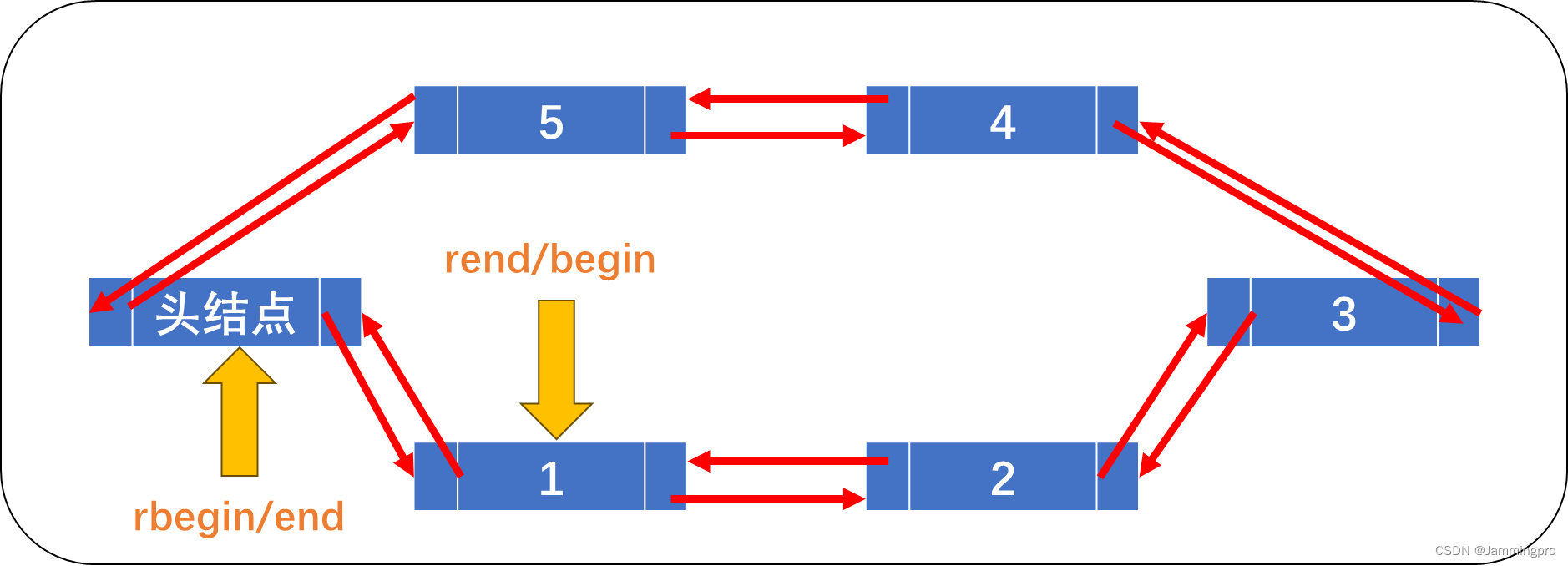
list底层是带头双向链表,begin指向第一个有效元素(头结点的后继节点),end指向头结点,迭代器begin每次++,每次向后移动,当与end重合时,则正向迭代结束。rbegin指向头结点,end指向第一个有效元素(头结点的后继节点),当要对rbegin解引用时,rbegin底层会执行*(rbegin->prev),返回rbegin指向节点的前驱节点的数据。即使rbegin指向头结点,但对它解引用获得的是头节后前驱节点的数据;当rbegin与end重合时则迭代结束。
下面来看一下list迭代器的使用示例代码↓↓↓
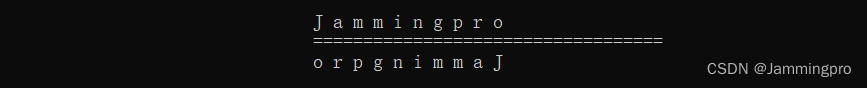
#include#include #include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
对于const类型的list容器,需要配套使用const_iterator/const_reverse_iterator来进行正反向迭代。★ps:begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动;rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动
属性与元素获取
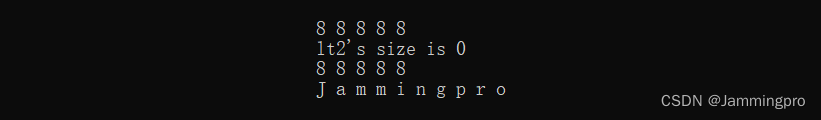
接口声明 接口声明 empty 检查list是否为空 size 返回list中有效节点的个数 front 返回list的第一个节点中的值的引用 back 返回list的最后一个节点中的值的引用 上面接口相较简单,这里这届给出示例代码↓↓↓
#include#include #include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
增删改操作
接口声明 接口说明 push_front 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 pop_front 删除list中第一个元素 push_back 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 pop_back 删除list中最后一个元素 insert 在pos位置中插入值为val的元素 erase 删除pos位置的元素 swap 交换两个list中的元素 clear 情况list中的有效元素 上面接口的使用示例代码如下↓↓↓
#include#include #include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
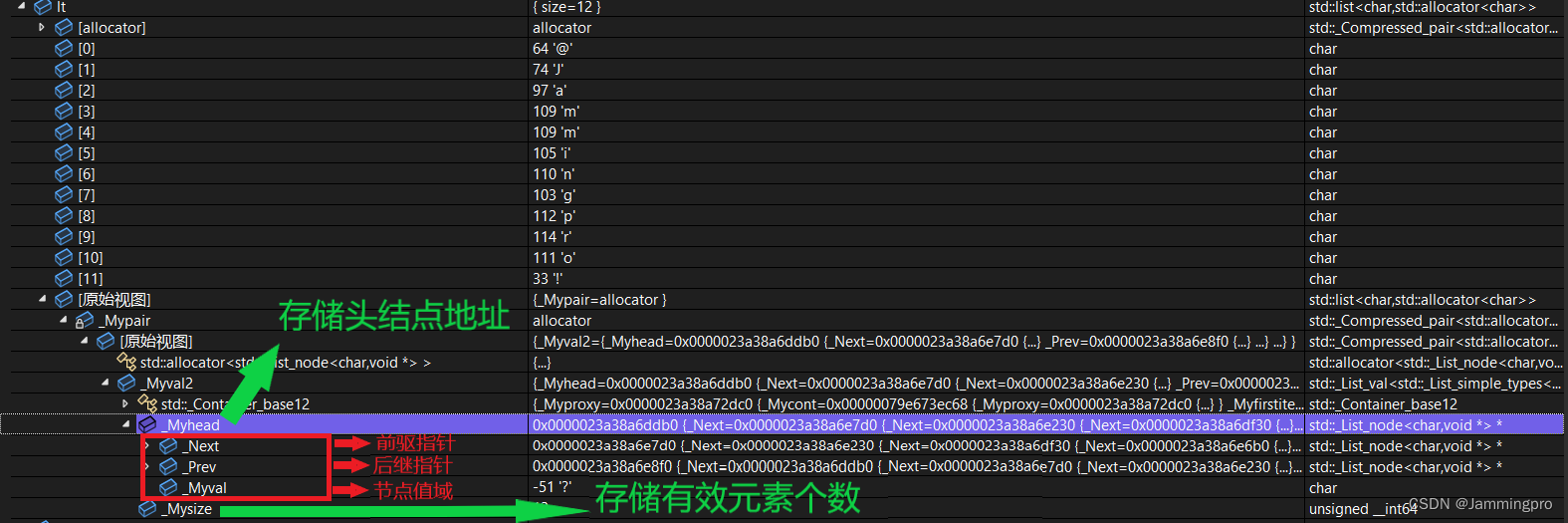
list底层结构探索
由监视窗口可以看到,list容器中包含指向头结点地址的指针及容器内有效元素的个数。每个节点包含前驱指针、后继指针及值域,故list底层是带头双向循环链表。
list模拟实现
在模拟list之前,由于list的结构是双向链表,因而需要定义节点类型。↓↓↓
template<class T> struct node { node* _prev = nullptr; node* _next = nullptr; T _data; node(const T& x = T()) :_data(x) {} };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
正向迭代器实现
由于链表的各个节点无法实现++或者–操作,因此,我们需要将迭代器封装为一个类(结构体)。在该类(接口体)中重载迭代器的各种操作。其中Ptr就是T*,Ref就是T&。
若定义
list,则*it是为了获取节点中存的数据,因此::iterator it operator*中中需要返回节点的数值,即_node->_data。对于it的其他运算符重载如下方代码所示↓↓↓template<class T, class Ptr, class Ref> struct __list_iterator { typedef __list_iterator<T, Ptr, Ref> Self; node<T>* _node; __list_iterator(node<T>* node) :_node(node) {} Ref operator*() { return _node->_data; } Self& operator++() { _node = _node->_next; return *this; } Self operator++(int) { Self tmp(_node); _node = _node->_next; return tmp; } Self& operator--() { _node = _node->_prev; return this; } Self operator--(int) { Self tmp(_node); _node = _node->_prev; return tmp; } bool operator==(const Self& lt) { return _node == lt._node; } bool operator!=(const Self& lt) { return _node != lt._node; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
增删操作
void push_back(const T& val) { Node* tail = _head->_prev; Node* newnode = new Node(val); tail->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = tail; newnode->_next = _head; _head->_prev = newnode; _size++; } void pop_back() { assert(!empty()); Node* tail = _head->_prev; Node* tailPrev = tail->_prev; tailPrev->_next = _head; _head->_prev = tailPrev; delete tail; _size--; } void push_front(const T& val) { Node* first = _head->_next; Node* newnode = new Node(val); _head->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = _head; newnode->_next = first; first->_prev = newnode; _size++; } void pop_front() { assert(!empty()); Node* first = _head->_next; Node* second = first->_next; _head->_next = second; second->_prev = _head; delete first; _size--; } void insert(iterator pos, const T& val) { Node* cur = pos._node; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* newnode = new Node(val); prev->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = prev; newnode->_next = cur; cur->_prev = newnode; _size++; } void erase(iterator it) { Node* cur = it._node; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* next = cur->_next; prev->_next = next; next->_prev = prev; delete cur; _size--; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
属性获取操作
bool empty() const { return _size == 0; } size_t size() const { return _size; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
构造类函数
list() :_head(new Node) { _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; } list(const list<T>& lt) { Node* prev = _head; Node* cur = _head; Node* p = lt._head->_next; while (p != lt._head) { cur = new Node(p->_data); prev->_next = cur; cur->_prev = prev; p = p->_next; } _head->_prev = cur; } template<class InputIterator> list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) { _head = new Node; _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; while (first != last) { push_back(*first); first++; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
整体代码汇总
由于我们自己模拟实现的list与库中重名,因此需要将其定义在命名空间内。
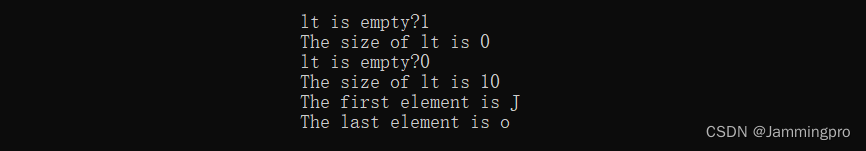
#include#include using namespace std; namespace jammingpro { template<class T> struct node { node* _prev = nullptr; node* _next = nullptr; T _data; node(const T& x = T()) :_data(x) {} }; template<class T, class Ptr, class Ref> struct __list_iterator { typedef __list_iterator<T, Ptr, Ref> Self; node<T>* _node; __list_iterator(node<T>* node) :_node(node) {} Ref operator*() { return _node->_data; } Self* operator->() { return _node; } Self& operator++() { _node = _node->_next; return *this; } Self operator++(int) { Self tmp(_node); _node = _node->_next; return tmp; } Self& operator--() { _node = _node->_prev; return this; } Self operator--(int) { Self tmp(_node); _node = _node->_prev; return tmp; } bool operator==(const Self& lt) { return _node == lt._node; } bool operator!=(const Self& lt) { return _node != lt._node; } }; template<class T> class list { typedef node<T> Node; public: //=====构造类函数===== typedef __list_iterator<T, T*, T&> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<const T, const T*, const T&> const_iterator; iterator begin() { return iterator(_head->_next); } iterator end() { return iterator(_head); } const_iterator begin() const { return const_iterator(_head->_next); } const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(_head); } list() :_head(new Node) { _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; } list(const list<T>& lt) { Node* prev = _head; Node* cur = _head; Node* p = lt._head->_next; while (p != lt._head) { cur = new Node(p->_data); prev->_next = cur; cur->_prev = prev; p = p->_next; } _head->_prev = cur; } template<class InputIterator> list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) { _head = new Node; _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; while (first != last) { push_back(*first); first++; } } //=====增删操作===== void push_back(const T& val) { Node* tail = _head->_prev; Node* newnode = new Node(val); tail->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = tail; newnode->_next = _head; _head->_prev = newnode; _size++; } void pop_back() { assert(!empty()); Node* tail = _head->_prev; Node* tailPrev = tail->_prev; tailPrev->_next = _head; _head->_prev = tailPrev; delete tail; _size--; } void push_front(const T& val) { Node* first = _head->_next; Node* newnode = new Node(val); _head->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = _head; newnode->_next = first; first->_prev = newnode; _size++; } void pop_front() { assert(!empty()); Node* first = _head->_next; Node* second = first->_next; _head->_next = second; second->_prev = _head; delete first; _size--; } void insert(iterator pos, const T& val) { Node* cur = pos._node; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* newnode = new Node(val); prev->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = prev; newnode->_next = cur; cur->_prev = newnode; _size++; } void erase(iterator it) { Node* cur = it._node; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* next = cur->_next; prev->_next = next; next->_prev = prev; delete cur; _size--; } //=====属性获取类函数===== bool empty() const { return _size == 0; } size_t size() const { return _size; } private: Node* _head; size_t _size = 0; }; void test() { list<int> lt; lt.push_back(1); lt.push_back(2); lt.push_back(3); lt.push_back(4); lt.push_back(5); lt.pop_back(); lt.pop_back(); lt.insert(lt.begin(), 888); lt.erase(lt.begin()); lt.push_front(666); lt.pop_front(); list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin(); while (it != lt.end()) { cout << *it << " "; ++it; } string s = "jammingpro"; list<char>lt2(s.begin(), s.end()); for (char ch : lt2) { cout << ch << endl; } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
list与vector比较
vector list 底层结构 动态顺序表,一段连续空间 带头双向循环链表 随机访问 支持随机访问,访问某个元素效率为O(1) 不支持随机访问,访问某个元素效率为O(N) 插入和删除 任意位置插入与删除效率低,需要移动数据,时间复杂度为O(N);同时,插入元素时可能需要扩容(开辟空间并拷贝旧数据,释放旧空间),导致效率较低 任意位置插入与删除效率高,无需移动数据,时间复杂度为O(N) 空间利用率 底层为连续空间,不容易造成内存碎片,空间利用率高,缓存利用率高 底层为动态开辟节点,小节点容易造成内存碎片,空间利用率低,缓存利用率低 迭代器 原生指针 对原生指针进行封装 迭代器失效 在插入元素是,要给迭代器重新赋值;因为插入元素可能导致扩容,导致迭代器指向旧空间(迭代器失效);删除数据时,也需要给迭代器重新赋值(VS下迭代器失效,g++下不失效) 插入元素不会导致迭代器失效,删除元素会导致迭代器失效 使用场景 需要高效存储,支持随机访问,不关心插入删除效率 大量插入和删除操作,不关心随机访问效率 🎈欢迎进入浅尝C++专栏,查看更多文章。
如果上述内容有任何问题,欢迎在下方留言区指正b( ̄▽ ̄)d -
相关阅读:
vue自定义组件实现v-model双向数据绑定
3. 工业大数据的创新价值
ASP.NET Core框架探索之主机搭建与运行
《LeetCode力扣练习》代码随想录——链表(反转链表---Java)
电子电气架构设计需要考虑哪些方面?
Python线性代数傅里叶分析和动态系统模拟分析之一
【Flink】FlinkSQL读取hive数据(批量)
斯坦福NLP课程 | 第12讲 - NLP子词模型
【Django-DRF】多年md笔记第5篇:Django-DRF的Request、Response和视图详解
Python修改证件照底色,get新技能
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_66926829/article/details/137282432
