-
Mysql的基本命令
1 服务相关命令
命令 描述 systemctl status mysql 查看MySQL服务的状态 systemctl stop mysql 停止MySQL服务 systemctl start mysql 启动MySQL服务 systemctl restart mysql 重启MySQL服务 ps -ef | grep mysql 查看mysql的进程 mysql -uroot -hlocalhost -p123456 登录MySQL help 显示MySQL的帮助信息 quite 退出当前数据库的连接 2 系统相关命令
命令 描述 show status; 查看MySQL的运行状态 show variables; 查看MySQL的所有系统变量 show variables like “warning_count”; 查看MySQL的某个系统变量 show processlist; 查看客户端的连接线程 show engines; 显示MySQL支持的引擎 show grants; 显示当前连接的权限 show errors 显示MySQL的错误信息 show warning 显示MySQL的警告信息 3 数据库相关的命令
命令 描述 show databases; 显示所有的数据库 use db_name 进入数据库中 create database test; 创建数据库,存在相同的数据库报错 create database if not exists test; 如果数据库不存在创建数据库,存在不操作 drop database test; 删除数据库,不存在则报错 drop database if exists test; 存在则删除数据库 show variable like “character_set”; 查看当前的编码格式 show variables like “collation%”; 查看当前的排序规则 1 显示所有的数据库
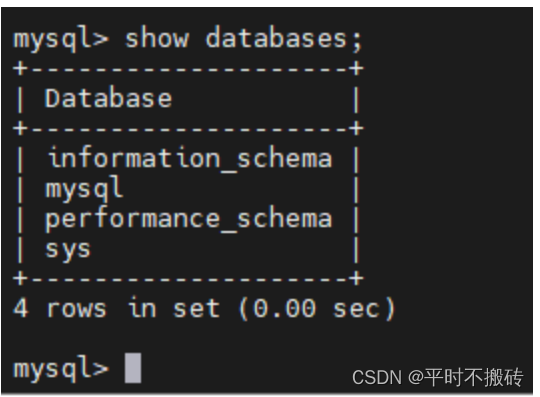
2 使用数据库
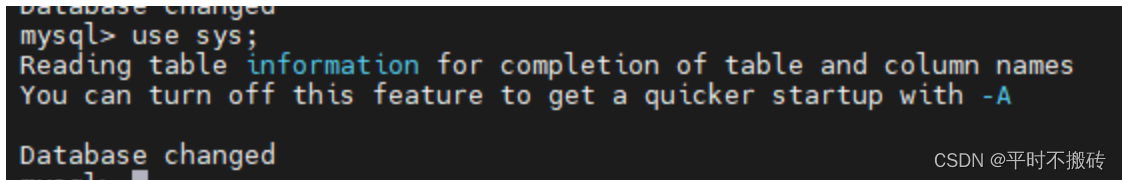
3 创建数据库# 创建数据库,编码格式使用utf8mb4默认排序utf8mb4_unicode_ci create database test character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_unicode_ci- 1
- 2

数据库存在报错

# 存在不会报错,不存在创建 create database if not exists test;- 1
- 2

4 删除数据库# 删除数据库,不存在则报错 drop database test; # 删除数据库不存在不会报错,存在删除 drop database if exists test;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
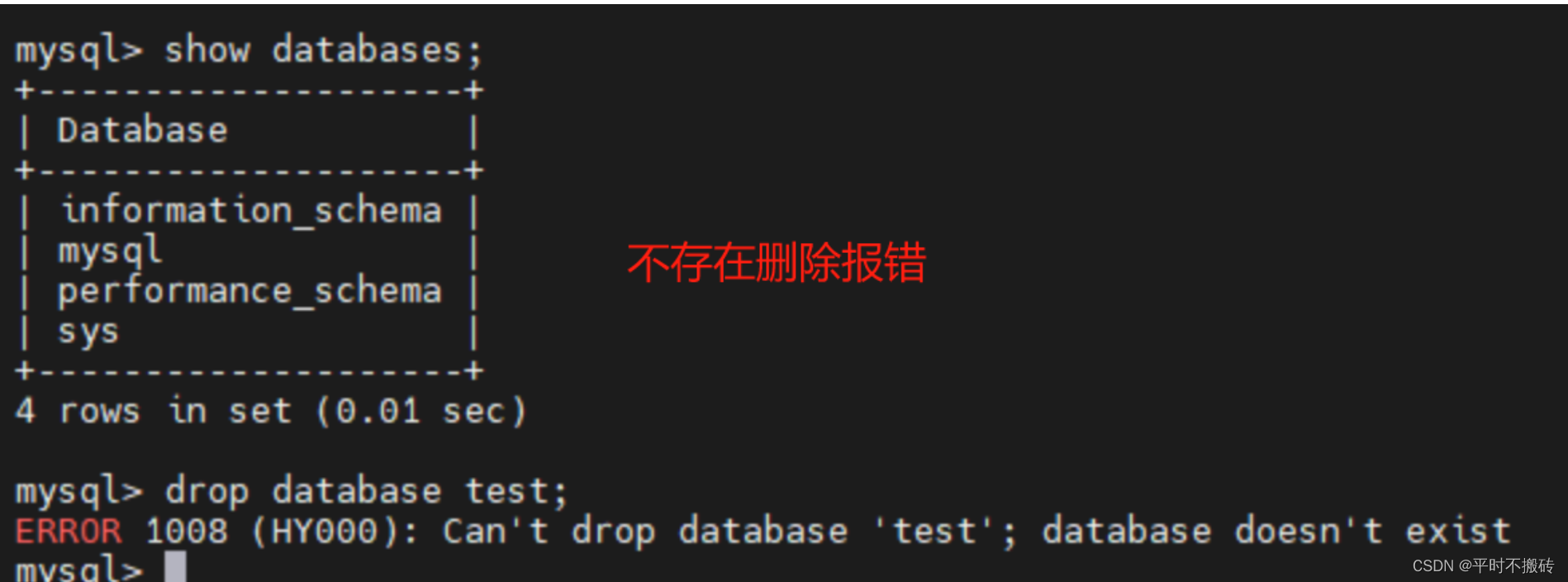

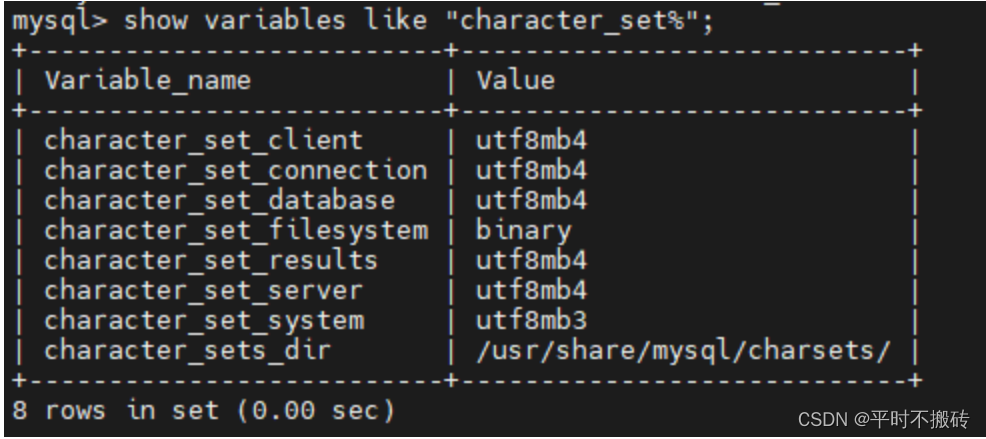
5 查看当前的编码格式
show variables like "character_set%"- 1
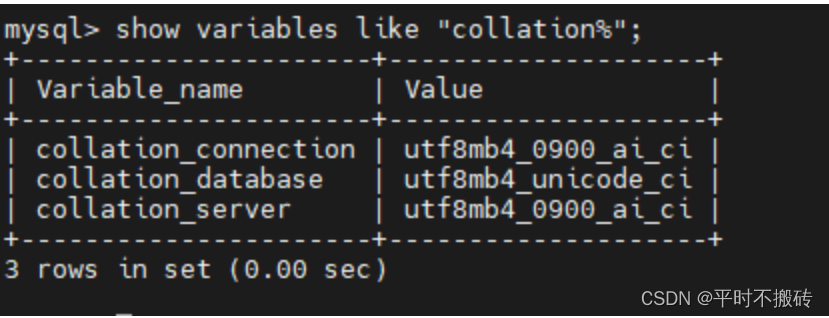
6 查看当前的排序规则show variables like "collation%"- 1
4 表相关的命令
命令 描述 show tables; 查看该数据库中所有的表 desc sys_config; 查看数据表的结构 show columns from sys_config; 查看数据表的结构 explain sys_config; 查看数据表的结构 create table_name (column1 datatype); 创建表 alter table table_name column; 修改表的字段 rename table table_name to new_table_name; 修改表名 drop table table_name; 删除表 truncate table table_name; 清空表的数据 show create table table_name; 显示创建表的语句 1 显示所有的表
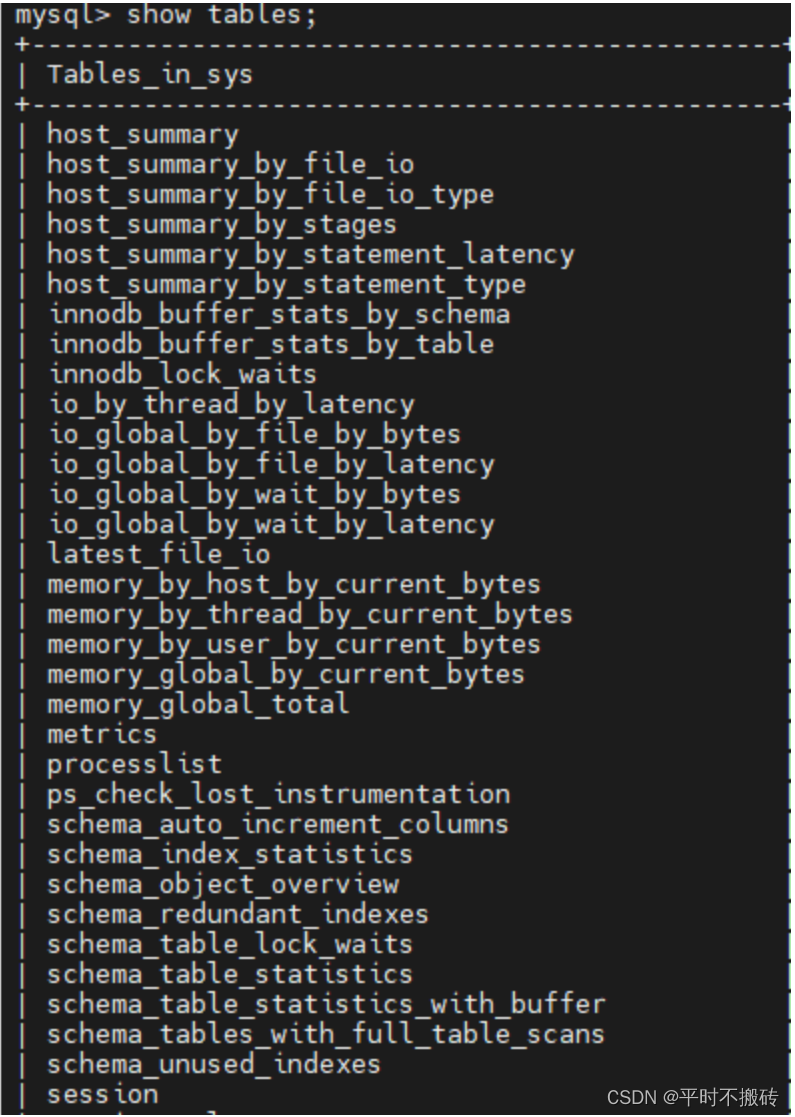
show tables;- 1
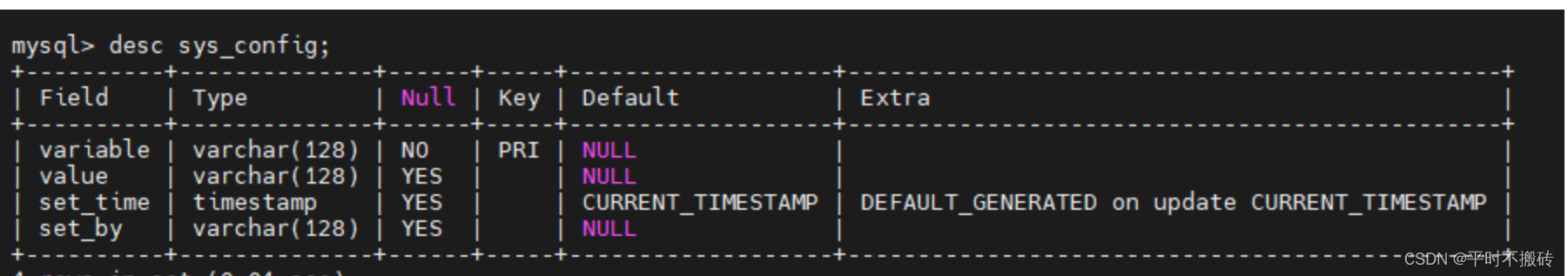
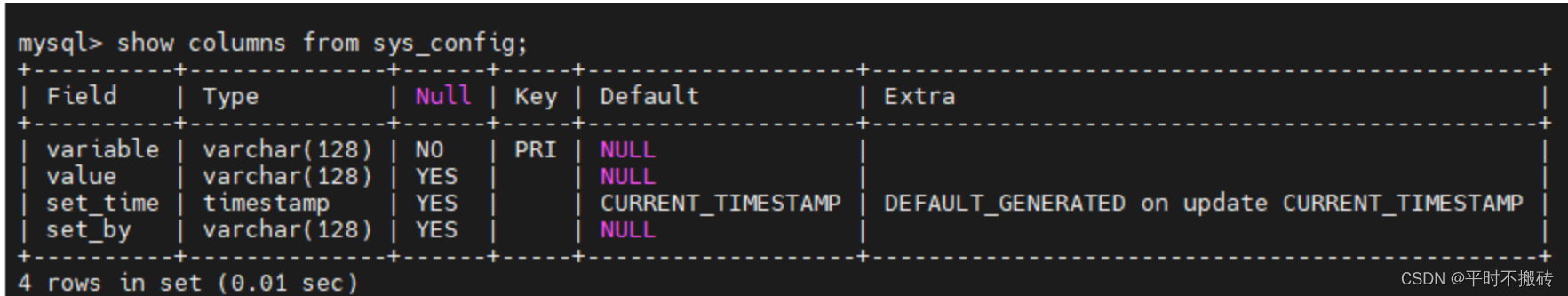
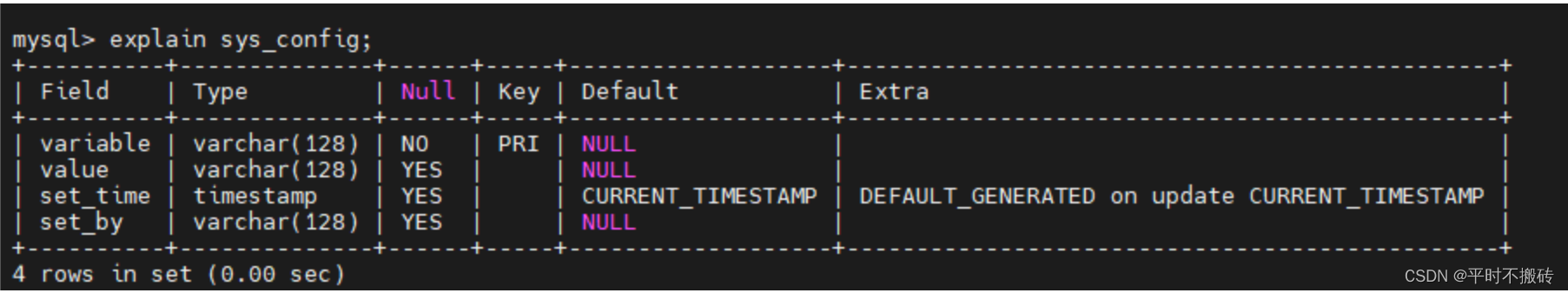
2 查看表结构desc sys_config; show columus from sys_config; explain sys_config;- 1
- 2
- 3
3 创建表# 示例 create table [if not exists] table_name ( column1 datatype, column2 datatype, ... ) engine=InnoDB default charset=utf-8;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
字段选项(可以不写,不选使用默认值):
NULL:表示该字段可以为空。NOT NULL:表示改字段不允许为空。DEFAULT 默认值:插入数据时若未对该字段赋值,则使用这个默认值。AUTO_INCREMENT:是否将该字段声明为一个自增列。PRIMARY KEY:将当前字段声明为表的主键。UNIQUE KEY:为当前字段设置唯一约束,表示不允许重复。COMMENT 字段描述:为当前字段添加备注信息,类似于代码中的注释。
表选项(可以不写,不选使用默认值):
ENGINE = 存储引擎名称:指定表的存储引擎,如InnoDB、MyISAM等。CHARACTER SET = 编码格式:指定表的编码格式,未指定使用库的编码格式。COLLATE = 排序规则:指定表的排序规则,未指定则使用库的排序规则。AUTO_INCREMENT = n:设置自增列的步长,默认为1。COMMENT 表描述:表的注释信息,可以在这里添加一张表的备注。
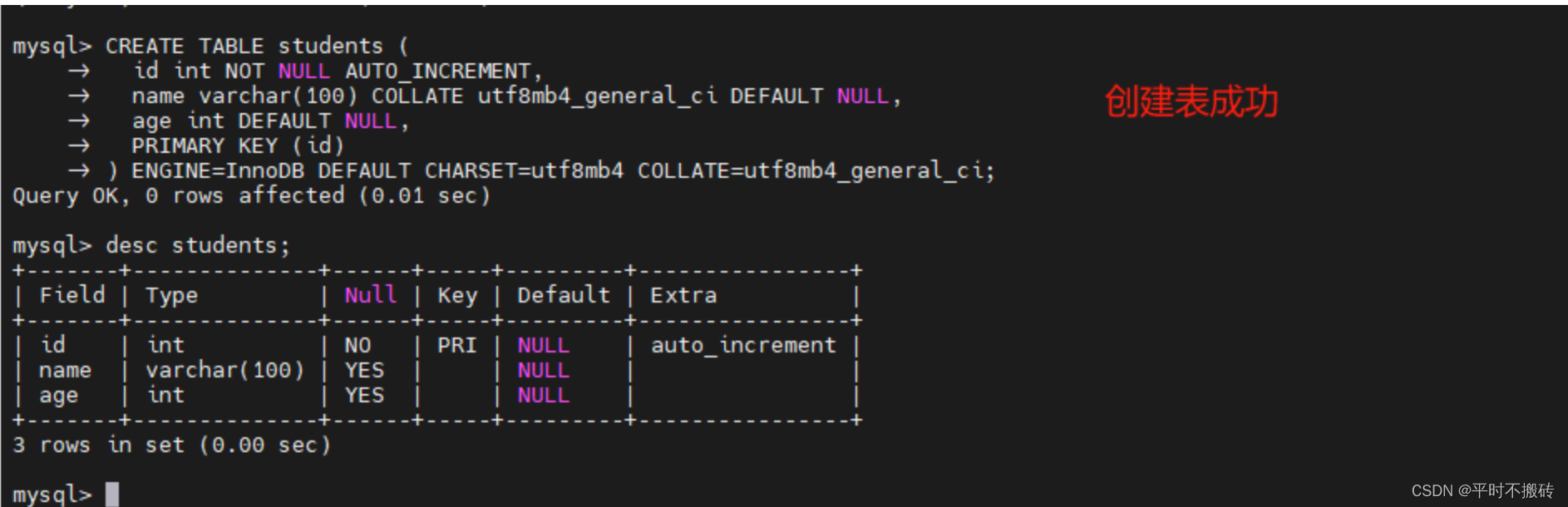
# 案例1 CREATE TABLE students ( id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, age int DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
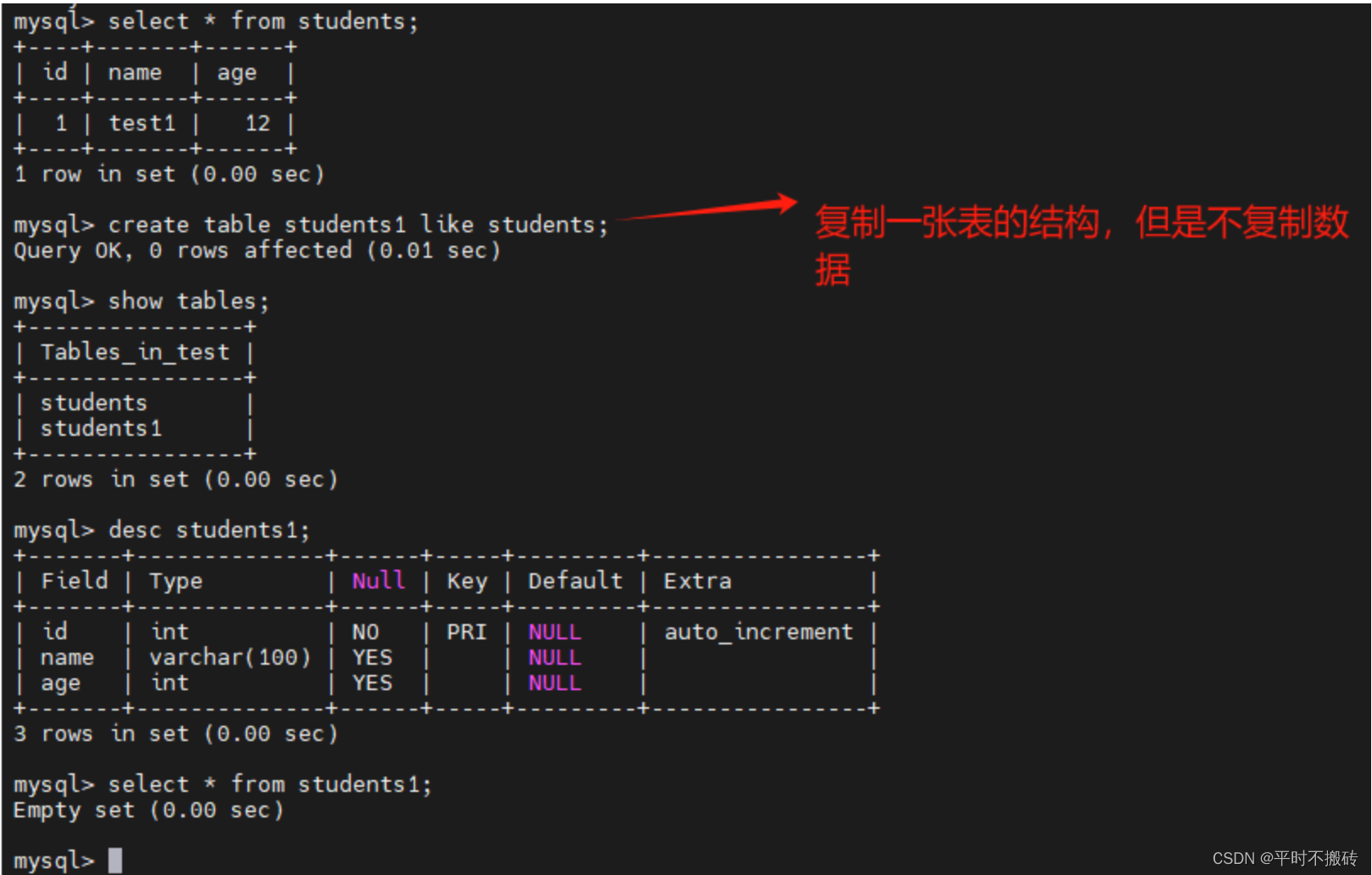
# 案例2, 复制表的结构,但是不复制数据 create table students1 like students;- 1
- 2
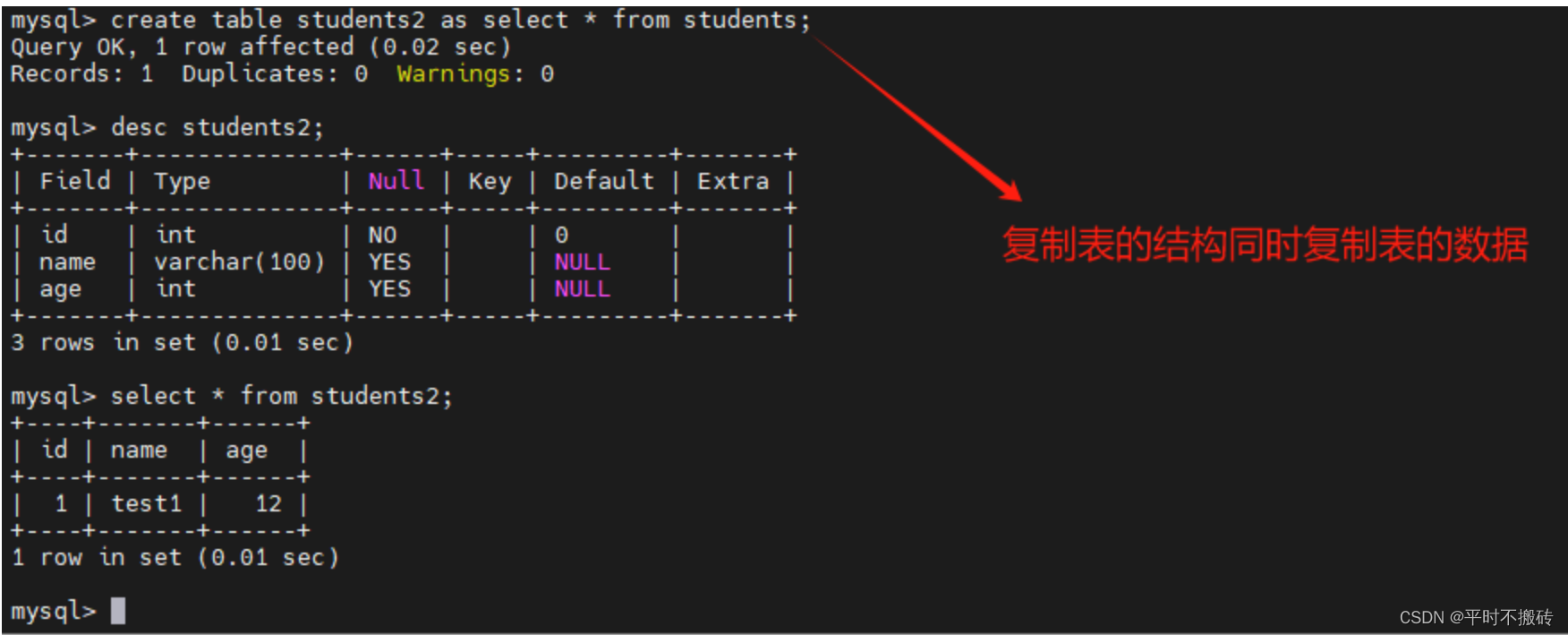
# 案例3, 复制表的结构同时复制表的数据 create table students2 as select * from students;- 1
- 2
4 修改表的字段# 示例1, 添加字段名称 # 创建表 create table test(id int, name varchar(100), age int); # 添加字段 alter table test add alias varchar(100); # 删除表 drop table test;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

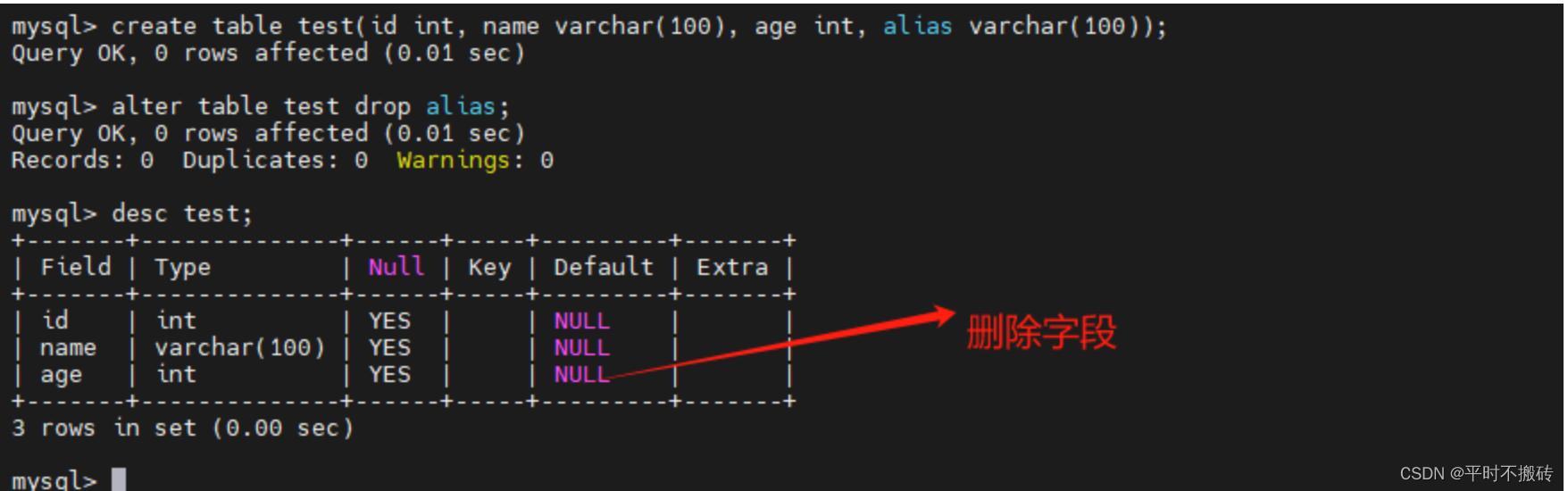
# 示例2, 删除字段 # 创建表 create table test(id int, name varchar(100), age int, alias varchar(100)); # 删除字段 alter table test drop alias; # 删除表 drop table test;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
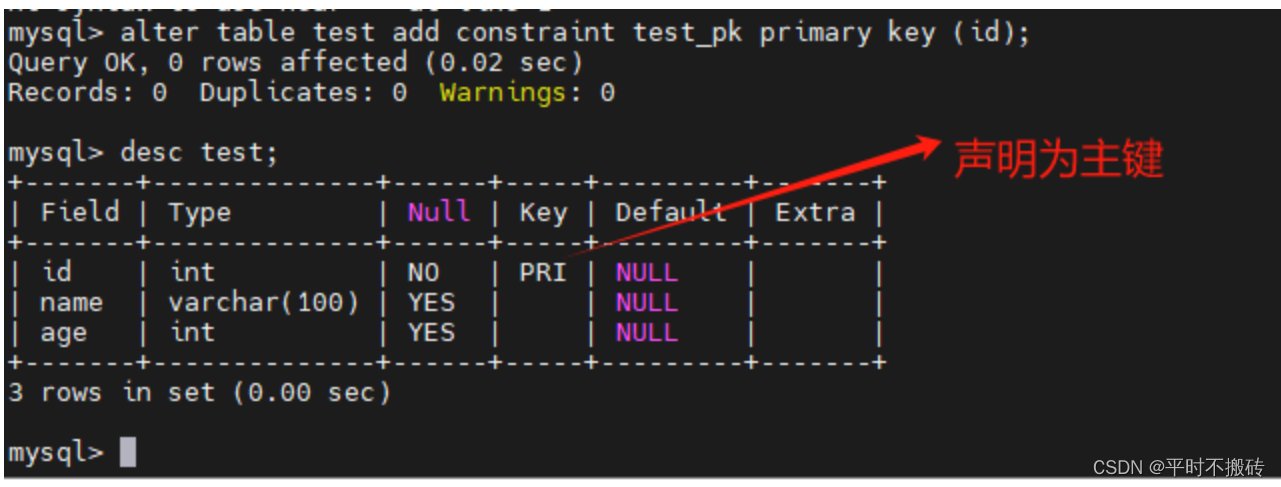
# 示例3, 添加主键 # 创建表 create table test(id int, name varchar(100), age int); # 声明为主键 alter table test add constraint test_pk primary key (id); # 删除表 drop table test- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
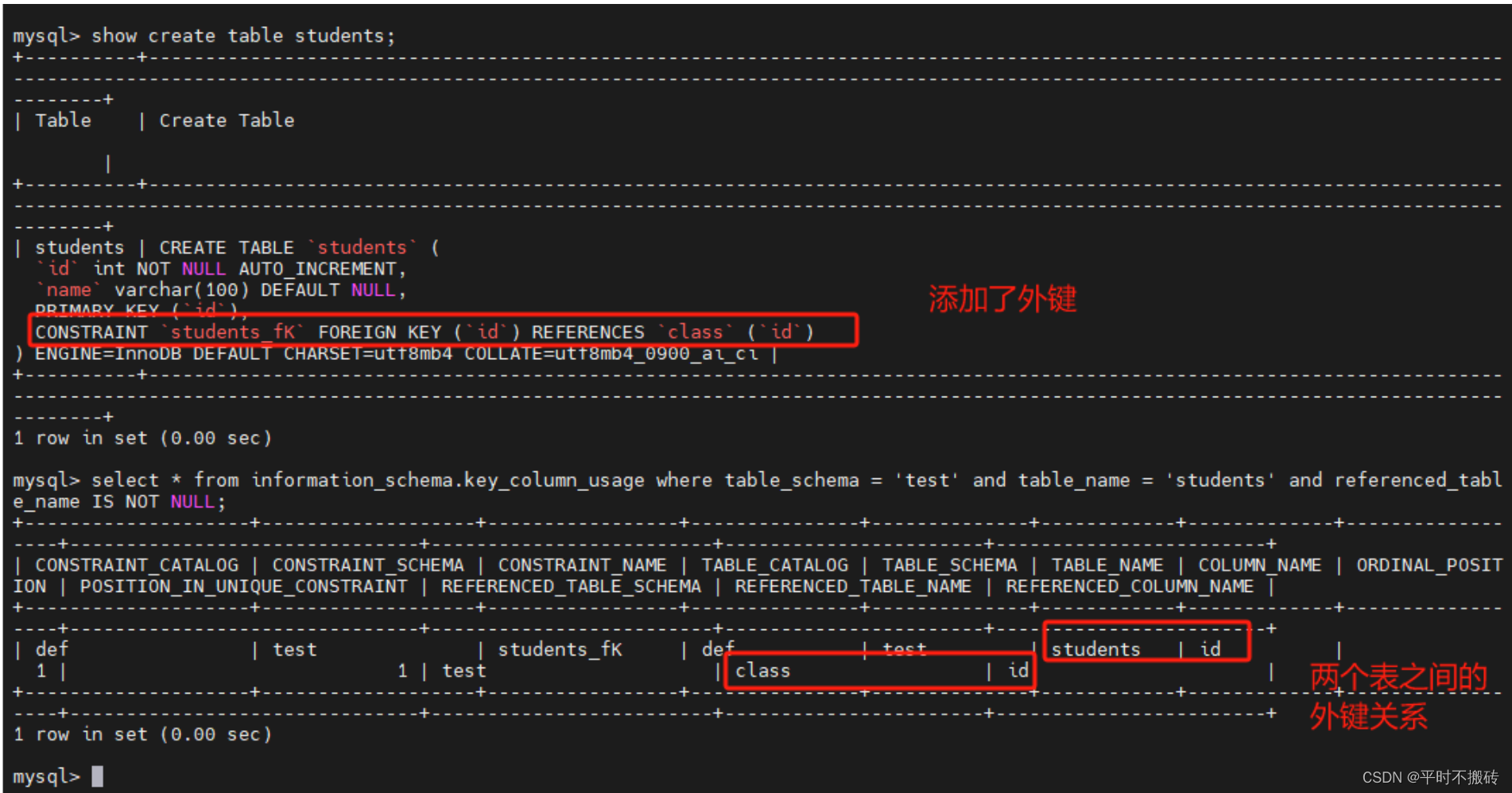
# 示例4, 添加为外键 # 创建表1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 创建表2 create table class(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key(id)); # 添加外键 alter table students add constraint students_fK foreign key (id) references class(id); # 查看表的创建语句 show create table students; # 查看表的外键关系 select * from information_schema.key_column_usage where table_schema = 'test' and table_name = 'students' and referenced_table_name IS NOT NULL; # 删除表 drop table students; drop table class;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
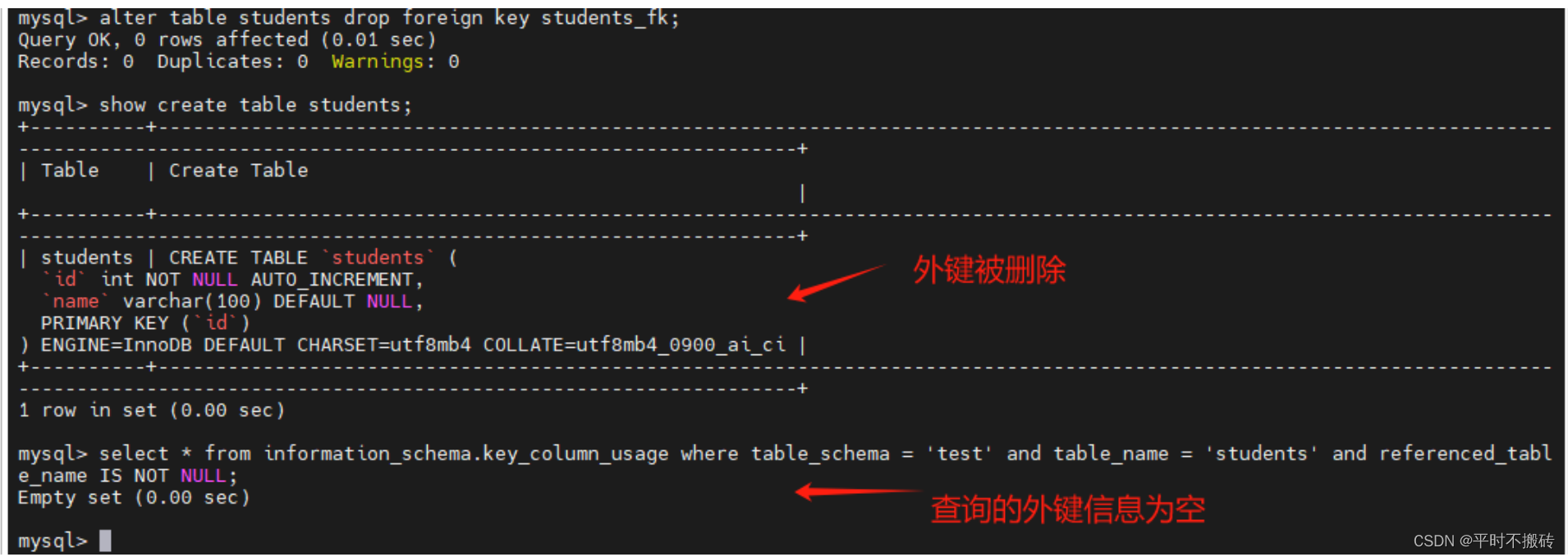
# 示例5, 删除外键 # 创建表2 create table class(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key(id)); # 创建表1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id), constraint students_fk foreign key(id) references class(id)); # 删除外键 ALTER TABLE test.students DROP FOREIGN KEY students_FK; # 查看表的创建语句 show create table students; # 查看表的外键关系 select * from information_schema.key_column_usage where table_schema = 'test' and table_name = 'students' and referenced_table_name IS NOT NULL; # 删除表 drop table students; drop table class;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
# 示例6, 添加唯一索引 # 创建表1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 添加唯一索引 alter table students add constraint students_un unique key(name); # 查看表的创建语句 show create table students; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
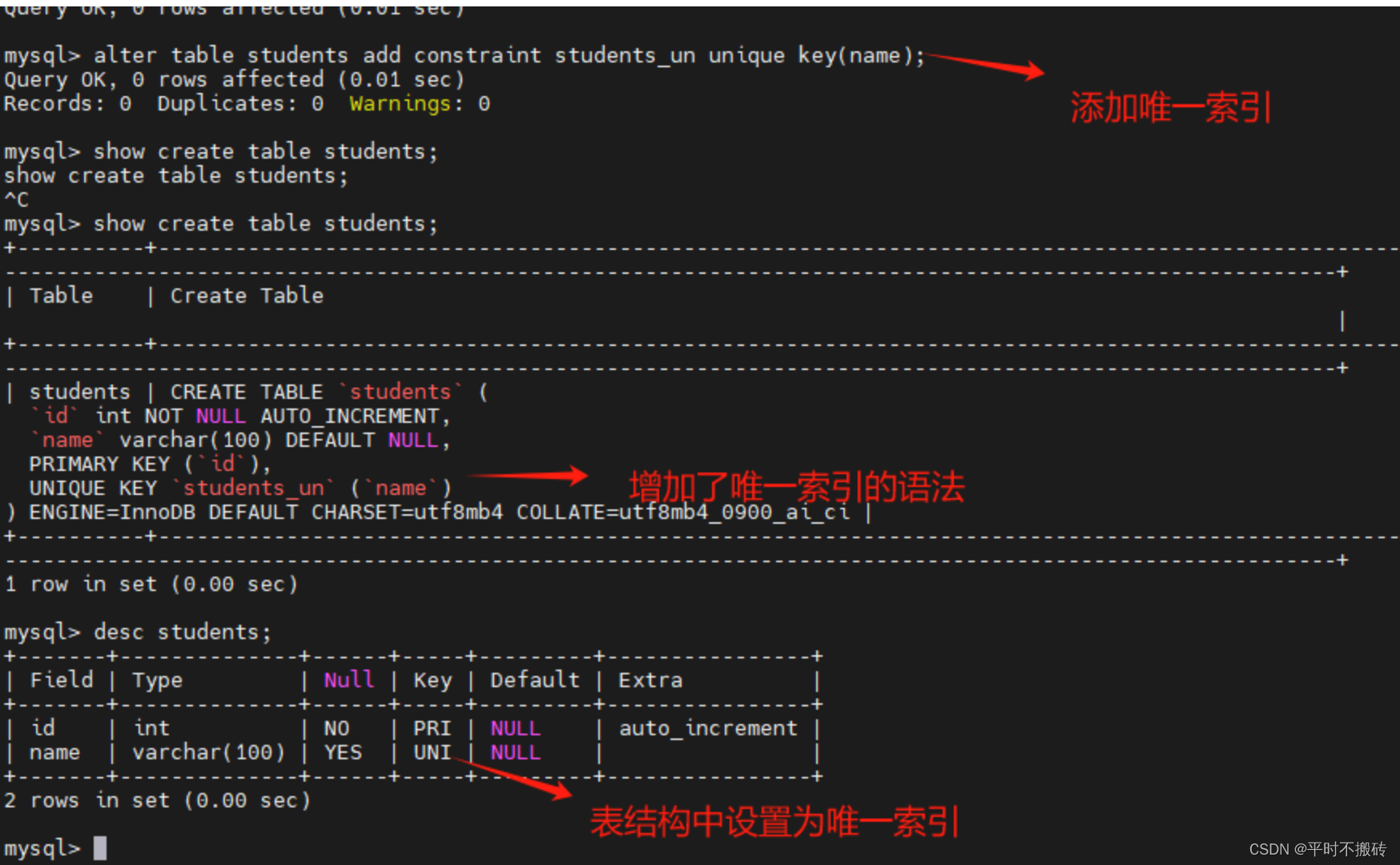
# 示例7, 删除唯一索引 # 创建表1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id), unique key students_un (name)); # 删除唯一索引 alter table students drop key students_un; # 查看表的创建语句 show create table students; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
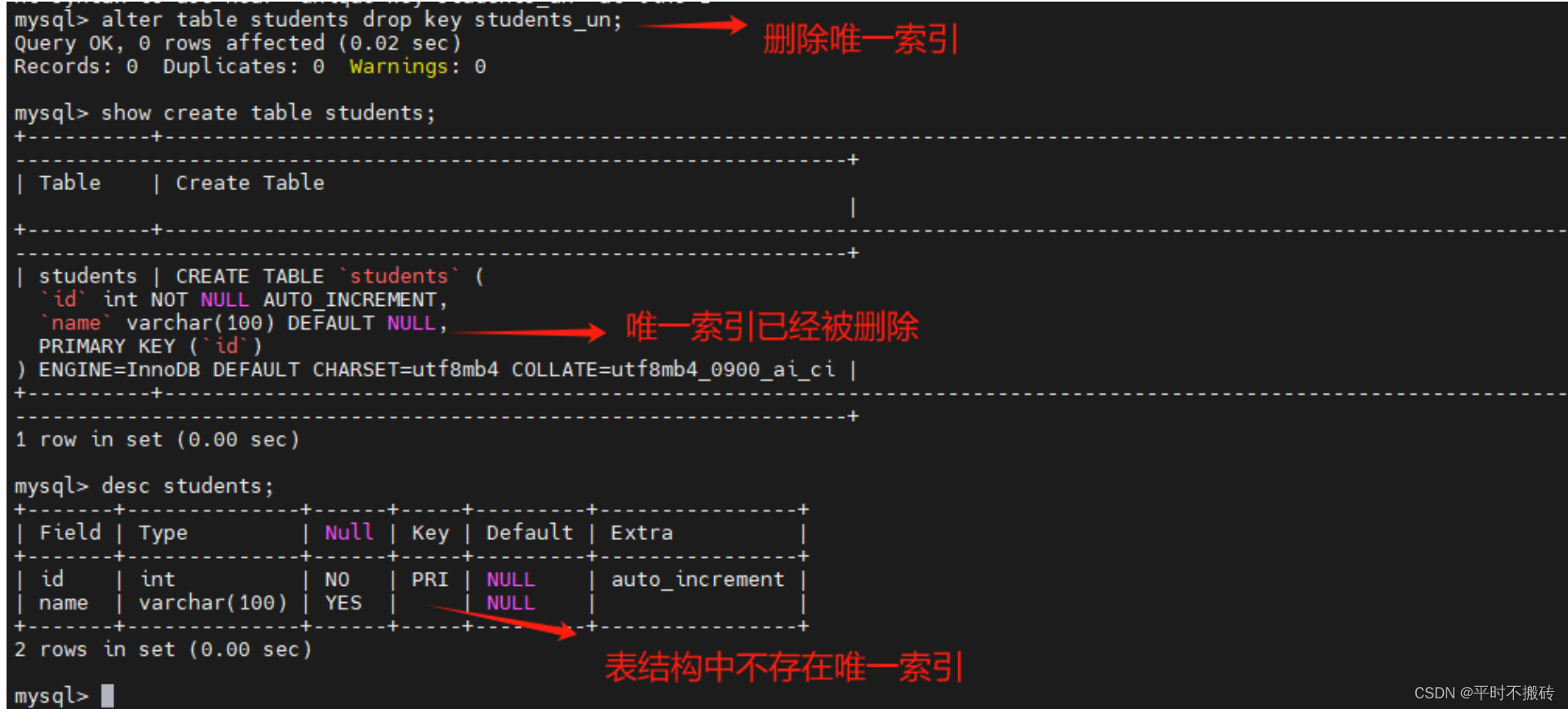
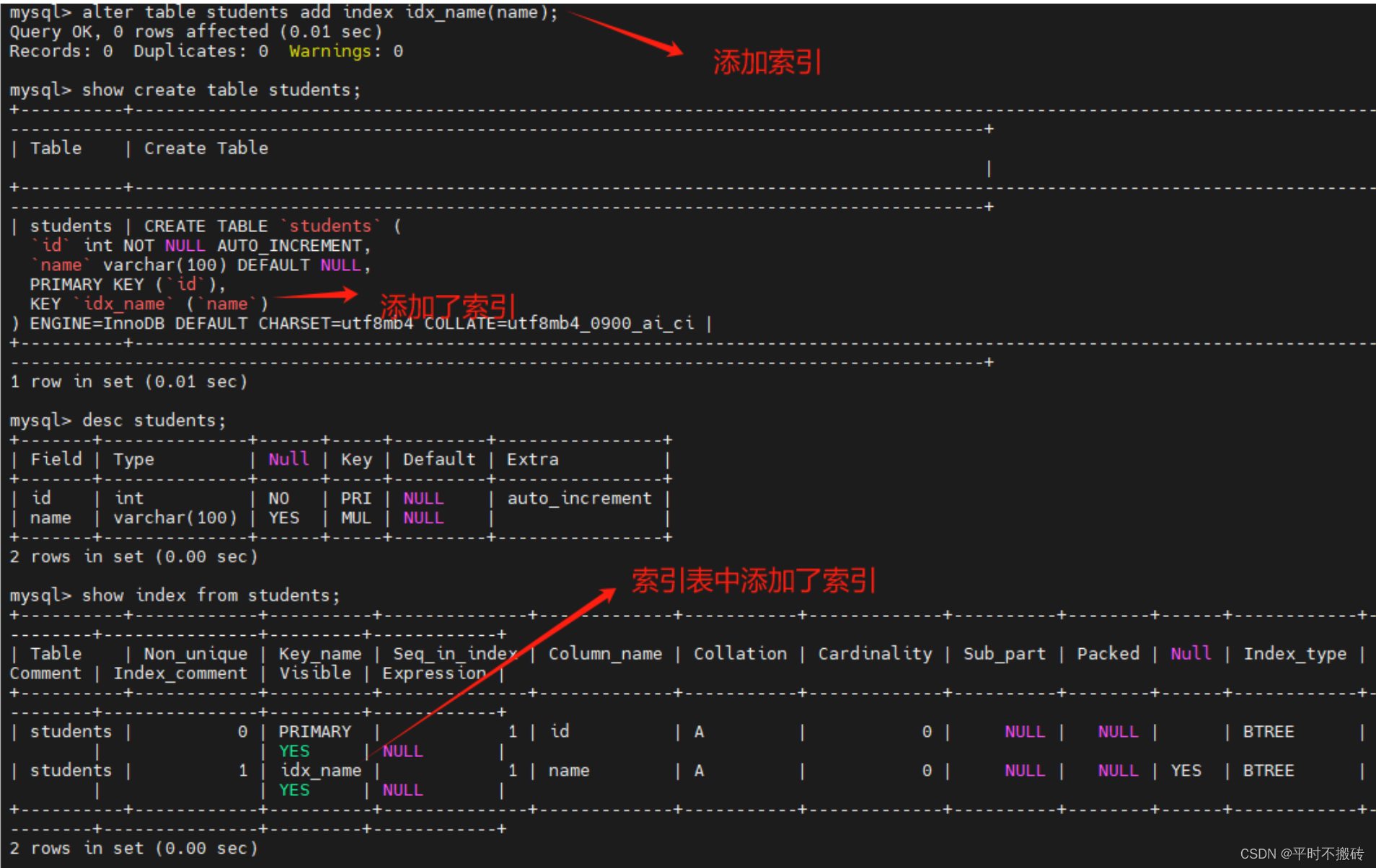
# 示例7, 添加索引 # 创建表1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 添加索引索引 alter table students add index idx_name(name); # 查看表的创建语句 show create table students; # 查看索引 show index from students; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
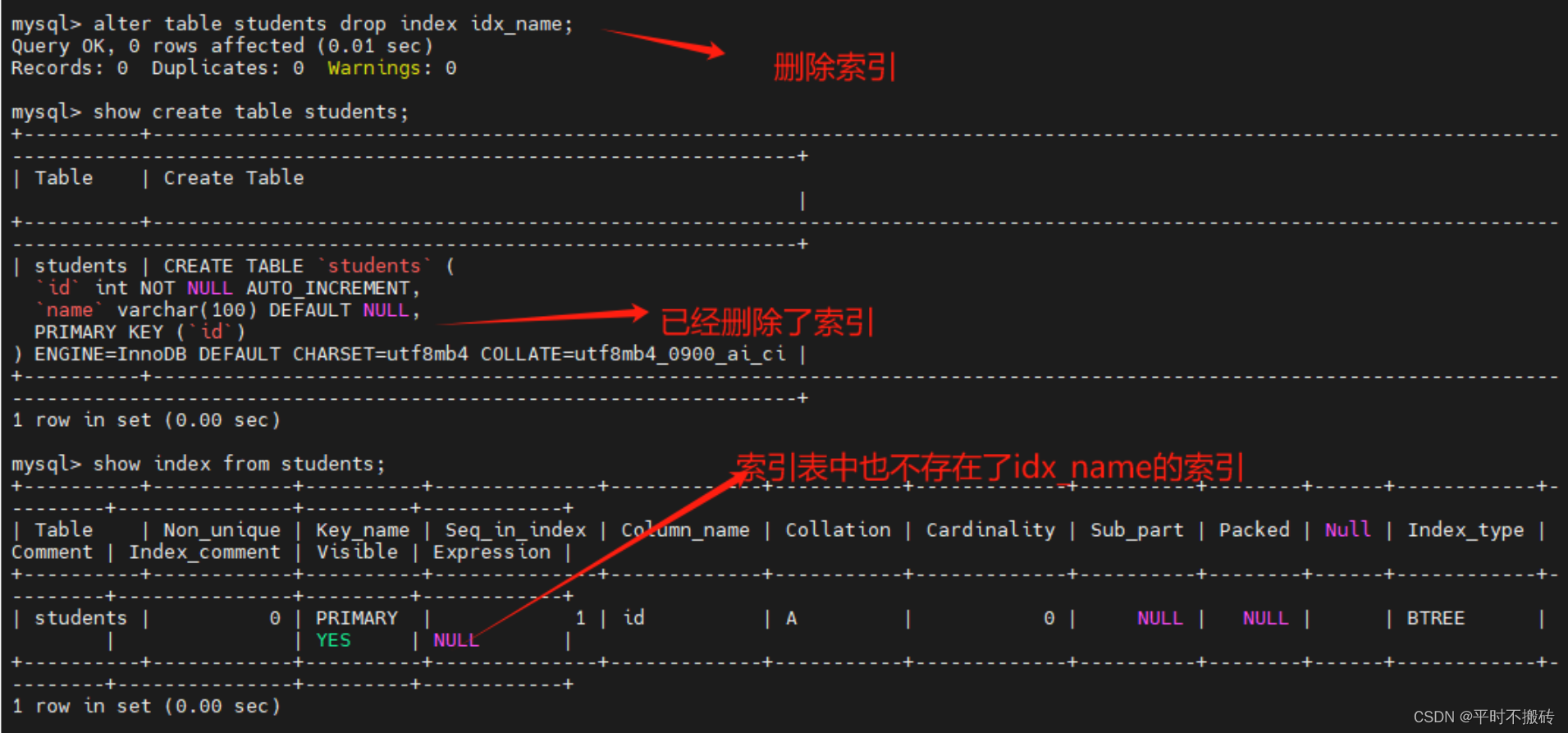
# 示例8, 删除索引 # 创建表1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id), key idx_name(name)); # 删除索引索引 alter table students drop index idx_name; # 查看表的创建语句 show create table students; # 查看索引 show index from students; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
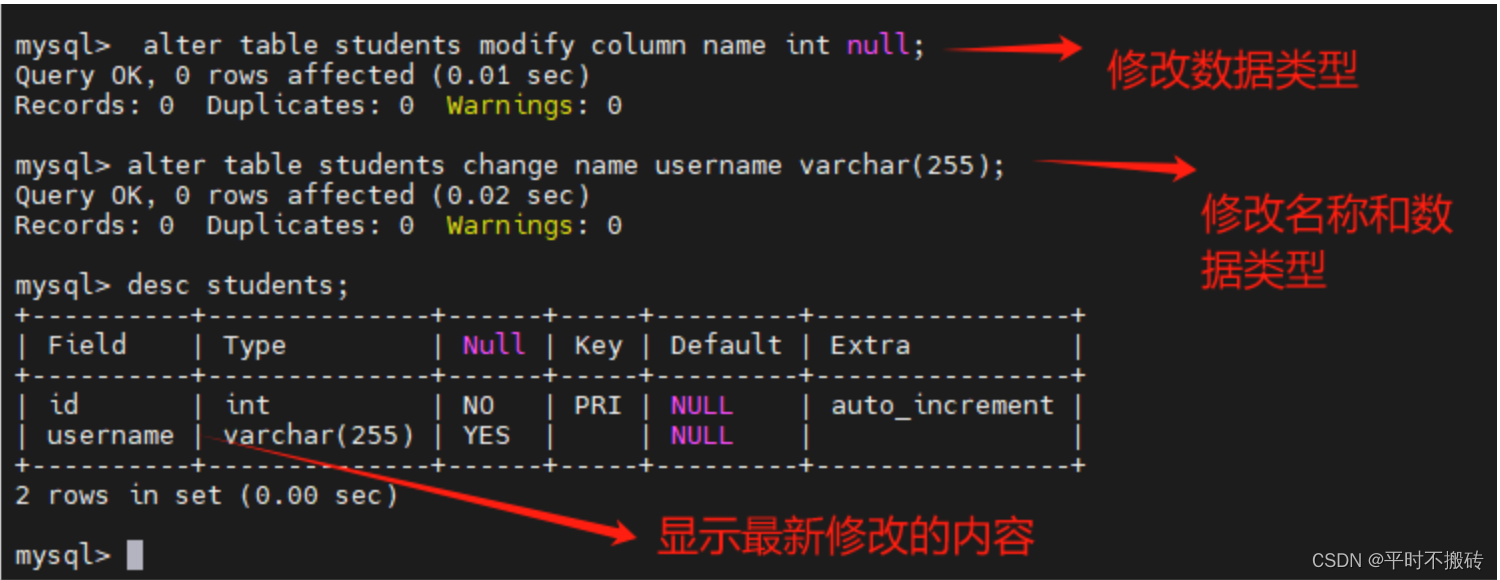
# 示例9, 修改列 # 创建表 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 修改字段数据类型 alter table students modify column name int null # 修改字段名名称和数据类型 alter table students drop index idx_name; # 修改字段数据类型 alter table students change name username varchar(255); # 查看表结构 desc students; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
# 示例10, 修改表名 # 创建表 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 修改表名 alter table students rename to new_students; # 查看表名 show tables; # 删除表 drop table new_students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
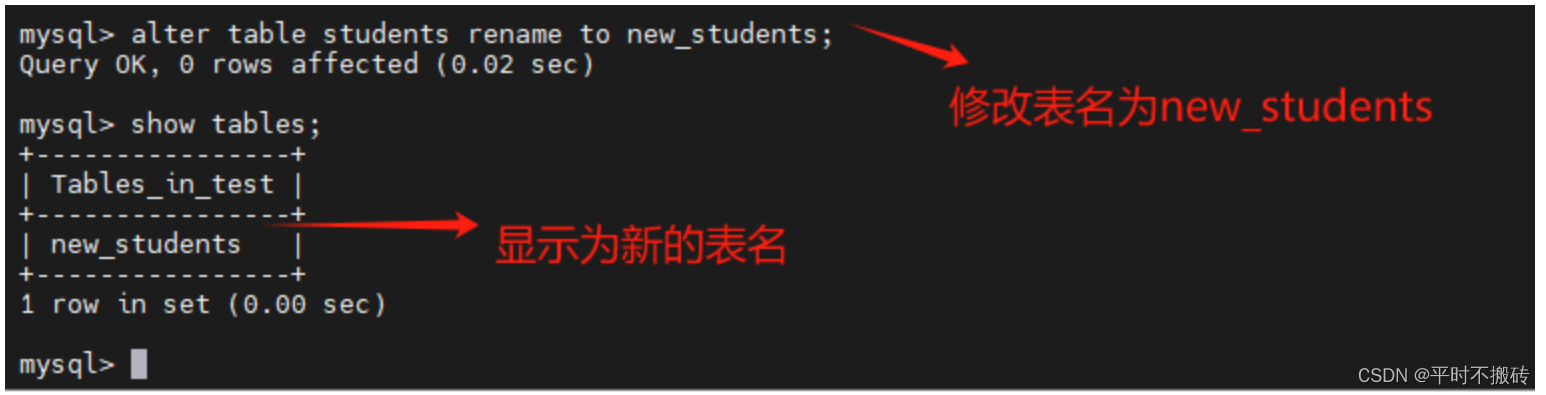
5 修改表名
# 示例1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 修改表名 rename table students to new_students; # 查看表 show tables; # 删除表 drop table new_students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

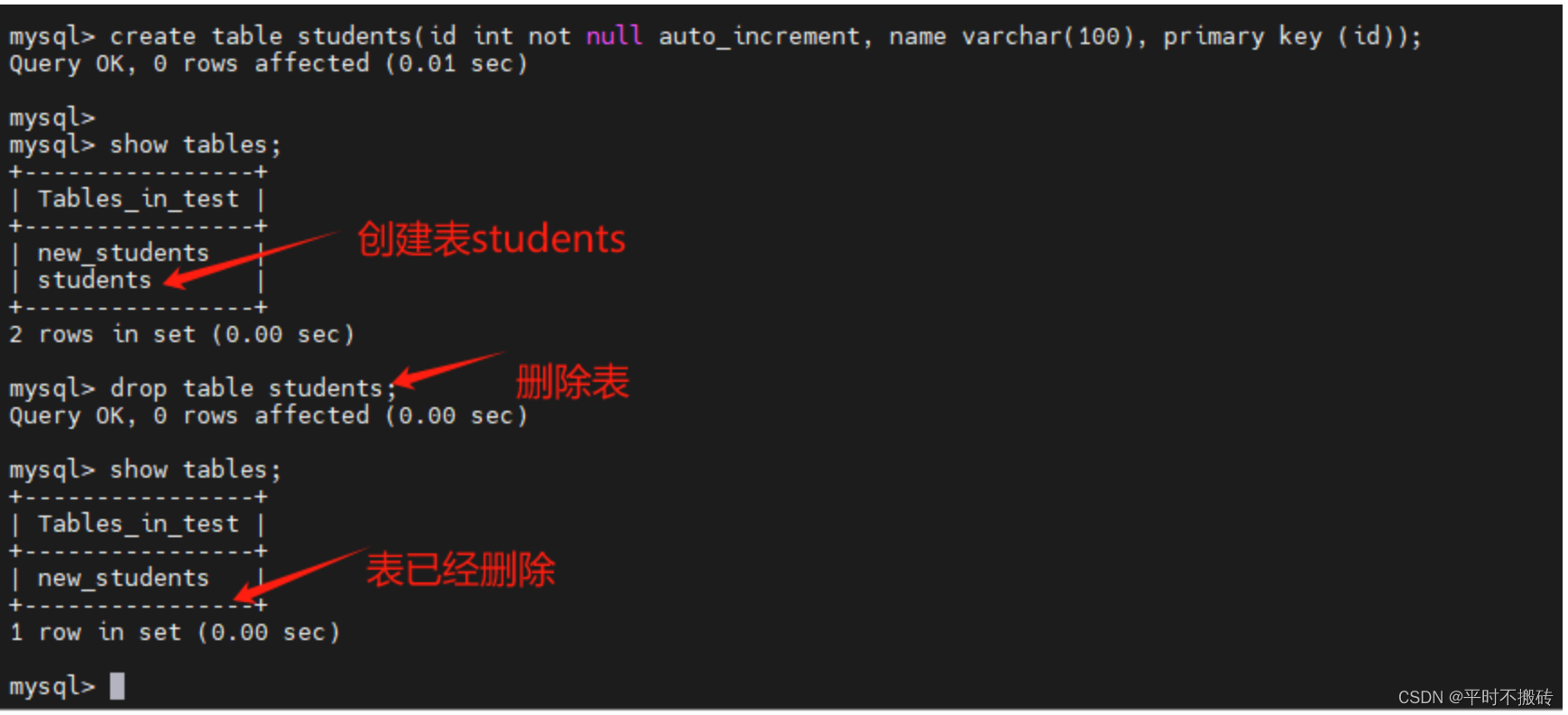
6 删除表# 示例1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 查看表 show tables; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
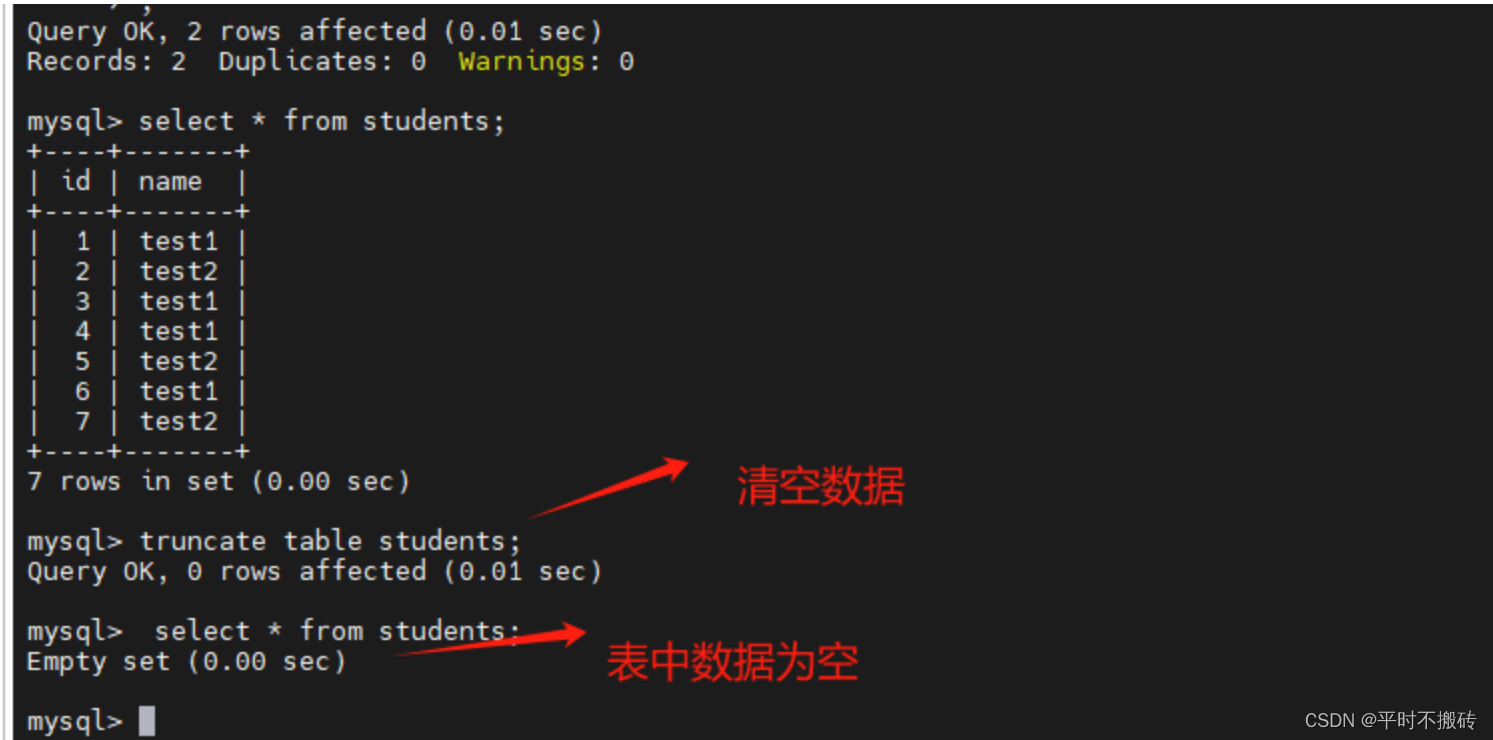
7 清空表的数据# 示例1 create table students(id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(100), primary key (id)); # 添加数据 insert into students(name) values("test1"), ("test2"); # 查看数据 select * from students; # 删除所有的数据 truncate table students; # 删除表 drop table students;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
5 操作数据
1 增
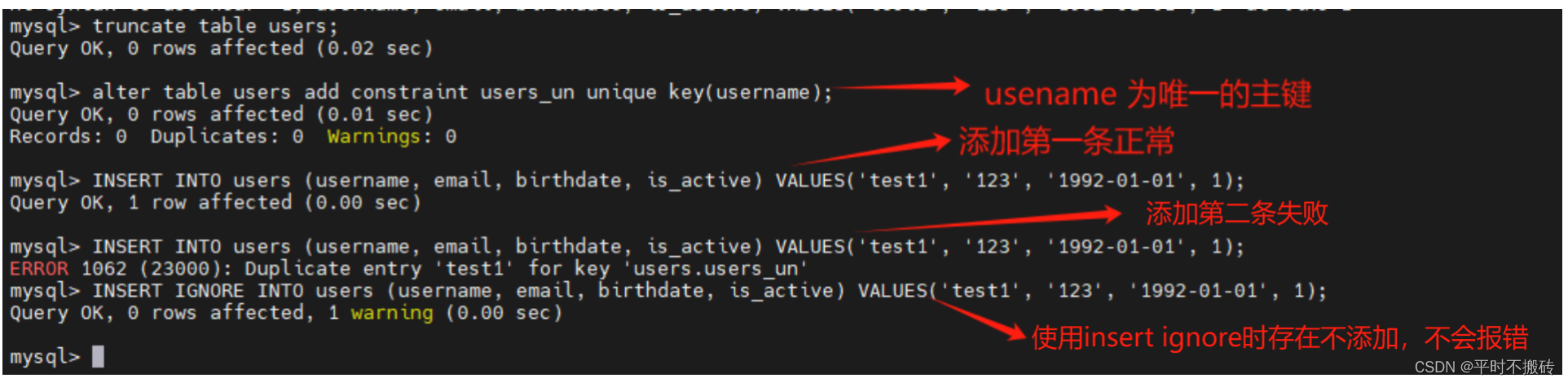
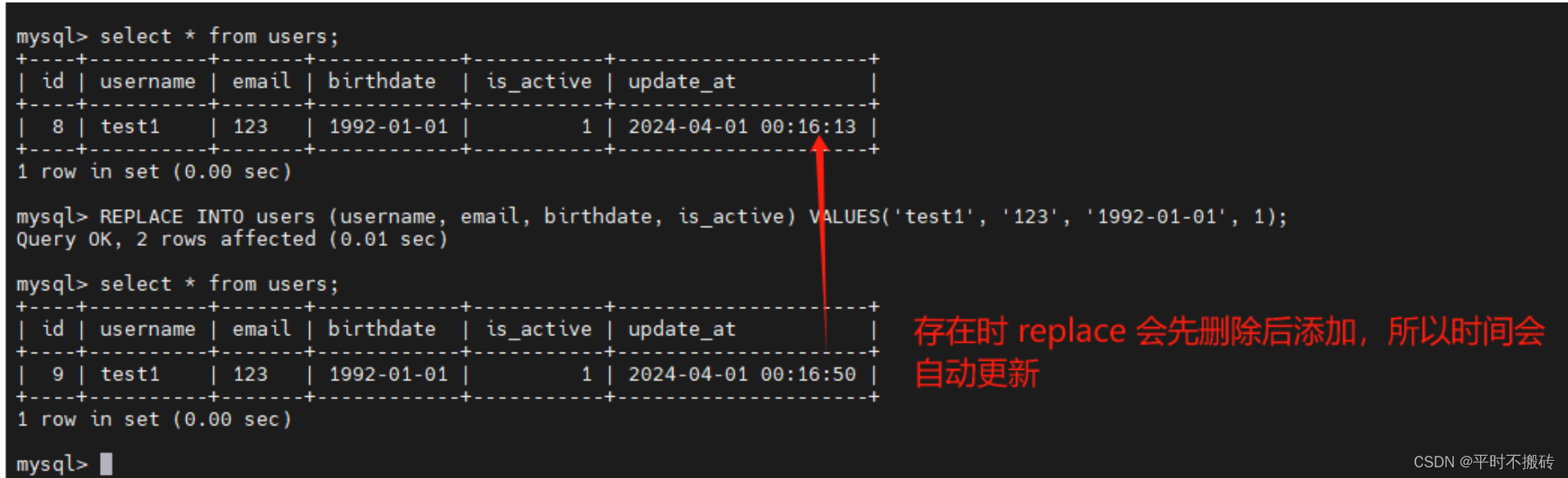
# 语法 INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...); # 创建表 REATE TABLE `users` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, `birthdate` date DEFAULT NULL, `is_active` tinyint(1) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) # 示例1 查看单行 INSERT INTO users (username, email, birthdate, is_active) VALUES('test1', '123', '1992-01-01', 1); # 示例2 插入多行 insert into users(username, email, birthdate, is_active) values ("test1", "test1@qq.com", "1992-01-01", 1), ("test2", "test2@qq.com", "1992-01-01", 1), ("test3", "test3@qq.com", "1992-01-01", 1); # 示例3 # 先清除数据 truncate table users; # 将username修改为唯一主键 alter table users add constraint users_un unique key(username); # 添加第一条 INSERT INTO users (username, email, birthdate, is_active) VALUES('test1', '123', '1992-01-01', 1); # 添加唯一主键相同的数据报错 INSERT INTO users (username, email, birthdate, is_active) VALUES('test1', '123', '1992-01-01', 1); # 使用IGNORE 插入时存在唯一主键相同的不会报错,也不会插入 INSERT IGNORE INTO users (username, email, birthdate, is_active) VALUES('test1', '123', '1992-01-01', 1); # 示例4 # 添加一个字段随着更新自动更新时间 ALTER TABLE your_table_name ADD COLUMN update_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP; # 插入数据, 如果存在唯一索引的值,会先删除数据之后再更新,不存在正常插入 REPLACE INTO users (username, email, birthdate, is_active) VALUES('test1', '123', '1992-01-01', 1); # 删除数据库 drop table users- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
INSERT IGNORE INTO操作
REPLACE INTO 操作
2 删
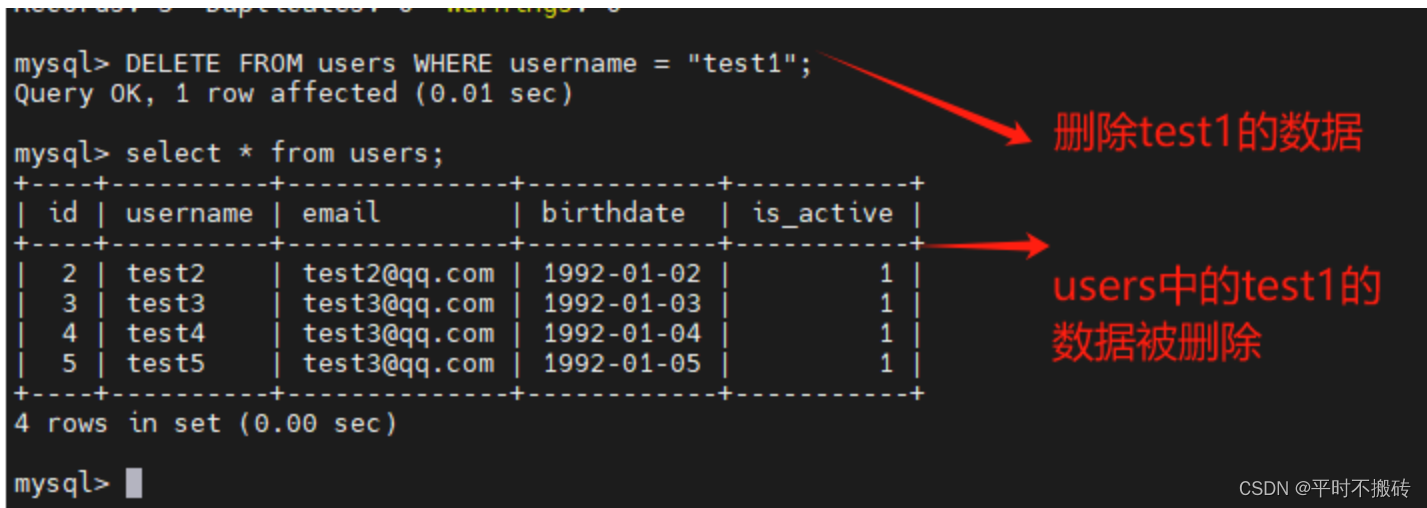
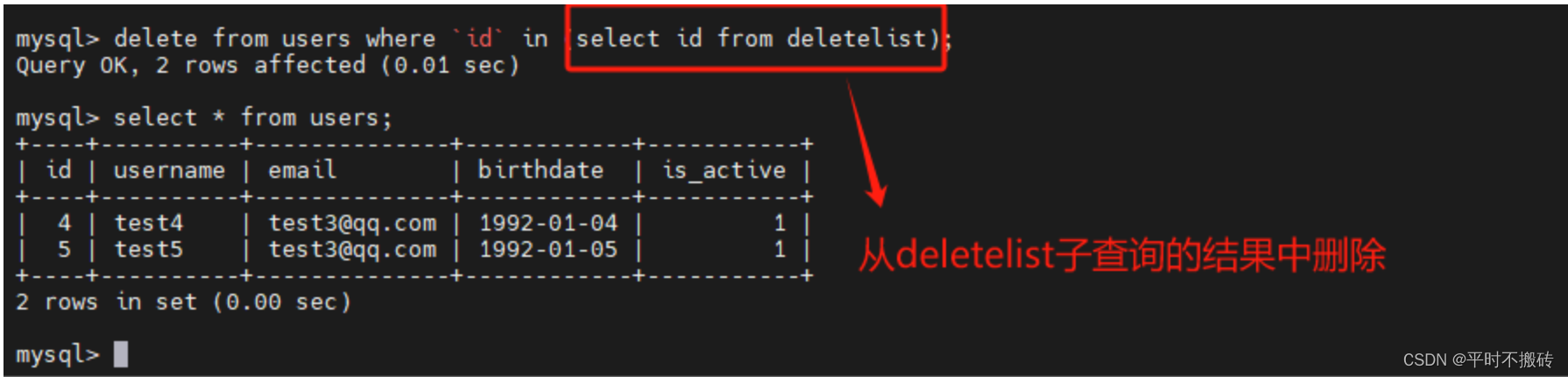
# 语法 DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition; # 创建数据表 CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, `birthdate` date DEFAULT NULL, `is_active` tinyint(1) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ); # 创建待删除表 CREATE TABLE deletelist ( id INT auto_increment NOT NULL, name varchar(100) NULL, CONSTRAINT deletelist_PK PRIMARY KEY (id) ); # 插入测试数据 insert into users(username, email, birthdate, is_active) values ("test1", "test1@qq.com", "1992-01-01", 1), ("test2", "test2@qq.com", "1992-01-02", 1), ("test3", "test3@qq.com", "1992-01-03", 1), ("test4", "test3@qq.com", "1992-01-04", 1), ("test5", "test3@qq.com", "1992-01-05", 1); # 插入待删除数据 insert into deletelist(name) values ("test1"), ("test2"), ("test3"); # 示例1, 删除符合条件的数据 DELETE FROM users WHERE username = "test1"; # 示例2 使用子查询删除符合条件的行: DELETE FROM users WHERE id IN (SELECT id FROM users WHERE birthdate < '1992-01-03'); # 示例3,删除所有的数据 DELETE FROM orders; # 删除表 drop table users;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
删除指定条件的数据
删除子查询的条件
清空所有的数据

3 改
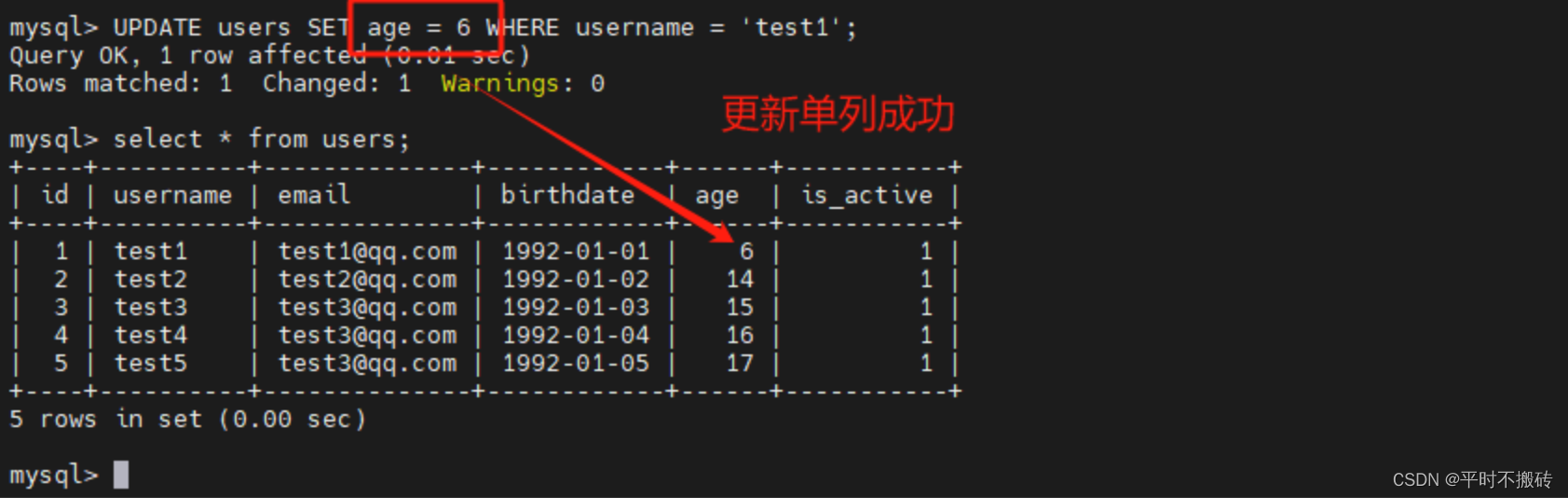
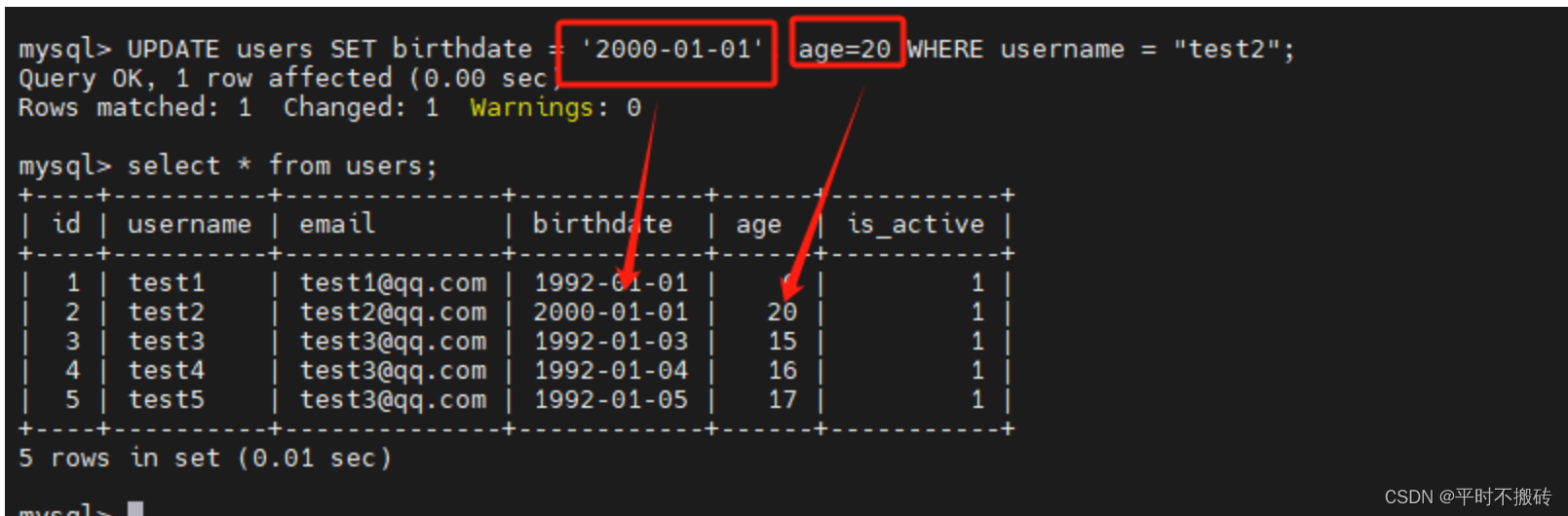
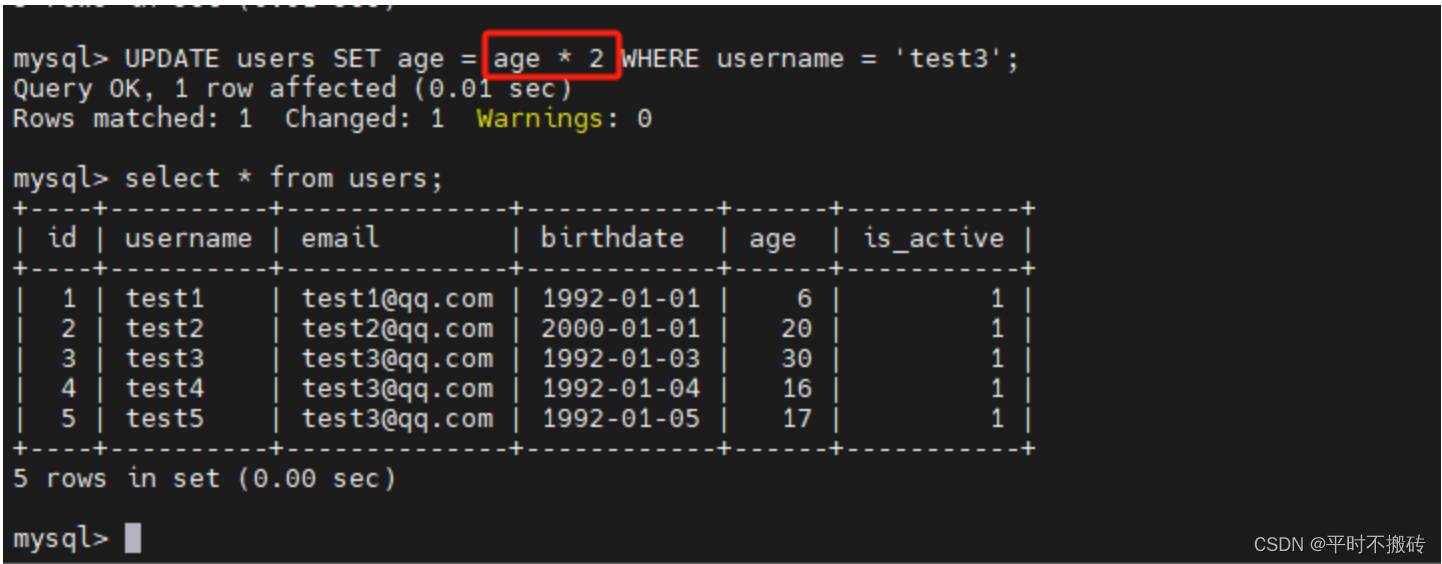
# 语法 UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...WHERE condition; # 创建数据表 CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL, `birthdate` date DEFAULT NULL, `age` int, `is_active` tinyint(1) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ); # 插入测试数据 insert into users(username, email, age, birthdate, is_active) values ("test1", "test1@qq.com", 12, "1992-01-01", 1), ("test2", "test2@qq.com", 14, "1992-01-02", 1), ("test3", "test3@qq.com", 15, "1992-01-03", 1), ("test4", "test3@qq.com", 16, "1992-01-04", 1), ("test5", "test3@qq.com", 17, "1992-01-05", 1); # 示例1 更新单个列的值: UPDATE users SET age = 6 WHERE username = 'test1'; # 示例2 更新多个列的值: UPDATE users SET birthdate = '2000-01-01', age=20 WHERE username = "test2"; # 示例3 使用表达式更新值: UPDATE users SET age = age * 2 WHERE username = 'test3'; # 示例4 更新所有的数据: UPDATE users SET age = 12;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
更新单例的值
更新多个列的值
利用表达式更新值
4 查询
基本使用
-- 语法 SELECT column1, column2, ...FROM table_name [WHERE condition] [ORDER BY column_name [ASC | DESC]] [LIMIT number]; -- 选择所有列的所有行 SELECT * FROM users; -- 选择特定列的所有行 SELECT username, email FROM users; -- 添加 WHERE 子句,选择满足条件的行 SELECT * FROM users WHERE is_active = TRUE; -- 添加 ORDER BY 子句,按照某列的升序排序 SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY birthdate; -- 添加 ORDER BY 子句,按照某列的降序排序 SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY birthdate DESC; -- 添加 LIMIT 子句,限制返回的行数 SELECT * FROM users LIMIT 10; -- 使用 AND 运算符和通配符 SELECT * FROM users WHERE username LIKE 'j%' AND is_active = TRUE; -- 使用 OR 运算符 SELECT * FROM users WHERE is_active = TRUE OR birthdate < '1990-01-01'; -- 使用 IN 子句 SELECT * FROM users WHERE birthdate IN ('1990-01-01', '1992-03-15', '1993-05-03'); # 查询最后最后插入行的自增值 SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
where语句使用
--等于条件: SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = 'test'; --不等于条件: SELECT * FROM users WHERE username != 'runoob'; --大于条件: SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > 50.00; --小于条件: SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_date < '2023-01-01'; --大于等于条件: SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary >= 50000; --小于等于条件: SELECT * FROM students WHERE age <= 21; --组合条件(AND、OR): SELECT * FROM products WHERE category = 'Electronics' AND price > 100.00; SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_date >= '2023-01-01' OR total_amount > 1000.00; --模糊匹配条件(LIKE): SELECT * FROM customers WHERE first_name LIKE 'J%'; --IN 条件: SELECT * FROM countries WHERE country_code IN ('US', 'CA', 'MX'); --NOT 条件: SELECT * FROM products WHERE NOT category = 'Clothing'; --BETWEEN 条件: SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-12-31'; --IS NULL 条件 SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department IS NULL; --IS NOT NULL 条件: SELECT * FROM customers WHERE email IS NOT NULL;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
5 模糊查询
IKE 子句是在 MySQL 中用于在 WHERE 子句中进行模糊匹配的关键字。它通常与通配符一起使用,用于搜索符合某种模式的字符串。
LIKE 子句中使用百分号 %字符来表示任意字符,如果没有使用百分号 %, LIKE 子句与等号 = 的效果是一样的。
--语法 SELECT column1, column2,FROM table_name WHERE column_name LIKE pattern; --百分号通配符 %: # % 通配符表示零个或多个字符。例如,'a%' 匹配以字母 'a' 开头的任何字符串。 SELECT * FROM customers WHERE last_name LIKE 'S%'; --下划线通配符 _: -- _ 通配符表示一个字符。例如,'_r%' 匹配第二个字母为 'r' 的任何字符串。 SELECT * FROM products WHERE product_name LIKE '_a%'; -- 组合使用 % 和 _: SELECT * FROM users WHERE username LIKE 'a%o_'; -- 不区分大小写的匹配: SELECT * FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE 'smi%' COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
6 UNION查询
MySQL UNION 操作符用于连接两个以上的 SELECT 语句的结果组合到一个结果集合,并去除重复的行。
UNION 操作符必须由两个或多个 SELECT 语句组成,每个 SELECT 语句的列数和对应位置的数据类型必须相同。
-- 语法 SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table1 WHERE condition1 UNION SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table2 WHERE condition2 [ORDER BY column1, column2, ...]; -- 将选择客户表和供应商表中所有城市的唯一值,并按城市名称升序排序。 ELECT city FROM customers UNION SELECT city FROM suppliers ORDER BY city; -- 将选择电子产品和服装类别的产品名称,并按产品名称升序排序。 SELECT product_name FROM products WHERE category = 'Electronics' UNION SELECT product_name FROM products WHERE category = 'Clothing' ORDER BY product_name; -- UNION ALL 将客户表和供应商表中的所有城市合并在一起,不去除重复行。 SELECT city FROM customers UNION ALL SELECT city FROM suppliers ORDER BY city;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
7 排序
如果我们需要对读取的数据进行排序,我们就可以使用 MySQL 的 ORDER BY 子句来设定你想按哪个字段哪种方式来进行排序,再返回搜索结果。
MySQL ORDER BY(排序) 语句可以按照一个或多个列的值进行升序(ASC)或降序(DESC)排序。
-- 语法 SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name ORDER BY column1 [ASC | DESC], column2 [ASC | DESC], ...; -- 单列排序: SELECT * FROM products ORDER BY product_name ASC; -- 多列排序: SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY department_id ASC, hire_date DESC; -- 使用数字表示列的位置: SELECT first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY 3 DESC, 1 ASC; -- 使用表达式排序: SELECT product_name, price * discount_rate AS discounted_price FROM products ORDER BY discounted_price DESC; -- 使用 NULLS FIRST 或 NULLS LAST 处理 NULL 值:将 NULL 值排在最后。 SELECT product_name, price FROM products ORDER BY price DESC NULLS LAST;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
8 分组查询
GROUP BY 语句根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组,在分组的列上我们可以使用 聚合函数COUNT, SUM, AVG,等。
-- 语法 SELECT column1, aggregate_function(column2) FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column1; -- 根据customer_id分组,统计order_amount SELECT customer_id, SUM(order_amount) AS total_amount FROM orders GROUP BY customer_id; -- 根据name分组统计name数量 SELECT name, COUNT(*) FROM employee_tbl GROUP BY name;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
9 连表查询

JOIN 按照功能大致分为如下三类:- INNER JOIN(内连接,或等值连接):获取两个表中字段匹配关系的记录。
- **LEFT JOIN(左连接):**获取左表所有记录,即使右表没有对应匹配的记录。
- RIGHT JOIN(右连接): 与 LEFT JOIN 相反,用于获取右表所有记录,即使左表没有对应匹配的记录。
- FULL OUTER JOIN(全连接): 两张表的数据数据全部连接,条件不相等的显示为空,一般不这样使用这个
# 语法 SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
10 正则查询
MySQL 中使用 REGEXP 和 RLIKE操作符来进行正则表达式匹配。
模式 描述 ^ 匹配输入字符串的开始位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,^ 也匹配 ‘\n’ 或 ‘\r’ 之后的位置。 $ 匹配输入字符串的结束位置。如果设置了RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,$ 也匹配 ‘\n’ 或 ‘\r’ 之前的位置。 . 匹配除 “\n” 之外的任何单个字符。要匹配包括 ‘\n’ 在内的任何字符,请使用像 ‘[.\n]’ 的模式。 […] 字符集合。匹配所包含的任意一个字符。例如, ‘[abc]’ 可以匹配 “plain” 中的 ‘a’。 [^…] 负值字符集合。匹配未包含的任意字符。例如, ‘[^abc]’ 可以匹配 “plain” 中的’p’。 p1|p2|p3 匹配 p1 或 p2 或 p3。例如,‘z|food’ 能匹配 “z” 或 “food”。‘(z|f)ood’ 则匹配 “zood” 或 “food”。 * 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。例如,zo* 能匹配 “z” 以及 “zoo”。* 等价于{0,}。 + 匹配前面的子表达式一次或多次。例如,‘zo+’ 能匹配 “zo” 以及 “zoo”,但不能匹配 “z”。+ 等价于 {1,}。 {n} n 是一个非负整数。匹配确定的 n 次。例如,‘o{2}’ 不能匹配 “Bob” 中的 ‘o’,但是能匹配 “food” 中的两个 o。 {n,m} m 和 n 均为非负整数,其中n <= m。最少匹配 n 次且最多匹配 m 次。 正则表达式匹配的字符类
.:匹配任意单个字符。^:匹配字符串的开始。$:匹配字符串的结束。*:匹配零个或多个前面的元素。+:匹配一个或多个前面的元素。?:匹配零个或一个前面的元素。[abc]:匹配字符集中的任意一个字符。[^abc]:匹配除了字符集中的任意一个字符以外的字符。[a-z]:匹配范围内的任意一个小写字母。\d:匹配一个数字字符。\w:匹配一个字母数字字符(包括下划线)。\s:匹配一个空白字符。
-- 语法 SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE column_name REGEXP 'pattern'; -- 查找 name 字段中以 'st' 为开头的所有数据: SELECT name FROM person_tbl WHERE name REGEXP '^st'; -- 查找 name 字段中以 'ok' 为结尾的所有数据 SELECT name FROM person_tbl WHERE name REGEXP 'ok$'; -- 查找 name 字段中包含 'mar' 字符串的所有数据 SELECT name FROM person_tbl WHERE name REGEXP 'mar'; -- 找 name 字段中以元音字符开头或以 'ok' 字符串结尾的所有数据: SELECT name FROM person_tbl WHERE name REGEXP '^[aeiou]|ok$'; -- 选择订单表中描述中包含 "item" 后跟一个或多个数字的记录。 SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_description REGEXP 'item[0-9]+'; -- 使用 BINARY 关键字,使得匹配区分大小写: SELECT * FROM products WHERE product_name REGEXP BINARY 'apple'; -- 使用 OR 进行多个匹配条件,以下将选择姓氏为 "Smith" 或 "Johnson" 的员工记录: SELECT * FROM employees WHERE last_name REGEXP 'Smith|Johnson';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
-
相关阅读:
D-Wave 推出快速退火功能,扩大量子计算性能增益
【Q&A】Troubleshooting R Studio
MyBatis基于配置文件实现对数据库的增删改查
计算机毕业设计(附源码)python中草药管理系统
pyqt5的组合式部件制作(一)
2022年10个最佳地理空间数据分析 GIS 软件
第 43 章 MDK 的编译过程及文件类型全解
Oracle 11g R2 Rman备份与恢复(二)
[第四篇]——Windows Docker 安装
睿趣科技:抖音小店申请流程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43413871/article/details/137241823