-
ES分片均衡策略分析与改进
从故障说起
某日早高峰收到 Elasticsearch 大量查询超时告警,不同于以往,查看 Elasticsearch 查询队列监控后发现,仅123节点存在大量查询请求堆积。
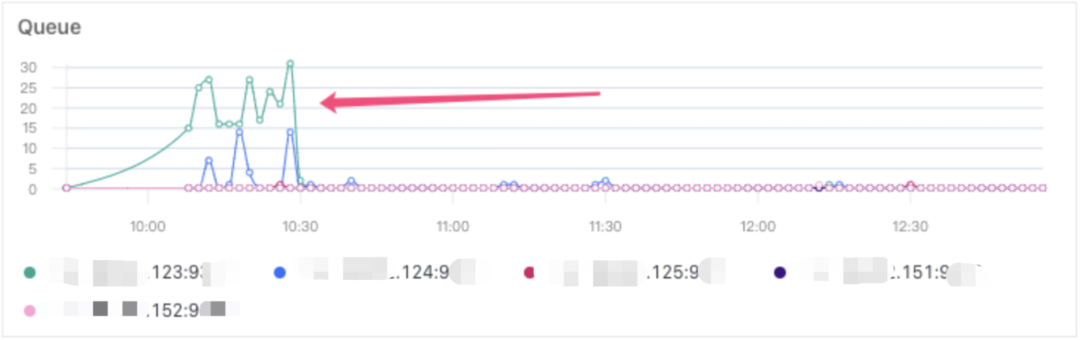
各节点查询队列堆积情况
查看节点监控发现,123节点的 IO 占用远高于其他节点。
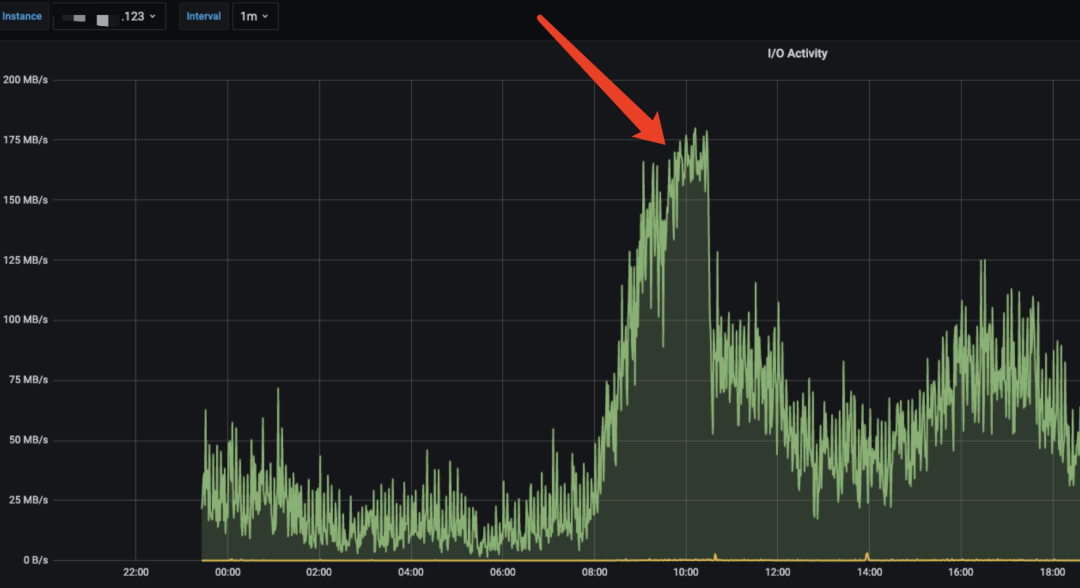

节点间IO占用对比
最终查明原因是,某些高负载(高读写 qps、大数据量、复杂查询)的索引分片相对集中在123节点上,导致整体集群节点间负载不均衡,严重时甚至引发故障。那么这种现象是普遍存在的吗?
在观察了其他集群后发现,各个集群均有不同程度的“负载不均衡”现象,同为数据节点,有的 IO 比其他节点高出一倍以上,有的 CPU 占用大幅超过其他节点。我们知道 Elasticsearch 的读写速度遵循木桶原理,即某台节点如果表现不佳的话会拖慢整个请求的 RT。严重时甚至出现线上故障。因此,尽可能的保持节点间负载的均衡,既能保证集群性能处于最优状态,又能最大限度利用硬件资源,保障集群稳定性。
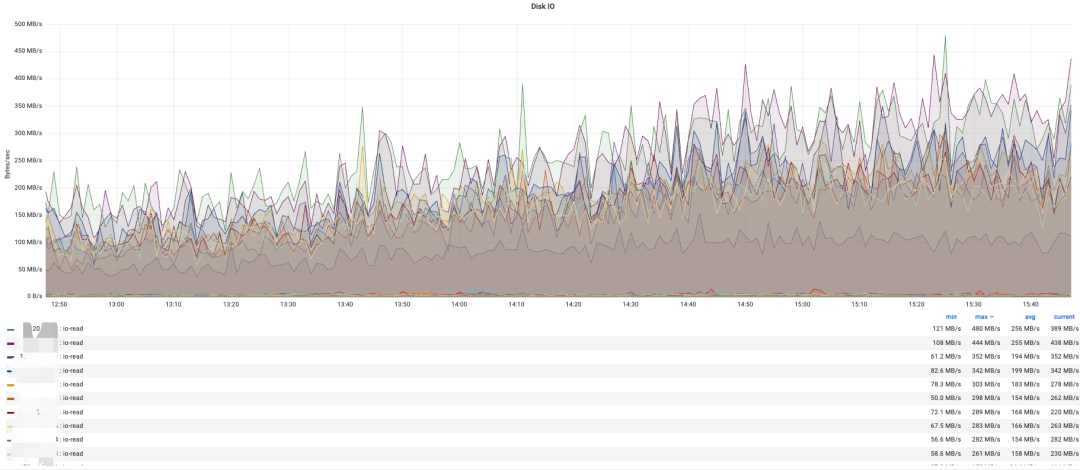
各节点IO占用情况

各节点CPU占用情况
然而,其实 Elasticsearch 自己是有集群分配自动均衡能力的,但是为什么还会出现上述情况呢?这里需要我们深入分析一下。
ES分片均衡策略
概念
首先来看下 LLM 对 Elasticsearch 分片均衡的解释:
Elasticsearch 的分片均衡是指将索引的分片均匀地分布在集群中的各个节点上,以实现负载均衡和高可用性。在 Elasticsearch 中,索引被分为多个分片,每个分片可以在不同的节点上进行存储和处理。分片均衡的目标是确保每个节点上的分片数量大致相等,避免某些节点负载过重,而其他节点负载较轻的情况。似乎只提到了“确保每个节点上的分片数量大致相等”,事实是这样吗?不多说,直接翻源码一探究竟。
均衡策略
这里展示了核心的分片权重计算部分代码,indexBalance 和 shardBalance 分别表示索引维度权重因子和分片维度权重因子。node.numShards() 表示该节点目前总共的分片数。balancer.avgShardsPerNode() 表示总分片数/总结点数,也就是理想状态下单个节点应该被分配的分片数。node.numShards(index) 表示该索引在当前节点的分片数。balancer.avgShardsPerNode(index) 表示该索引总分片数/总结点数,也就是理想状态下单个节点该索引应该被分配的分片数。
- WeightFunction(float indexBalance, float shardBalance) {
- float sum = indexBalance + shardBalance;
- if (sum <= 0.0f) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Balance factors must sum to a value > 0 but was: " + sum);
- }
- theta0 = shardBalance / sum;
- theta1 = indexBalance / sum;
- this.indexBalance = indexBalance;
- this.shardBalance = shardBalance;
- }
- float weight(Balancer balancer, ModelNode node, String index) {
- final float weightShard = node.numShards() - balancer.avgShardsPerNode();
- final float weightIndex = node.numShards(index) - balancer.avgShardsPerNode(index);
- return theta0 * weightShard + theta1 * weightIndex;
- }
即权重公式为:分片权重因子 * (当前节点分片数 - 理想平均分片数) + 索引权重因子 * (当前节点该索引分片数 - 理想该索引平均分片数)
- // get the delta between the weights of the node we are checking and the node that holds the shard
- float currentDelta = absDelta(nodeWeight, currentWeight);
- // checks if the weight delta is above a certain threshold; if it is not above a certain threshold,
- // then even though the node we are examining has a better weight and may make the cluster balance
- // more even, it doesn't make sense to execute the heavyweight operation of relocating a shard unless
- // the gains make it worth it, as defined by the threshold
- boolean deltaAboveThreshold = lessThan(currentDelta, threshold) == false;
当我们得到节点当前的权重后,下一步需要和其他节点权重相比较,若权重差值超过 threshold ,则认为当前分片分布不均匀,需要重新均衡。
相关配置
上述逻辑涉及到以下几个配置:
-
cluster.routing.allocation.balance.shard: 0.45f(默认)
-
分片权重因子 越高节点层面分片数量的均衡权重越高
-
-
cluster.routing.allocation.balance.index: 0.55f(默认)
-
索引权重因子 越高索引层面分片数量的均衡权重越高
-
-
cluster.routing.allocation.balance.threshold: 1.0f(默认)
-
重新分配分片阈值 越高触发自均衡的条件越苛刻
-
除此之外还有以下配置涉及分片分布、均衡:
-
cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node: -1(默认)
-
单节点最大允许的分片数量,默认不限制
-
-
cluster.routing.allocation.cluster_concurrent_rebalance: 2(默认)
-
集群内因“不均衡”而触发的最大分片迁移并发数量。
-
-
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries: 2(默认)
-
单个节点因“不均衡”而触发的最大分片迁移并发数量。
-
举个栗子

分片均衡前
假设当前集群有两个节点,两个索引(A索引4分片,B索引2分片,C索引2分片),分布状态如上图。
此时Node 1的权重为 0.45 * (4 - 3) + 0.55 * (2 - 1.5) = 0.725,Node 2的权重为0.45 * (2 - 3) + 0.55 * (1 - 1.5) = -0.725。Node 1和Node 2的权重差为 1.45 超过了阈值 1,此时就可能出发索引分片迁移。将分配从高权重节点挪到低权重节点。
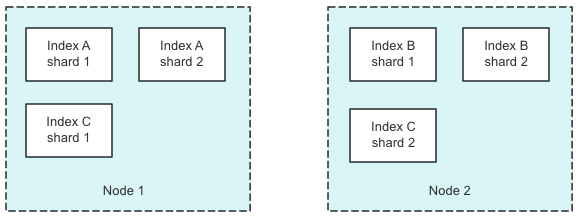
分片均衡后
触发条件
在实际生产环境中,有时尽管满足了上述的“权重公式”,但却没有发生分配自动均衡。这是因为除了满足“权重公式”以外,还需要满足以下条件。
均衡范围
-
cluster.routing.rebalance.enable: all
- public Decision canRebalance(ShardRouting shardRouting, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
- if (allocation.ignoreDisable()) {
- return allocation.decision(Decision.YES, NAME, "allocation is explicitly ignoring any disabling of rebalancing");
- }
- Settings indexSettings = allocation.metadata().getIndexSafe(shardRouting.index()).getSettings();
- final Rebalance enable;
- final boolean usedIndexSetting;
- if (INDEX_ROUTING_REBALANCE_ENABLE_SETTING.exists(indexSettings)) {
- enable = INDEX_ROUTING_REBALANCE_ENABLE_SETTING.get(indexSettings);
- usedIndexSetting = true;
- } else {
- enable = this.enableRebalance;
- usedIndexSetting = false;
- }
- switch (enable) {
- case ALL:
- return allocation.decision(Decision.YES, NAME, "all rebalancing is allowed");
- case NONE:
- return allocation.decision(Decision.NO, NAME, "no rebalancing is allowed due to %s", setting(enable, usedIndexSetting));
- case PRIMARIES:
- if (shardRouting.primary()) {
- return allocation.decision(Decision.YES, NAME, "primary rebalancing is allowed");
- } else {
- return allocation.decision(
- Decision.NO,
- NAME,
- "replica rebalancing is forbidden due to %s",
- setting(enable, usedIndexSetting)
- );
- }
- case REPLICAS:
- if (shardRouting.primary() == false) {
- return allocation.decision(Decision.YES, NAME, "replica rebalancing is allowed");
- } else {
- return allocation.decision(
- Decision.NO,
- NAME,
- "primary rebalancing is forbidden due to %s",
- setting(enable, usedIndexSetting)
- );
- }
- default:
- throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown rebalance option");
- }
- }
-
all:允许所有分片自动均衡(默认)
-
primaries:只允许主分片自动均衡
-
replicas:只允许副本分片自动均衡
-
none:不允许自动均衡
分片状态
不健康的分片状态,可能会导致分片均衡失败,甚至因失败而丢失数据。
-
cluster.routing.allocation.allow_rebalance: indices_all_active
- public Decision canRebalance(RoutingAllocation allocation) {
- final RoutingNodes routingNodes = allocation.routingNodes();
- switch (type) {
- case INDICES_PRIMARIES_ACTIVE:
- // check if there are unassigned primaries.
- if (routingNodes.hasUnassignedPrimaries()) {
- return NO_UNASSIGNED_PRIMARIES;
- }
- // check if there are initializing primaries that don't have a relocatingNodeId entry.
- if (routingNodes.hasInactivePrimaries()) {
- return NO_INACTIVE_PRIMARIES;
- }
- return YES_ALL_PRIMARIES_ACTIVE;
- case INDICES_ALL_ACTIVE:
- // check if there are unassigned shards.
- if (routingNodes.hasUnassignedShards()) {
- return NO_UNASSIGNED_SHARDS;
- }
- // in case all indices are assigned, are there initializing shards which
- // are not relocating?
- if (routingNodes.hasInactiveShards()) {
- return NO_INACTIVE_SHARDS;
- }
- // fall-through
- default:
- // all shards active from above or type == Type.ALWAYS
- return YES_ALL_SHARDS_ACTIVE;
- }
- }
-
always:无视分片状态,始终允许自动均衡
-
indices_primaries_active:仅在所有主分片可用时
-
indices_all_active:仅当所有分片都激活时(默认)
磁盘水位
如果分片均衡的目标节点磁盘使用率过高,此时不应该继续往改节点分配分片。
-
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.threshold_enabled: true(默认)
-
启用基于磁盘的分发策略
-
-
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.low: "85%"(默认)
-
硬盘使用率高于这个值的节点,则不会分配分片
-
-
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.high: "90%"(默认)
-
如果硬盘使用率高于这个值,则会重新分片该节点的分片到别的节点
-
- public Decision canAllocate(ShardRouting shardRouting, RoutingNode node, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
- ... ...
- if (freeDiskPercentage < diskThresholdSettings.getFreeDiskThresholdLow()) {
- // If the shard is a replica or is a non-empty primary, check the low threshold
- if (skipLowThresholdChecks == false) {
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug(
- "more than the allowed {} used disk threshold ({} used) on node [{}], preventing allocation",
- Strings.format1Decimals(usedDiskThresholdLow, "%"),
- Strings.format1Decimals(usedDiskPercentage, "%"),
- node.nodeId()
- );
- }
- return allocation.decision(
- Decision.NO,
- NAME,
- "the node is above the low watermark cluster setting [%s=%s], using more disk space than the maximum allowed [%s%%], actual free: [%s%%]",
- CLUSTER_ROUTING_ALLOCATION_LOW_DISK_WATERMARK_SETTING.getKey(),
- diskThresholdSettings.getLowWatermarkRaw(),
- usedDiskThresholdLow,
- freeDiskPercentage
- );
- }
- }
- ... ...
- if (freeBytes < diskThresholdSettings.getFreeBytesThresholdHigh().getBytes()) {
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug(
- "less than the required {} free bytes threshold ({} bytes free) on node {}, shard cannot remain",
- diskThresholdSettings.getFreeBytesThresholdHigh(),
- freeBytes,
- node.nodeId()
- );
- }
- return allocation.decision(
- Decision.NO,
- NAME,
- "the shard cannot remain on this node because it is above the high watermark cluster setting [%s=%s] "
- + "and there is less than the required [%s] free space on node, actual free: [%s]",
- CLUSTER_ROUTING_ALLOCATION_HIGH_DISK_WATERMARK_SETTING.getKey(),
- diskThresholdSettings.getHighWatermarkRaw(),
- diskThresholdSettings.getFreeBytesThresholdHigh(),
- new ByteSizeValue(freeBytes)
- );
- }
- ... ...
- }
原来如此,Elasticsearch 的分片均衡策略并没有我们想象中的那么智能,甚至可以说是简陋。光从分片的数量出发做均衡显然是不明智的,忽略了数据量、读写复杂度、热点流量、热点数据分布、硬件差异等重要参考因素,达不到生产所需要的要求。既然知道了这东西好像不太靠谱,那我们该如何进一步的提高分片“负载均衡度”呢?
如何改进
分片数量调整
这个方法最简单,0门槛。只需确保索引的分片数量是集群的数据节点数量的整数倍即可。结合 Elasticsearch 的自动均衡策略,不考虑主副差异的话,可以做到相对完美的均衡。
但也有一些缺点和副作用:
-
节点数量比较多的话,分片数量设置不灵活,要么太多,过度消耗 CPU 资源,要么太少,单分片数据量过大。
-
随着业务的变迁,集群规模往往会发生变动,尤其是数据节点。一旦发生变动,之前保持的平衡被完全破坏。需要话大把的精力修改分片数量、重建索引再次保持平衡(大规模的集群基本做不到)。
-
不兼容集群的动态扩缩容
自研分片均衡工具
我们需要一个在任意分片数量下也尽可能保持负载均衡的策略/工具。
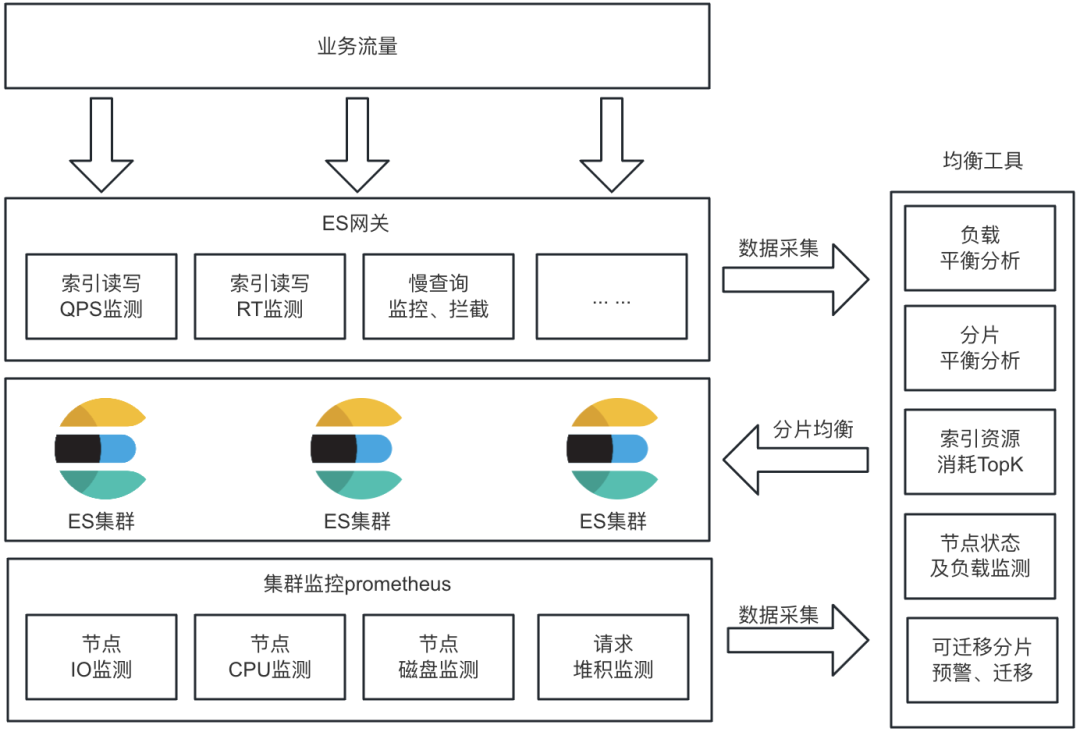
分片均衡工具
为了确保最终实现的是真正的负载均衡,因此,分片均衡的依据只能是集群的负载(而不是数量)。
首先确定几个需要平衡的指标,如 CPU 、 IO 、MBPS、RAM 等。对数据节点上的这些指标做监控,并统一送到均衡工具侧分析处理。
给定公式
$$ {E}{i}=o\times {IO}{i}+d\times {MBPS}{i}+c\times {CPU}{i}+r\times {RAM}_{i} $$
表示节点i的负载指标,o、d、c、r 分别为 IO 使用率、网络带宽使用率、CPU 使用率、内存使用率。
当负载指标出现不均衡时,如最高的节点超过最低的节点50%,且最高的节点此项负载达到50%以上时。此时需要将高负载节点上的部分分片均衡到低负载节点上。
此时,结合 Elasticsearch 业务网关侧的流量指标数据,取请求时长最高(请求数量 * avg(RT))的索引(热点索引),若该索引分片在高负载节点上的数量多于低负载节点,则将该索引的高负载节点分片迁移到低负载节点,单次只迁移一个分片。否则取下一个时长最高的索引分析处理。
在实际生产环境中,分片迁移会带来额外的 IO 开销,这极有可能会影响到线上业务,甚至加剧“不平衡”。因此,我们需要确保分片只在可允许的时间范围内迁移。由于我们的业务晚上负载大幅降低,因此晚上是我们的分片迁移窗口。
有些集群的业务比较特殊或者重要,也可以选择不自动迁移分片,只提供分片可平衡预警。
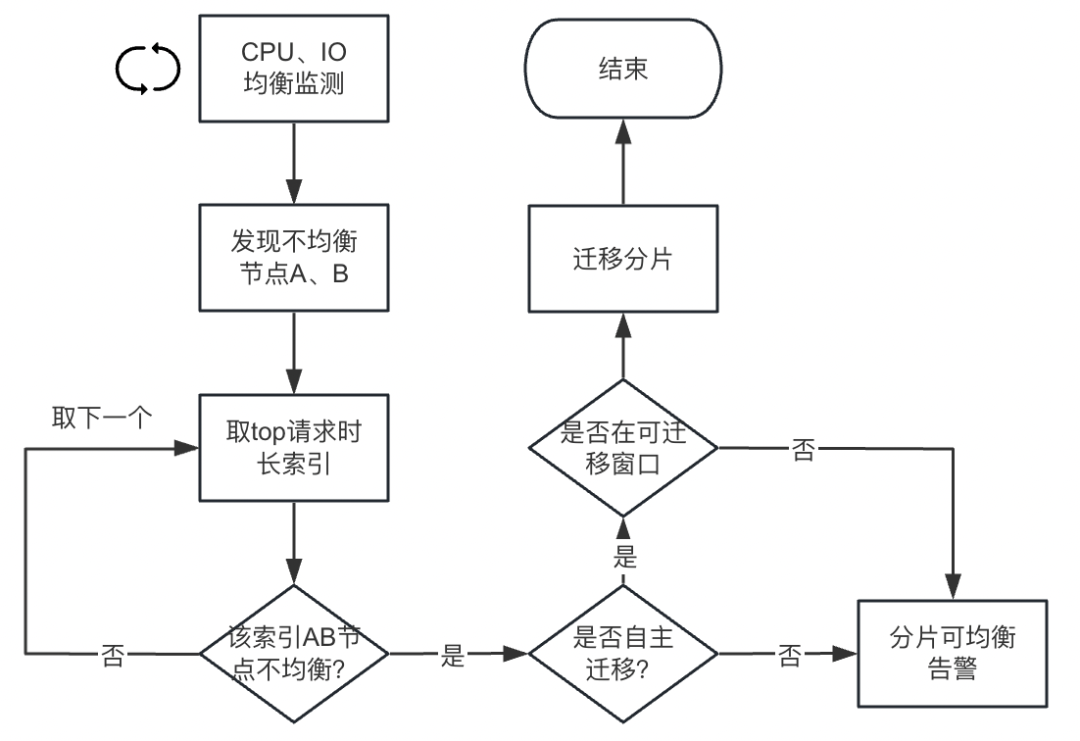
分片均衡流程
未来展望
智能化均衡策略
未来的分片均衡工具可能会更智能化,可能会引入更复杂的算法,以更准确地评估节点间的负载状况,从而更精准地进行分片迁移和分配。
实时监控和反馈
未来的工具可能会提供更实时的监控和反馈机制,可以及时发现节点负载不均衡的情况,并采取相应的措施。这可能包括更频繁的监控检测、更灵活的告警机制以及更快速的响应方式,以便更快地调整分片的分布。
动态迁移窗口
为了减少对线上业务的影响,未来的工具可能会引入更智能的分片迁移策略。这可能包括在业务低谷期间动态选择分片迁移窗口,以最小化对实时业务的干扰。
自定义调整策略
未来工具可能会提供更多的可配置选项,允许用户根据自己的业务特性和需求定制分片均衡策略。这可能包括调整均衡阈值、指定特定索引的均衡规则等。
总结一下
基于 Elasticsearch 的读写原理及特性:
读的时候:取所有节点的查询数据汇总并返回最终结果。
写的时候:确保主分片和副本分片都写入成功后,才返回写入成功。
不均衡的集群节点,会导致读写RT上涨,严重时请求堆积甚至拒绝从而产生故障。节点均衡能最大限度的发挥 Elasticsearch 底层硬件的能力,提高资源利用率。而 Elasticsearch 的分片均衡策略比我们想象的弱的多的多,千万步v不要盲目信任(来自故障的血的教训),单纯的做到分片数量均衡并不代表节点负载就均衡了。在实际生产中,不同分片的数据量、数据热度、读写复杂度均不相同,要做到真正的节点间负载均衡只能从“负载”出发。结合集群、业务两方面的监控数据,分析对节点负载影响最大的索引、分片,优先均衡高负载分片,最少迁移分片,最快均衡分片。
-
相关阅读:
[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django-大学生健康档案管理
力扣104. 二叉树的最大深度(java,DFS,BFS解法)
oracle学习48-oracle命令窗口执行sql语句
使用vscode开发esp32
Redis6 十二:Redis中的事务
FusionDiff:第一个基于扩散模型实现的多聚焦图像融合的论文
uniapp 树状数据无限极 进行展示并选择
【PDF技巧】网上下载的pdf文件怎么才能编辑
基于springboot+vue开发的教师工作量管理系
java计算机毕业设计基于安卓Android微信小程序的应急求救信息发布系统小程序uniAPP
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/woshaguayi/article/details/136653109
