-
数据结构小记【Python/C++版】——B树篇
一,基础概念
B树也是一种自平衡搜索树,常用于数据库中索引的实现。
B树和AVL树的区别在于:
B树是一种多路平衡查找树,B树的节点可以有两个以上的子节点(AVL树是二叉树,最多只能有两个子节点)。
B树的每个节点可以存储一个以上的数据域(在之前介绍过的树结构中,一个节点只有一个数据域)。由于B树的节点可以存放多条数据,因此B树特别适合应用在块存储的开发场景。
B树和AVL树的相同点在于:
B树的节点分布也是按照左小右大排列,子节点与节点的大小比较结果决定了子节点的位置。
每个节点中,左子树的数据比当前节点都小,右子树的数据比当前节点都大。
关于B树的阶:
M阶B树表示该树每个节点最多有M个子树。若B树中一个节点的子节点数目的最大值为4,则该树为4阶。
M阶B树可以定义为M路搜索树:
节点的最多子节点数为M。
节点的最大数据量为M-1。
所有非叶子节点(根节点除外)应该至少有M/2个子节点。
所有节点(根节点除外)应该至少有M/2-1条数据。
B树的阶数可以帮助我们确定节点在B树中可以容纳的子节点数。如果B树的阶数为3,则子节点的最小数量为2,最大数量为3,节点最多可以存放2个数据。类似地,如果B树的阶数为4,则子节点的最小和最大数量将分别为2和4,节点最多可以存放3个数据。
B树的基本结构:
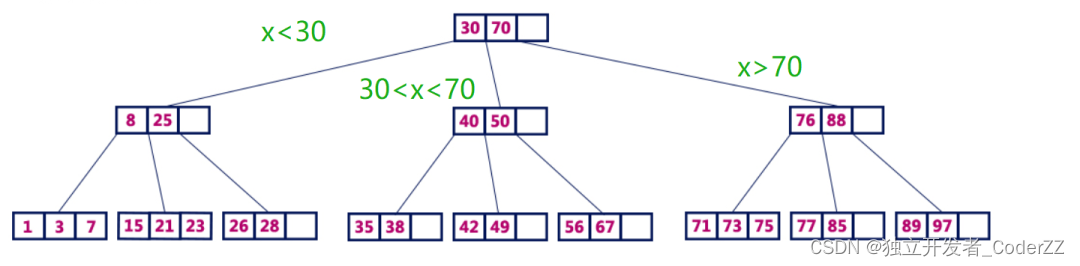
B树的结构特点:
所有叶子节点都出现在同一水平高度。
B树是一棵扁平树,层数很小,B树的节点不再只存储一条数据。
B树节点内的所有数据必须按键值升序排列。
B树的设计原则就是,将尽可能多的数据放入B树的每个节点中,从而使B树的层数保持在最小值。由于不用遍历很多层节点,与其他平衡树相比,B树的访问速度更快。
二,B树的基本操作
搜索节点:
节点在B树中的搜索步骤与BST树中的类似。
插入节点:
如果树为空,则创建一个新节点并将其作为根节点插入到树中。
如果树不为空,插入节点包含两个操作:
1.搜索合适的位置以插入节点
按照升序插入节点。
2.当节点的数据量过大时拆分节点
插入新节点以后,节点中数据的数量超过了限制(节点的最大数据量为M-1),则按中位数拆分。将中间节点推往上一层,使左边节点成为左子节点,右边节点成为右子节点。
图示样例:

三,完整代码实现
C++实现:
- #include
- using namespace std;
- class Node {
- int* keys;
- int t;
- Node** C;
- int n;
- bool leaf;
- public:
- Node(int _t, bool _leaf);
- void insertNonFull(int k);
- void splitChild(int i, Node* y);
- void traverse();
- friend class BTree;
- };
- class BTree {
- Node* root;
- int t;
- public:
- BTree(int _t) {
- root = NULL;
- t = _t;
- }
- void traverse() {
- if (root != NULL)
- root->traverse();
- }
- void insert(int k);
- };
- Node::Node(int t1, bool leaf1) {
- t = t1;
- leaf = leaf1;
- keys = new int[2 * t - 1];
- C = new Node * [2 * t];
- n = 0;
- }
- //遍历节点
- void Node::traverse() {
- int i;
- for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- if (leaf == false)
- C[i]->traverse();
- cout << " " << keys[i];
- }
- if (leaf == false)
- C[i]->traverse();
- }
- void BTree::insert(int k) {
- if (root == NULL) {
- root = new Node(t, true);
- root->keys[0] = k;
- root->n = 1;
- }
- else {
- if (root->n == 2 * t - 1) {
- Node* s = new Node(t, false);
- s->C[0] = root;
- s->splitChild(0, root);
- int i = 0;
- if (s->keys[0] < k)
- i++;
- s->C[i]->insertNonFull(k);
- root = s;
- }
- else
- root->insertNonFull(k);
- }
- }
- void Node::insertNonFull(int k) {
- int i = n - 1;
- if (leaf == true) {
- while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k) {
- keys[i + 1] = keys[i];
- i--;
- }
- keys[i + 1] = k;
- n = n + 1;
- }
- else {
- while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k)
- i--;
- if (C[i + 1]->n == 2 * t - 1) {
- splitChild(i + 1, C[i + 1]);
- if (keys[i + 1] < k)
- i++;
- }
- C[i + 1]->insertNonFull(k);
- }
- }
- //拆分节点
- void Node::splitChild(int i, Node* y) {
- Node* z = new Node(y->t, y->leaf);
- z->n = t - 1;
- for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
- z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + t];
- if (y->leaf == false) {
- for (int j = 0; j < t; j++)
- z->C[j] = y->C[j + t];
- }
- y->n = t - 1;
- for (int j = n; j >= i + 1; j--)
- C[j + 1] = C[j];
- C[i + 1] = z;
- for (int j = n - 1; j >= i; j--)
- keys[j + 1] = keys[j];
- keys[i] = y->keys[t - 1];
- n = n + 1;
- }
- int main() {
- BTree t(3);
- t.insert(8);
- t.insert(9);
- t.insert(10);
- t.insert(11);
- t.insert(15);
- t.insert(20);
- t.insert(17);
- cout << "The B-tree is: ";
- t.traverse();
- }
运行结果:
The B-tree is: 8 9 10 11 15 17 20Python实现:
- class BTreeNode:
- def __init__(self, leaf=False):
- self.leaf = leaf
- self.keys = []
- self.child = []
- class BTree:
- def __init__(self, t):
- self.root = BTreeNode(True)
- self.t = t
- def insert(self, k):
- root = self.root
- if len(root.keys) == (2 * self.t) - 1:
- temp = BTreeNode()
- self.root = temp
- temp.child.insert(0, root)
- self.split_child(temp, 0)
- self.insert_non_full(temp, k)
- else:
- self.insert_non_full(root, k)
- def insert_non_full(self, x, k):
- i = len(x.keys) - 1
- if x.leaf:
- x.keys.append((None, None))
- while i >= 0 and k[0] < x.keys[i][0]:
- x.keys[i + 1] = x.keys[i]
- i -= 1
- x.keys[i + 1] = k
- else:
- while i >= 0 and k[0] < x.keys[i][0]:
- i -= 1
- i += 1
- if len(x.child[i].keys) == (2 * self.t) - 1:
- self.split_child(x, i)
- if k[0] > x.keys[i][0]:
- i += 1
- self.insert_non_full(x.child[i], k)
- def split_child(self, x, i):
- t = self.t
- y = x.child[i]
- z = BTreeNode(y.leaf)
- x.child.insert(i + 1, z)
- x.keys.insert(i, y.keys[t - 1])
- z.keys = y.keys[t: (2 * t) - 1]
- y.keys = y.keys[0: t - 1]
- if not y.leaf:
- z.child = y.child[t: 2 * t]
- y.child = y.child[0: t - 1]
- def print_tree(self, x, l=0):
- print("Level ", l, " ", len(x.keys), end=":")
- for i in x.keys:
- print(i, end=" ")
- print()
- l += 1
- if len(x.child) > 0:
- for i in x.child:
- self.print_tree(i, l)
- def main():
- B = BTree(3)
- for i in range(10):
- B.insert((i, 2 * i))
- B.print_tree(B.root)
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
四,参考阅读
https://iq.opengenus.org/b-tree-searching-insertion/
https://www.programiz.com/dsa/insertion-into-a-b-tree
https://www.programiz.com/dsa/b-plus-tree
-
相关阅读:
C 语言函数
adb 获取 Android 设备中已安装的 apk 文件
MISC驱动
java综合布线设备管理系统的研究与实现
Spring Boot: Lombok 注解原理分析及实践
SparkSQL---简介及RDD V.S DataFrame V.S Dataset编程模型详解
多个电商平台API接口聚合解析,实现根据关键词取商品列表
springCloud在pom中快速修改运行环境,让配置不再繁琐
基于STM32智能环境系统
数字政府!3DCAT实时云渲染助推上海湾区数字孪生平台
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/CoderZZ_2024/article/details/136521785
