-
顺序表漫谈

目录
1.线性表
- 线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
- 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表有:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
- 线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。

2.顺序表
2.1概念及结构
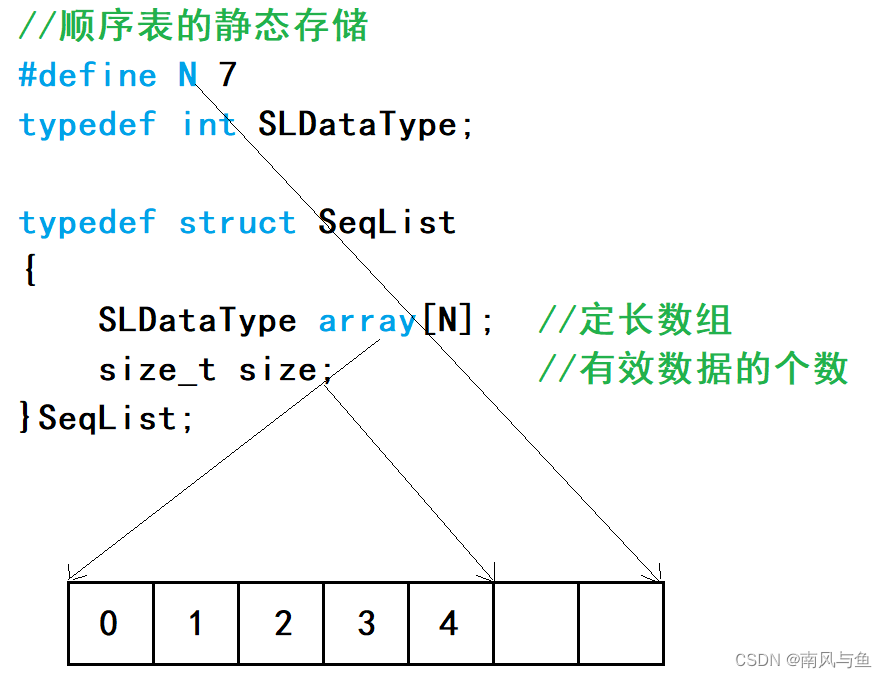
顺序表是一种线性表的实现方式,它通过一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素,数据元素之间的逻辑关系通过元素在内存中的相对位置来表示,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表简单来说就是一个数组,它和数组的唯一区别就是里边的数据只能从头开始连续存储。
🌵顺序表一般可以分为:
1.静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素
2.动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储元素
2.2接口实现
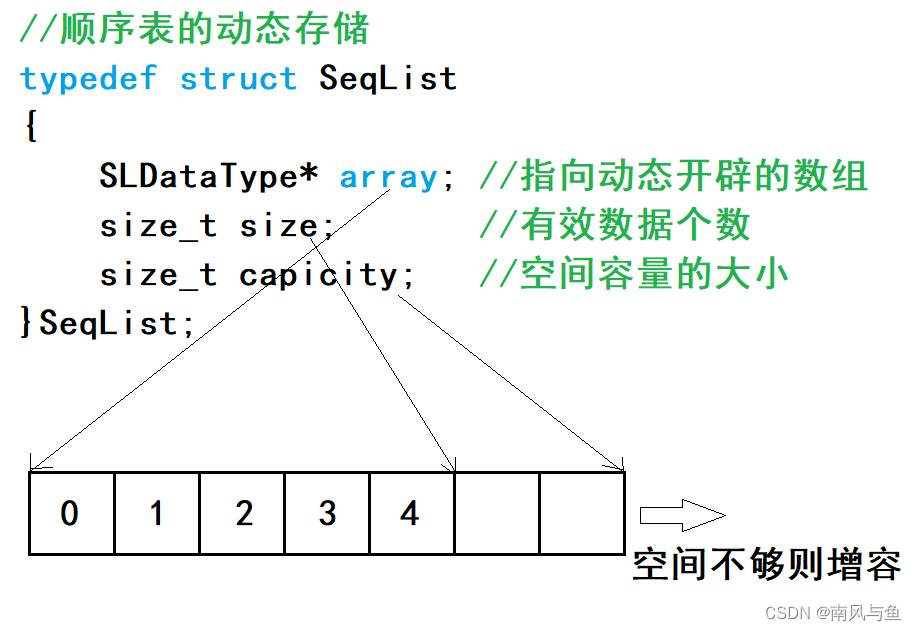
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存储数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间大小,所以下面我们实现动态顺序表。
1.顺序表的动态存储
要实现动态的顺序表,我们首先得有一个指向数组的指针,因为内存是malloc或者realloc出来的。还得有一个size,知道到底存了多少个数据,以及得有一个capacity,用来记录空间容量。
- typedef int SLDataType;
- typedef struct SeqList
- {
- assert(psl);
- SLDataType* arr; //指向动态开辟的数组
- int size; //有效数据个数,看作下标时,它指向最后一个数据的下一个位置
- int capacity; //空间容量
- }SeqList;
2.顺序表初始化
因为形参是实参的一份临时拷贝,改变形参的值不会影响实参,所以传值的时候要传地址,形参用指针接收。
- //顺序表初始化
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- psl->arr = NULL;
- psl->size = 0;
- psl->capacity = 0;
- }
3.顺序表销毁
- //顺序表销毁
- void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- if (psl->arr != NULL)
- {
- free(psl->arr);
- psl->arr = NULL;
- psl->size = 0;
- psl->capacity = 0;
- }
- }
4.顺序表增容
即检查空间,如果满了,就进行增容。因为头插和尾插都需要增容,所以我们把它成一个公共的函数,方便管理。 关于动态内存开辟有不清楚的铁子们可以看这篇博客:动态内存管理详解
- //增容
- void SeqListCheckCapacity(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
- {
- int newCapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2;
- //防止扩容失败将原来的空间给覆盖掉,所以用一个临时变量来接收
- SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->arr, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc");
- return;
- }
- psl->arr = tmp;
- psl->capacity = newCapacity;
- }
- }
5.顺序表头插
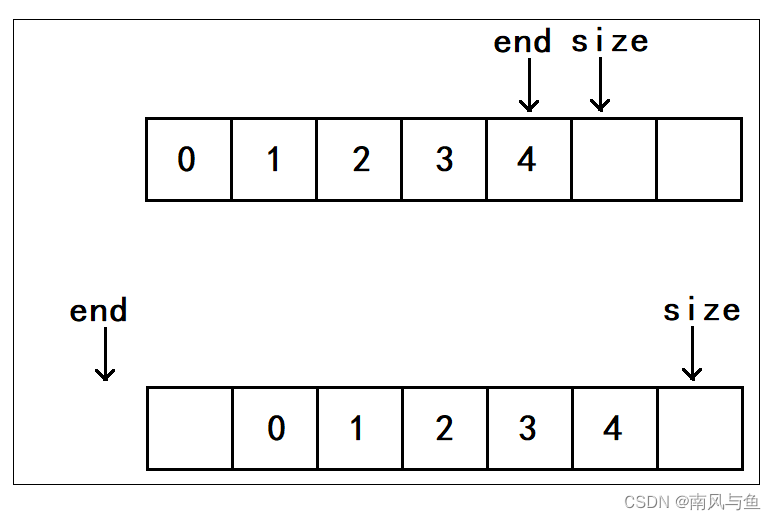
要想在头部插入数据,必须将所有的数据先向后挪动一个位置,然后将要插入的数据放在第一个位置。我们可以先定义一个变量end,让它等于最后一个数据,然后利用while循环将所有的数据向后挪动一个位置,再将数据插入头部,然后让数据个数size+1。
- //头插
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- SeqListCheckCapacity(psl);
- //挪动数据
- int end = psl->size - 1;
- while (end >= 0)
- {
- psl->arr[end + 1] = psl->arr[end];
- end--;
- }
- psl->arr[0] = x;
- psl->size++;
- }

6.顺序表尾插
尾插相对来说比较简单,如果空间不够,增容之后直接将要插入的数据放在尾部即可,然后将数据个数size+1。
- //尾插
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- //增容
- SeqListCheckCapacity(psl);
- psl->arr[psl->size] = x;
- psl->size++;
- }

7.顺序表头删
头删时我们采用的方法还是挪动数据,但是要从前面开始挪动,因为如果从后往前挪的话会将前面的数据给覆盖掉。先定义一个变量begin,让它等于1,然后利用while循环将所有的数据向前挪动一个位置(让后一个数据将前一个数据覆盖掉),直到begin小于size就跳出循环,然后让数据个数size-1。

- //头删
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- //暴力检查
- assert(psl->size);
- int begin = 1;
- while (begin < psl->size)
- {
- psl->arr[begin - 1] = psl->arr[begin];
- begin++;
- }
- psl->size--;
- }
8.顺序表尾删
尾删时我们只需让有效数据 size-- 就行,但是必须进行检查看顺序表是否为空,因为如果为空,后面我们在头插时就会出现问题。
- //尾删
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- //若顺序表为空,则进行检查
- //温柔的检查
- /*if (psl->size == 0)
- {
- return;
- }*/
- //暴力检查
- assert(psl->size > 0);
- psl->size--;
- }
9.顺序表打印
- //顺序表打印
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
- {
- printf("%d ", psl->arr[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
10.顺序表在任意下标位置插入数据
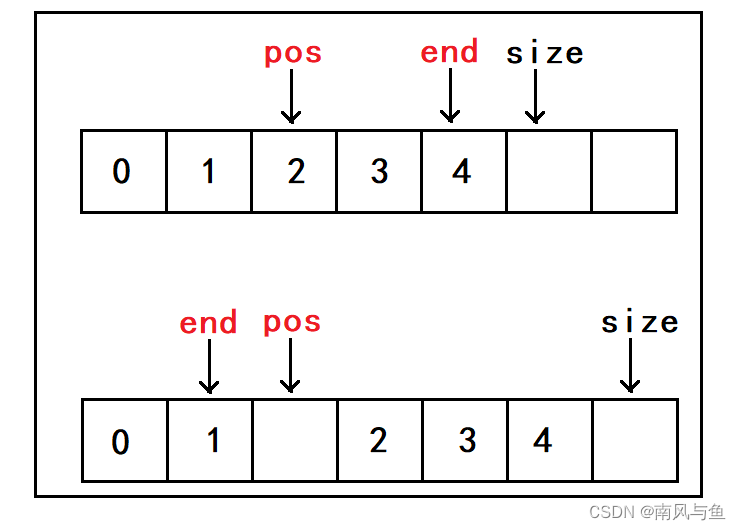
首先要保证指针不为空以及pos位置的合法性。然后定义变量end,让它指向最后一个数据的位置,通过while循环将 pos到end 位置的值向后挪动一个位置,将要插入的数据放入pos位置,再将size+1。
- //顺序表在任意下标位置插入数据
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, int pos, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
- int end = psl->size - 1;
- while (end >= pos)
- {
- psl->arr[end + 1] = psl->arr[end];
- end--;
- }
- psl->arr[pos] = x;
- psl->size++;
- }

11.顺序表删除任意下标位置的值
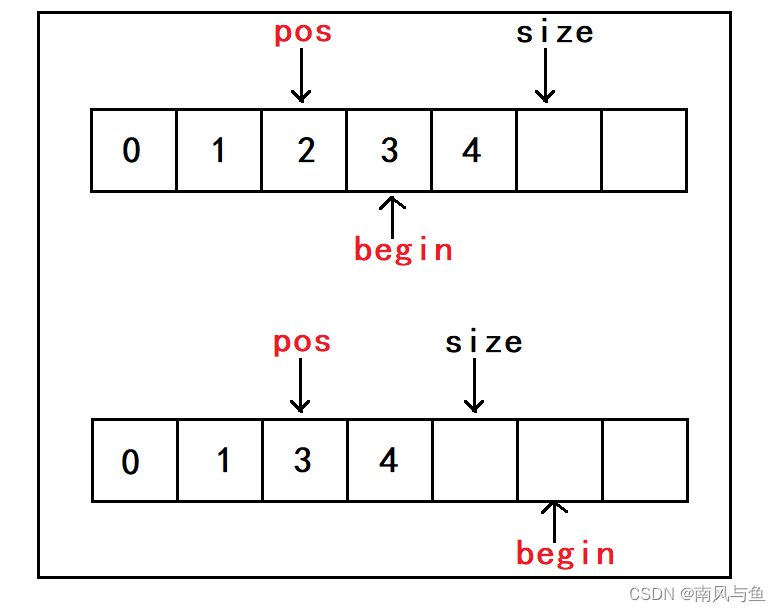
- //顺序表删除任意下标位置的值
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, int pos)
- {
- assert(psl);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos < psl->size);
- //挪动数据
- int begin = pos + 1;
- while (begin < psl->size)
- {
- psl->arr[begin - 1] = psl->arr[begin];
- begin++;
- }
- psl->size--;
- }

12.顺序表查找
在顺序表中查找数据,如果找到了,就返回下标;如果没有找到,则返回-1。
- //顺序表查找
- int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
- {
- if (psl->arr[i] == x)
- {
- return i;
- break;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
2.3菜单
- void menu()
- {
- printf("*************************************\n");
- printf("*** 1.头插数据 2.尾插数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 3.头删数据 4.尾删数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 5.查找数据 6.打印顺序表 ***\n");
- printf("*** 7.在任意下标位置插入数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 8.删除任意下标位置的数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 0.退出系统 ***\n");
- printf("*************************************\n");
- }
- void Test()
- {
- SeqList sl;
- SeqListInit(&sl);//初始化
- int x = 0, pos = 0;
- int input = 0;
- do
- {
- printf("欢迎来到顺序表系统!\n");
- menu();
- printf("请输入你的选择:>");
- scanf("%d", &input);
- switch (input)
- {
- case 1:
- printf("请输入你要头插的数据:\n");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- SeqListPushFront(&sl, x);
- printf("头插成功!\n");
- break;
- case 2:
- printf("请输入你要尾插的数据:\n");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- SeqListPushBack(&sl, x);
- printf("尾插成功!\n");
- break;
- case 3:
- SeqListPopFront(&sl);
- printf("头删成功!\n");
- break;
- case 4:
- SeqListPopBack(&sl);
- printf("尾删成功!\n");
- break;
- case 5:
- printf("请输入你要查找的数据(查找成功则返回下标, 负责返回-1):\n");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- int pos = SeqListFind(&sl, x);
- printf("%d\n", pos);
- break;
- case 6:
- printf("顺序表目前的数据为:\n");
- SeqListPrint(&sl);
- break;
- case 7:
- printf("请输入你要插入的数据:");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- printf("请输入你要插入数据的下标(下标从0开始):");
- scanf("%d", &pos);
- SeqListInsert(&sl, pos, x);
- printf("插入数据成功!\n");
- break;
- case 8:
- printf("请输入你要删除数据的下标:");
- scanf("%d", &pos);
- SeqListErase(&sl, pos);
- printf("删除成功!\n");
- break;
- case 0:
- printf("退出系统!\n");
- break;
- default:
- printf("选择错误,请重新选择!\n");
- break;
- }
- } while (input);
- SeqListDestory(&sl);//销毁
- }
3.源码
🌻test.c
- #include "SeqList.h"
- void menu()
- {
- printf("*************************************\n");
- printf("*** 1.头插数据 2.尾插数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 3.头删数据 4.尾删数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 5.查找数据 6.打印顺序表 ***\n");
- printf("*** 7.在任意下标位置插入数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 8.删除任意下标位置的数据 ***\n");
- printf("*** 0.退出系统 ***\n");
- printf("*************************************\n");
- }
- void Test()
- {
- SeqList sl;
- SeqListInit(&sl);
- int x = 0, pos = 0;
- int input = 0;
- do
- {
- printf("欢迎来到顺序表系统!\n");
- menu();
- printf("请输入你的选择:>");
- scanf("%d", &input);
- switch (input)
- {
- case 1:
- printf("请输入你要头插的数据:\n");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- SeqListPushFront(&sl, x);
- printf("头插成功!\n");
- break;
- case 2:
- printf("请输入你要尾插的数据:\n");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- SeqListPushBack(&sl, x);
- printf("尾插成功!\n");
- break;
- case 3:
- SeqListPopFront(&sl);
- printf("头删成功!\n");
- break;
- case 4:
- SeqListPopBack(&sl);
- printf("尾删成功!\n");
- break;
- case 5:
- printf("请输入你要查找的数据(查找成功则返回下标, 负责返回-1):\n");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- int pos = SeqListFind(&sl, x);
- printf("%d\n", pos);
- break;
- case 6:
- printf("顺序表目前的数据为:\n");
- SeqListPrint(&sl);
- break;
- case 7:
- printf("请输入你要插入的数据:");
- scanf("%d", &x);
- printf("请输入你要插入数据的下标(下标从0开始):");
- scanf("%d", &pos);
- SeqListInsert(&sl, pos, x);
- printf("插入数据成功!\n");
- break;
- case 8:
- printf("请输入你要删除数据的下标:");
- scanf("%d", &pos);
- SeqListErase(&sl, pos);
- printf("删除成功!\n");
- break;
- case 0:
- printf("退出系统!\n");
- break;
- default:
- printf("选择错误,请重新选择!\n");
- break;
- }
- } while (input);
- SeqListDestory(&sl);
- }
- int main()
- {
- Test();
- return 0;
- }
🌻SeqList.h
- #pragma once
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int SLDataType;
- typedef struct SeqList
- {
- SLDataType* arr;//指向动态开辟的数组
- int size; //有效数据
- int capacity; //空间容量
- }SeqList;
- //顺序表初始化
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl);
- //顺序表销毁
- void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl);
- //顺序表打印
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl);
- //增容
- void SeqListCheckCapacity(SeqList* psl);
- //头插
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
- //尾插
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
- //头删
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl);
- //尾删
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl);
- //顺序表在任意位置插入数据
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, int pos, SLDataType x);
- //顺序表删除任意位置的值
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, int pos);
- //顺序表查找
- int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
🌻SeqList.c
- #include "SeqList.h"
- //顺序表初始化
- void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- psl->arr = NULL;
- psl->size = 0;
- psl->capacity = 0;
- }
- //顺序表销毁
- void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- if (psl->arr != NULL)
- {
- free(psl->arr);
- psl->arr = NULL;
- psl->size = 0;
- psl->capacity = 0;
- }
- }
- //顺序表打印
- void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
- {
- printf("%d ", psl->arr[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- //增容
- void SeqListCheckCapacity(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
- {
- int newCapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2;
- //防止扩容失败将原来的空间给覆盖掉,所以用一个临时变量来接收
- SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->arr, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc");
- return;
- }
- psl->arr = tmp;
- psl->capacity = newCapacity;
- }
- }
- //头插
- void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- SeqListCheckCapacity(psl);
- //挪动数据
- int end = psl->size - 1;
- while (end >= 0)
- {
- psl->arr[end + 1] = psl->arr[end];
- end--;
- }
- psl->arr[0] = x;
- psl->size++;
- }
- //尾插
- void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- //增容
- SeqListCheckCapacity(psl);
- psl->arr[psl->size] = x;
- psl->size++;
- }
- //头删
- void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- //暴力检查
- assert(psl->size);
- int begin = 1;
- while (begin < psl->size)
- {
- psl->arr[begin - 1] = psl->arr[begin];
- begin++;
- }
- psl->size--;
- }
- //尾删
- void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl)
- {
- assert(psl);
- //若顺序表为空,则进行检查
- //温柔的检查
- /*if (psl->size == 0)
- {
- return;
- }*/
- //暴力检查
- assert(psl->size);
- psl->size--;
- }
- //顺序表在任意下标位置插入数据
- void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, int pos, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
- int end = psl->size - 1;
- while (end >= pos)
- {
- psl->arr[end + 1] = psl->arr[end];
- end--;
- }
- psl->arr[pos] = x;
- psl->size++;
- }
- //顺序表删除任意下标位置的值
- void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, int pos)
- {
- assert(psl);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos < psl->size);
- int begin = pos + 1;
- while (begin < psl->size)
- {
- psl->arr[begin - 1] = psl->arr[begin];
- begin++;
- }
- psl->size--;
- }
- //顺序表查找
- int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(psl);
- for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
- {
- if (psl->arr[i] == x)
- {
- return i;
- break;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
-
相关阅读:
【附源码】计算机毕业设计SSM体育场馆预定网站
Pygame中Sprite的使用方法6-4
【Rust日报】2023-10-10 使用 Cackle 抵御 Rust 供应链攻击
DockerCompose
泛型与反射,看这篇就够了
SpringBoot工程启动顺序以及自定义监听
java计算机毕业设计高校实习实训管理系统源码+mysql数据库+系统+lw文档+部署
Java 集合的常用操作(ArrayList, LinkedList, HashSet, HashMap)
3_服务调用_resttemplate_feign
win10更新错误0x800f0922的解决方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_65931202/article/details/136177367
