-
数据结构之队列
💕"
开朗些,勇敢些
"💕

 作者:Mylvzi
作者:Mylvzi 
 文章主要内容:数据结构之队列及其面试题
文章主要内容:数据结构之队列及其面试题 

一.队列
1.概念
队列:只允许在一端进行数据的插入(队尾),在另一端进行数据的删除(队头)的特殊线性表,和栈不同的是,队列具有先进先出的特性(FIFO)
2.java中的队列
Java中队列是一个接口,底层是通过链表实现的;既然是接口,就不能直接实例化对象,要利用实现queue接口的类去实例化对象
源码

二.队列的模拟实现
队列的底层是是LinkdList,所以可以使用双向链表实现队列

- /**
- * 实现队尾进,队头出
- */
- public void offer(int x) {
- ListNode node = new ListNode(x);
- if (rear == null) {
- front = rear = node;
- this.usedSize++;
- return;
- }
- rear.next = node;
- node.prev = rear;
- rear = node;
- this.usedSize++;
- }
- public int poll() {
- if (front == null) {
- throw new QueueEmptyException("队列为空,无法返回数据");
- }
- int ret = front.val;
- // 如果只有一个节点 要把front和rear都置空 否则在执行front.prev = null这句代码时会报错
- if (front.next == null) {
- front = null;
- rear = null;
- return ret;
- }
- front = front.next;
- front.prev = null;
- this.usedSize--;
- return ret;
- }
- public int peek() {
- if (front == null) {
- throw new QueueEmptyException("队列为空,无法返回数据");
- }
- int ret = front.val;
- return ret;
- }
- public int size() {
- return this.usedSize;
- }
- public boolean empty() {
- return this.usedSize==0;
- }
- }
3.Deque
Deque也是Java中和队列有关的数据结构,它是一种双端队列,即队头,队尾都可以实现数据插入与删除,deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称。同时Deque也是Java中最常用的queue结构
源码:

4.循环队列的实现
所谓循环队列就是front和rear一直在绕着圆走,和普通队列不一样的是,它可以重复利用空间
循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
一般的队列

循环队列

循环队列的难点在于如何判满,这里我们提供两种方法
循环队列的实现1:使用计数器
- class MyCircularQueue {
- private int[] elem;
- private int front;
- private int rear;
- private int cnt = 0;
- public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
- this.elem = new int[k];
- }
- public boolean enQueue(int value) {
- // 插入数据
- if(isFull()) {
- return false;
- }
- this.elem[rear] = value;
- rear = (rear+1) % elem.length;
- cnt++;
- return true;
- }
- public boolean deQueue() {
- if(isEmpty()) {
- return false;
- }
- front = (front+1) % elem.length;
- cnt--;
- return true;
- }
- public int Front() {
- if(isEmpty()) {
- return -1;
- }
- return this.elem[front];
- }
- public int Rear() {
- if (isEmpty()) {
- return -1;
- }
- int index = (rear == 0) ? (elem.length-1) : (rear-1);
- return this.elem[index];
- }
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return cnt == 0;
- }
- public boolean isFull() {
- return cnt == this.elem.length;
- }
- }
循环队列的实现2:预留一个空间

- class MyCircularQueue {
- private int[] elem;
- private int front;
- private int rear;
- public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
- this.elem = new int[k+1];
- }
- public boolean enQueue(int value) {
- // 插入数据
- if(isFull()) {
- return false;
- }
- this.elem[rear] = value;
- rear = (rear+1) % elem.length;
- return true;
- }
- public boolean deQueue() {
- if(isEmpty()) {
- return false;
- }
- front = (front+1) % elem.length;
- return true;
- }
- public int Front() {
- if(isEmpty()) {
- return -1;
- }
- return this.elem[front];
- }
- public int Rear() {
- if(isEmpty()) {
- return -1;
- }
- int index = (rear == 0) ? (elem.length-1) : (rear-1);
- return this.elem[index];
- }
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return rear == front;
- }
- public boolean isFull() {
- return (rear+1) % elem.length == front;
- }
- }
注意:为了实现循环,rear和front的变化不能直接写成rear++或者front++,否则会发生越界
rear = (rear+1) % elem.length;
front = (front+1) % elem.length;
用队列实现栈
1.使用两个队列
利用两个队列实现栈
如果是入栈,入到不为空的队列之中
如果是出栈,先找到不为空的队列,将队尾之前的所有元素出到另一个队列之中,最后再出队尾元素,实现后进先出
如果是返回栈顶元素,和出栈的思路一样,栈顶就是不为空队列的队尾
栈为空:当两个队列都为空时,栈为空
- /**
- * 用队列实现栈 使用两个队列实现栈
- * 队列:先进先出 栈:后进先出
- * 要明白,一个队列无法实现栈,他们有本质上的区别
- * 入栈:入到不为空的队列之中 如果两个都为空,入到第一个队列之中
- * 出栈:出栈顶元素,后进先出 对应的是队列中的队尾元素 将队尾元素之前的所有元素转移到另一个队列之中,再返回队尾元素
- */
- class MyStack2 {
- private Queue
que1; - private Queue
que2; - public MyStack2() {
- this.que1 = new LinkedList<>();
- this.que2 = new LinkedList<>();
- }
- public void push(int x) {
- // 入栈到不为空的队列之中
- if(!que1.isEmpty()) {
- que1.offer(x);
- } else if (!que2.isEmpty()) {
- que2.offer(x);
- }else {
- que1.offer(x);
- }
- }
- public int pop() {
- // 出栈
- // 为空 直接返回
- if (empty()) {
- return -1;
- }
- if (!que1.isEmpty()) {
- int size = que1.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
- // 将que1队尾元素前面的所有元素转移到que2中
- que2.offer(que1.poll());
- }
- return que1.poll();
- } else {
- int size = que2.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
- // 将que2队尾元素前面的所有元素转移到que1中
- que1.offer(que2.poll());
- }
- return que2.poll();
- }
- }
- public int top() {
- // 为空 直接返回
- if (empty()) {
- return -1;
- }
- int tmp = -1;
- if (!que1.isEmpty()) {
- int size = que1.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- // 将que1队尾元素前面的所有元素转移到que2中
- tmp = que1.poll();
- que2.offer(tmp);
- }
- return tmp;
- } else {
- int size = que2.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
- // 将que2队尾元素前面的所有元素转移到que1中
- tmp = que2.poll();
- que1.offer(tmp);
- }
- return tmp;
- }
- }
- public boolean empty() {
- // 当两个队列都为空时,栈就为空
- return que1.isEmpty() && que2.isEmpty();
- }
- }
2.使用一个队列
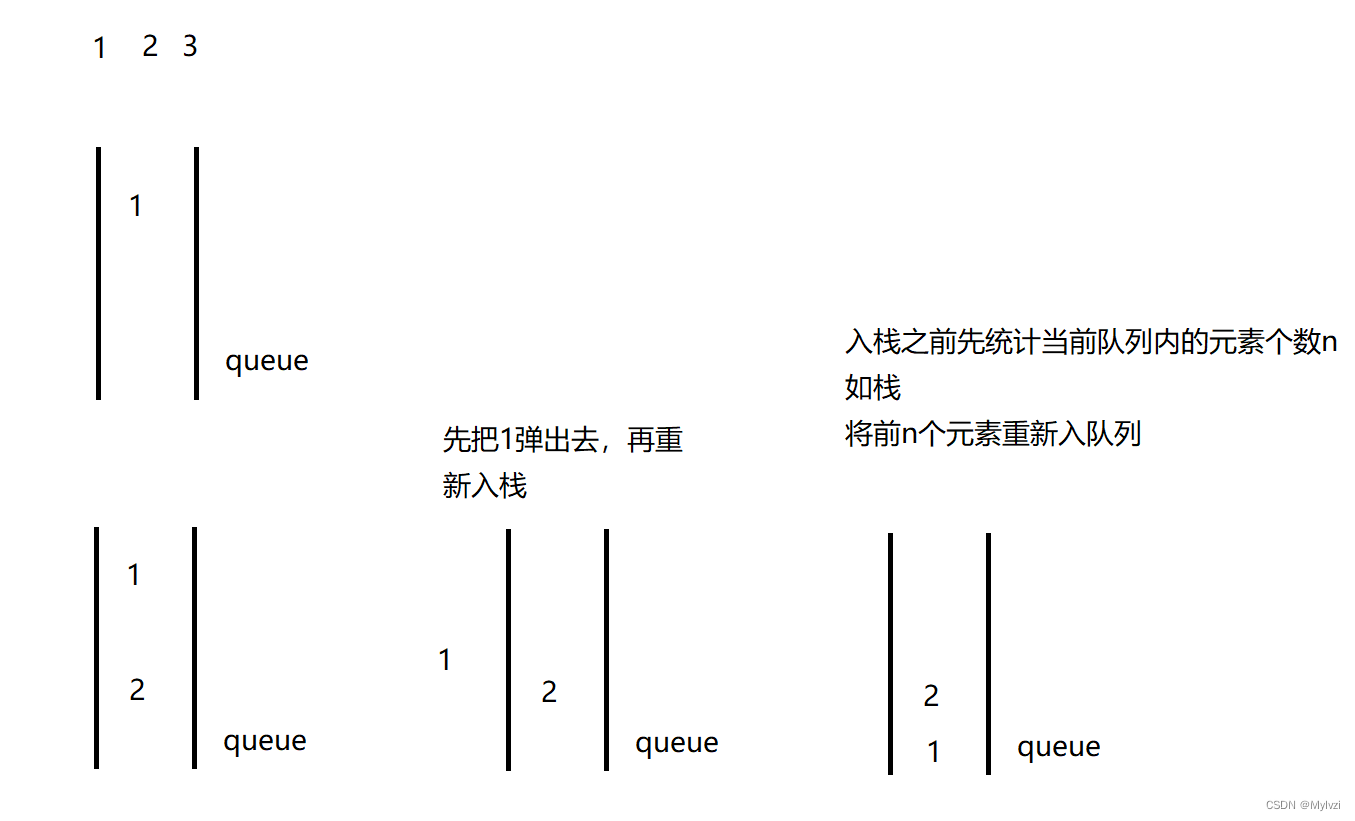
- /**
- * 思路2:使用一个队列实现栈
- * 栈:后进先出 队列:先进后出
- * 保证队头的元素时最后一个入栈的
- * 新入一个元素的时候将之前所有元素都poll出去,再重新入队,那么新元素就是队头了
- * 这样就实现了后进先出
- */
- class MyStack2 {
- Queue
queue; - public MyStack2() {
- this.queue = new LinkedList<>();
- }
- public void push(int x) {
- int n = queue.size();
- queue.offer(x);
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- // 重新入队
- queue.offer(queue.poll());
- // int ret = queue.poll();
- // queue.offer(ret);
- }
- }
- public int pop() {
- return queue.poll();
- }
- public int top() {
- return queue.peek();
- }
- public boolean empty() {
- return queue.isEmpty();
- }
- }
可以带入数据尝试一下 之所以需要%N,是因为rear有可能处于下标为0的位置

-
相关阅读:
【CSS】笔记4-浮动
selenium 实现自动登录功能【Use 缓存】
1688代采系统:解决全球化采购难题的技术创新
React脚手架介绍和Demo
九、计算机视觉-形态学基础概念
【机器学习】21天挑战赛学习/论文总结(第二周)
Charles 抓包工具教程(二) Charles 抓包HTTPS请求
如何学习存储性系统
day41
【C语言_文件_进程_进程间通讯 常用函数/命令 + 实例】.md_update:23/10/27
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Mylvzi/article/details/134531373
