-
Java基础(程序控制结构篇)
Java的程序控制结构与C语言一致,分为顺序结构、选择结构(分支结构)和循环结构三种。
一、顺序结构
如果程序不包含选择结构或是循环结构,那么程序中的语句就是顺序的逐条执行,这就是顺序结构。
import java.util.Scanner; public class SequenceConstruct{ public static void main(String[] args){ //以下就使程序的顺序结构 //语句是从上到下逐个执行的,没有跳转 int a = 10; char b = 'a'; double c = 1.23; String str = ""; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入一句话:"); str = scanner.next(); System.out.println(str); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
二、选择结构
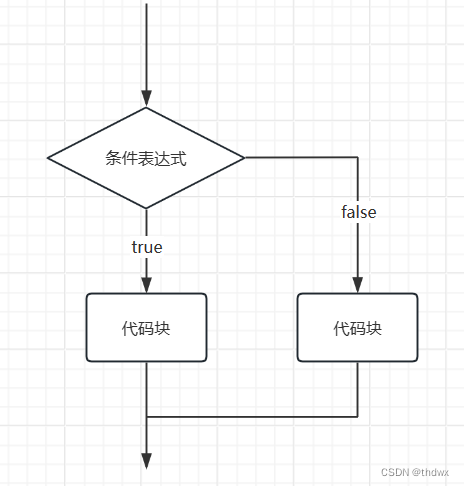
1. if-else
在if-else分支结构中,else会与上方最近的if匹配。
1.1 单分支

//单分支 import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectConstruct01{ public static void main(String[] args){ String str = ""; System.out.println("请输入一个名字:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); str = scanner.next(); if("jack".equals(str)) System.out.println("你输入的名字是jack"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

1.2 双分支
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectConstruct02{ public static void main(String[] args){ //双分支 // System.out.print("请输入你的名字:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scanner.next(); if("jack".equals(name)) System.out.println("你的名字是jack"); else System.out.println("你的名字不是jack"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23

1.3 多分支
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectConstruct03{ public static void main(String[] args){ //多分支 //输入保国同志的芝麻信用分: // 如果: // 1) 信用分为 100 分时,输出 信用极好; // 2) 信用分为(80,99]时,输出 信用优秀; // 韩顺平循序渐进学 Java 零基础 // 第 100页 // 3) 信用分为[60,80]时,输出 信用一般; // 4) 其它情况 ,输出 信用 不及格 // 5) 请从键盘输入保国的芝麻信用分,并加以判断 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入信用分:"); int score = scanner.nextInt(); if(score > 100 || score < 0) System.out.println("信用分输入有误!"); else if(score == 100) System.out.println("信用极好"); else if(score > 80) System.out.println("信用优秀"); else if(score >= 60) System.out.println("信用一般"); else System.out.println("信用不及格"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
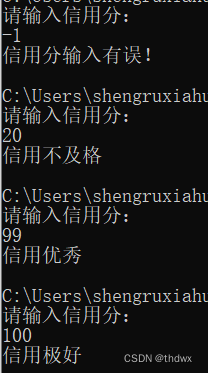
1.4 嵌套分支
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectConstruct04{ public static void main(String[] args){ //嵌套分支 //在一个分支结构中嵌套了另一个分支结构 //参加歌手比赛,如果初赛成绩大于 8.0 进入决赛,否则提示淘汰。 //并且根据性别提示进入男子组或女子组。 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入初赛成绩:"); double score = scanner.nextDouble(); System.out.print("请输入性别:"); char sex = scanner.next().charAt(0); if(score > 8.0) if(sex == '男') System.out.println("进入男子组"); else if(sex == '女') System.out.println("进入女子组"); else System.out.println("性别输入有误"); else System.out.println("淘汰"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30

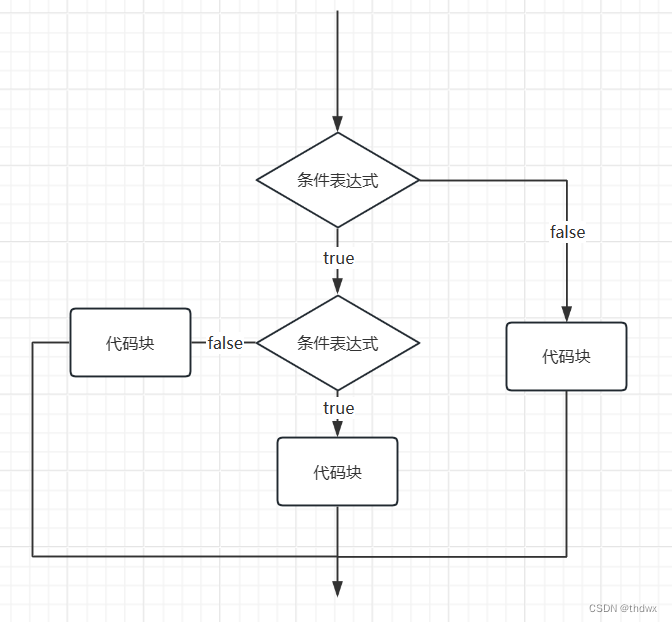
2. switch
- switch括号中的表达式结果类型必须是(byte,short,int,char,enum,String)中的一种。
- case后的常量类型必须与switch括号中表达式结果的类型一致,或是可以自动转换(switch括号中的类型转换成case关键字后的类型)成可以比较的类型。
- case后必须是常量,不能是变量。
- default是可选的。
- break用于跳出当前switch语句块,如果没有break关键字,那么就会发生穿透,语句会一直执行到switch语句块的末尾或是遇到break。
import java.util.Scanner; public class SwitchStructrue{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean flag = true; while(flag){ System.out.println("输入1表示退出循环:"); if(scanner.nextInt() == 1){ flag = false; continue; } System.out.print("输入一个字符(a-g):"); char input = scanner.next().charAt(0); switch(input){ case 'a': System.out.println("Monday"); break; case 'b': System.out.println("Tuesday"); break; case 'c': System.out.println("Wensday"); break; case 'd': System.out.println("Thursday"); break; case 'e': System.out.println("Friday"); break; case 'f': System.out.println("Saturday"); break; case 'g': System.out.println("Sunday"); break; default: System.out.println("error,please input again"); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41

3. switch与if-else的比较
- 如果判断的数值不多,并且是固定不变的,例如星期、月份等内容,推荐使用switch。
- 对区间的判断,结果为boolean类型的判断等,使用if-else。
三、循环结构
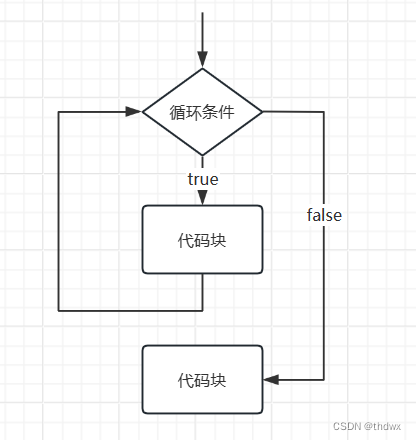
1. for循环
for循环的结构:for(循环变量初始化;循环条件;循环变量迭代){循环体}.可以一次性初始化多个变量(用逗号隔开),但是它们的类型要一致,循环变量的迭代处也可以有多条语句(用逗号隔开)。
public class ForStructrue{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){ String str = j + "*" + i + " = " + i * j; System.out.print(str + " "); } System.out.println(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
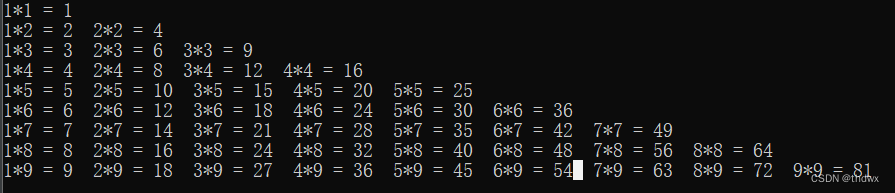
2. while循环
while循环的结构:while(循环条件){循环体}.

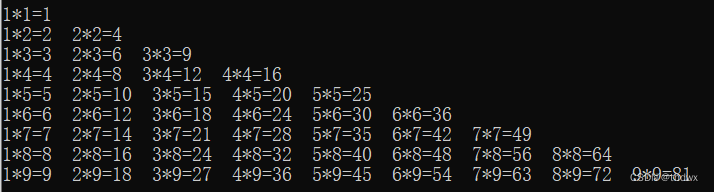
public class WhileStructrue{ public static void main(String[] rags){ int i = 1, j = 1; while(i <= 9){ j = 1; while(j <= i){ System.out.print(j+"*"+i+"="+i*j+" "); j++; } System.out.println(); i++; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
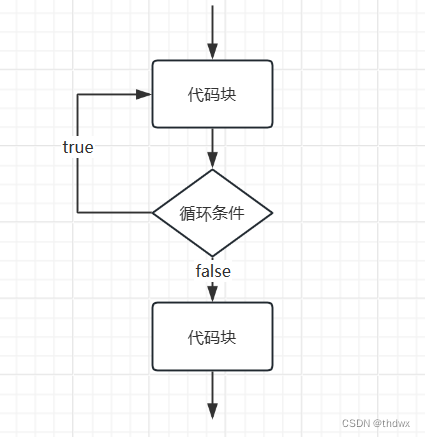
3. dowhile循环
dowhile循环与while循环基本一样,除了当初始条件不满足时,dowhile会执行一次,而while一次都不会执行。注意while括号后有分号。
public class DoWhileStructrue{ public static void main(String[] args){ boolean flag = false; while(flag){ System.out.println("This is while"); } do{ System.out.println("This is dowhile"); }while(flag); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
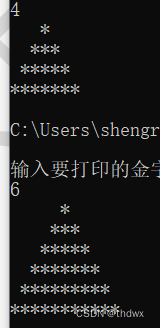
4. 多重循环
多重循环就是一层循环为另一个循环的循环体,打印乘法表就需要使用多重循环来完成,下面使用多重循环打印金字塔。
import java.util.Scanner; public class MulCirculation{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("输入要打印的金字塔规模:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int num = scanner.nextInt(); for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++){ int j = 0; while(j < num - i){ System.out.print(" "); j++; } for(j = 0; j < 2 * i - 1; j++){ System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
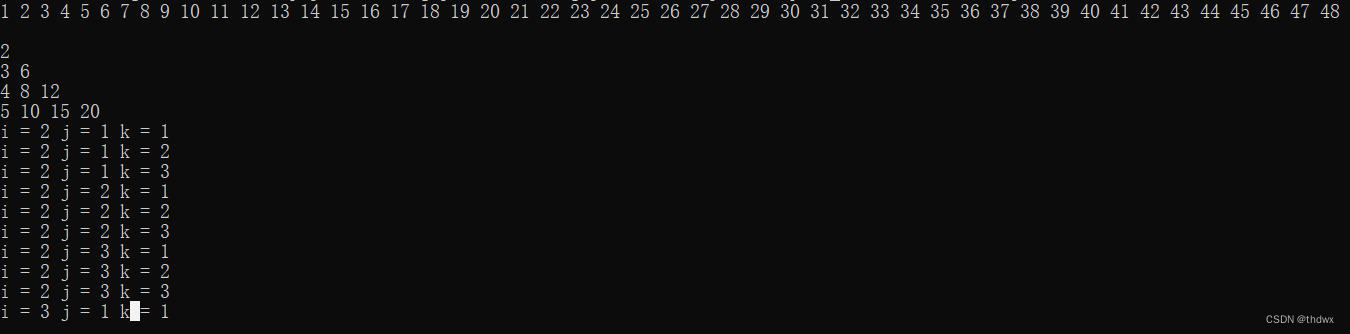
5. break关键字
用于跳出当前层循环语句或跳出switch语句块。可以使用标签来指定跳出哪一层循环(尽量不要使用标签)。
public class BreakTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){ if(i == 49) break; System.out.print(i + " "); } System.out.println(); for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= 5; j++){ if(j == i) break; System.out.print(i*j+" "); } System.out.println(); } circulation1: for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ circulation2: for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++){ circulation3: for(int k = 1; k <= 3; k++){ if(i == 1){ break circulation2; } System.out.println("i = " + i + " j = " + j + " k = " + k); if(i == 3) break circulation1; } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
6. continue关键字
用于跳过本次迭代时continue关键字之后的所有语句,并进行下一次迭代,但不会跳过for循环中循环变量的迭代语句。可以使用标签指定层次。
public class ContinueTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++){ if(i == j) continue; System.out.print("i = " + i + " j = " + j + " "); } System.out.println(); } circulation1: for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){ circulation2: for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++){ circulation3: for(int k = 1; k <= 3; k++){ if(i == 2) continue circulation1; if(j == 1) continue circulation2; System.out.print("i = " + i + " j = " + j + " k = " + k + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

7. return关键字
return关键字用于跳出所在方法。
public class ReturnTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i = 1; while(i <= 10){ if(i == 6) return; System.out.println("i = " + i++); } System.out.println("在main方法中"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

-
相关阅读:
分布式存储系统Ceph应用详解
超详细教程:在Blender中打造毛毡风格角色
HTML5网页设计成品:汽车介绍特斯拉 (dreamweaver作业静态HTML网页设计模板)
IPv6的主要优势有哪些?
改进YOLOv8:结合ConvNeXt V2骨干网络!使用MAE共同设计和扩展ConvNet
Spring WebFlux使用函数式编程模型构建异步非阻塞服务
seata分布式事务1.4版本TM注册全局事务之源码分析(五)
【HuggingFace文档学习】Bert的token分类与句分类
shell统计每一行字符数的三种方法
虚拟机基本使用 IV
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/thdwx/article/details/134550357
