-
Java-认识String类
本章重点:
1. 认识 String 类
2. 了解 String 类的基本用法
3. 熟练掌握 String 类的常见操作
4. 认识字符串常量池
5. 认识 StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder
1.String类的重要性
在C语言中已经涉及到字符串了,但是在C语言中要表示字符串只能使用字符数组或者字符指针,可以使用标准库提 供的字符串系列函数完成大部分操作,但是这种将数据和操作数据方法分离开的方式不符合面相对象的思想,而字 符串应用又非常广泛,因此Java语言专门提供了String类。
2.常用方法
2.1 字符串构造
以下是常用的三种:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // 使用常量串构造
- String s1 = "hello xiaofan";
- System.out.println(s1);
- // 直接newString对象
- String s2 = new String("hello xiaofan");
- System.out.println(s1);
- // 使用字符数组进行构造
- char[] array = {'a','b','c','d'};
- String s3 = new String(array);
- System.out.println(s1);
- }
注意:
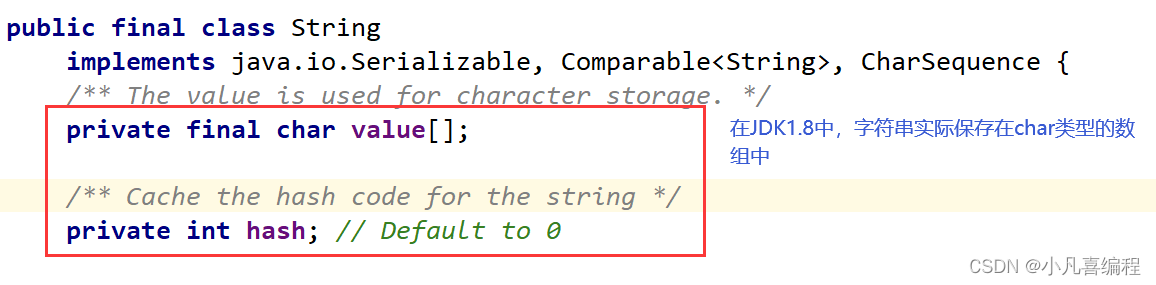
1. String是引用类型,内部并不存储字符串本身,在String类的实现源码中,String类实例变量如下:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // s1和s2引用的是不同对象 s1和s3引用的是同一对象
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("world");
- String s3 = s1;
- System.out.println(s1.length()); // 获取字符串长度---输出5
- System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); // 如果字符串长度为0,返回true,否则返回false
- }

2.2 String对象的比较
字符串的比较是常见操作之一,比如:字符串排序。Java中总共提供了4中方式:
1. ==比较是否引用同一个对象,比较的是地址相不相同
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int a = 10;
- int b = 20;
- int c = 10;
- // 对于基本类型变量,==比较两个变量中存储的值是否相同
- System.out.println(a == b); // false
- System.out.println(a == c); // true
- // 对于引用类型变量,==比较两个引用变量引用的是否为同一个对象
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("hello");
- String s3 = new String("world");
- String s4 = s1;
- System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
- System.out.println(s2 == s3); // false
- System.out.println(s1 == s4); // true
- }
2. boolean equals(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比较
字典序:字符大小的顺序 String类重写了父类Object中equals方法,Object中equals默认按照==比较,String重写equals方法后,按照 如下规则进行比较,比如: s1.equals(s2)
- public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
- // 1. 先检测this 和 anObject 是否为同一个对象比较,如果是返回true
- if (this == anObject) {
- return true;
- }
- // 2. 检测anObject是否为String类型的对象,如果是继续比较,否则返回false
- if (anObject instanceof String) {
- // 将anObject向下转型为String类型对象
- String anotherString = (String)anObject;
- int n = value.length;
- // 3. this和anObject两个字符串的长度是否相同,是继续比较,否则返回false
- if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
- char v1[] = value;
- char v2[] = anotherString.value;
- int i = 0;
- // 4. 按照字典序,从前往后逐个字符进行比较
- while (n-- != 0) {
- if (v1[i] != v2[i])
- return false;
- i++;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("hello");
- String s3 = new String("Hello");
- // s1、s2、s3引用的是三个不同对象,因此==比较结果全部为false
- System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
- System.out.println(s1 == s3); // false
- // equals比较:String对象中的逐个字符
- // 虽然s1与s2引用的不是同一个对象,但是两个对象中放置的内容相同,因此输出true
- // s1与s3引用的不是同一个对象,而且两个对象中内容也不同,因此输出false
- System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
- System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false
- }
3. int compareTo(String s) 方法: 按照字典序进行比较
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
1. 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
2. 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("abc");
- String s2 = new String("ac");
- String s3 = new String("abc");
- String s4 = new String("abcdef");
- System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
- System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0
- System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
- }
4. int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("abc");
- String s2 = new String("ac");
- String s3 = new String("ABc");
- String s4 = new String("abcdef");
- System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
- System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0
- System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
- }
2.3 字符串查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的常用查找的方法

- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
- System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); // 'b'
- System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); // 6
- System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10)); // 15
- System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb")); // 3
- System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10)); // 12
- System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c')); // 17
- System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10)); // 8
- System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb")); // 12
- System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10)); // 3
- }
2.4 转化
1. 数值和字符串转化
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // 数字转字符串
- String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
- String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
- String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
- //String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
- System.out.println(s1);
- System.out.println(s2);
- System.out.println(s3);
- //System.out.println(s4);
- System.out.println("=================================");
- // 字符串转数字
- // 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型,这个后面会讲到
- int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
- double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
- System.out.println(data1);
- System.out.println(data2);
- }
2. 大小写转换
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello";
- String s2 = "HELLO";
- // 小写转大写
- System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
- // 大写转小写
- System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
- }
3. 字符串转数组
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "hello";
- // 字符串转数组
- char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
- for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
- System.out.print(ch[i]);
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 数组转字符串
- String s2 = new String(ch);
- System.out.println(s2);
- }
4. 格式化
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);
- System.out.println(s);
- }
2.5 字符串替换
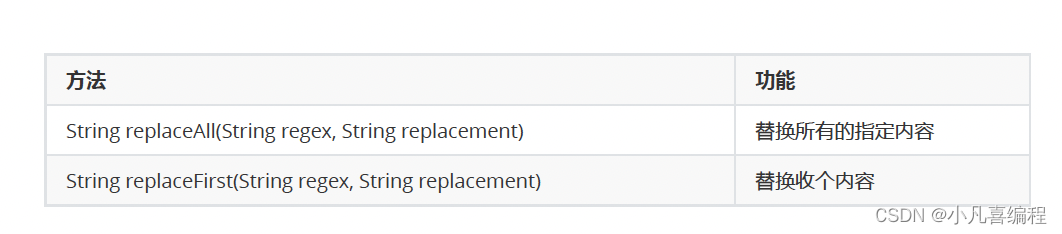
使用一个指定的新的字符串替换掉已有的字符串数据,可用的方法如下:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String str = "helloworld" ;
- System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "_")); //替换所有
- System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "_")); //替换第一个
- }
由于字符串是不可变对象, 替换不修改当前字符串, 而是产生一个新的字符串.
2.6 字符串拆分
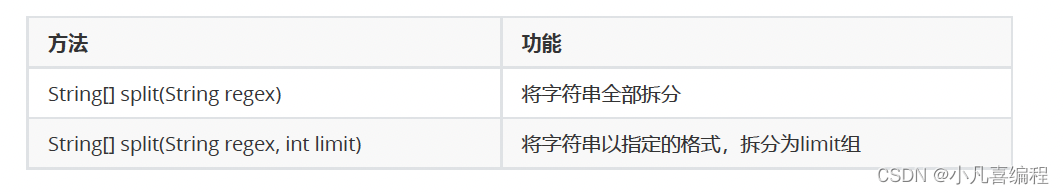
可以将一个完整的字符串按照指定的分隔符划分为若干个子字符串。
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String str = "hello world hello xiaofan" ;
- String[] result = str.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分
- for(String s: result) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- String str1 = "hello world hello xiaofan" ;
- String[] result1 = str.split(" ",2) ;
- for(String s: result1) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- //特殊情况,拆分ip地址
- String str = "192.168.1.1" ;
- String[] result = str.split("\\.") ;
- for(String s: result) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }
注意事项:
1. 字符"|","*","+"都得加上转义字符,前面加上"\\" .
2. 而如果是"\\" ,那么就得写成"\\\\" .
3. 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符.
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //多次拆分
- String str = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ;
- String[] result = str.split("&") ;
- for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
- String[] temp = result[i].split("=") ;
- System.out.println(temp[0]+" = "+temp[1]);
- }
- }
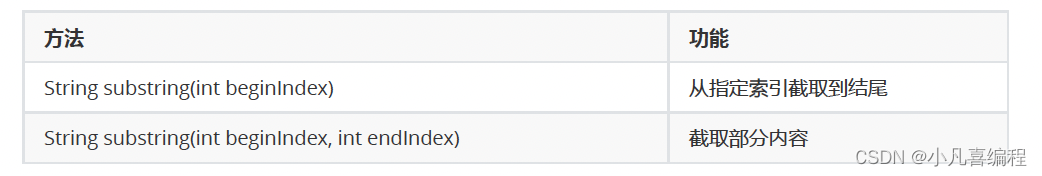
2.7 字符串截取
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String str = "helloworld" ;
- System.out.println(str.substring(5));
- System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));
- }
1. 索引从0开始
2. 注意前闭后开区间的写法, substring(0, 5) 表示包含 0 号下标的字符, 不包含 5 号下标
2.8 其他操作方法
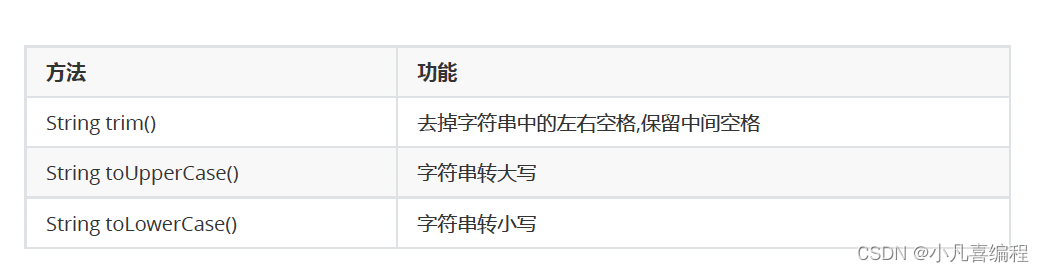
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //trim 会去掉字符串开头和结尾的空白字符(空格, 换行, 制表符等).
- String str = " hello world " ;
- System.out.println("["+str+"]");
- System.out.println("["+str.trim()+"]");
- }
2.9 字符串的不可变性
String是一种不可变对象. 字符串中的内容是不可改变。字符串不可被修改,是因为:
1. String类在设计时就是不可改变的,String类实现描述中已经说明了

2. 所有涉及到可能修改字符串内容的操作都是创建一个新对象,改变的是新对象

final修饰类表明该类不想被继承,final修饰引用类型表明该引用变量不能引用其他对象,但是其引用对象中的内 容是可以修改的。
为什么 String 要设计成不可变的?(不可变对象的好处是什么?)
1. 方便实现字符串对象池. 如果 String 可变, 那么对象池就需要考虑写时拷贝的问题了.
2. 不可变对象是线程安全的.
3. 不可变对象更方便缓存 hash code, 作为 key 时可以更高效的保存到 HashMap 中.
2.10 字符串修改
注意:尽量避免直接对String类型对象进行修改,因为String类是不能修改的,所有的修改都会创建新对象,效率非常低下。
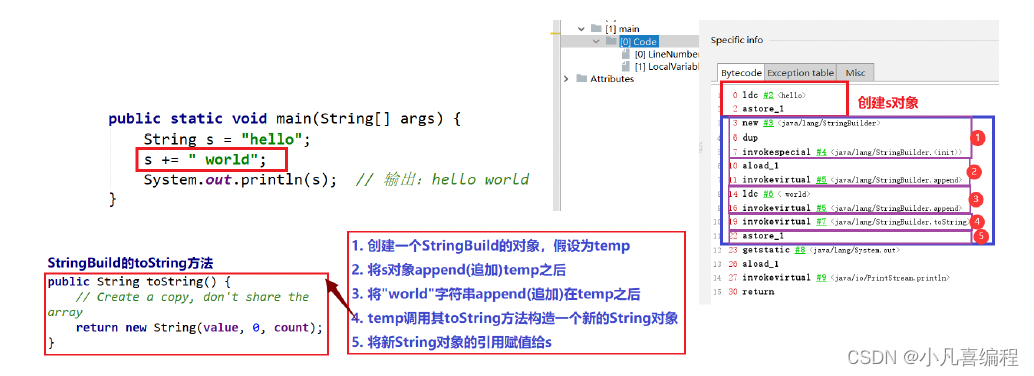
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "hello";
- s += " world";
- System.out.println(s); // 输出:hello world
- long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
- String s = "";
- for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
- s += i;
- }
- long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
- System.out.println(end - start);
- start = System.currentTimeMillis();
- StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer("");
- for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
- sbf.append(i);
- }
- end = System.currentTimeMillis();
- System.out.println(end - start);
- start = System.currentTimeMillis();
- StringBuilder sbd = new StringBuilder();
- for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
- sbd.append(i);
- }
- end = System.currentTimeMillis();
- System.out.println(end - start);
- }
可以看待在对String类进行修改时,效率是非常慢的,因此:尽量避免对String的直接需要,如果要修改建议尽量 使用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder。 借助StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder来修改
3. StringBuilder和StringBuffer
3.1 StringBuilder的介绍
由于String的不可更改特性,为了方便字符串的修改,Java中又提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer类。这两个类大 部分功能是相同的,这里介绍 StringBuilder常用的一些方法

- public static void main(String[] args) {
- StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("hello");
- StringBuilder sb2 = sb1;
- // 追加:即尾插-->字符、字符串、整形数字
- sb1.append(' '); // hello
- sb1.append("world"); // hello world
- sb1.append(123); // hello world123
- System.out.println(sb1); // hello world123
- System.out.println(sb1 == sb2); // true
- System.out.println(sb1.charAt(0)); // 获取0号位上的字符 h
- System.out.println(sb1.length()); // 获取字符串的有效长度14
- System.out.println(sb1.capacity()); // 获取底层数组的总大小
- sb1.setCharAt(0, 'H'); // 设置任意位置的字符 Hello world123
- sb1.insert(0, "Hello world!!!"); // Hello world!!!Hello world123
- System.out.println(sb1);
- System.out.println(sb1.indexOf("Hello")); // 获取Hello第一次出现的位置
- System.out.println(sb1.lastIndexOf("hello")); // 获取hello最后一次出现的位置
- sb1.deleteCharAt(0); // 删除首字符
- sb1.delete(0,5); // 删除[0, 5)范围内的字符
- String str = sb1.substring(0, 5); // 截取[0, 5)区间中的字符以String的方式返回
- System.out.println(str);
- sb1.reverse(); // 字符串逆转
- str = sb1.toString(); // 将StringBuffer以String的方式返回
- System.out.println(str);
- }
String和StringBuilder最大的区别在于String的内容无法修改,而StringBuilder的内容可以修改。频繁修改字符串的情况考虑使用StringBuilder。
注意:String和StringBuilder类不能直接转换。如果要想互相转换,可以采用如下原则: String变为StringBuilder: 利用StringBuilder的构造方法或append()方法 StringBuilder变为String: 调用toString()方法。
String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别:
String的内容不可修改,StringBuffer与StringBuilder的内容可以修改.
StringBuffer与StringBuilder大部分功能是相似的
StringBuffer采用同步处理,属于线程安全操作;而StringBuilder未采用同步处理,属于线程不安全操作
String的OJ练习题:
- import jdk.nashorn.internal.ir.WhileNode;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Scanner;
- /**
- * @author xiaofan
- * @version 1.0
- * @date 2023/11/18 22:03
- */
- public class Test1 {
- //字符串中的第一个唯一字符
- //在给定一个字符s,找到它的第一个不重复的字符,并返回它的索引,如果不存在,则返回-1
- public static int firstUniqChar(String s){
- int[] count = new int[26];
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- char ch = s.charAt(i);
- count[ch-'a']++;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- char ch = s.charAt(i);
- if (count[ch-'a'] == 1){
- return i;
- }
- }
- return 1;
- }
- public static void main1(String[] args) {
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- String input = scanner.nextLine();
- System.out.println(firstUniqChar(input));
- }
- //计算字符串最后一个单词的长度,单词以空格隔开
- public static void main2(String[] args) {
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- while (scanner.hasNext()){
- String s = scanner.nextLine();
- String[] str = s.split(" ");
- //int index = s.lastIndexOf(' ');
- //String str = s.substring(index+1);
- //int s1 = str[str.length-1].length();
- System.out.println(str[str.length-1].length());
- }
- }
- //如果在将所有大写字符转换为小写字符、并移除所有非字母数字字符之后,短语正着读和反着读都一样。则可以认为该短语是一个 回文串 。
- //字母和数字都属于字母数字字符
- public boolean isNumOrCharacter(char ch){
- if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' || ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z'){
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- public boolean isPalindrome(String s){
- s = s.toLowerCase();
- //1. 定义i 和 j
- int i = 0;
- int j = s.length()-1;
- //2. 如果i != j
- while (ichar ch = s.charAt(i);//3. i要一直走到一个合法的字符哪里,有可能i要走很多步while (i < j && !isNumOrCharacter(s.charAt(i))){i++;}//4. j要一直走到一个合法的字符哪里,有可能i要走很多步while (i < j && !isNumOrCharacter(s.charAt(j))){j--;}//5. 对应下标字符一样if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){i++;j--;} else {//6. 对应下标字符不一样return false;}}return true;}}
- 相关阅读:
Vue3 -- Composition API setup函数 reactive ref ...
荧光素PEG活性酯,FITC-PEG-NHS,FITC-PEG-SCM,荧光素聚乙二醇琥珀酰亚胺乙酸酯
关于模型融合Stacking的一些改进思路
day2_C++
Redis缓存穿透和缓存击穿
【冒泡排序】
多线程编程的核心思想
StarRocks从入门到精通系列三:创建表和导入和查询数据
贪心算法作业之汽车加油问题
事务管理 vs. 锁控制:你真的分得清吗?何时使用何种并发控制策略?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61658398/article/details/134527578
