-
Linux shell编程学习笔记28:脚本调试 set命令
0 引入
在Linux Shell 脚本编程的过程中,编写简单功能的脚本,代码不多,一般阅读起来没什么难度,有问题也比较有查出原因和修正。但是当脚本要实现的功能较多,代码变得较为复杂时,阅读起来就不那么容易看明白了,如果其中存在问题,要排查原因并修正所面临的困难也更大了,所以掌握一些调试方法还是很有必要的。
Linux shell的调试方法比较多,现在我们先看看shell内建命令set。
1 set 命令的功能
set命令用于查看和修改 Shell 环境的运行参数,我们可以依照不同的需求来设置shell的执行方式,实现定制 Shell 脚本的运行环境。
2 在bash中查看set命令的帮助信息
2.1 set --help:查看set命令格式
csdn @ edu ~ $ set --help
bash: set: --: invalid option
set: usage: set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...]
set 命令没有--help这个参数,但它提供了set命令的格式。
2.2 help set:完整的帮助信息
csdn @ edu ~ $ help set
set: set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...]
Set or unset values of shell options and positional parameters.
Change the value of shell attributes and positional parameters, or
display the names and values of shell variables.
Options:
-a Mark variables which are modified or created for export.
-b Notify of job termination immediately.
-e Exit immediately if a command exits with a non-zero status.
-f Disable file name generation (globbing).
-h Remember the location of commands as they are looked up.
-k All assignment arguments are placed in the environment for a
command, not just those that precede the command name.
-m Job control is enabled.
-n Read commands but do not execute them.
-o option-name
Set the variable corresponding to option-name:
allexport same as -a
braceexpand same as -B
emacs use an emacs-style line editing interface
errexit same as -e
errtrace same as -E
functrace same as -T
hashall same as -h
histexpand same as -H
history enable command history
ignoreeof the shell will not exit upon reading EOF
interactive-comments
allow comments to appear in interactive commands
keyword same as -k
monitor same as -m
noclobber same as -C
noexec same as -n
noglob same as -f
nolog currently accepted but ignored
notify same as -b
nounset same as -u
onecmd same as -t
physical same as -P
pipefail the return value of a pipeline is the status of
the last command to exit with a non-zero status,
or zero if no command exited with a non-zero status
posix change the behavior of bash where the default
operation differs from the Posix standard to
match the standard
privileged same as -p
verbose same as -v
vi use a vi-style line editing interface
xtrace same as -x
-p Turned on whenever the real and effective user ids do not match.
Disables processing of the $ENV file and importing of shell
functions. Turning this option off causes the effective uid and
gid to be set to the real uid and gid.
-t Exit after reading and executing one command.
-u Treat unset variables as an error when substituting.
-v Print shell input lines as they are read.
-x Print commands and their arguments as they are executed.
-B the shell will perform brace expansion
-C If set, disallow existing regular files to be overwritten
by redirection of output.
-E If set, the ERR trap is inherited by shell functions.
-H Enable ! style history substitution. This flag is on
by default when the shell is interactive.
-P If set, do not follow symbolic links when executing commands
such as cd which change the current directory.
-T If set, the DEBUG trap is inherited by shell functions.
-- Assign any remaining arguments to the positional parameters.
If there are no remaining arguments, the positional parameters
are unset.
- Assign any remaining arguments to the positional parameters.
The -x and -v options are turned off.
Using + rather than - causes these flags to be turned off. The
flags can also be used upon invocation of the shell. The current
set of flags may be found in $-. The remaining n ARGs are positional
parameters and are assigned, in order, to $1, $2, .. $n. If no
ARGs are given, all shell variables are printed.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option is given.
2.3 这些命令在zsh中无效
csdn @ edu zsh $ help set
zsh: command not found: help
csdn @ edu zsh $ set --helpcsdn @ edu zsh $

3 set 命令格式和说明
3.1 set 命令格式
set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...]
3.2 set 命令说明
选项
选项名
功能说明 -a
allexport
标示已修改的变量,以供输出至环境变量。 -b
braceexpand
使被中止的后台程序立刻回报执行状态。 -C
noclobber
转向所产生的文件无法覆盖已存在的文件。 -d
Shell预设会用杂凑表记忆使用过的指令,以加速指令的执行。使用-d参数可取消。 emacs 使用emacs内置编辑器进行命令行编辑,是一个默认设置 -e
errexit
若指令传回值不等于0,则立即退出shell。 -f
取消使用通配符 。 -h
自动记录函数的所在位置。 history 启用命令行历史、默认为启用 -H
histexpand
Shell可利用"!"加<指令编号>的方式来执行history中记录的指令。 ignoreeof 禁止用EOF(Ctrl+D)键退出shell。必须键入exit才能退出。等价于设置shell变量IGNOREEOF=10 interactive-comments 对于交互式shell,把#符后面的文本作为注释 -k
keyword
指令所给的参数都会被视为此指令的环境变量。 -l
记录for循环的变量名称。 -m
monitor
使用监视模式。 -n
noexec
只读取指令,而不实际执行。 -o [option-name] 启动指定选项的设置。如果未指定选项名称,则显示所有配置情况。 +o [option-name] 取消指定选择的设置。
如果未指定选项名称,功能在bash和zsh中不完全相同:
- 在bash中,会显示所有配置情况。
- 在zsh中,会显示所有的启用的配置情况。
-p
privileged
启动优先顺序模式。shell不读取.profile或ENV文件,且不从环境继承shell函数,将自动为setuid脚本开启特权 -P
physical
启动-P参数后,执行指令cd或pwd时,会以实际的文件或目录来取代符号连接。 -t
onecmd
执行完随后的指令,即退出shell。 -u
nounset 当执行时使用到未定义过的变量,则显示错误信息。 -v
verbose
显示shell所读取的输入值 vi 使用vi内置编辑器进行命令行编辑 -x
xtrace 为调试打开echo模式,执行命令后,会先显示该命令及所带的参数,再显示命令执行的结果 +<参数>
取消某个set曾启动的参数。 4 实例
4.1 set:不带任何参数,会显示所有的环境变量和 Shell 函数。
csdn @ edu ~ $ set
BASH=/usr/bin/bash
BASHOPTS=checkwinsize:cmdhist:expand_aliases:extquote:force_fignore:histappend:hostcomplete:interactive_comments:progcomp:promptvars:sourcepath
BASH_ALIASES=()
BASH_ARGC=()
BASH_ARGV=()
BASH_CMDS=()
BASH_LINENO=()
BASH_SOURCE=()
BASH_VERSINFO=([0]="4" [1]="2" [2]="46" [3]="2" [4]="release" [5]="x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu")
BASH_VERSION='4.2.46(2)-release'
COLUMNS=193
DIRSTACK=()
EUID=1000
GROUPS=()
HISTFILE=/home/csdn/.bash_history
HISTFILESIZE=500
HISTSIZE=500
HOME=/home/csdn
HOSTNAME=edu
HOSTTYPE=x86_64
IFS=$' \t\n'
LC_ALL=zh_CN.UTF-8
LESS=-R
LINES=39
LOGNAME=csdn
LSCOLORS=Gxfxcxdxbxegedabagacad
LS_COLORS='rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:mi=01;05;37;41:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arc=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lha=01;31:*.lz4=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.tzo=01;31:*.t7z=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lrz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.lzo=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.alz=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.cab=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.axv=01;35:*.anx=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=01;36:*.au=01;36:*.flac=01;36:*.mid=01;36:*.midi=01;36:*.mka=01;36:*.mp3=01;36:*.mpc=01;36:*.ogg=01;36:*.ra=01;36:*.wav=01;36:*.axa=01;36:*.oga=01;36:*.spx=01;36:*.xspf=01;36:'
MACHTYPE=x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu
MAILCHECK=60
OPTERR=1
OPTIND=1
OSTYPE=linux-gnu
PAGER=less
PATH=/home/csdn/.local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
PIPESTATUS=([0]="0")
PPID=133
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\007" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
PS1='csdn @ edu \w $ '
PS2='> '
PS4='+ '
PWD=/home/csdn
SHELL=/bin/bash
SHELLOPTS=braceexpand:emacs:hashall:histexpand:history:interactive-comments:monitor
SHLVL=2
TERM=xterm
UID=1000
ZSH=/home/csdn/.oh-my-zsh
_=
colors=/home/csdn/.dircolors
4.2 set -o:显示所有配置情况(不同的shell配置数量不同)
4.2.1 bash中(27个)
csdn @ edu bash ~ $ set -o
allexport off
braceexpand on
emacs on
errexit off
errtrace off
functrace off
hashall on
histexpand on
history on
ignoreeof off
interactive-comments on
keyword off
monitor on
noclobber off
noexec off
noglob off
nolog off
notify off
nounset off
onecmd off
physical off
pipefail off
posix off
privileged off
verbose off
vi off
xtrace off
bash中配置数量为 27个,跟帮助信息中数量一致。
4.2.2 在zsh中(169个)
csdn @edu zsh $ set -o
noaliases off
allexport off
noalwayslastprompt off
alwaystoend on
noappendhistory off
autocd on
autocontinue off
noautolist off
noautomenu off
autonamedirs off
noautoparamkeys off
noautoparamslash off
autopushd on
noautoremoveslash off
autoresume off
nobadpattern off
nobanghist off
nobareglobqual off
bashautolist off
bashrematch off
nobeep off
nobgnice off
braceccl off
bsdecho off
nocaseglob off
nocasematch off
cbases off
cdablevars off
chasedots off
chaselinks off
nocheckjobs off
noclobber off
combiningchars off
completealiases off
completeinword on
continueonerror off
correct off
correctall off
cprecedences off
cshjunkiehistory off
cshjunkieloops off
cshjunkiequotes off
cshnullcmd off
cshnullglob off
nodebugbeforecmd off
dvorak off
emacs off
noequals off
errexit off
errreturn off
noevallineno off
noexec off
extendedglob off
extendedhistory on
noflowcontrol on
nofunctionargzero off
noglob off
noglobalexport off
noglobalrcs off
globassign off
globcomplete off
globdots off
globsubst off
nohashcmds off
nohashdirs off
hashexecutablesonly off
nohashlistall off
histallowclobber off
nohistbeep off
histexpiredupsfirst on
histfcntllock off
histfindnodups off
histignorealldups off
histignoredups on
histignorespace on
histlexwords off
histnofunctions off
histnostore off
histreduceblanks off
nohistsavebycopy off
histsavenodups off
histsubstpattern off
histverify on
nohup off
ignorebraces off
ignoreclosebraces off
ignoreeof off
incappendhistory off
interactive on
interactivecomments on
ksharrays off
kshautoload off
kshglob off
kshoptionprint off
kshtypeset off
kshzerosubscript off
nolistambiguous off
nolistbeep off
listpacked off
listrowsfirst off
nolisttypes off
localoptions off
localtraps off
login off
longlistjobs on
magicequalsubst off
mailwarning off
markdirs off
menucomplete off
monitor on
nomultibyte off
nomultifuncdef off
nomultios off
nonomatch off
nonotify off
nullglob off
numericglobsort off
octalzeroes off
overstrike off
pathdirs off
pathscript off
posixaliases off
posixbuiltins off
posixcd off
posixidentifiers off
posixjobs off
posixstrings off
posixtraps off
printeightbit off
printexitvalue off
privileged off
promptbang off
nopromptcr off
nopromptpercent off
nopromptsp off
promptsubst on
pushdignoredups on
pushdminus on
pushdsilent off
pushdtohome off
rcexpandparam off
rcquotes off
norcs off
recexact off
rematchpcre off
restricted off
rmstarsilent off
rmstarwait off
sharehistory on
shfileexpansion off
shglob off
shinstdin on
shnullcmd off
shoptionletters off
noshortloops off
shwordsplit off
singlecommand off
singlelinezle off
sourcetrace off
sunkeyboardhack off
transientrprompt off
trapsasync off
typesetsilent off
nounset off
verbose off
vi off
warncreateglobal off
xtrace off
zle on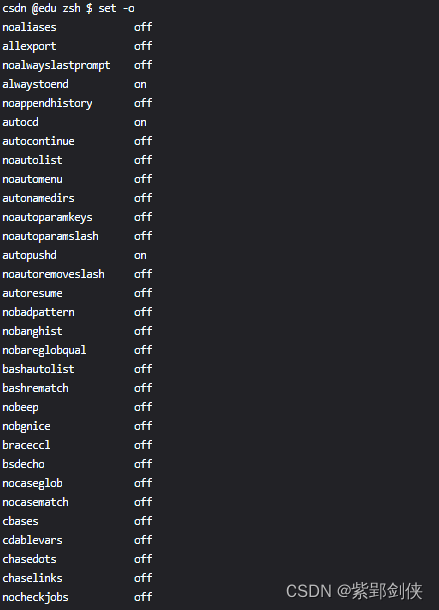
zsh的配置数量是169个,要比bash多得多,所以上面的截图没有全部截,只截了其中一部分。
4.3 set +o:功能因shell而异
4.3.1 在bash中 (27个)
csdn @ edu bash ~ $ set +o
set +o allexport
set -o braceexpand
set -o emacs
set +o errexit
set +o errtrace
set +o functrace
set -o hashall
set -o histexpand
set -o history
set +o ignoreeof
set -o interactive-comments
set +o keyword
set -o monitor
set +o noclobber
set +o noexec
set +o noglob
set +o nolog
set +o notify
set +o nounset
set +o onecmd
set +o physical
set +o pipefail
set +o posix
set +o privileged
set +o verbose
set +o vi
set +o xtrace
在bash中,显示的配置数量仍然为 27个,与 set -o命令一样。
4.3.2 在zsh中(20个)
csdn @edu zsh $ set +o
set -o alwaystoend
set -o autocd
set -o autopushd
set -o completeinword
set -o extendedhistory
set -o noflowcontrol
set -o histexpiredupsfirst
set -o histignoredups
set -o histignorespace
set -o histverify
set -o interactive
set -o interactivecomments
set -o longlistjobs
set -o monitor
set -o promptsubst
set -o pushdignoredups
set -o pushdminus
set -o sharehistory
set -o shinstdin
set -o zle
在zsh中,set +o命令显示的配置数量为 20个,比set -o要少得多。
对比发现,zsh中,set +o命令显示的是启用的配置,为了验证这个结论是否正确,我们先执行命令set -o nohup 把nohup启用,再来看看 set +o 命令的反馈。
csdn @ edu zsh $ set -o nohup
csdn @ edu zsh $ set +o
set -o alwaystoend
set -o autocd
set -o autopushd
set -o completeinword
set -o extendedhistory
set -o noflowcontrol
set -o histexpiredupsfirst
set -o histignoredups
set -o histignorespace
set -o histverify
set -o nohup
set -o interactive
set -o interactivecomments
set -o longlistjobs
set -o monitor
set -o promptsubst
set -o pushdignoredups
set -o pushdminus
set -o sharehistory
set -o shinstdin
set -o zle
由于启用的选项增加了nohup,set +o命令的反馈的配置变成了21个。
4.4 set + :功能因shell而异
4.4.1 在bash中(无反馈)
csdn @ edu bash ~ $ set +
csdn @ edu bash ~ $
4.4.2 在zsh中(196个)
csdn @ edu zsh $ set +
!
#
$
*
-
0
?
@
ARGC
BG
CDPATH
COLUMNS
CPUTYPE
EGID
ERRNO
EUID
FG
FIGNORE
FPATH
FX
GID
HISTCHARS
HISTCMD
HISTFILE
HISTSIZE
HOME
HOST
HOSTNAME
IFS
KEYBOARD_HACK
KEYTIMEOUT
LC_ALL
LESS
LINENO
LINES
LISTMAX
LOGCHECK
LOGNAME
LSCOLORS
LS_COLORS
MACHTYPE
MAILCHECK
MAILPATH
MANPATH
MODULE_PATH
NULLCMD
OLDPWD
OPTARG
OPTIND
OSTYPE
PAGER
PATH
POSTEDIT
PPID
PROMPT
PROMPT2
PROMPT3
PROMPT4
PS1
PS2
PS3
PS4
PSVAR
PWD
RANDOM
READNULLCMD
RPROMPT
RPROMPT2
RPS1
RPS2
SAVEHIST
SCREEN_NO
SECONDS
SHLVL
SHORT_HOST
SPROMPT
TERM
TIMEFMT
TMPPREFIX
TRY_BLOCK_ERROR
TTY
TTYIDLE
UID
USERNAME
VENDOR
WATCH
WATCHFMT
WORDCHARS
YS_VCS_PROMPT_CLEAN
YS_VCS_PROMPT_DIRTY
YS_VCS_PROMPT_PREFIX1
YS_VCS_PROMPT_PREFIX2
YS_VCS_PROMPT_SUFFIX
ZSH
ZSH_CACHE_DIR
ZSH_COMPDUMP
ZSH_CUSTOM
ZSH_EVAL_CONTEXT
ZSH_NAME
ZSH_PATCHLEVEL
ZSH_SUBSHELL
ZSH_THEME
ZSH_THEME_GIT_PROMPT_CLEAN
ZSH_THEME_GIT_PROMPT_DIRTY
ZSH_THEME_GIT_PROMPT_PREFIX
ZSH_THEME_GIT_PROMPT_SUFFIX
ZSH_THEME_RUBY_PROMPT_PREFIX
ZSH_THEME_RUBY_PROMPT_SUFFIX
ZSH_THEME_RVM_PROMPT_OPTIONS
ZSH_THEME_TERM_TAB_TITLE_IDLE
ZSH_THEME_TERM_TITLE_IDLE
ZSH_VERSION
_
_comp_assocs
_comp_dumpfile
_comp_options
_comp_setup
_compautos
_comps
_lastcomp
_patcomps
_postpatcomps
_services
aliases
argv
bg
bg_bold
bg_no_bold
bold_color
builtins
cdpath
color
colors
colour
commands
comppostfuncs
compprefuncs
custom_config_file
d
dirstack
dis_aliases
dis_builtins
dis_functions
dis_galiases
dis_reswords
dis_saliases
exit_code
fg
fg_bold
fg_no_bold
fignore
fpath
funcfiletrace
funcsourcetrace
funcstack
functions
functrace
galiases
git_info
hg_info
histchars
history
historywords
jobdirs
jobstates
jobtexts
keymaps
langinfo
mailpath
manpath
module_path
modules
nameddirs
options
parameters
path
pipestatus
plugin
plugins
precmd_functions
preexec_functions
prompt
psvar
reset_color
reswords
saliases
signals
status
termcap
terminfo
userdirs
usergroups
watch
widgets
zsh_eval_context
zsh_scheduled_events4.5 set -o noclobber:防止文件在重定向时被重写
我们将执行以下面命令序列来看看noclobber在防止文件在重定向时被重写的控制效果。
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
4.5.1 直接在命令行执行
在命令行直接输入和执行以下命令:set -o | grep noclobber;echo a > a.txt;echo -n a.txt:;cat a.txt;echo b > a.txt;echo -n a.txt:; cat a.txt;set -o noclobber;set -o | grep noclobber;echo c > a.txt; echo -n a.txt:; cat a.txt;set +o noclobber;set -o | grep noclobber;echo c >> a.txt;echo -n a.txt:;cat a.txt,效果如下:
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $
o | grep noclobber;echo c >> a.txt;echo -n a.txt:;cat a.txtet +o noclobber;set -
noclobber off
a.txt:a
a.txt:b
noclobber on
bash: a.txt: cannot overwrite existing file
a.txt:b
noclobber off
a.txt:b
c
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $
虽然命令执行结果是我们预期的,但命令行没有完全显示出来。
我们还是用cp /dev/stdin a.sh命令创建一个脚本文件a.sh来测试吧
4.5.2 创建脚本文件a.sh来测试
4.52.1 创建脚本文件a.sh,
- 注意:在输入所有命令后要按Ctrl+D结束
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $
4.5.2.2 查看脚本文件a.sh 的内容
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ cat a.sh
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $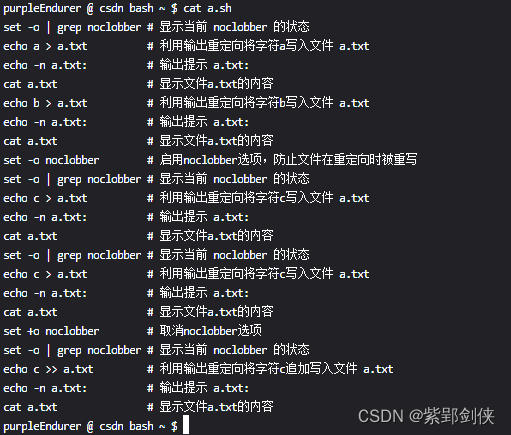
4.5.2.3 执行脚本文件 a.sh
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ . a.sh
noclobber off
a.txt:a
a.txt:b
noclobber on
bash: a.txt: cannot overwrite existing file
a.txt:b
noclobber on
bash: a.txt: cannot overwrite existing file
a.txt:b
noclobber off
a.txt:b
c
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $
脚本开始执行时,a.txt 的内容为:
a
由于noclobber选项未启用(noclobber off),所以 echo b > a.txt 命令执行成功,文件a.txt内容变为:
b
当命令set -o noclobber执行后,noclobber选项启用(noclobber on),echo c > a.txt 命令未能成功执行,bash提示:a.txt: cannot overwrite existing file
当命令set +o noclobber执行后, noclobber选项不再启用,echo c >> a.txt命令执行成功,a.txt内容变为:
b
c
在上面命令序列中
- set -o noclobber 也可以简写为 set -C
- set +o noclobber 也可以简写为 set +C
4.6 set -e:当命令返回一个非零退出状态(失败)时退出
我们在上面的a.sh文件的第1行命令后面增加两行命令:
- set -e # 启用errexit选项,当命令返回一个非零退出状态(失败)时退出
- set -o | grep errexit # 显示当前 errexit 的状态
即:
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- set -e # 启用errexit选项,当命令返回一个非零退出状态(失败)时退出
- set -o | grep errexit # 显示当前 errexit 的状态
- echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
4.6.1 创建脚本文件a.sh
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
set -e # 启用errexit选项,当命令返回一个非零退出状态(失败)时退出
set -o | grep errexit # 显示当前 errexit 的状态
echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $
4.6.2 执行脚本文件a.sh
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ . a.sh
noclobber off
errexit on
a.txt:a
a.txt:b
noclobber on
bash: a.txt: cannot overwrite existing file
可以看到,在命令echo c > a.txt 没能执行成功时,由于其返回值非零,脚本直接退出了。
4.7 set -x:在输出命令运行结果之前,先输出所执行的命令
为了对4.6中的例子执行情况有更直观的了解,我们在a.sh的开头增加两行命令:
- set -x # 启用xtrace选项,在输出命令运行结果之前,先输出所执行的命令
- set -o | grep xtrace # 显示当前 xtrace 的状态
即:
- set -x # 启用xtrace选项,在输出命令运行结果之前,先输出所执行的命令
- set -o | grep xtrace # 显示当前 xtrace 的状态
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- set -e # 启用errexit选项,当命令返回一个非零退出状态(失败)时退出
- set -o | grep errexit # 显示当前 errexit 的状态
- echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
- set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
- set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
- echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
- echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
- cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
4.7.1 创建脚本文件a.sh
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
set -x # 启用xtrace选项,在输出命令运行结果之前,先输出所执行的命令
set -o | grep xtrace # 显示当前 xtrace 的状态
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
set -e # 启用errexit选项,当命令返回一个非零退出状态(失败)时退出
set -o | grep errexit # 显示当前 errexit 的状态
echo a > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符a写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
echo b > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符b写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o noclobber # 启用noclobber选项,防止文件在重定向时被重写
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c > a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
set +o noclobber # 取消noclobber选项
set -o | grep noclobber # 显示当前 noclobber 的状态
echo c >> a.txt # 利用输出重定向将字符c追加写入文件 a.txt
echo -n a.txt: # 输出提示 a.txt:
cat a.txt # 显示文件a.txt的内容
4.7.2 执行脚本文件a.sh
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ . a.sh
++ set -o
++ grep --color=auto xtrace
xtrace on
++ grep --color=auto noclobber
++ set -o
noclobber off
++ set -e
++ grep --color=auto errexit
++ set -o
errexit on
++ echo a
++ echo -n a.txt:
a.txt:++ cat a.txt
a
++ echo b
++ echo -n a.txt:
a.txt:++ cat a.txt
b
++ set -o noclobber
++ grep --color=auto noclobber
++ set -o
noclobber on
++ echo c
bash: a.txt: cannot overwrite existing file

启用了 xtrace选项后,我们可以直观地看到脚本在执行echo c > a.txt 命令没有成功后退出。
4.8 set -u:当执行时使用到未定义过的变量,则显示错误信息。
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
set -x # 启用xtrace选项,在输出命令运行结果之前,先输出所执行的命令
set -o | grep xtrace # 显示当前 xtrace 的状态
set -o | grep nounse # 显示当前 nounset 的状态
b=b # 定义变量b,并初始化其值为b
echo a=$a # 显示变量a
echo b=$b # 显示变量b
set -u # 启用nounset选项,当执行时使用到未定义过的变量时,则显示错误信息
set -o | grep nounse # 显示当前 nounset 的状态
echo a=$a # 显示变量a
echo b=$b # 显示变量b
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ . a.sh
++ grep --color=auto xtrace
++ set -o
xtrace on
++ set -o
++ grep --color=auto nounse
nounset off
++ b=b
++ echo a=
a=
++ echo b=b
b=b
++ set -u
++ grep --color=auto nounse
++ set -o
nounset on
bash: a: unbound variable
++ echo b=b
b=b
bash: USER: unbound variable
purpleEndurer @ csdn bash ~ $ ~ bash默认 nounset选项是未启用的,所以尽管并没有定义变量a,在执行命令echo a=$a时没出错信息,而是显示:a=
bash默认 nounset选项是未启用的,所以尽管并没有定义变量a,在执行命令echo a=$a时没出错信息,而是显示:a=当我们执行命令set -u , 启用nounset选项后,再次执行命令echo a=$a时,显示了出错信息:bash: a: unbound variable
-
相关阅读:
Linux内存管理(二):页面查询过程简述
重装系统后没声音如何解决
java栈和自定义栈
Redis实用篇(结合场景落地实现)
10月13日上课内容 Ansible 的脚本 --- playbook 剧本
Qt学习总结之QSlider、QDial
CSDN 成为开放原子开源基金会黄金捐赠人,共建中国十万亿技术大生态
怎么导入别人的android项目
UI框架、css预处理与vuex状态管理
完全数(Perfect number),又称完美数或完备数,是一些特殊的自然数。它所有的真因子(即除了自身以外的约数)的和,恰好等于它本身。
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134506337
