-
Java进阶API第四章
Java进阶API第四章
一.异常的介绍

1.错误
Error
特点:
- 不常见
- 基本上不能解决
- 尽量避免
2.异常
Exception
特点:
- 常见
- 可以定位,通过修改代码解决
- 不是编译失败问题,代码语法没有问题
二. 异常举例以及解决常见错误bug方案
- 定位错误:编写好程序后,运行程序,在输入运行结果栏中会存在异常提示,红色中蓝色链接,就能找到自己的代码错误
- 解决错误:先阅读异常提示,如果了解就直接修改,如果不了解那就搜索异常提示,了解问题所在,解决问题

三.RuntimeException
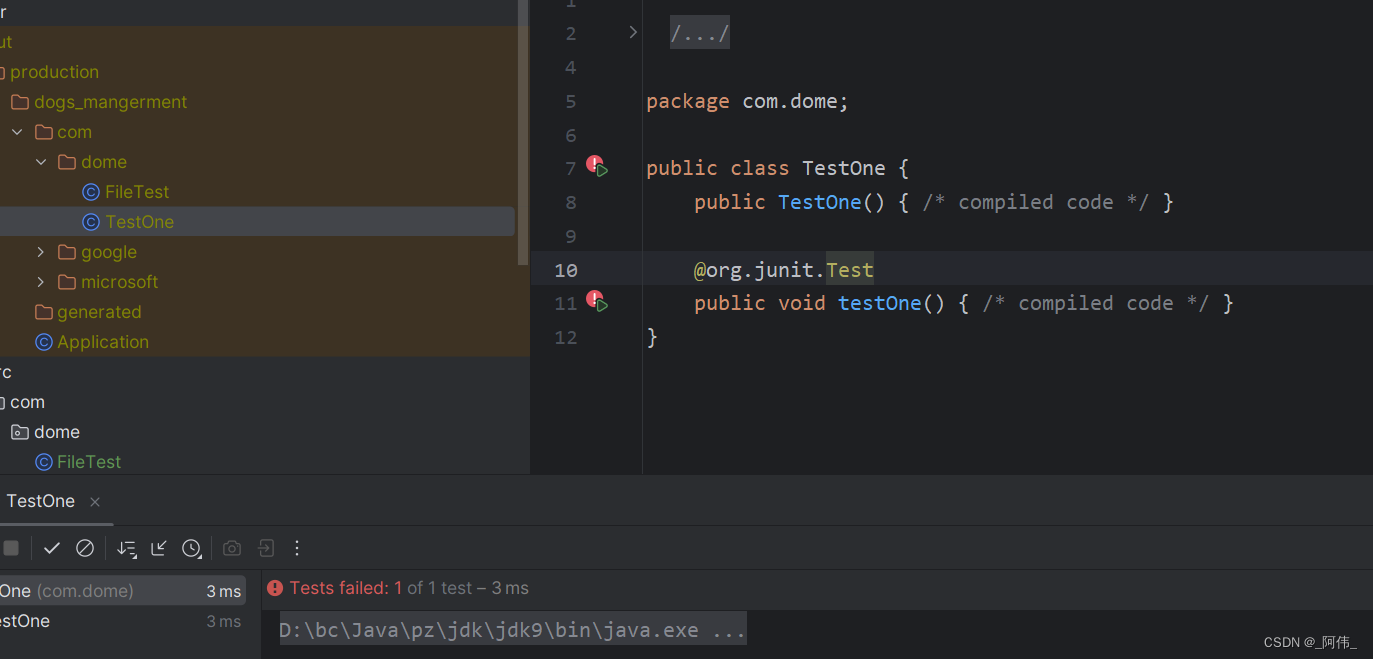
这样刚才那个异常生成的可执行文件(Class),说明此异常为执行时异常的子类(RuntimeException)。
异常类有两个主要的子类:
IOException类和RuntimeException类。
1.运行时异常
- 运行时异常可修改也可不修改,不会对项目运行产生影响
- 运行时异常像游戏漏洞,它不影响我们玩游戏,但是我们有一些漏洞可以捡,比如更新以后某个英雄的技能,在某个时间可以无限的放或者平A就能秒死人
2.非运行时异常
- 非运行时异常必须修改,因为这样会使得项目直接无法运行(现在的编译器比较智能,一定会让你try catch)但是非运行时异常导致你进不去游戏
- 编译器中,运行时异常不会要求你捕获,但是非运行时异常会强制要求你捕获,所以我们在编写自定义异常的时候不会定成运行时异常
四. 捕获异常 try catch
1.定位一个代码块的异常,运行完成这个代码块后,抛出这个代码块的异常
快捷键: 选中对象使用Ctrl+Alt+t
- // try表示监控区域
- try {
- // 监控对象
- System.out.println(1 / 0);
- // catch表示捕获异常,()Exception内表示异常类型,e表示异常对象
- } catch (Exception e) {
- // 捕获成功后,输出语句
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
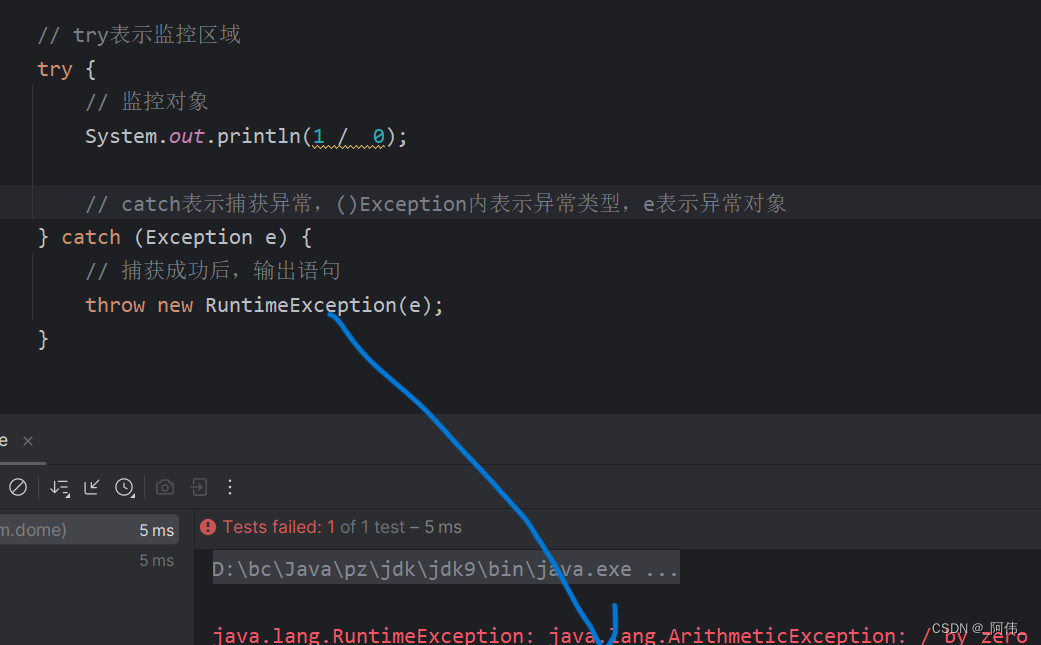
如果没有throw new RuntimeException(e);或e.printStackTrace();语句,就不抛出与输出异常语句。

2.try catch可以搭配finally使用
- // try表示监控区域
- try {
- // 监控对象
- System.out.println(1 / 0);
- // catch表示捕获异常,()Exception内表示异常类型,e表示异常对象
- } catch (Exception e) {
- // 捕获成功后,输出语句
- e.printStackTrace();
- // finally表示善后工作,可以不写,因为默认存在。
- // 但在一些情况中,必须写,如io流,资源,等等
- } finally {
- System.out.println("善后工作");
- }

3.捕获错误
- public class TestOne {
- @Test
- public void testOne() {
- // 这段代码可以理解为创建了一个 TestOne 类的对象,并调用了该对象的 one() 方法。
- // 具体来说,new Test() 创建了一个 Test 类的匿名对象,并通过该对象调用了 one() 方法。
- // 这种方式常用于一次性调用某个类的方法而不需要保留对象的引用。
- new TestOne().one();
- }
- public void one() {
- two();
- }
- public void two() {
- one();
- }
- }

- public void testOne() {
- try {
- new TestOne().one();
- } catch (Error e) {
- System.out.println("虚拟机出现错误");
- } finally {
- System.out.println("善后工作");
- }
- }
- public void one() {
- two();
- }
- public void two() {
- one();
- }

四.多层捕获
如果不知道异常类型可以使用多层捕获,但括号中的捕获类型必须从小到大。

- public void testOne() {
- try {
- System.out.println(1/0);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- System.out.println("Exception");
- } catch (Error e) {
- System.out.println("Error");
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- System.out.println("Throwable");
- } finally {
- System.out.println("善后工作");
- }
- }

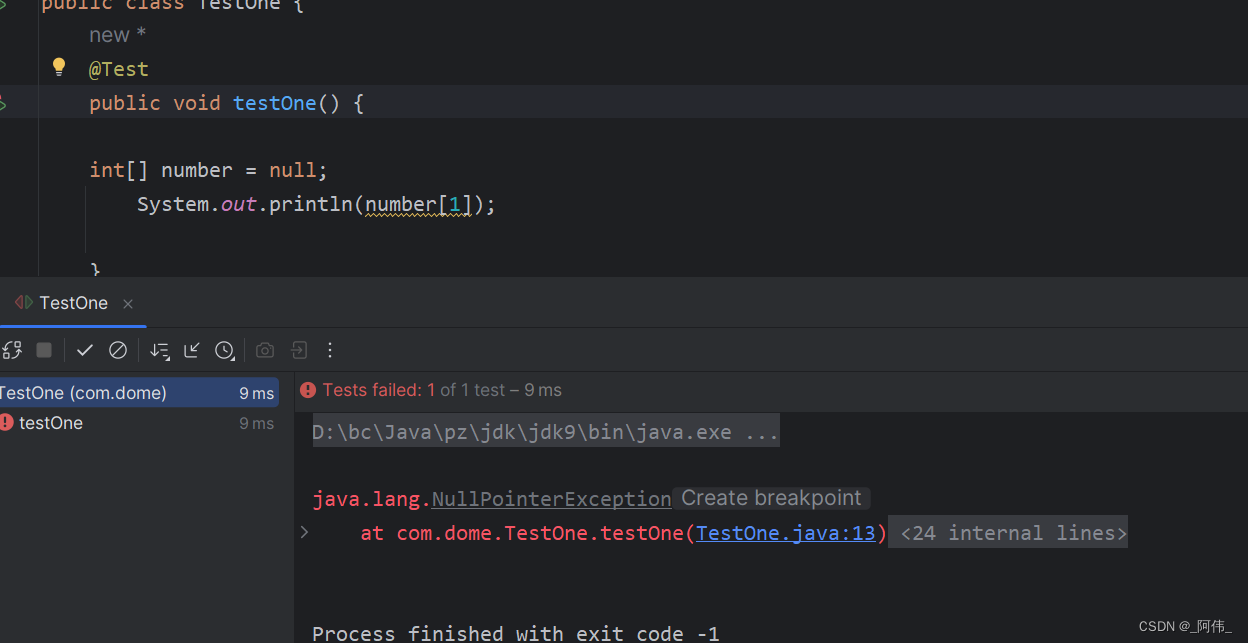
五.NullPointerException空指针异常
空指针异常的情况:
- Calling the instance method of a null object. 调用空对象的实例方法
- Accessing or modifying the field of a null object.访问或修改空对象的字段
- Taking the length of null as if it were an array.将null的长度当作一个数组
- Accessing or modifying the slots of null as if it were an array.访问或修改null的插槽,就好像它是一个数组一样
- Throwing null as if it were a Throwable value.将null视为Throwable值
六.抛出异常 throws
- 通过捕获异常的功能,我们可以写判断或抛出异常的方法
- 在不通过的情况下提醒程序员,这样程序员可以快速的更改代码,以防止程序在后面出现更严重的问题
抛出异常: throw,throws,一般在方法中使用
- public class TestOne {
- @Test
- public void testOne() {
- new TestOne().test(1,0);
- }
- public void test(int one,int two) {
- if(two == 0) {
- // two等于0,就抛出异常
- throw new ArithmeticException();
- }
- }
- }

throws
- public class TestOne {
- @Test
- public void testOne() {
- new TestOne().test(1,0);
- }
- // 如果方法中,处理不了这个异常,那就方法上抛出异常
- public void test(int one,int two) throws ArithmeticException {
- if(two == 0) {
- // two等于0,就抛出异常
- throw new ArithmeticException();
- }
- }
- }
七.自定义异常
自定义异常一般由企业里的架构师负责。
1.第一步:创建
ErrorCode接口。- public interface ErrorCode {
- /**
- * 获取错误码
- * @return
- */
- String getcode();
- /**
- * 获取错误信息
- * @return
- */
- String getMsg();
- }
2.创建
MyCodeEnum枚举类,编写代码实现接口中的所有方法。- public enum MyCodeEnum implements ErrorCode{
- // 错误端口与信息
- NOT_FOUND_PAGE("404","找不到网站资源"),
- NOT_FOUND_FILE("888","找不到文件"),
- NOT_O_TEN("bad", "只能求10以内的加法")
- ;
- // 此处必须有一个code,Msg
- private final String code;
- private final String Msg;
- // 有参构造
- MyCodeEnum(String code, String msg) {
- this.code = code;
- Msg = msg;
- }
- // 实现接口中的所有方法
- @Override
- public String getcode() {
- return code;
- }
- @Override
- public String getMsg() {
- return Msg;
- }
- }
3.创建
MyException类继承Exception- public class MyException extends Exception{
- // 有参构造,参数为自己写的异常接口与调用接口的getMsg方法(获取错误信息)
- public MyException(ErrorCode errorCode) {
- super(errorCode.getMsg());
- }
- }
4.使用异常
- public class TestOne {
- public int sum(int a,int b) throws MyException {
- if(a > 10 || b > 10 || a < 0 || b < 0) {
- // 抛出自己写的异常MyException,参数为错误信息为自己写的MyCodeEnum
- throw new MyException(MyCodeEnum.NOT_O_TEN);
- }
- return a+b;
- }
- @Test
- public void testOne() {
- // 自己写的异常,继承Exception,就必须使用try catch捕获
- try {
- sum(10,33);
- } catch (MyException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }

-
相关阅读:
解决 Ajax:Ensure CORS response header values are valid 跨域问题
iOS APP上架App Store其中一个步骤就是要把ipa文件上传到App Store
TMS FMX Cloud提供集成元素
lua-web-utils库
职场必看!性能测试响应很慢怎么排查?
企业级DevOps平台搭建及技术选型-项目管理篇
Pyinstaller生成的exe程序,运行时找不到自定义模块
Apache Kafka 快速学习大纲
传统数据库逐渐“难适应”,云原生数据库脱颖而出
JAVA总结作业----集合
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_76556912/article/details/134491430
