-
TensorRt推理加速框架Python API服务器部署教程以及运行Helloworld程序
一、确认cuda工具包和n卡相关驱动是否安装
在终端中输入以下命令:
nvcc -V- 1
如果出现以下提示,则已经成功安装
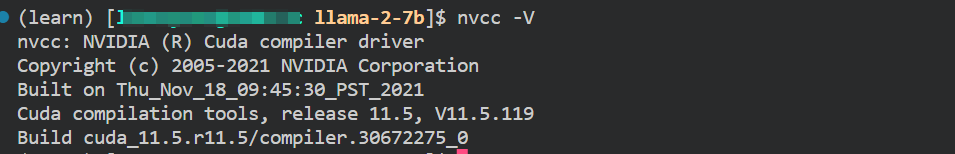
在终端中输入以下命令:nvidia-smi- 1
如果出现即为成功,我在这里就不去介绍怎么下载cuda和驱动怎么下载了,大家可以看一下网上的其他安装教程
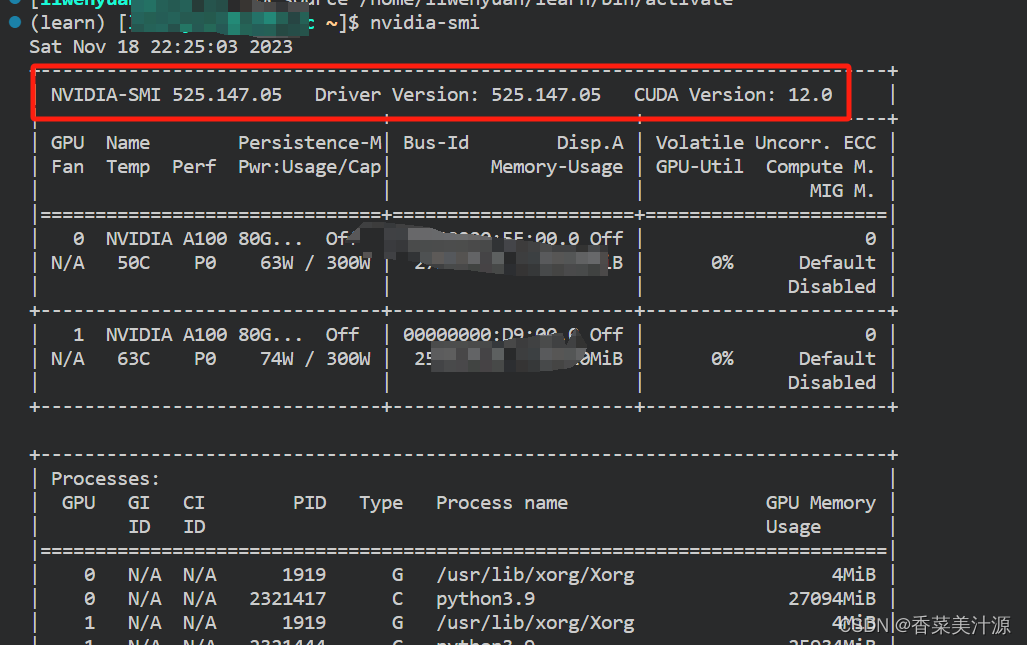
二、pip安装tensorRT API
此步骤在python的虚拟环境下进行:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade tensorrt- 1
三、验证tensort库安装结果
>>> import tensorrt >>> print(tensorrt.__version__) 8.6.1 >>> assert tensorrt.Builder(tensorrt.Logger()) [11/04/2023-11:19:33] [TRT] [W] CUDA lazy loading is not enabled. Enabling it can significantly reduce device memory usage and speed up TensorRT initialization. See "Lazy Loading" section of CUDA documentation https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#lazy-loading- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
四、安装Cuda-python
这里如果遇到网络问题可以加上清华源
-i [https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple](https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple)pip install cuda-python- 1
五、验证cuda-python是否安装成功
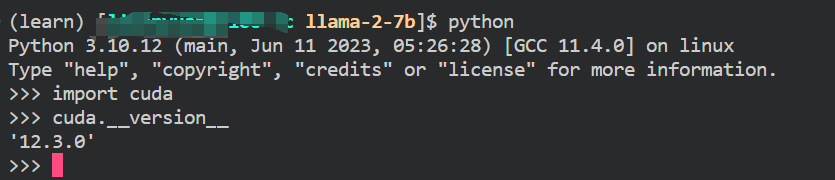
进入python,如果能成功导入库,则成功安装开库
python import cuda- 1
- 2
六、克隆TensorRT HelloWorld程序
项目地址:https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT/tree/main/samples/python/network_api_pytorch_mnist
(1)克隆整个项目git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT.git- 1
这里如果网络不行,可以直接上github下载zip文件,一样的
(2)进入pytorch版本的例子目录,安装依赖cd TensorRT/samples/python/network_api_pytorch_mnist pip install -r requirements.txt- 1
- 2
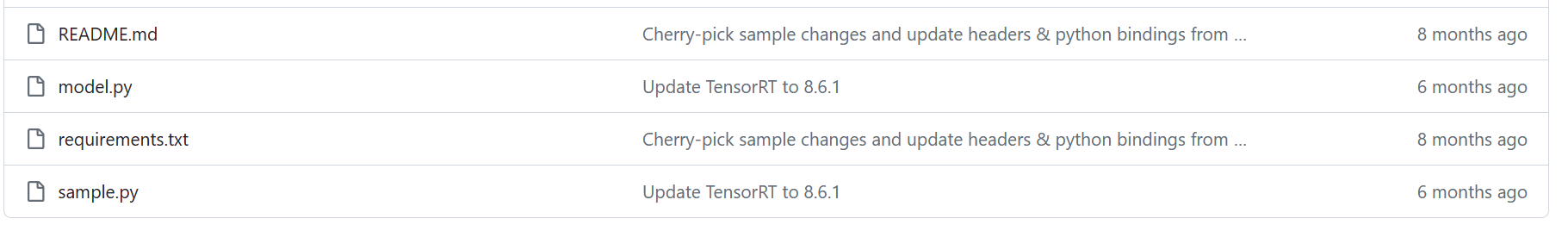
这里面包含了两个python源代码文件,其中model.py是一个卷积神经网络的代码,sample.py是调用这个网络对minist数据集进行训练预测的代码,并将训练好的模型转换文tensorRT的格式进行推理。
(3)运行sample.py文件python sample.py- 1
运行上述命令后,会产生以下输出:
训练过程:
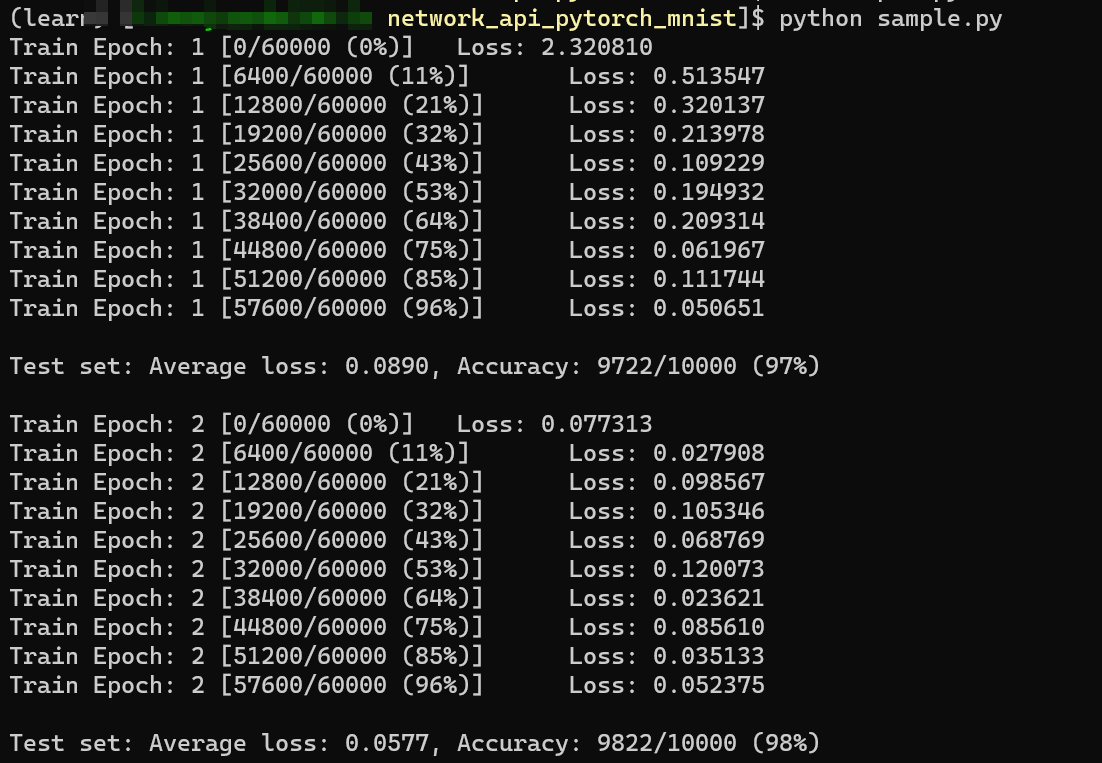
最终结果:

**此时,你就已经成功运行了tensorRT的pytorch版本的HelloWorld程序!**下面我们对这个HelloWorld进行深入分析。六、代码分析-Todo
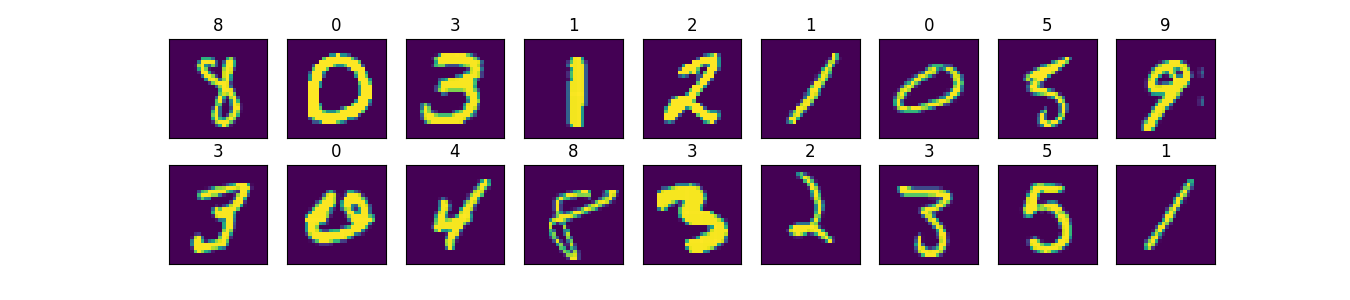
这个样例采用了经典的mnist数据集,它是一些单通道的二维图像组成的数据集,可视化后如下:
从下述代码,可以知道,作者构造了一个由两个卷积层和两个全连接层组成的简单神经网络,用来训练在mnist数据集上的预测模型,并且提供了get_weights方法,方便下载训练好的参数。import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms from torch.autograd import Variable import numpy as np import os from random import randint # 这是一个简单的神经的网络,由两个卷积层和两个全连接层组成 # Network class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, kernel_size=5) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 50, kernel_size=5) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(800, 500) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500, 10) def forward(self, x): x = F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), kernel_size=2, stride=2) x = F.max_pool2d(self.conv2(x), kernel_size=2, stride=2) x = x.view(-1, 800) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = self.fc2(x) return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) # 这个类主要实现用上述网络结构来训练的功能 class MnistModel(object): def __init__(self): # 一系列超参数 self.batch_size = 64 self.test_batch_size = 100 self.learning_rate = 0.0025 self.sgd_momentum = 0.9 self.log_interval = 100 # 加载mnist的训练数据和测试数据 self.train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( datasets.MNIST( "/tmp/mnist/data", train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))]), ), batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=1, timeout=600, ) self.test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( datasets.MNIST( "/tmp/mnist/data", train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))]), ), batch_size=self.test_batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=1, timeout=600, ) # 初始化网络对象 self.network = Net() def learn(self, num_epochs=2): """这个函数用来训练网络,默认训练两轮""" # 每一个单轮训练 def train(epoch): # 切换到训练模式 self.network.train() # 使用随机梯度下降法来作为优化器 optimizer = optim.SGD(self.network.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate, momentum=self.sgd_momentum) # 每一个batch训练数据 for batch, (data, target) in enumerate(self.train_loader): data, target = Variable(data), Variable(target) optimizer.zero_grad() output = self.network(data) loss = F.nll_loss(output, target) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # 输出损失信息 if batch % self.log_interval == 0: print( "Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}".format( epoch, batch * len(data), len(self.train_loader.dataset), 100.0 * batch / len(self.train_loader), loss.data.item(), ) ) # 测试函数 def test(epoch): # 切换到验证模式 self.network.eval() test_loss = 0 correct = 0 for data, target in self.test_loader: with torch.no_grad(): data, target = Variable(data), Variable(target) output = self.network(data) test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target).data.item() pred = output.data.max(1)[1] correct += pred.eq(target.data).cpu().sum() test_loss /= len(self.test_loader) # 输出测试损失 print( "\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n".format( test_loss, correct, len(self.test_loader.dataset), 100.0 * correct / len(self.test_loader.dataset) ) ) # 训练num_epochs轮 for e in range(num_epochs): train(e + 1) test(e + 1) def get_weights(self): """返回network的权重参数""" return self.network.state_dict() def get_random_testcase(self): """从名字可以看出,这是一个从测试数据中随机抽取样本来进行推理""" data, target = next(iter(self.test_loader)) case_num = randint(0, len(data) - 1) test_case = data.numpy()[case_num].ravel().astype(np.float32) test_name = target.numpy()[case_num] return test_case, test_name- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
从下述代码可知,作者使用了tensorRT对使用pytorch构建的神经网络进行了再构建,没有使用到parser自动解析网络框架。随着网络层数越深,这种方式会越来越麻烦。
import os import sys import model import numpy as np import tensorrt as trt sys.path.insert(1, os.path.join(sys.path[0], "..")) import common TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING) class ModelData(object): INPUT_NAME = "data" INPUT_SHAPE = (1, 1, 28, 28) OUTPUT_NAME = "prob" OUTPUT_SIZE = 10 DTYPE = trt.float32 def populate_network(network, weights): # 从这个函数可以看出,这里对model.py中的网络架构又重新进行了创建,并没有使用parser来自动构建网络,如果网络层数更深,使用这种方法会非常麻烦 # Configure the network layers based on the weights provided. input_tensor = network.add_input(name=ModelData.INPUT_NAME, dtype=ModelData.DTYPE, shape=ModelData.INPUT_SHAPE) def add_matmul_as_fc(net, input, outputs, w, b): assert len(input.shape) >= 3 m = 1 if len(input.shape) == 3 else input.shape[0] k = int(np.prod(input.shape) / m) assert np.prod(input.shape) == m * k n = int(w.size / k) assert w.size == n * k assert b.size == n input_reshape = net.add_shuffle(input) input_reshape.reshape_dims = trt.Dims2(m, k) filter_const = net.add_constant(trt.Dims2(n, k), w) mm = net.add_matrix_multiply( input_reshape.get_output(0), trt.MatrixOperation.NONE, filter_const.get_output(0), trt.MatrixOperation.TRANSPOSE, ) bias_const = net.add_constant(trt.Dims2(1, n), b) bias_add = net.add_elementwise(mm.get_output(0), bias_const.get_output(0), trt.ElementWiseOperation.SUM) output_reshape = net.add_shuffle(bias_add.get_output(0)) output_reshape.reshape_dims = trt.Dims4(m, n, 1, 1) return output_reshape conv1_w = weights["conv1.weight"].numpy() conv1_b = weights["conv1.bias"].numpy() conv1 = network.add_convolution( input=input_tensor, num_output_maps=20, kernel_shape=(5, 5), kernel=conv1_w, bias=conv1_b ) conv1.stride = (1, 1) pool1 = network.add_pooling(input=conv1.get_output(0), type=trt.PoolingType.MAX, window_size=(2, 2)) pool1.stride = (2, 2) conv2_w = weights["conv2.weight"].numpy() conv2_b = weights["conv2.bias"].numpy() conv2 = network.add_convolution(pool1.get_output(0), 50, (5, 5), conv2_w, conv2_b) conv2.stride = (1, 1) pool2 = network.add_pooling(conv2.get_output(0), trt.PoolingType.MAX, (2, 2)) pool2.stride = (2, 2) fc1_w = weights["fc1.weight"].numpy() fc1_b = weights["fc1.bias"].numpy() fc1 = add_matmul_as_fc(network, pool2.get_output(0), 500, fc1_w, fc1_b) relu1 = network.add_activation(input=fc1.get_output(0), type=trt.ActivationType.RELU) fc2_w = weights["fc2.weight"].numpy() fc2_b = weights["fc2.bias"].numpy() fc2 = add_matmul_as_fc(network, relu1.get_output(0), ModelData.OUTPUT_SIZE, fc2_w, fc2_b) fc2.get_output(0).name = ModelData.OUTPUT_NAME network.mark_output(tensor=fc2.get_output(0)) def build_engine(weights): # For more information on TRT basics, refer to the introductory samples. builder = trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) network = builder.create_network(common.EXPLICIT_BATCH) config = builder.create_builder_config() runtime = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) config.max_workspace_size = common.GiB(1) # Populate the network using weights from the PyTorch model. populate_network(network, weights) # Build and return an engine. plan = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config) return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(plan) # Loads a random test case from pytorch's DataLoader def load_random_test_case(model, pagelocked_buffer): # Select an image at random to be the test case. img, expected_output = model.get_random_testcase() # Copy to the pagelocked input buffer np.copyto(pagelocked_buffer, img) return expected_output def main(): common.add_help(description="Runs an MNIST network using a PyTorch model") # 训练pytorch模型 mnist_model = model.MnistModel() mnist_model.learn() # 训练结束后,可以获得训练后的权重字典 weights = mnist_model.get_weights() # 使用训练好的权重来构建tensorrt的引擎对象 engine = build_engine(weights) # Build an engine, allocate buffers and create a stream. # For more information on buffer allocation, refer to the introductory samples. inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = common.allocate_buffers(engine) context = engine.create_execution_context() # 随机抽取推理样本,保存在inputs中,case_num是抽出的样本的真实值 case_num = load_random_test_case(mnist_model, pagelocked_buffer=inputs[0].host) # For more information on performing inference, refer to the introductory samples. # The common.do_inference function will return a list of outputs - we only have one in this case. # 开始推理,并产生推理结果output [output] = common.do_inference_v2(context, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream) pred = np.argmax(output) # 清除缓存 common.free_buffers(inputs, outputs, stream) # 输出真实值 print("Test Case: " + str(case_num)) # 输出测试值 print("Prediction: " + str(pred)) if __name__ == "__main__": main()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
代码没时间看的,后续完成后我再补上-~
-
相关阅读:
Linux安装Tomcat最新版
【ARM】关于指令集架构?
HTML 简介
一张图进阶 RocketMQ - 消息发送
【22-23春】AI作业10-经典卷积网络
K210-CanMV IDE开发软件
Confluence的安装部署
驶入产业发展快车道,汉鑫科技人工智能研发中心正式启用!
接入API接口文档1688阿里巴巴获取跨境属性数据参考示例
Springboot林业企业销售系统模块58udx计算机毕业设计-课程设计-期末作业-毕设程序代做
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Li_black/article/details/134484923
