-
JavaWeb-CSS
一、什么是CSS
CSS(Cascading Style Sheets,层叠样式表)能够对网页中元素的位置排版进行精确的控制,拥有对网页对象和模型样式的编辑能力,简单来说就是页面美化。
CSS样式代码中的注释需要使用/**/。二、CSS的引入方式
1.使用style属性
通过开始标签的style属性引入,样式语法为:style_name:style_value;style_name:style_value;
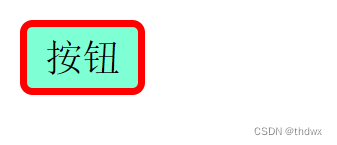
<body> <input type="button" value="按钮" style=" display: block;/*display定义该元素显示的类型*/ width: 50px;/*定义元素的宽*/ height: 30px;/*定义元素的高*/ color: black;/*定义字体的颜色*/ background-color: aquamarine;/*定义背景色*/ border: 3px solid red;/*定义边框的大小样式和颜色*/ font-size: 15px;/*定义字体大小*/ font-family: '宋体';/*定义字体*/ line-height: 20px;/*定义行间距,影响行框的布局*/ border-radius: 5px;/*定义边框的圆角*/" /> body>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
缺点:- HTML代码和CSS样式代码交杂在一起,增加阅读难度和维护成本。
- CSS样式代码仅对当前元素有效,代码复用性低。
2.在head中使用style标签
- 在head标签中使用style标签定义CSS样式。
- CSS样式的作用范围需要使用选择器控制。
- 选择器根据标签名确定样式,语法为 tag_name{CSS code}。
- 多个选择器的定义可以放在一个style标签里,也可以放在多个style标签里。
- 选择器分为元素选择器、id选择器和class选择器。
- CSS代码仍在HTML文件中,但是与body标签是分离的。
- CSS代码只能作用于该文件,复用性仍然有限。
2.1 元素选择器
- 元素选择器:
- 元素选择器的样式只能作用在同名标签上,其他标签无法使用。
- 同名标签未必需要相同的样式,不同名的标签可能需要相同的样式,所以元素选择器仍旧不太方便。
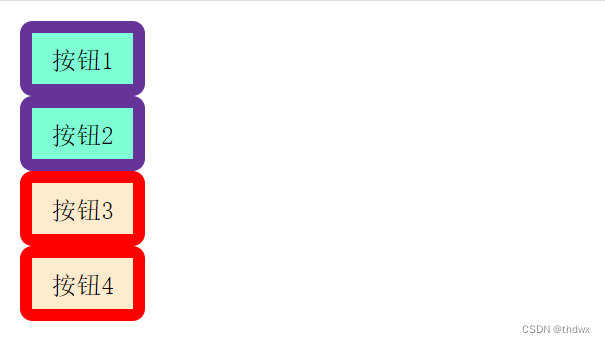
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>IntroWayBySelectortitle> <style> /*通过选择器控制CSS的作用范围 选择器是通过指定应用该样式的标签名来控制作用对象的*/ input{/*作用域inpu标签*/ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: aquamarine; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } style> <style> button{/*作用于button标签*/ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color:blanchedalmond; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid red; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } style> head> <body> <input type="button" value="按钮1" /> <input type="button" value="按钮2" /> <button type="button">按钮3button> <button type="button">按钮4button> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
2.2 id选择器
- id选择器:
- id选择器通过元素的id属性确定样式的作用范围,语法为 #id{CSS code}。
- 元素的id属性在HTML文档中是唯一的,也就是说一个id只能对应一个元素,因此使用id选择器的样式只能作用于一个元素,不够灵活。
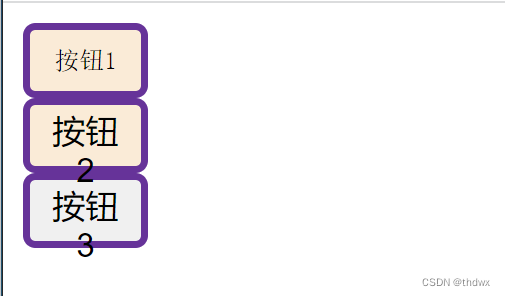
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>IntroWayBySelectortitle> <style> /*通过选择器控制CSS的作用范围 选择器是通过指定应用该样式的标签名来控制作用对象的*/ #btn1{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: antiquewhite; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } #btn2{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: aqua; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid red; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } #btn3{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: azure; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } style> head> <body> <input type="button" value="按钮1" id="btn1" /> <button type="button" id="btn2">按钮2button> <button type="button" id="btn3">按钮3button> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60

2.3 class选择器
- class选择器:
- 根据元素的class属性值确定样式的作用范围,语法为 .class_name{CSS code}。
- 元素的class属性值可以有一个或多个,一个class值也可以对应多个元素。
- class选择器的样式可以用于多个元素,一个元素也可以叠加多个class样式,所以class选择器最为灵活,使用的也最多。
- 在定义class时,可以参考Java中类的定义,将相似的属性定义在一个class中。
- 如果两个class选择器中有相同的属性,并且某个元素同时具有这两个class样式,那么相同的属性会实现后定义的那个。
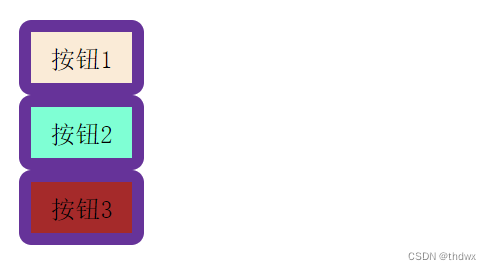
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>IntroWayBySelectortitle> <style> /*通过选择器控制CSS的作用范围 选择器是通过指定应用该样式的标签名来控制作用对象的*/ .fontClass{ color: red; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; line-height: 20px; } .colorClass{ background-color: antiquewhite; color: black; } .shapeClass{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; border: 3px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; } style> head> <body> <input type="button" class="shapeClass colorClass fontClass" value="按钮1" /> <button type="button" class="shapeClass colorClass">按钮2button> <button type="button" class="shapeClass">按钮3button> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
3.使用link标签
- 可以在head标签中使用link标签引入外部的CSS代码
- 将CSS代码从HTML文件中剥离,有利于代码的维护
- 可以被多个HTML文件使用,作用范围更广,提高了代码的复用性
- 外部的CSS代码可以使用三种选择器:元素选择器、id选择器或class选择器。
3.1 元素选择器
input{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: aqua; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 5px; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>ByLinkTagAndAttributeSelectortitle> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../CSSFile/AttributeSelector.css" type="text/css" /> head> <body> <input type="button" value="按钮1" /> <input type="button" value="按钮2" /> <button type="button">按钮2button> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

3.2 id选择器
#btn1{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: antiquewhite; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } #btn2{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: aquamarine; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; } #btn3{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; background-color: brown; color: black; font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; line-height: 20px; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>ByLinkTagAndAttributeSelectortitle> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../CSSFile/IdSelector.css" type="text/css"> head> <body> <input type="button" value="按钮1" id="btn1" /> <button type="button" id="btn2">按钮2button> <input type="button" value="按钮3" id="btn3" /> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
3.3 class选择器
.shapeClass{ display: block; width: 50px; height: 30px; border: 5px solid rebeccapurple; border-radius: 5px; } .colorClass{ background-color: aqua; color: black; } .fontClass{ font-size: 10px; font-family: '宋体'; line-height: 20px; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>ByLinkTagAndClassSelectortitle> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../CSSFile/ClassSelector.css" type="text/css" /> head> <body> <input type="button" class="shapeClass colorClass fontClass" value="按钮1" /> <button type="button" class="shapeClass colorClass">按钮2button> <button type="button" class="shapeClass">按钮3button> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
三、CSS浮动
- CSS浮动使元素脱离文档流,按照指定方向移动,直到外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。
- 浮动设计的初衷是为了解决文字环绕图片问题,图片浮动后一定不会将文字挡住。
- 文档流是文档中可显示对象在排列时所占用的位置或空间,脱离文档流就是在页面中不占位置了。
- 下面通过代码展示浮动。
1. 向右浮动
假设有三个div块(编号从上到下为1、2、3)上下排列,如果将1号块设置为浮动,那么1号块占据的位置就会释放出来,那么2号块就会占据原来1号的位置,3号会占据原来2号的位置。1号块会向右浮动至边框停止。将2号块设置为浮动,它会向右浮动至1号块的边框停止。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>RightFloattitle> <style> .shapeClass{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } style> head> <body> <div class="shapeClass" style="background-color: antiquewhite; float: right;">第一个块div> <div class="shapeClass" style="background-color: aquamarine; float: right;">第二个块div> <div class="shapeClass" style="background-color: brown; float: right;">第三个块div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
未设置浮动 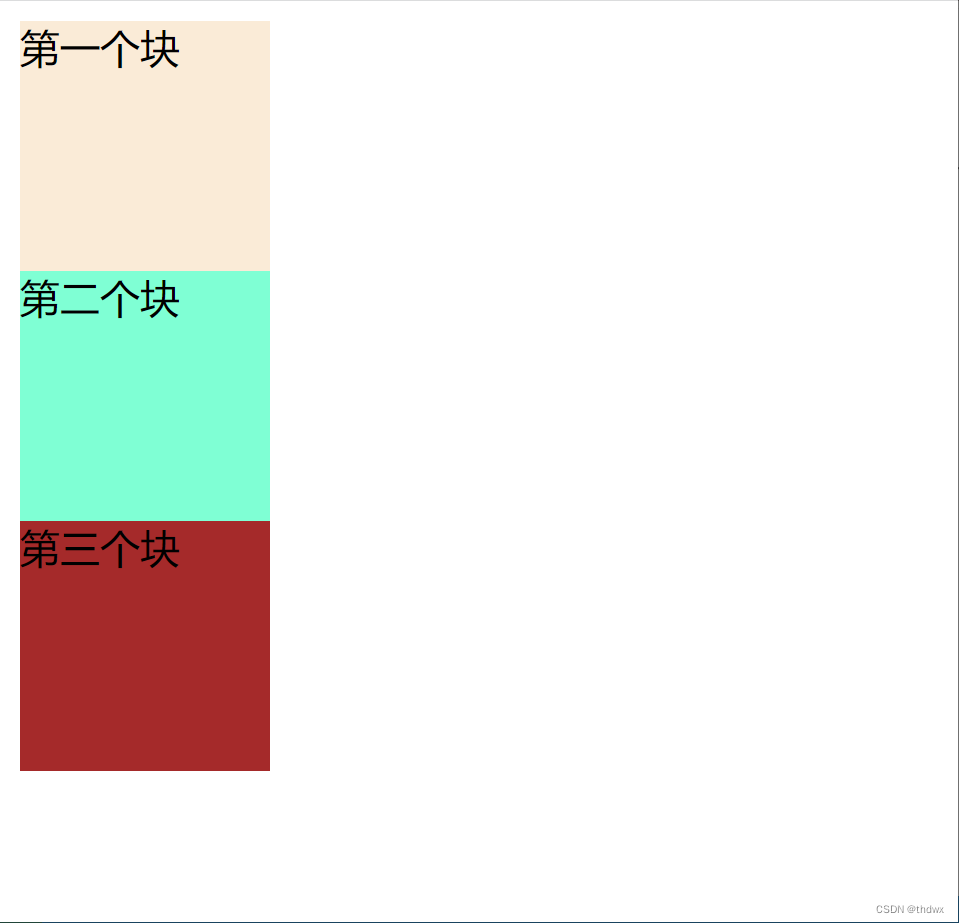
将第一个块设置为浮动 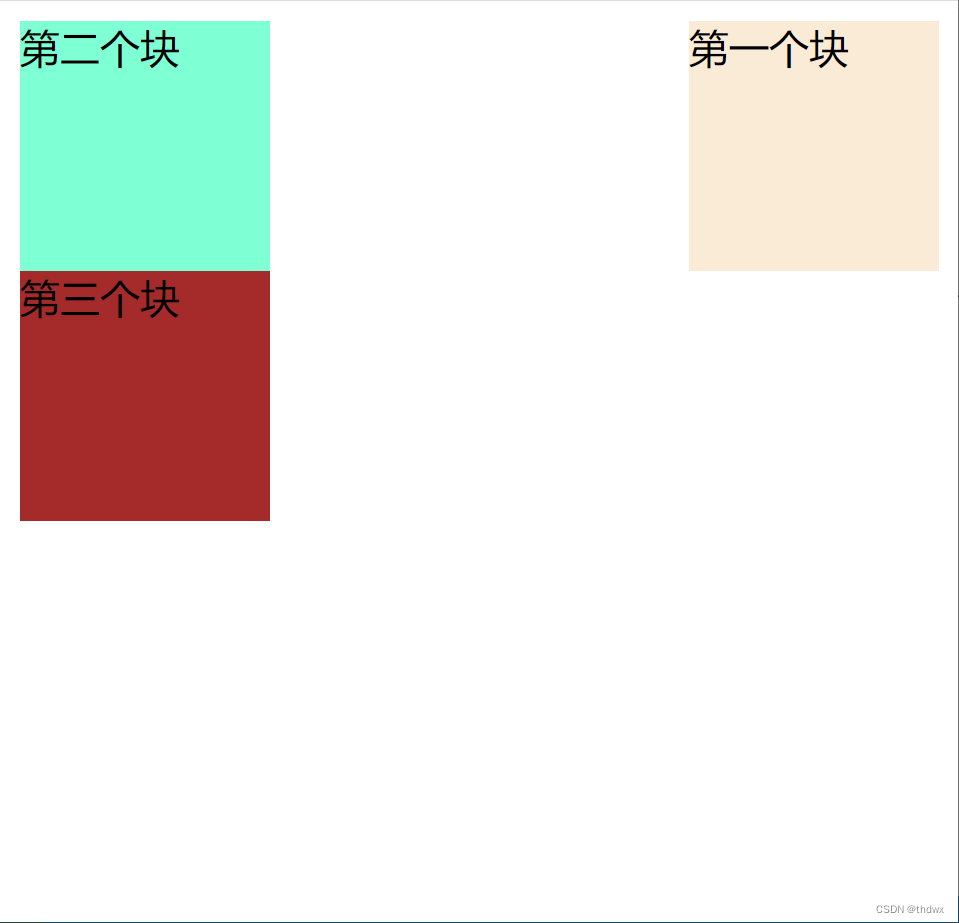
将三个块都设置为浮动 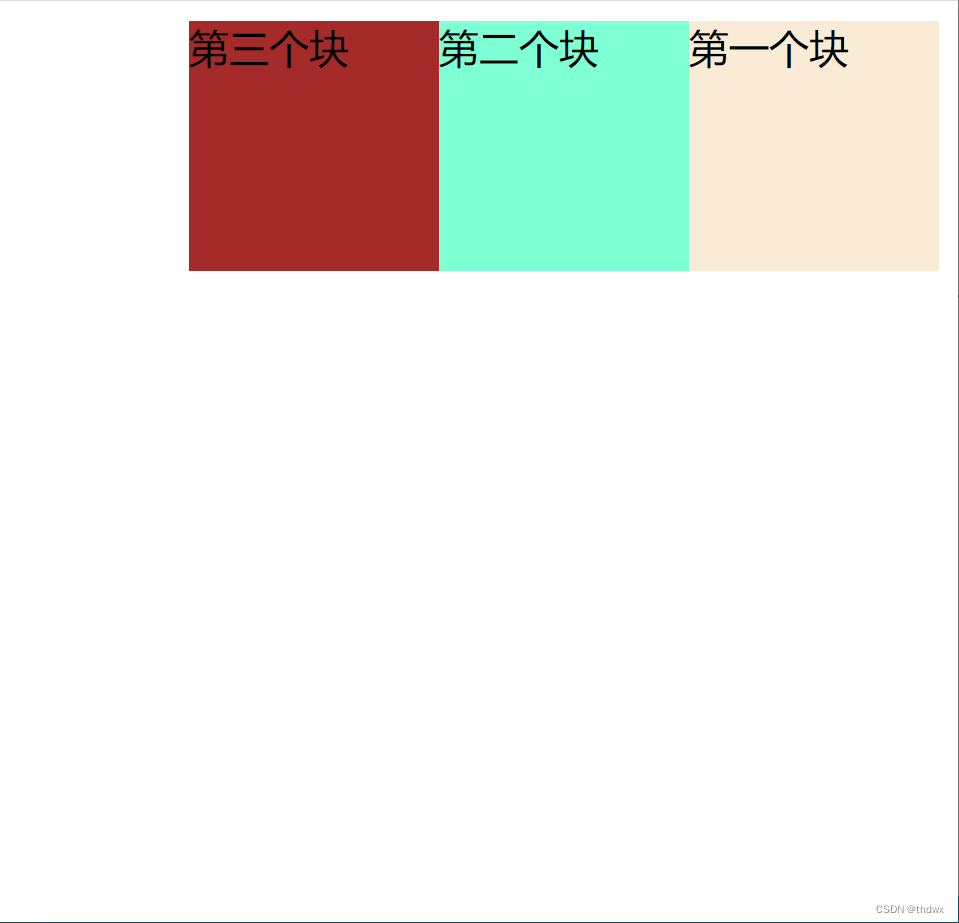
2. 向左浮动
假设如上,如果将1号块设置为向左浮动,那么1号块占据的位置会释放出来,2号块会占据1号块的位置,3号块会占据2号块的位置。但是由于1号块是向左浮动,并且初始位置就已经在页面的最左边,所以当2号块占据1号块的位置时,1号块由于浮动会在2号块的上方,覆盖了2号块。并且由于浮动最初是为了解决文字环绕问题,2号块的文字会被挤到下方。当接着设置2号块为浮动时,3号块会占据2号的位置,2号块会位于1号块的右侧(向左浮动碰到了1号块的边框),并且3号块会被1号块覆盖。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>LeftFloattitle> head> <body> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: antiquewhite; float: left;">第一个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aqua; float: left;">第二二二二个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: brown; float: left;">第三个块div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
未设置浮动 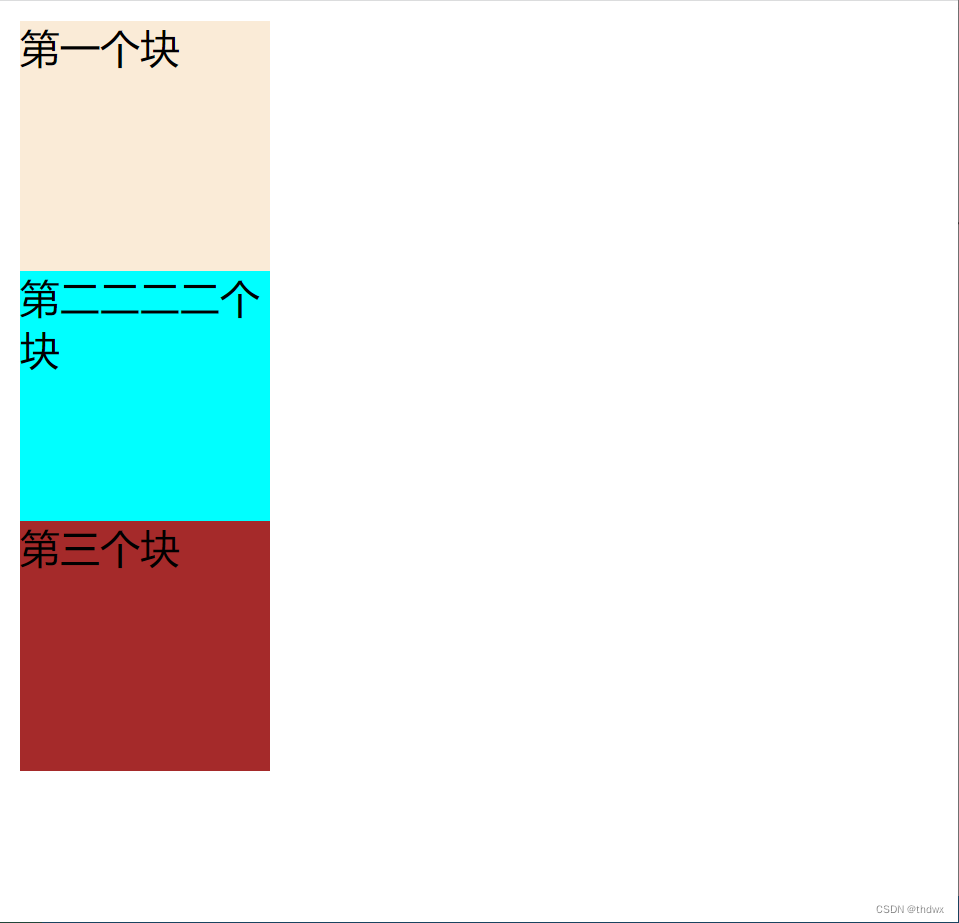
第一个块向左浮动 
三个块都向左浮动 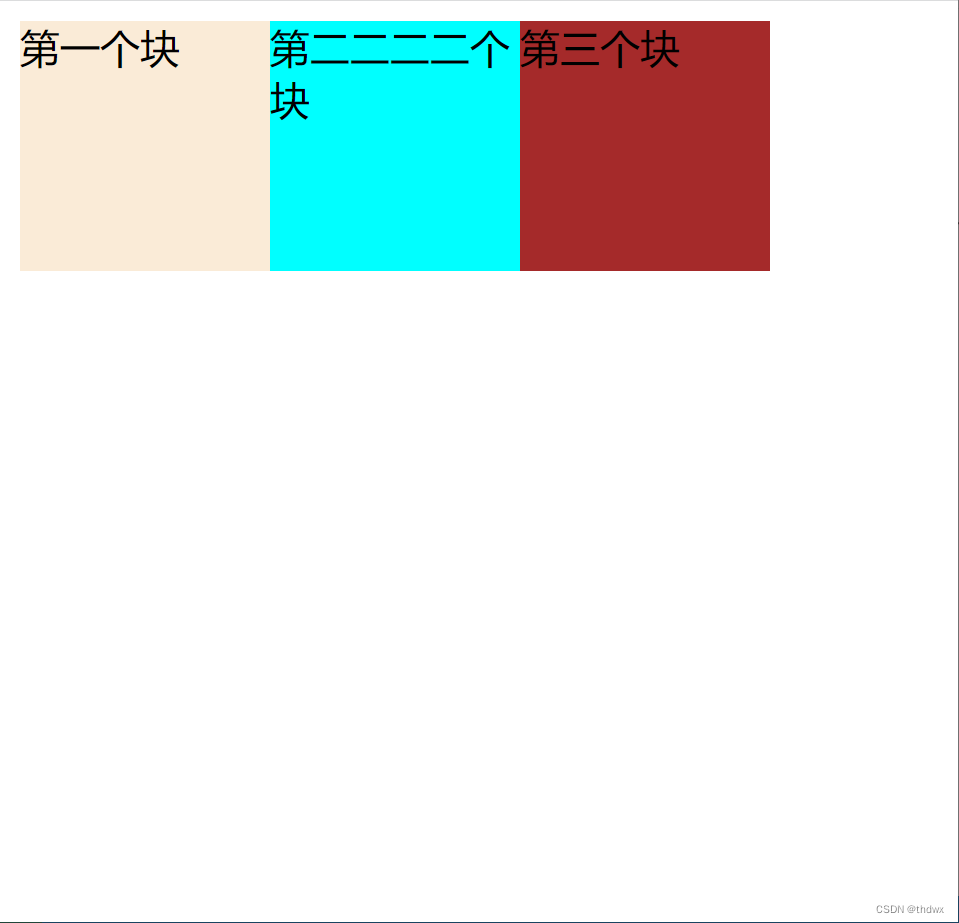
四、CSS定位
在CSS中,元素可以使用顶部、底部、左侧和右侧属性定位,但如果不设定position属性,position默认为static方式,这些定位属性无法生效。position属性有五种定位方式:static、fixed、relative、absolute和sticky。注意在设置位置属性时,top和bottom只用设置一个,因为上方位置确定,下方位置也就确定了,left和right也是同理。元素的定位与文档流无关,因此它们可以覆盖到其他元素上。本节不讨论sticky定位。
4.1 static
静态定位(默认定位方式),元素不会受到top等定位属性的影响。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>NoPositiontitle> head> <body> <div style="top: 0px; left: 0px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: antiquewhite;">块div> <div style="top: 100px; left: 100px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aquamarine; position: static;">块div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

4.2 fixed
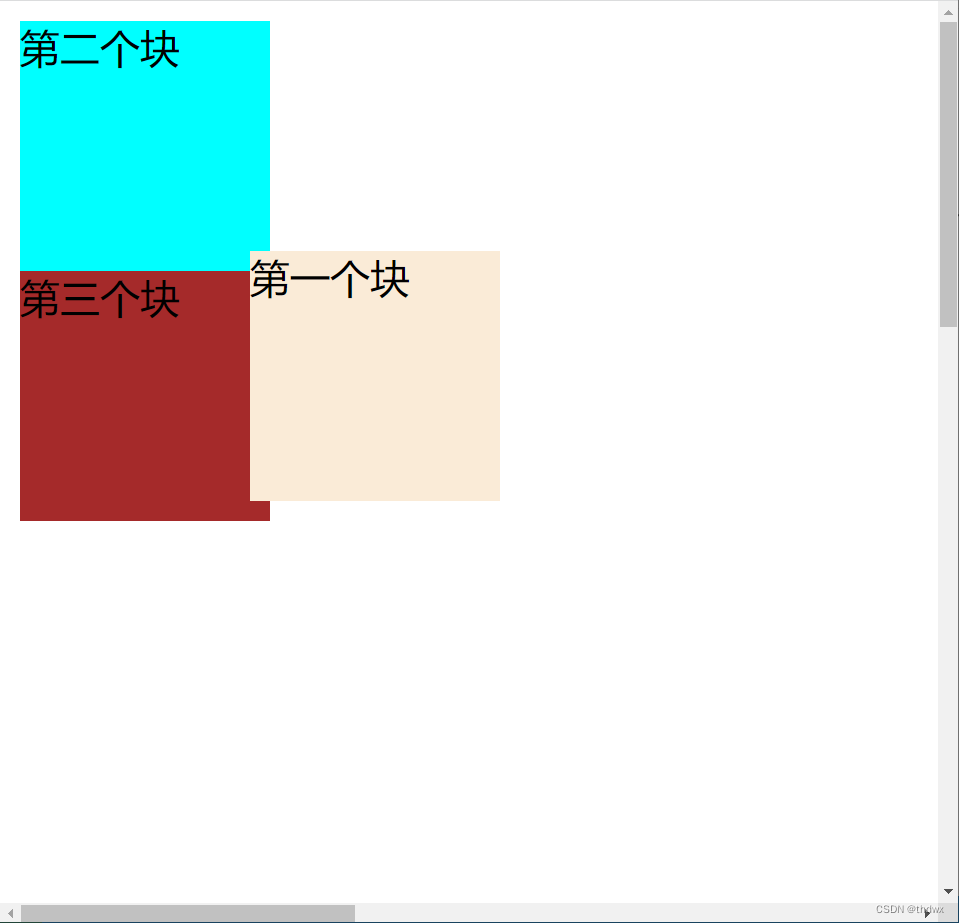
元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定的,可以覆盖在其他元素之上,窗口的广告就可以用这种定位方式。会使元素脱离文档流。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>FixedPositiontitle> head> <body> <div style="width: 1000px; height: 1000px;"> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: antiquewhite; position: fixed; top: 100px; left: 100px;">第一个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aqua;">第二个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: brown;">第三个块div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

4.3 relative
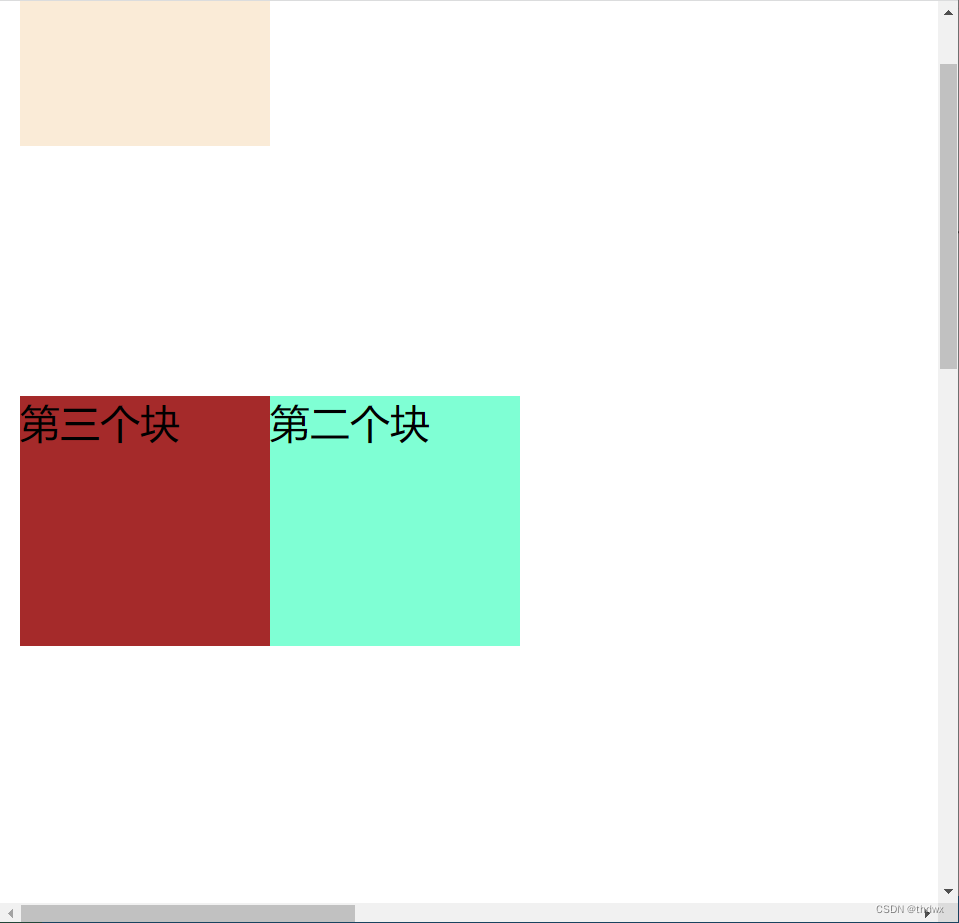
元素的定位是相对于其正常位置。元素正常的位置不会空出来。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>RelativePositiontitle> head> <body> <div style="width: 1000px; height: 1000px;"> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: antiquewhite;">第一个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aquamarine; position: relative; top: 100px; left: 100px;">第二个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: brown;">第三个块div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
4.4 absolute
绝对定位的元素的位置相对于其最近的父元素,如果没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置就是相对于HTML页面的。会使元素脱离文档流。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>AbsolutePositiontitle> head> <body> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: antiquewhite; position: absolute; top: 100px; left: 300px;">第一个块div> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: brown;">第二个块div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

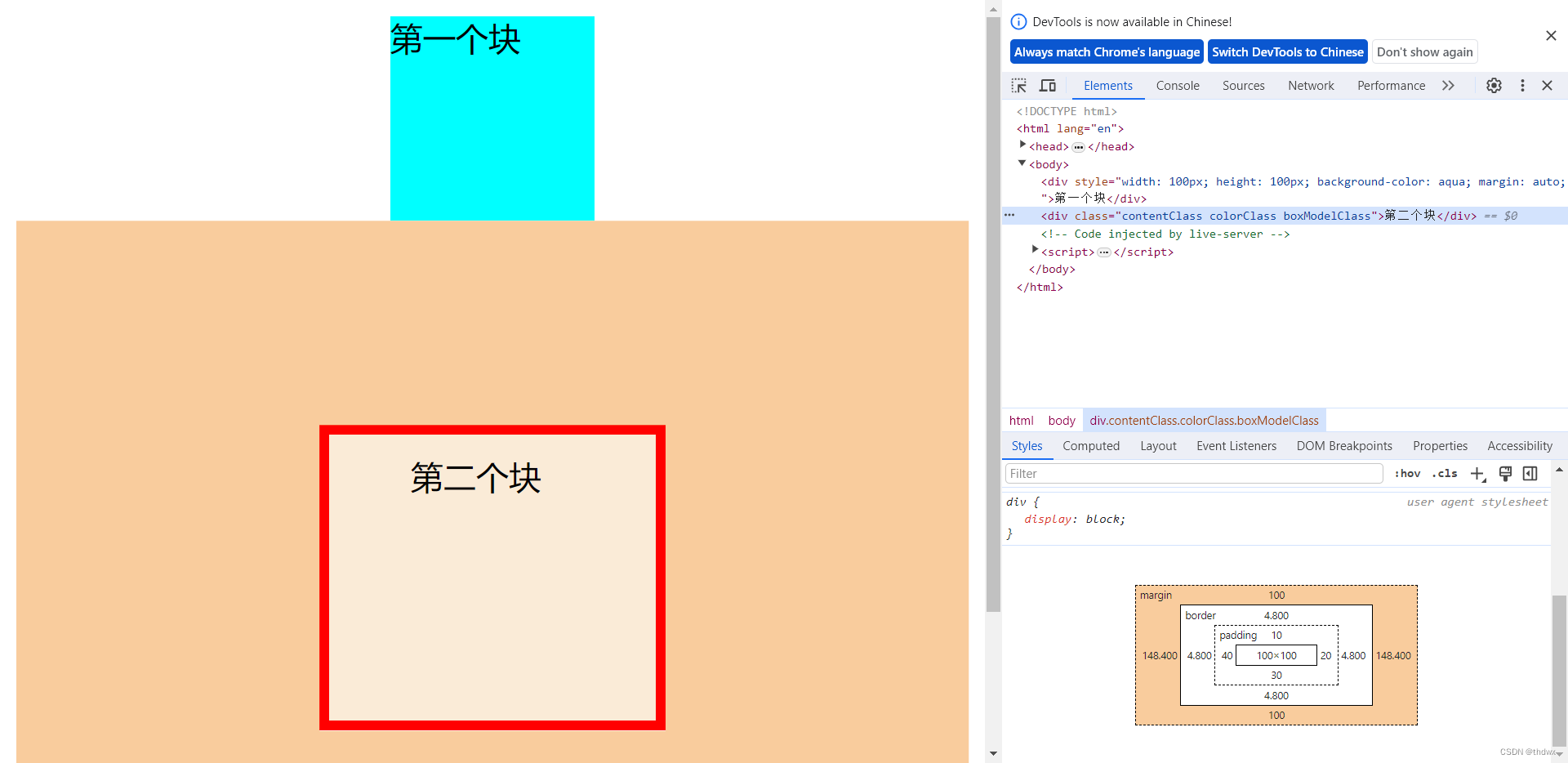
五、CSS盒子模型
所有HTML元素可以看作盒子,盒子模型可以封装周围的HTML元素:边距、边框、填充和实际内容。
- margin:外边距,清楚边框外特定区域的内容,外边距是透明的。四个参数代表上右下左,两个参数表示上下(为一组)、左右(为一组),一个参数表示四个方向都为此大小。
- border:边框,围绕在内边距外的边框。
- padding:内边距,清楚内容周围的区域,内边距是透明的。参数用法与margin一致。
- content:盒子的内容,显示文本和图像。内边距、外边距和边框都不会占用内容区域的空间,也就是说,在指定了width和height之后,内容区域的大小就是不变的。
- 在浏览器中使用F12可以查看盒子模型。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>BoxModeltitle> <style> .contentClass{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .colorClass{ background-color: antiquewhite; } .boxModelClass{ margin: 100px auto; border: 5px solid red; padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px; } style> head> <body> <div style="width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: aqua; margin: auto;">第一个块div> <div class="contentClass colorClass boxModelClass">第二个块div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
-
相关阅读:
微软hotmail邮箱的存储空间查询
ubuntu16因swap分区uuid错误启动慢排查
6.824 lab2
华为机试真题 C++ 实现【最大平分数组】【2022.11 Q4新题】
通过Shell脚本自动安装Hive&JDBC测试&提供CDH5网盘地址
Java并发编程学习7-阻塞队列
智能合约安全分析,假充值攻击如何突破交易所的防御?
dy系滑块协议2022/11/1
【FPGA教程案例55】深度学习案例2——基于FPGA的CNN卷积神经网络之ReLu激活层verilog实现
Lru-k在Rust中的实现及源码解析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/thdwx/article/details/134416803
