-
c++虚函数纯虚函数详解加代码解释
c++虚函数纯虚函数详解加代码解释
一.概念:
虚函数和纯虚函数是面向对象编程中的概念,用于实现多态性和抽象类特性。
虚函数(Virtual Function)是在基中声明的函数,通过在函数前面加上virtual关键字来标识。虚函数可以在派生类中被重写,实现函数的多态性。在运行时,根据对象的实际类型来确定调用哪个版本的虚函数。通过基类的指针或引用调用虚函数时,会根据指针或引用所指向的对象类型来调用相应的函数。
纯虚函数(Pure Virtual Function)是在基类中声明的没有实际实现的函数,通过在函数声明后面加上= 0来标识。纯虚函数用于定义接口,要求派生类必须实现函数。有了纯虚函数,基类就成为了抽象类,无法创建对象,只能作为其他类的基类来派生出新的类。
纯虚函数的作用是实现接口的统一和规范,确保派生类都实现了基类中定义的接口。纯虚函数可以在派类中重写,也可以不重写如果某个派类重写纯虚函数,那么该派生类也成为抽象类,无法创建对象。二.虚函数示例及解析:
#includeusing namespace std; class Animal { public: virtual void speak() { cout << "Animal speaks!" <<endl; } }; class Dog : public Animal { public: void override() { cout << "Dog barks!" << endl; } }; class Cat : public Animal { public: void speak() { cout<< "Cat meows!" << endl; } }; int main() { Animal* animal1 = new Dog(); Animal* animal2 = new Cat(); animal1->speak(); // 输出:Dog barks! animal2->speak(); // 输出:Cat meows! delete animal1; delete animal2; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36

虚函数是在基类中声明的具有虚函数特性的函数,通过在声明前加上键字virtual来标识。它允许在派生类中重写该函数,实现多态性。在运行时,根据对象的实际类型来确定调用哪个版本虚函数。
在上述中,Animal类是基类,其中的speak()函数被声明为虚Dog和Cat类是派生类,它们分别重写了speak()`函数。
在main()函数中,我们通过基类指针分别创建了Dog和Cat对象,并调用了speak()函数。由于speak()函数是虚函数,所以在运行时会根据对象的实际类型来确定调用哪个版本的函数因此,输出结果分别是"Dog barks!“和"Cat meows!”。三.纯虚函数示例及解析:
#includeusing namespace std; class Shape { public: virtual double getArea() = 0; }; class Rectangle : public Shape { private: double length; double width; public: Rectangle(double len, double wid) : length(len), width(wid) {} double getArea() override { cout << "Rectangle" << endl; return length*width; } }; class Square : public Shape { private: double length; public: Square(double len) : length(len){} double getArea() override { cout << "Square" << endl; return length * length; } }; class Circle : public Shape { private: double radius; public: Circle(double r) : radius(r){} double getArea() override { cout << "Circle" << endl; return 3.14 * radius * radius; } }; int main() { Shape* shape1 = new Rectangle(5, 4); Shape* shape2 = new Circle(3); Shape* shape3 = new Square(5); cout << "Area of rectangle: " << shape1->getArea() << endl; cout << "Area of circle: " << shape2->getArea() << endl; cout << "Area of square:" << shape3->getArea() << endl; delete shape1; delete shape2; delete shape3; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
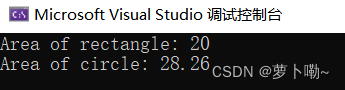
纯虚函数是在基类中声明的没有实际实现的函数,通过函数声明后加上= 0来标识。它用于定义接口求派生类必须实现该函数。
在上述代码中,Shape类是基类,其中的getArea()函数被声明为纯虚函数。Rectangle``Circle类是派生类,它们必须实现getArea()函数。
在main()函数中,我们通过基类指针分别创建了Rectangle和Circle,并调用了getArea()函数。由于getArea()函数是纯虚函数,所以基类Shape无法创建对象,只能通过派生类来实现具体的功能因此,输出结果分别是矩形的面积和圆的面。四.验证和实际使用及解析:
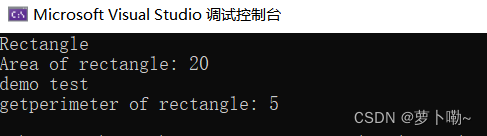
1.子类没有对父类的函数重载,mian()函数调用,是直接返回父类的值
#includeusing namespace std; class Shape { public: virtual double getArea() = 0; virtual double getperimeter() { cout << "demo test" << endl; return 5; }; }; class Rectangle : public Shape { private: double length; double width; public: Rectangle(double len, double wid) : length(len), width(wid) {} double getArea() override { cout << "Rectangle" << endl; return length * width; } }; int main() { Shape* shape1 = new Rectangle(5, 4); cout << "Area of rectangle: " << shape1->getArea() << endl; cout << "getperimeter of rectangle: " << shape1->getperimeter() << endl; delete shape1; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
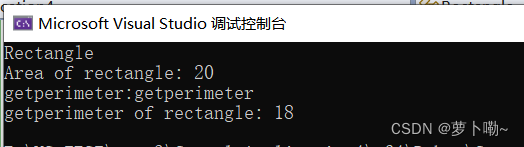
2.子类对父类的函数重载,mian()函数调用,是直接返回子类重载后的返回值
#includeusing namespace std; class Shape { public: virtual double getArea() = 0; virtual double getperimeter() { cout << "demo test" << endl; return 5; }; }; class Rectangle : public Shape { private: double length; double width; public: Rectangle(double len, double wid) : length(len), width(wid) {} double getArea() override { cout << "Rectangle" << endl; return length * width; } double getperimeter(){ cout <<"getperimeter:getperimeter" << endl; return length * 2 + width * 2; } }; int main() { Shape* shape1 = new Rectangle(5, 4); cout << "Area of rectangle: " << shape1->getArea() << endl; cout << "getperimeter of rectangle: " << shape1->getperimeter() << endl; delete shape1; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41

3.子类对父类的函数重载,但子类调用自己函数,mian()函数调用时,报错,是因为,类的定义指向父类重新定义子类,父类中没有的子类也不能调用。
将:Shape* shape1 = new Rectangle(5, 4); 修改为:Rectangle* shape1 = new Rectangle(5, 4);- 1
- 2
我们才能调用子类中父类没有定义的函数
#includeusing namespace std; class Shape { public: virtual double getArea() = 0; }; class Rectangle : public Shape { private: double length; double width; public: Rectangle(double len, double wid) : length(len), width(wid) {} double getArea() override { cout << "Rectangle" << endl; return length * width; } double getperimeter(){ cout <<"getperimeter:getperimeter" << endl; return length * 2 + width * 2; } }; int main() { Rectangle* shape1 = new Rectangle(5, 4); cout << "Area of rectangle: " << shape1->getArea() << endl; cout << "getperimeter of rectangle: " << shape1->getperimeter() << endl; delete shape1; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
五.总结:
虚函数用于实现多性,允许在派生类中重写基类的函数。
纯虚函数用于定义接口,要求派生必须实现函数,可以在派生类中重写或不重写。补充override关键字作用:
如果派生类在虚函数声明时使用了override描述符,那么该函数必须重载其基类中的同名函数,否则代码将无法通过编译
-
相关阅读:
SpringMVC+统一表现层返回值+异常处理器
企业微信设置可信域名
kafka随笔
springboot超市库存管理系统java ssm
String.format() 拼接字符串
Cisco IOS XE Web UI 命令执行漏洞
微信小程序|使用小程序制作一个世界杯球员识别工具
【原创】FFMPEG录屏入门指南
Linux篇 五、Ubuntu与Linux板卡建立NFS服务
【JIRA 学习】如何配置工作流转换的时候触发弹出界面,并填写相关信息
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44913716/article/details/134442338
