-
[模版总结] - 树的基本算法2 - BST
BST定义
BST - Binary Search Tree, 即二叉搜索树(有序二叉树)
特性
- 中序遍历有序
- 查找/插入/删除某个数值可以通过
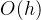 即树的高度,最优
即树的高度,最优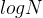 ,最坏
,最坏 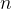 .
.
- 有多种改进BST可以动态维持插入删除后树结构能尽可能保持平衡
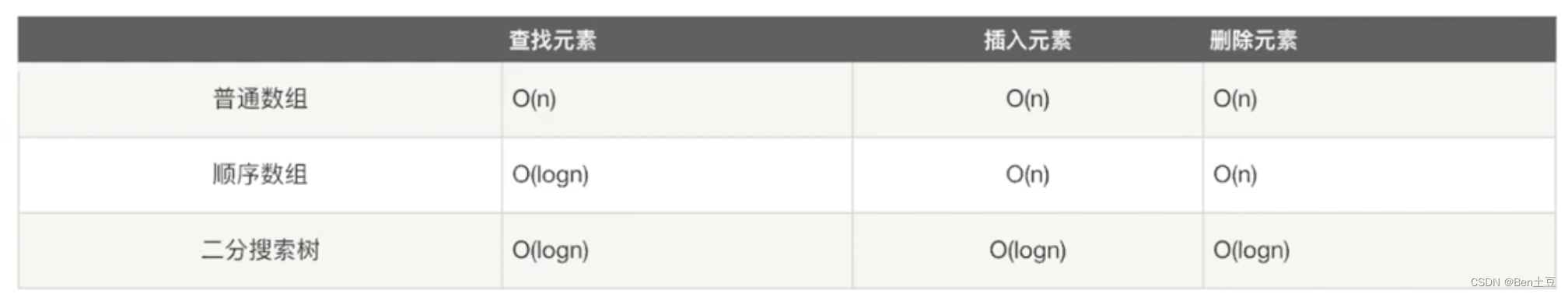
BST基本操作
查询 - 二分查找
- 搜索数值 - 二分法
- class Solution {
- public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
- while(root!=null) {
- if (root.valroot = root.right;} else if (root.val>val) {root = root.left;} else {return root;}}return null;}}
- 搜索临近数值
- class Solution {
- double min = Double.MAX_VALUE;
- int res = -1;
- public int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
- dfs(root, target);
- return res;
- }
- private void dfs(TreeNode root, double target) {
- if (root==null) return;
- if (Math.abs(root.val - target) < min) {
- min = Math.abs(root.val - target);
- res = root.val;
- } else if (Math.abs(root.val - target) == min) {
- res = root.val}if (root.val>target) dfs(root.left, target);else dfs(root.right, target);}}
插入
插入则是首先找到需要插入的位置,然后插入新结点
- class Solution {
- public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
- return dfs(root, val);
- }
- private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root, int val) {
- if (root==null) {
- root = new TreeNode(val);
- return root;
- }
- if (root.val > val) root.left = dfs(root.left, val);
- else root.right = dfs(root.right, val);
- return root;
- }
- }
删除
删除操作较为复杂一点,我们在删除之后还需要维护当前二叉搜索树的性质,有三种情况:
- 删除叶子结点,不会影响BST性质,直接删除即可
- 删除结点没有右子树,也就是删除后左子树不会影响BST性质,将左子树root直接顶替删除结点的位置即可
- 删除结点有左右子树,为了保证BST性质,我们选择删除点的后继结点作为顶替结点,也就是删除结点右子树最左边的那个点,因为可以保证右子树所有点都大于该点,维持了BST性质
- class Solution {
- public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
- /**
- 删除三种情况
- 1. 叶子结点
- 2. 只存在一个子树
- 3. 左右都存在子树
- */
- return dfs(root, key);
- }
- private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root, int key) {
- if (root==null) return null;
- if (root.val==key) {
- if (root.left==null && root.right==null) return null;
- else if (root.left==null || root.right==null) {
- if (root.left!=null) return root.left;
- if (root.right!=null) return root.right;
- } else {
- // 找到root的后继结点,也就是右子树最左边的那个点
- TreeNode dum = root.right;
- while (dum.left!=null) {
- dum = dum.left;
- }
- root.val = dum.val;
- root.right = dfs(root.right, root.val);
- }
- } else if (root.val>key) {
- root.left = dfs(root.left, key);
- } else {
- root.right = dfs(root.right, key);
- }
- return root;
- }
- }
前驱/后继结点
求解某一个点的前驱结点思路存储一个变量prev来保存进行下一层递归前的结点信息,如果中序遍历递归遍历到目标结点,其实保存的prev就是该结点的前驱结点
- private void preSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
- if (node==null) return;
- preSuccessor(node.left, p);
- if (root==p) return prev;
- prev = root;
- preSuccessor(node.right, p);
- }
求解后躯结点较为复杂,需要考虑到几种情况:
- 目标结点有右子树,那么后继结点则是右子树中leftmost结点
- 如果目标结点没有右子树,那么后继结点则可能是parent中的某个结点
求解上述第二类后继结点思路类似,前驱结点是当前递归层处理的结点是目标结点时,prev保存的值即为前驱结点;后继结点可以理解为当前递归层的前驱结点时目标结点时,那么当前结点就是目标结点的后继结点,有点逆向思维哈哈。

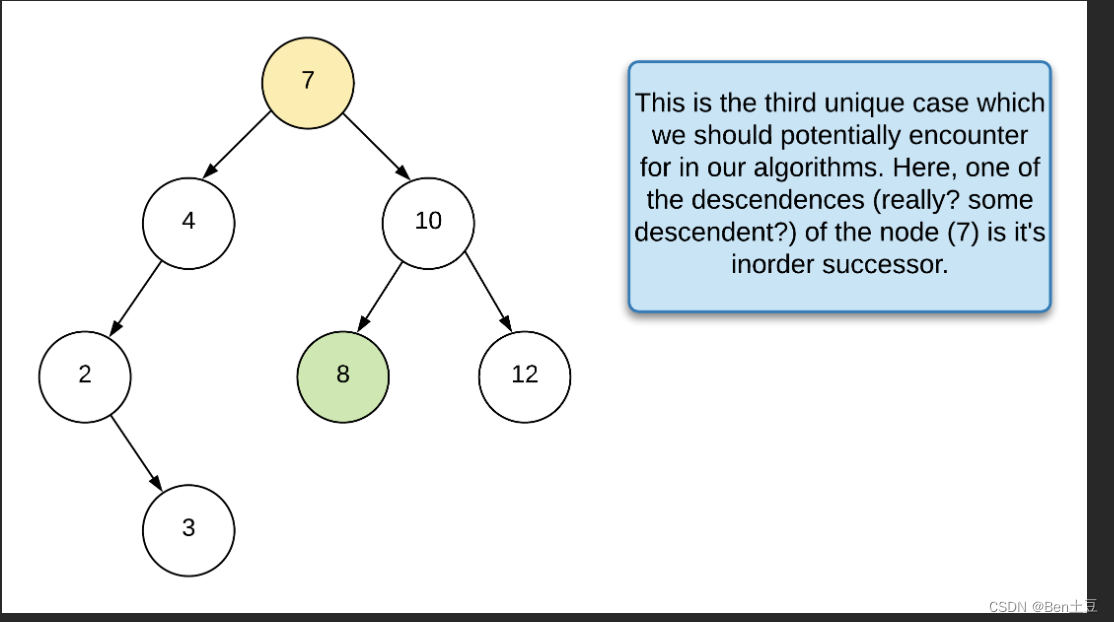
- class Solution {
- // 需要前驱结点信息
- TreeNode prev;
- TreeNode insuccessor;
- public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
- if (p.right!=null) {
- TreeNode node = p.right;
- while (node.left!=null) {
- node = node.left;
- }
- return node;
- } else {
- helper(root, p);
- }
- return insuccessor;
- }
- private void helper(TreeNode node, TreeNode p) {
- if (node==null) return;
- helper(node.left, p);
- // check 当前结点
- if (prev!=null && prev==p) {
- insuccessor = node;
- }
- prev = node; //如果 当前结点前驱结点==p那么这个结点就是p的后驱结点
- helper(node.right, p);
- }
- }
验证是否为BST
基本思路就是确保左结点 < 根结点 < 右结点,但是还需要保证局部正确的同时,左子树全部结点 < 根结点 < 右子树全部结点。所以每一次向下递归左子树时要以当前结点值作为上限值,遍历右子树时以当前结点值作为下限值
- class Solution {
- public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
- return helper(root, null, null);
- }
- private boolean helper(TreeNode root, Integer low, Integer high) {
- if (root==null) return true;
- if ((low!=null && root.val<=low) || (high!=null && root.val>=high)) {
- return false;
- }
- return helper(root.left, low, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, high);
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
老外贸人谈沟通技巧
Spring Controller内存马
展锐平台NewGallery2内存泄露分析
量化投资学习——股票分红对期指的影响
JVM-满老师
多级式多传感器信息融合中的状态估计(Matlab代码实现)
leetcode做题笔记150. 逆波兰表达式求值
java+python+vue学习资源共享网站
Ceres 数值导数 (NumericDerivatives)进阶
SpringBoot校验手机验证码案例:默认缓存、Ehcache缓存、数据淘汰策略、redis缓存
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ok1382038/article/details/134343947
