-
【人工智能实验】遗传算法求解旅行商问题 golang
人工智能经典问题旅行商求解
使用遗传算法求解,算法流程如下:
- 读取所有的城市坐标,记作集合initCitys
- 生成popSize个种群,记为pops
- 取出种群中适应度最高的,记作rank0
- 使用轮盘算法,从rank0中选出eliteSize个个体,生成下一代,记作pops2
- 对pops2进行交叉
- 对pops2进行概率为rate的随机变异
- 如果繁衍次数大于generation,则跳出,反之回到3
进阶
因为有随机事件,所以即使是同样的参数(initCitys, popSize, eliteSize, rate, generation)也可能得到不同的结果。
因此,为了提高运行效率,我采用了并发的方式,对同一参数进行多次并发,并得到最终的结果。
使用go语言实现如下
-
main.go
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/gookit/color" "log" "os" "os/signal" "runtime" "sync" "syscall" ) var ( wg sync.WaitGroup numGoroutines = 25 ) var ( msgChan = make(chan string) quitChan = make(chan os.Signal, 1) doneChan = make(chan bool) ) func main() { runtime.LockOSThread() color.BgCyan.Println("Y02114562 ") cityList, err := readCityData("city.txt") if err != nil { log.Fatalln("Read file error ", err) } wg.Add(numGoroutines) for i := 0; i < numGoroutines; i++ { go goSolve(i, CopyCity(cityList), 100, 20, 0.01, 3000) } signal.Notify(quitChan, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM) go func() { wg.Wait() doneChan <- true }() sel: select { case <-quitChan: color.Red.Println("接收到终止信号") break case msg := <-msgChan: color.BgLightYellow.Println(msg) goto sel case <-doneChan: color.Green.Println("所有协程执行完毕") break } <-quitChan runtime.UnlockOSThread() } func goSolve(goID int, cityList []City, popSize, eliteSize int, rate float64, generation int) { defer wg.Done() msgChan <- fmt.Sprintf("协程%d开启求解", goID) float64s := solve(goID, cityList, popSize, eliteSize, rate, generation) runtime.Gosched() min := findMin(float64s) msgChan <- fmt.Sprintf("协程%d的最短路径为%f", goID, min) } func solve(goID int, cityList []City, popSize, eliteSize int, rate float64, generation int) []float64 { population := initPop(cityList, popSize) process := make([]float64, 0) for i := 0; i < generation; i++ { population = updatePop(population, eliteSize, rate) runtime.Gosched() process = append(process, 1.0/rank(population)[0].Fitness) } idxRankPop := rank(population)[0].Index cities := population[idxRankPop] var index = 0 writeToFile(fmt.Sprintf("out/%d.txt", goID), func() (bool, float64, float64) { if index >= len(cities) { return false, 0, 0 } x, y := cities[index].x, cities[index].y index++ runtime.Gosched() return true, x, y }) return process }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
-
city.go
package main type City struct { x float64 y float64 } func NewCity(x, y float64) City { return City{x: x, y: y} } func CopyCity(input []City) []City { copied := make([]City, len(input)) copy(copied, input) return copied }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
-
tool.go
package main import ( "bufio" "fmt" "log" "math" "math/rand" "os" "sort" "strconv" "strings" ) // distance 城市的距离 func distance(ca, cb City) float64 { dx := math.Abs(ca.x - cb.x) dy := math.Abs(ca.y - cb.y) return math.Sqrt(math.Pow(dx, 2) + math.Pow(dy, 2)) } // distancePop 个体的值 func distancePop(pop []City) float64 { sum := 0.0 for i := 0; i < len(pop); i++ { sum += distance(pop[i], pop[(i+1)%len(pop)]) } return sum } // fitness 个体的适应度 func fitness(pop []City) float64 { return 1.0 / distancePop(pop) } // rank 种群的排序 func rank(population [][]City) []struct { Index int Fitness float64 } { rankPopSlice := make([]struct { Index int Fitness float64 }, len(population)) for i, pop := range population { fit := fitness(pop) rankPopSlice[i] = struct { Index int Fitness float64 }{i, fit} } sort.Slice(rankPopSlice, func(i, j int) bool { return rankPopSlice[i].Fitness > rankPopSlice[j].Fitness }) return rankPopSlice } // initPop 初始化种群 func initPop(cityList []City, popSize int) [][]City { pop := make([][]City, popSize) for i := 0; i < popSize; i++ { newCityList := make([]City, len(cityList)) copy(newCityList, cityList) rand.Shuffle(len(newCityList), func(j, k int) { newCityList[j], newCityList[k] = newCityList[k], newCityList[j] }) pop[i] = newCityList } return pop } // updatePop 更新种群 func updatePop(oldPop [][]City, eliteSize int, rate float64) [][]City { oldRank := rank(oldPop) selectedPop := selectPopulation(oldPop, oldRank, eliteSize) breadPop := cross(selectedPop, eliteSize) return mutate(breadPop, rate) } // mutate 变异 func mutate(pop [][]City, mutationRate float64) [][]City { mutationPop := make([][]City, 0) for i := 0; i < len(pop); i++ { for j := 0; j < len(pop[i]); j++ { rate := rand.Float64() if rate < mutationRate { a := rand.Intn(len(pop[i])) pop[i][a], pop[i][j] = pop[i][j], pop[i][a] } } mutationPop = append(mutationPop, pop[i]) } return mutationPop } // cross 交叉操作 func cross(pop [][]City, eliteSize int) [][]City { breedPop := make([][]City, 0) for i := 0; i < eliteSize; i++ { breedPop = append(breedPop, pop[i]) } i := 0 for i < (len(pop) - eliteSize) { // 随机选择两个个体 a 和 b 进行交叉 a := rand.Intn(len(pop)) b := rand.Intn(len(pop)) if a != b { fa := pop[a] fb := pop[b] // 随机选择交叉点,确定交叉片段的起始和结束位置 geneA := rand.Intn(len(pop[a])) geneB := rand.Intn(len(pop[b])) startGene := min(geneA, geneB) endGene := max(geneA, geneB) child1 := make([]City, 0) // 将交叉片段从个体 a 复制到子代个体 child1 中 for j := startGene; j < endGene; j++ { child1 = append(child1, fa[j]) } child2 := make([]City, 0) // 将个体 b 中不在 child1 中的城市复制到子代个体 child2 中 for _, j := range fb { if !contains(child1, j) { child2 = append(child2, j) } } // 将 child1 和 child2 合并形成一个新的子代个体,加入到子代种群中 breedPop = append(breedPop, append(child1, child2...)) i = i + 1 } } return breedPop } func min(a, b int) int { if a < b { return a } return b } func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a } return b } func contains(slice []City, elem City) bool { for _, e := range slice { if e == elem { return true } } return false } // selectPopulation 精英选择策略(轮盘) func selectPopulation(pop [][]City, popRank []struct { Index int Fitness float64 }, eliteSize int) [][]City { selectPop := make([][]City, 0) for i := 0; i < eliteSize; i++ { selectPop = append(selectPop, pop[popRank[i].Index]) } cumSum := 0.0 cumSumList := make([]float64, 0) // 求累计概率 tempPop := make([]struct { Index int Fitness float64 }, len(popRank)) copy(tempPop, popRank) for i := 0; i < len(tempPop); i++ { cumSum += tempPop[i].Fitness cumSumList = append(cumSumList, cumSum) } for i := 0; i < len(tempPop); i++ { cumSumList[i] /= cumSum } // 剩余的按顺序返回 for i := len(tempPop) - eliteSize; i > 0; i-- { rate := rand.Float64() for j := 0; j < len(tempPop); j++ { if cumSumList[j] > rate { selectPop = append(selectPop, pop[tempPop[i].Index]) break } } } return selectPop } func readCityData(filepath string) ([]City, error) { cityList := make([]City, 0) file, err := os.Open(filepath) if err != nil { return nil, err } defer func(file *os.File) { _ = file.Close() }(file) scanner := bufio.NewScanner(file) for scanner.Scan() { line := scanner.Text() line = strings.TrimSpace(line) cityInfo := strings.Split(line, "\t") if len(cityInfo) != 3 { return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid city data: %s", line) } x, err := strconv.ParseFloat(strings.TrimSpace(cityInfo[1]), 64) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid city X coordinate: %s", cityInfo[1]) } y, err := strconv.ParseFloat(strings.TrimSpace(cityInfo[2]), 64) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid city Y coordinate: %s", cityInfo[2]) } cityList = append(cityList, NewCity(x, y)) } if err := scanner.Err(); err != nil { return nil, err } return cityList, nil } func findMin(slice []float64) float64 { min := math.Inf(1) for _, value := range slice { if value < min { min = value } } return min } func writeToFile(name string, getData func() (bool, float64, float64)) { file, err := os.Create(name) if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } defer func(file *os.File) { _ = file.Close() }(file) for true { if has, x, y := getData(); has { line := fmt.Sprintf("%f|%f\n", x, y) _, err := file.WriteString(line) if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } } else { return } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
-
city.txt
A 18 54 B 87 76 C 74 78 D 71 71 E 25 38 F 55 35 G 4 50 H 13 40 I 18 40 J 24 42 K 71 44 L 64 60 M 68 58 N 83 69 O 58 69 P 54 62 Q 51 67 R 37 84 S 41 94 T 2 99 U 7 64 V 22 60 W 25 62 X 62 32 Y 87 7 Z 91 38 A2 83 45 B2 41 26 C2 45 21 D2 44 35- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
-
city2.txt
北京 116.46 39.92 天津 117.2 39.13 上海 121.48 31.22 重庆 106.54 29.59 拉萨 91.11 29.97 乌鲁木齐 87.68 43.77 银川 106.27 38.47 呼和浩特 111.65 40.82 南宁 108.33 22.84 哈尔滨 126.63 45.75 长春 125.35 43.88 沈阳 123.38 41.8 石家庄 114.48 38.03 太原 112.53 37.87 西宁 101.74 36.56 济南 117 36.65 郑州 113.6 34.76 南京 118.78 32.04 合肥 117.27 31.86 杭州 120.19 30.26 福州 119.3 26.08 南昌 115.89 28.68 长沙 113 28.21 武汉 114.31 30.52 广州 113.23 23.16 台北 121.5 25.05 海口 110.35 20.02 兰州 103.73 36.03 西安 108.95 34.27 成都 104.06 30.67 贵阳 106.71 26.57 昆明 102.73 25.04 香港 114.1 22.2 澳门 113.33 22.13- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
因为go语言的gui绘制能力过于羸弱,我采用了python进行绘制,代码如下
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt if __name__ == '__main__': x_labels = [] y_labels = [] with open(r'D:\Desktop\GolandProjects\AI2\out\24.txt', 'r') as file: for line in file: parts = line.strip().split('|') x_labels.append(float(parts[0])) y_labels.append(float(parts[1])) x_labels.append(x_labels[0]) y_labels.append(y_labels[0]) plt.figure() plt.scatter(x_labels, y_labels, c='r', marker='*', s=200, alpha=0.5) plt.plot(x_labels, y_labels, "b", ms=20) plt.savefig('_route.jpg') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行结果
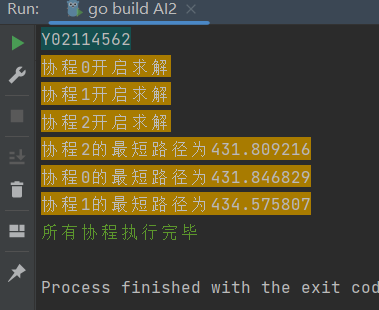
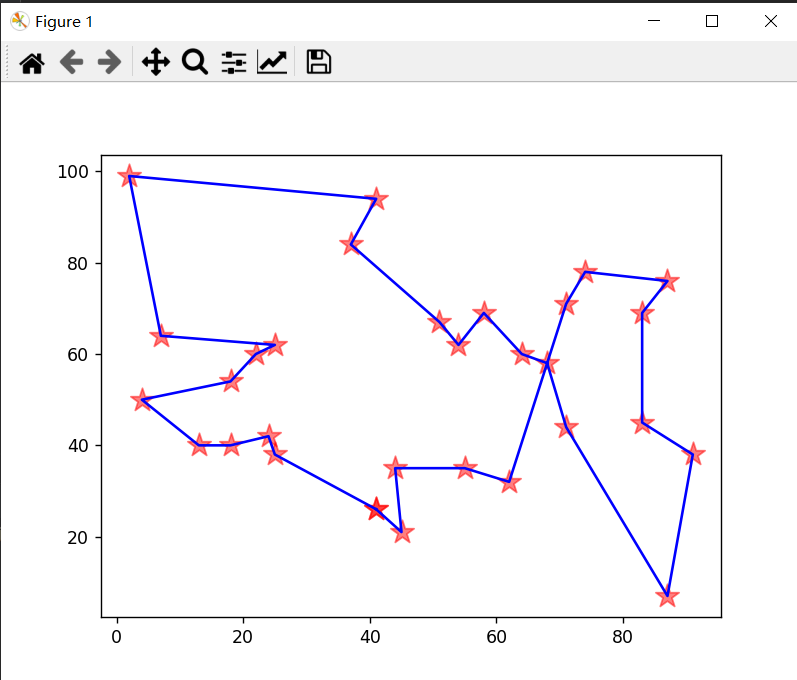
-
相关阅读:
好用的PDF解密工具哪个好?
华为OD机试真题 Java 实现【最长公共后缀】【2023 B卷 100分】,等于白送
智能SQL生成:后端技术与LLM的完美结合
解决react报错“JSX 表达式必须具有一个父元素“
FRED应用:激光二极管的模拟
【自然语言处理】【实体匹配】AutoBlock:一个用于实体匹配的自动化Blocking框架
这才是你应该了解的Redis数据结构!
RK3288 Android11 mini-pcie接口 4G模组EC200A适配(含自适应功能)
Git | 详解 | 命令
Feign
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38177830/article/details/134437055
