-
YOLOv8改进 | 如何在网络结构中添加注意力机制、C2f、卷积、Neck、检测头
一、本文介绍
本篇文章的内容是在大家得到一个改进版本的C2f一个新的注意力机制、或者一个新的卷积模块、或者是检测头的时候如何替换我们YOLOv8模型中的原有的模块,从而用你的模块去进行训练模型或者检测。因为最近开了一个专栏里面涉及到挺多改进的地方,不能每篇文章都去讲解一遍如何修改,就想着在这里单独出一期文章进行一个总结性教程,大家可以从我的其它文章中拿到修改后的代码,从这篇文章学会如何去添加到你的模型结构中去。
YOLOv8专栏:YOLOv8改进有效涨点专栏->持续复现各种最新机制
本文的讲解举例都以最新的YOLOv8的目录结构为例,老版本的其实方法都一样只是目录构造不一样找到同样的文件名即可。
适用对象->本文适合那些拿到源码却不知道如何添加到网络结构中的朋友
目录
二、导入修改内容
大家拿到任何一个代码,想要加入到模型的内部,我们都需要先将其导入到模型的内部,才可以将其添加到模型的结构中去,下面的代码是一个ODConv,和我创建的一个ODConv_yolo的类(官方的代码报错进行一定的处理想知道为啥可以看我单独讲解它的博客), 我们先拿其进行举例。
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- import torch.autograd
- class Attention(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, groups=1, reduction=0.0625, kernel_num=4, min_channel=16):
- super(Attention, self).__init__()
- attention_channel = max(int(in_planes * reduction), min_channel)
- self.kernel_size = kernel_size
- self.kernel_num = kernel_num
- self.temperature = 1.0
- self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
- self.fc = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, attention_channel, 1, bias=False)
- self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(attention_channel)
- self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
- self.channel_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, in_planes, 1, bias=True)
- self.func_channel = self.get_channel_attention
- if in_planes == groups and in_planes == out_planes: # depth-wise convolution
- self.func_filter = self.skip
- else:
- self.filter_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, out_planes, 1, bias=True)
- self.func_filter = self.get_filter_attention
- if kernel_size == 1: # point-wise convolution
- self.func_spatial = self.skip
- else:
- self.spatial_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, kernel_size * kernel_size, 1, bias=True)
- self.func_spatial = self.get_spatial_attention
- if kernel_num == 1:
- self.func_kernel = self.skip
- else:
- self.kernel_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, kernel_num, 1, bias=True)
- self.func_kernel = self.get_kernel_attention
- self._initialize_weights()
- def _initialize_weights(self):
- for m in self.modules():
- if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
- nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
- if m.bias is not None:
- nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
- if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
- nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
- nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
- def update_temperature(self, temperature):
- self.temperature = temperature
- @staticmethod
- def skip(_):
- return 1.0
- def get_channel_attention(self, x):
- channel_attention = torch.sigmoid(self.channel_fc(x).view(x.size(0), -1, 1, 1) / self.temperature)
- return channel_attention
- def get_filter_attention(self, x):
- filter_attention = torch.sigmoid(self.filter_fc(x).view(x.size(0), -1, 1, 1) / self.temperature)
- return filter_attention
- def get_spatial_attention(self, x):
- spatial_attention = self.spatial_fc(x).view(x.size(0), 1, 1, 1, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size)
- spatial_attention = torch.sigmoid(spatial_attention / self.temperature)
- return spatial_attention
- def get_kernel_attention(self, x):
- kernel_attention = self.kernel_fc(x).view(x.size(0), -1, 1, 1, 1, 1)
- kernel_attention = F.softmax(kernel_attention / self.temperature, dim=1)
- return kernel_attention
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.avgpool(x)
- x = self.fc(x)
- # x = self.bn(x) # 在外面我提供了一个bn这里会报错
- x = self.relu(x)
- return self.func_channel(x), self.func_filter(x), self.func_spatial(x), self.func_kernel(x)
- class ODConv2d(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1,
- reduction=0.0625, kernel_num=4):
- super(ODConv2d, self).__init__()
- kernel_size = kernel_size[0]
- in_planes = in_planes
- self.in_planes = in_planes
- self.out_planes = out_planes
- self.kernel_size = kernel_size
- self.stride = stride
- self.padding = padding
- self.dilation = dilation
- self.groups = groups
- self.kernel_num = kernel_num
- self.attention = Attention(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, groups=groups,
- reduction=reduction, kernel_num=kernel_num)
- self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(kernel_num, out_planes, in_planes//groups, kernel_size, kernel_size),
- requires_grad=True)
- self._initialize_weights()
- if self.kernel_size == 1 and self.kernel_num == 1:
- self._forward_impl = self._forward_impl_pw1x
- else:
- self._forward_impl = self._forward_impl_common
- def _initialize_weights(self):
- for i in range(self.kernel_num):
- nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.weight[i], mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
- def update_temperature(self, temperature):
- self.attention.update_temperature(temperature)
- def _forward_impl_common(self, x):
- # Multiplying channel attention (or filter attention) to weights and feature maps are equivalent,
- # while we observe that when using the latter method the models will run faster with less gpu memory cost.
- channel_attention, filter_attention, spatial_attention, kernel_attention = self.attention(x)
- batch_size, in_planes, height, width = x.size()
- x = x * channel_attention
- x = x.reshape(1, -1, height, width)
- aggregate_weight = spatial_attention * kernel_attention * self.weight.unsqueeze(dim=0)
- aggregate_weight = torch.sum(aggregate_weight, dim=1).view(
- [-1, self.in_planes // self.groups, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size])
- output = F.conv2d(x, weight=aggregate_weight, bias=None, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding,
- dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups * batch_size)
- output = output.view(batch_size, self.out_planes, output.size(-2), output.size(-1))
- output = output * filter_attention
- return output
- def _forward_impl_pw1x(self, x):
- channel_attention, filter_attention, spatial_attention, kernel_attention = self.attention(x)
- x = x * channel_attention
- output = F.conv2d(x, weight=self.weight.squeeze(dim=0), bias=None, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding,
- dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups)
- output = output * filter_attention
- return output
- def forward(self, x):
- return self._forward_impl(x)
拿到这种代码之后,一般都很长,有一些博主推荐直接将其复制粘贴到YOLOv8的"ultralytics/nn/modules/conv.py"或者"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py"目录下面,这种方法可不可以?答案是可以的,但是我建议大家最好新建一个文件在conv.py的同级目录下,为什么这么做,因为我们修改的模块越来越多,你往conv.py文件或则block.py文件里面加的代码越来越多很容易就把代码改崩溃了,最后就跌卸载进行重新下载包,我们通过建立文件导入其中类的形式,如果我们不用了,也不会对我们的代码做出任何影响,实在不行把新建立的文件删除了都可以,下面开始进行实际操作的讲解。
2.1创建新文件导入新模块
我们将我们得到的任何一个Conv或者想要修改的任何一个模块都可以像下面的图片一样直接建立一个文件复制粘贴进去即可。

建立好上面的文件之后,我们此时呢有两种情况,一周呢官方的代码可以直接使用,另一种呢需要进行一定的处理,我们下面分别进行讲解两种情况。
2.1.1情况一
这种情况是官方的代码可以直接使用,此时我们直接修改"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py"文件就可以了,修改如下->
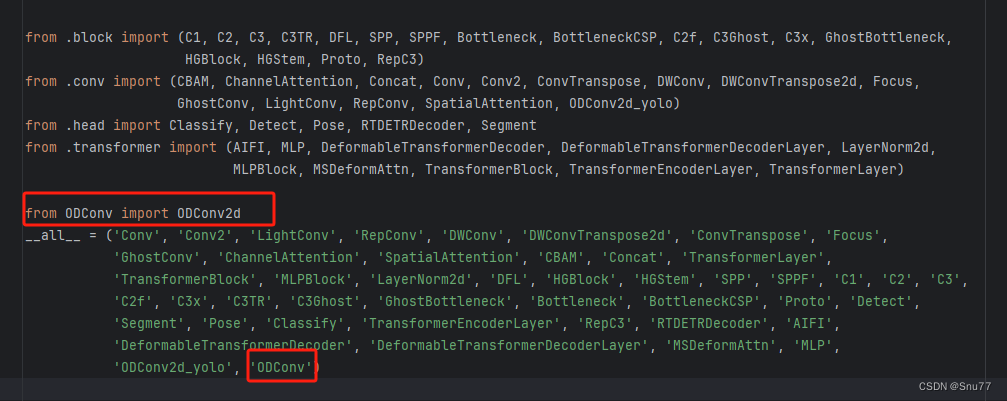
2.1.2情况二
另一种情况(绝大多数):官方的代码不能直接使用我们本文的例子ODConv就是这种情况,所以我们需要对其进行一定的处理,我们找到如下的文件->"ultralytics/nn/modules/conv.py"对其进行修改如下->
修改一、导入模块

修改二、将额外处理代码添加至conv模块
将如下代码添加至该文件中的末尾处->
- class ODConv2d_yolo(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):
- super().__init__()
- self.conv = Conv(in_channels, out_channels, k=1)
- self.dcnv3 = ODConv2d(out_channels,out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, groups=groups,
- dilation=dilation)
- self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
- self.gelu = nn.GELU()
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.conv(x)
- x = self.dcnv3(x)
- x = self.gelu(self.bn(x))
- return x
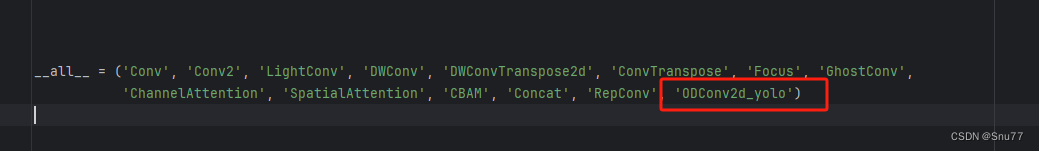
修改三、配置头文件
修改如下->
修改四 、重复情况一的步骤
修改"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py"文件如下

总结:通过建立文件这种方法导入想要加入到模型中的模块(这里举例的是ODConv2d)其已经在我们新创建的.py文件中定义好了然后直接导过来就可以用了,从而不修改原有的conv.py文件就做到了,这样就算我们随时不用了,直接删除文件然后需要改的地方也很直观,否则时间久了代码早晚跌崩溃。
三、Conv模块
上面我们已经把定义好的卷积模块代码中了,此时我们还需要配置其位置,当然不同的模块导入的方式也有可能略有不同。
3.1修改一
我们找到如下的文件"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py",图片如下->

我们先把我们在上面"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py" 文件的函数头中导入的类,在下面的地方导入进"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py"文件中,修改内容如下->

3.2修改二
我们在这个文件中找到一个方法(def定义的就叫方法),因为其代码很长,我们一行一行搜索很麻烦,我们适用文件搜索功能(快捷键Ctrl + F),弹出快捷栏如下->

我们搜索下面这个代码"parse_model" 然后进行翻滚很容易就找到了下面的部分,同时进行红框内部的修改

3.3修改三
到此我们就已经将我们定义的三个模块添加到我们的模型中了,已经可以修改yaml文件进行网络结构的配置了,我们找到该文件"ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8.yaml"进行配置。
我们可以在其中的任何一个位置进行替换,当然我们的替换要符合逻辑,类似于之前这个位置是Conv那么你可以将你修改的卷积替换上,之前这个位置是C2f那么你就将修改后的C2f替换上。
我们在yaml文件中进行了如下修改。
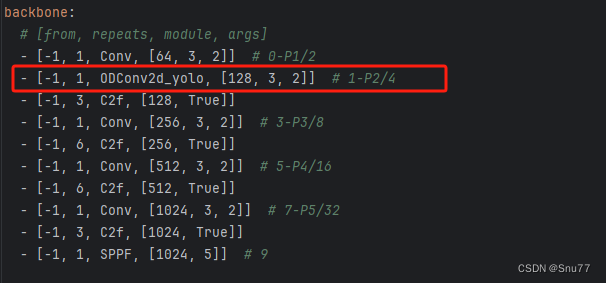
到此我们就配置完成了此时进行训练就可以开始训练了~

四、C2f、Bottleneck模块
下面我们拿修改后的C2f、和Bottleneck举例,这两个模块定义在该文件中"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py",所以如果我们想添加修改后的C2f和Bottleneck(这俩一般配套使用),就需要在该文件中进行修改,修改步骤如下->
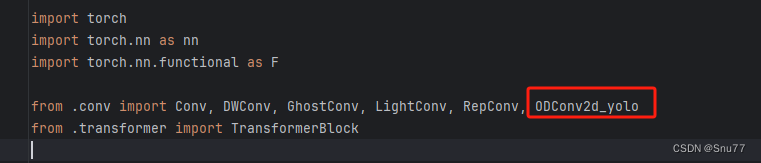
4.1修改一
找到该文件"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py",进行如下修改->
4.2步骤二
添加修改后的C2f和Bottleneck模块,这里起名为C2f_ODConv和Bottleneck_ODConv,
- class Bottleneck_ODConv(nn.Module):
- """Standard bottleneck."""
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5):
- """Initializes a bottleneck module with given input/output channels, shortcut option, group, kernels, and
- expansion.
- """
- super().__init__()
- c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
- self.cv2 = ODConv2d_yolo(c_, c2, k[1], 1, groups=g)
- self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
- def forward(self, x):
- """'forward()' applies the YOLO FPN to input data."""
- return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
- class C2f_ODConv(nn.Module):
- """Faster Implementation of CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
- """Initialize CSP bottleneck layer with two convolutions with arguments ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups,
- expansion.
- """
- super().__init__()
- self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
- self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck_ODConv(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))
- def forward(self, x):
- """Forward pass through C2f layer."""
- y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))
- y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
- return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
- def forward_split(self, x):
- """Forward pass using split() instead of chunk()."""
- y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
- y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
- return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
将以上代码复制到文件"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py"的末尾,
4.3修改三
修改头文件如下->
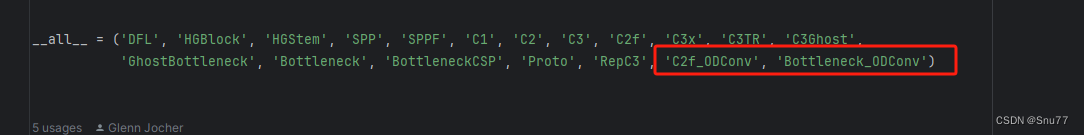
4.4修改四
找到文件"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py",修改如下->
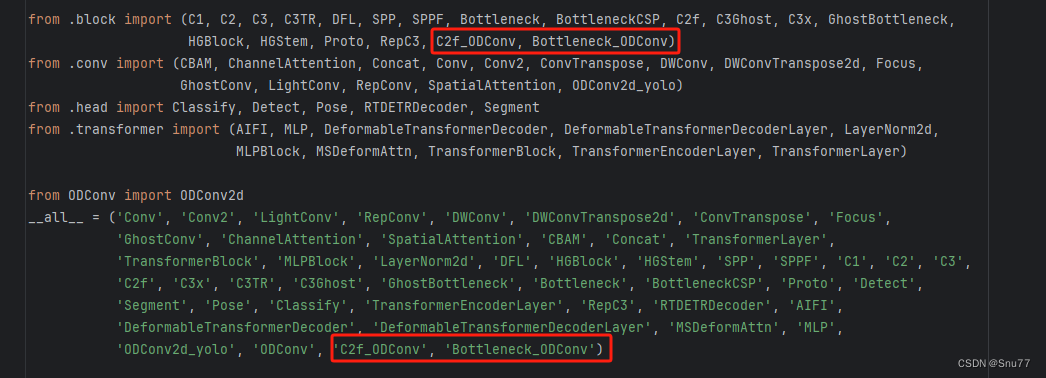
4.5修改五
找到该文件我们找到如下的文件"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py"进行修改(其实和卷积模块的一模一样),
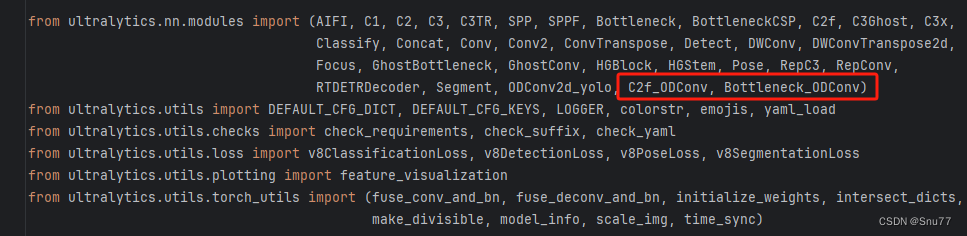
4.6修改六
我们在这个文件中找到一个方法(def定义的就叫方法),因为其代码很长,我们一行一行搜索很麻烦,我们适用文件搜索功能(快捷键Ctrl + F),弹出快捷栏如下->

我们搜索下面这个代码"parse_model" 然后进行翻滚很容易就找到了下面的部分,同时进行红框内部的修改

4.7修改七
到此我们就已经将我们定义的三个模块添加到我们的模型中了,已经可以修改yaml文件进行网络结构的配置了,我们找到该文件"ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8.yaml"进行配置。
我们可以在其中的任何一个位置进行替换,当然我们的替换要符合逻辑,类似于之前这个位置是Conv那么你可以将你修改的卷积替换上,之前这个位置是C2f那么你就将修改后的C2f替换上。
在yaml文件中进行了如下修改。

到此就完成了修改C2f和Bottleneck模块了,已经可以开始进行训练了~

至于修改这个ODConv的 效果如何可以看我的其它博客里面有详细的讲解~
四、注意力机制
修改注意力机制的部分其实和上面都是类似只是在修改如下文件的时候有点不一样"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py",但是需要注意的是注意力机制分为两种,一种是有参数的注意力机制我们需要像其中传入参数,一种是无参数的注意力机制这两种机制的添加呢稍微有一些不同,我会在下面进行标注大家仔细看
4.1修改一
这里我们拿Biformer注意力机制为例(我们拿有参数的注意力机制为例),首先我们找到该目录'ultralytics/nn/modules'该目录的构造如下->

我们在其中创建一个名字为Biformer的py文件如图所示,我们在其中复制如下代码即可
- """
- Bi-Level Routing Attention.
- """
- from typing import Tuple, Optional
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- from einops import rearrange
- from torch import Tensor, LongTensor
- class TopkRouting(nn.Module):
- """
- differentiable topk routing with scaling
- Args:
- qk_dim: int, feature dimension of query and key
- topk: int, the 'topk'
- qk_scale: int or None, temperature (multiply) of softmax activation
- with_param: bool, wether inorporate learnable params in routing unit
- diff_routing: bool, wether make routing differentiable
- soft_routing: bool, wether make output value multiplied by routing weights
- """
- def __init__(self, qk_dim, topk=4, qk_scale=None, param_routing=False, diff_routing=False):
- super().__init__()
- self.topk = topk
- self.qk_dim = qk_dim
- self.scale = qk_scale or qk_dim ** -0.5
- self.diff_routing = diff_routing
- # TODO: norm layer before/after linear?
- self.emb = nn.Linear(qk_dim, qk_dim) if param_routing else nn.Identity()
- # routing activation
- self.routing_act = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
- def forward(self, query: Tensor, key: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor]:
- """
- Args:
- q, k: (n, p^2, c) tensor
- Return:
- r_weight, topk_index: (n, p^2, topk) tensor
- """
- if not self.diff_routing:
- query, key = query.detach(), key.detach()
- query_hat, key_hat = self.emb(query), self.emb(key) # per-window pooling -> (n, p^2, c)
- attn_logit = (query_hat * self.scale) @ key_hat.transpose(-2, -1) # (n, p^2, p^2)
- topk_attn_logit, topk_index = torch.topk(attn_logit, k=self.topk, dim=-1) # (n, p^2, k), (n, p^2, k)
- r_weight = self.routing_act(topk_attn_logit) # (n, p^2, k)
- return r_weight, topk_index
- class KVGather(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, mul_weight='none'):
- super().__init__()
- assert mul_weight in ['none', 'soft', 'hard']
- self.mul_weight = mul_weight
- def forward(self, r_idx: Tensor, r_weight: Tensor, kv: Tensor):
- """
- r_idx: (n, p^2, topk) tensor
- r_weight: (n, p^2, topk) tensor
- kv: (n, p^2, w^2, c_kq+c_v)
- Return:
- (n, p^2, topk, w^2, c_kq+c_v) tensor
- """
- # select kv according to routing index
- n, p2, w2, c_kv = kv.size()
- topk = r_idx.size(-1)
- # print(r_idx.size(), r_weight.size())
- # FIXME: gather consumes much memory (topk times redundancy), write cuda kernel?
- topk_kv = torch.gather(kv.view(n, 1, p2, w2, c_kv).expand(-1, p2, -1, -1, -1),
- # (n, p^2, p^2, w^2, c_kv) without mem cpy
- dim=2,
- index=r_idx.view(n, p2, topk, 1, 1).expand(-1, -1, -1, w2, c_kv)
- # (n, p^2, k, w^2, c_kv)
- )
- if self.mul_weight == 'soft':
- topk_kv = r_weight.view(n, p2, topk, 1, 1) * topk_kv # (n, p^2, k, w^2, c_kv)
- elif self.mul_weight == 'hard':
- raise NotImplementedError('differentiable hard routing TBA')
- # else: #'none'
- # topk_kv = topk_kv # do nothing
- return topk_kv
- class QKVLinear(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, dim, qk_dim, bias=True):
- super().__init__()
- self.dim = dim
- self.qk_dim = qk_dim
- self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, qk_dim + qk_dim + dim, bias=bias)
- def forward(self, x):
- q, kv = self.qkv(x).split([self.qk_dim, self.qk_dim + self.dim], dim=-1)
- return q, kv
- # q, k, v = self.qkv(x).split([self.qk_dim, self.qk_dim, self.dim], dim=-1)
- # return q, k, v
- class BiLevelRoutingAttention(nn.Module):
- """
- n_win: number of windows in one side (so the actual number of windows is n_win*n_win)
- kv_per_win: for kv_downsample_mode='ada_xxxpool' only, number of key/values per window. Similar to n_win, the actual number is kv_per_win*kv_per_win.
- topk: topk for window filtering
- param_attention: 'qkvo'-linear for q,k,v and o, 'none': param free attention
- param_routing: extra linear for routing
- diff_routing: wether to set routing differentiable
- soft_routing: wether to multiply soft routing weights
- """
- def __init__(self, dim, n_win=7, num_heads=8, qk_dim=None, qk_scale=None,
- kv_per_win=4, kv_downsample_ratio=4, kv_downsample_kernel=None, kv_downsample_mode='identity',
- topk=4, param_attention="qkvo", param_routing=False, diff_routing=False, soft_routing=False,
- side_dwconv=3,
- auto_pad=True):
- super().__init__()
- # local attention setting
- self.dim = dim
- self.n_win = n_win # Wh, Ww
- self.num_heads = num_heads
- self.qk_dim = qk_dim or dim
- assert self.qk_dim % num_heads == 0 and self.dim % num_heads == 0, 'qk_dim and dim must be divisible by num_heads!'
- self.scale = qk_scale or self.qk_dim ** -0.5
- ################side_dwconv (i.e. LCE in ShuntedTransformer)###########
- self.lepe = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=side_dwconv, stride=1, padding=side_dwconv // 2,
- groups=dim) if side_dwconv > 0 else \
- lambda x: torch.zeros_like(x)
- ################ global routing setting #################
- self.topk = topk
- self.param_routing = param_routing
- self.diff_routing = diff_routing
- self.soft_routing = soft_routing
- # router
- assert not (self.param_routing and not self.diff_routing) # cannot be with_param=True and diff_routing=False
- self.router = TopkRouting(qk_dim=self.qk_dim,
- qk_scale=self.scale,
- topk=self.topk,
- diff_routing=self.diff_routing,
- param_routing=self.param_routing)
- if self.soft_routing: # soft routing, always diffrentiable (if no detach)
- mul_weight = 'soft'
- elif self.diff_routing: # hard differentiable routing
- mul_weight = 'hard'
- else: # hard non-differentiable routing
- mul_weight = 'none'
- self.kv_gather = KVGather(mul_weight=mul_weight)
- # qkv mapping (shared by both global routing and local attention)
- self.param_attention = param_attention
- if self.param_attention == 'qkvo':
- self.qkv = QKVLinear(self.dim, self.qk_dim)
- self.wo = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
- elif self.param_attention == 'qkv':
- self.qkv = QKVLinear(self.dim, self.qk_dim)
- self.wo = nn.Identity()
- else:
- raise ValueError(f'param_attention mode {self.param_attention} is not surpported!')
- self.kv_downsample_mode = kv_downsample_mode
- self.kv_per_win = kv_per_win
- self.kv_downsample_ratio = kv_downsample_ratio
- self.kv_downsample_kenel = kv_downsample_kernel
- if self.kv_downsample_mode == 'ada_avgpool':
- assert self.kv_per_win is not None
- self.kv_down = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(self.kv_per_win)
- elif self.kv_downsample_mode == 'ada_maxpool':
- assert self.kv_per_win is not None
- self.kv_down = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(self.kv_per_win)
- elif self.kv_downsample_mode == 'maxpool':
- assert self.kv_downsample_ratio is not None
- self.kv_down = nn.MaxPool2d(self.kv_downsample_ratio) if self.kv_downsample_ratio > 1 else nn.Identity()
- elif self.kv_downsample_mode == 'avgpool':
- assert self.kv_downsample_ratio is not None
- self.kv_down = nn.AvgPool2d(self.kv_downsample_ratio) if self.kv_downsample_ratio > 1 else nn.Identity()
- elif self.kv_downsample_mode == 'identity': # no kv downsampling
- self.kv_down = nn.Identity()
- elif self.kv_downsample_mode == 'fracpool':
- # assert self.kv_downsample_ratio is not None
- # assert self.kv_downsample_kenel is not None
- # TODO: fracpool
- # 1. kernel size should be input size dependent
- # 2. there is a random factor, need to avoid independent sampling for k and v
- raise NotImplementedError('fracpool policy is not implemented yet!')
- elif kv_downsample_mode == 'conv':
- # TODO: need to consider the case where k != v so that need two downsample modules
- raise NotImplementedError('conv policy is not implemented yet!')
- else:
- raise ValueError(f'kv_down_sample_mode {self.kv_downsaple_mode} is not surpported!')
- # softmax for local attention
- self.attn_act = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
- self.auto_pad = auto_pad
- def forward(self, x, ret_attn_mask=False):
- """
- x: NHWC tensor
- Return:
- NHWC tensor
- """
- x = rearrange(x, "n c h w -> n h w c")
- # NOTE: use padding for semantic segmentation
- ###################################################
- if self.auto_pad:
- N, H_in, W_in, C = x.size()
- pad_l = pad_t = 0
- pad_r = (self.n_win - W_in % self.n_win) % self.n_win
- pad_b = (self.n_win - H_in % self.n_win) % self.n_win
- x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, # dim=-1
- pad_l, pad_r, # dim=-2
- pad_t, pad_b)) # dim=-3
- _, H, W, _ = x.size() # padded size
- else:
- N, H, W, C = x.size()
- assert H % self.n_win == 0 and W % self.n_win == 0 #
- ###################################################
- # patchify, (n, p^2, w, w, c), keep 2d window as we need 2d pooling to reduce kv size
- x = rearrange(x, "n (j h) (i w) c -> n (j i) h w c", j=self.n_win, i=self.n_win)
- #################qkv projection###################
- # q: (n, p^2, w, w, c_qk)
- # kv: (n, p^2, w, w, c_qk+c_v)
- # NOTE: separte kv if there were memory leak issue caused by gather
- q, kv = self.qkv(x)
- # pixel-wise qkv
- # q_pix: (n, p^2, w^2, c_qk)
- # kv_pix: (n, p^2, h_kv*w_kv, c_qk+c_v)
- q_pix = rearrange(q, 'n p2 h w c -> n p2 (h w) c')
- kv_pix = self.kv_down(rearrange(kv, 'n p2 h w c -> (n p2) c h w'))
- kv_pix = rearrange(kv_pix, '(n j i) c h w -> n (j i) (h w) c', j=self.n_win, i=self.n_win)
- q_win, k_win = q.mean([2, 3]), kv[..., 0:self.qk_dim].mean(
- [2, 3]) # window-wise qk, (n, p^2, c_qk), (n, p^2, c_qk)
- ##################side_dwconv(lepe)##################
- # NOTE: call contiguous to avoid gradient warning when using ddp
- lepe = self.lepe(rearrange(kv[..., self.qk_dim:], 'n (j i) h w c -> n c (j h) (i w)', j=self.n_win,
- i=self.n_win).contiguous())
- lepe = rearrange(lepe, 'n c (j h) (i w) -> n (j h) (i w) c', j=self.n_win, i=self.n_win)
- ############ gather q dependent k/v #################
- r_weight, r_idx = self.router(q_win, k_win) # both are (n, p^2, topk) tensors
- kv_pix_sel = self.kv_gather(r_idx=r_idx, r_weight=r_weight, kv=kv_pix) # (n, p^2, topk, h_kv*w_kv, c_qk+c_v)
- k_pix_sel, v_pix_sel = kv_pix_sel.split([self.qk_dim, self.dim], dim=-1)
- # kv_pix_sel: (n, p^2, topk, h_kv*w_kv, c_qk)
- # v_pix_sel: (n, p^2, topk, h_kv*w_kv, c_v)
- ######### do attention as normal ####################
- k_pix_sel = rearrange(k_pix_sel, 'n p2 k w2 (m c) -> (n p2) m c (k w2)',
- m=self.num_heads) # flatten to BMLC, (n*p^2, m, topk*h_kv*w_kv, c_kq//m) transpose here?
- v_pix_sel = rearrange(v_pix_sel, 'n p2 k w2 (m c) -> (n p2) m (k w2) c',
- m=self.num_heads) # flatten to BMLC, (n*p^2, m, topk*h_kv*w_kv, c_v//m)
- q_pix = rearrange(q_pix, 'n p2 w2 (m c) -> (n p2) m w2 c',
- m=self.num_heads) # to BMLC tensor (n*p^2, m, w^2, c_qk//m)
- # param-free multihead attention
- attn_weight = (
- q_pix * self.scale) @ k_pix_sel # (n*p^2, m, w^2, c) @ (n*p^2, m, c, topk*h_kv*w_kv) -> (n*p^2, m, w^2, topk*h_kv*w_kv)
- attn_weight = self.attn_act(attn_weight)
- out = attn_weight @ v_pix_sel # (n*p^2, m, w^2, topk*h_kv*w_kv) @ (n*p^2, m, topk*h_kv*w_kv, c) -> (n*p^2, m, w^2, c)
- out = rearrange(out, '(n j i) m (h w) c -> n (j h) (i w) (m c)', j=self.n_win, i=self.n_win,
- h=H // self.n_win, w=W // self.n_win)
- out = out + lepe
- # output linear
- out = self.wo(out)
- # NOTE: use padding for semantic segmentation
- # crop padded region
- if self.auto_pad and (pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0):
- out = out[:, :H_in, :W_in, :].contiguous()
- if ret_attn_mask:
- return out, r_weight, r_idx, attn_weight
- else:
- return rearrange(out, "n h w c -> n c h w")
4.2修改二
我们找到该文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'在其中添加如下一行代码
from ultralytics.nn.modules.Biformer import BiLevelRoutingAttention as Biformer添加完之后的效果如下图->
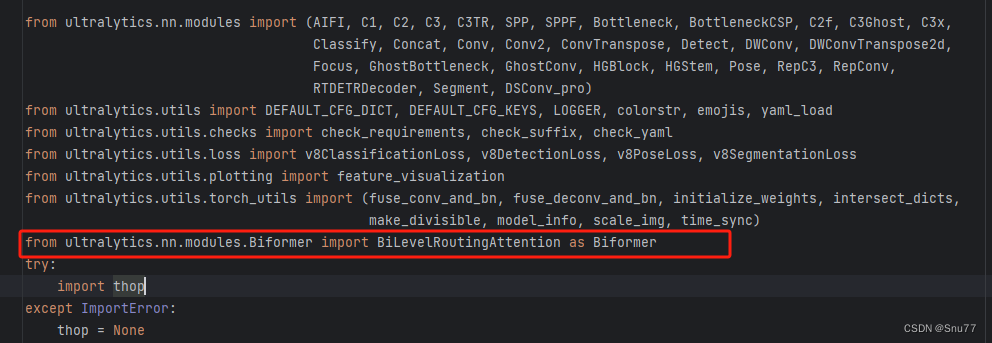
4.3修改三
这里需要注意体现出两种注意力机制的修改方式~
4.2.1有参数的注意力机制修改
现在我们已经将Biformer文件导入了模型中了,下一步我们就需要添加该机制到模型中让我们可以使用它,我们在步骤二的文件中''ultralytics/nn/tasks.py''按快捷键Ctrl+F可以进行文件搜索。

当然如果你不想用快捷键也可以自己寻找大概在 650行左右,有一个方法的名字叫"parse_model"
我们找到该方法对其进行修改,添加如下图所示内容。

这里我们定义了一个字典,我们以后在想导入其它的注意力机制就可以重复步骤一和步骤二,然后在步骤三这里定义的字典中添加你导入的注意力机制名字即可。
4.2.2无参数的注意力机制修改
无参数的注意力机制直接修改完步骤二就可以,直接跳过本步骤的修改直接进行配置注意力机制即可,无参数的注意力机制的修改三不用进行任何修改~
4.4配置注意力机制
恭喜你,到这里我们就已经成功的导入了注意力机制,离修改模型只差最后一步,我们需要找到如下文件进行修改"ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8.yaml",找到这个文件之后初始如下所示,
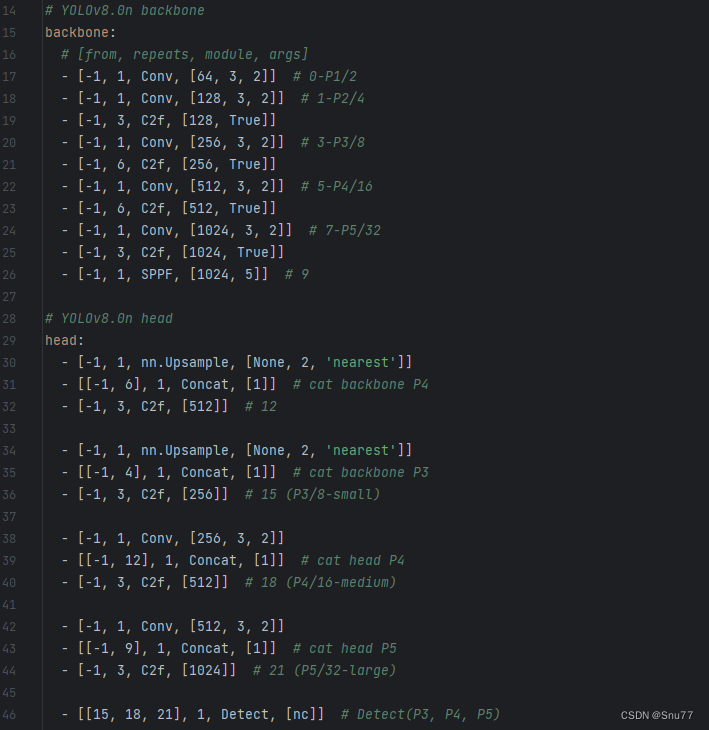
我们可以在某一层中添加Biformer注意力机制,具体添加到哪里由你自己决定,我这里建议添加到 Neck层,也就是我们的特征融合层,添加之后的效果如下,这里我在三个地方添加了Biformer注意力机制。
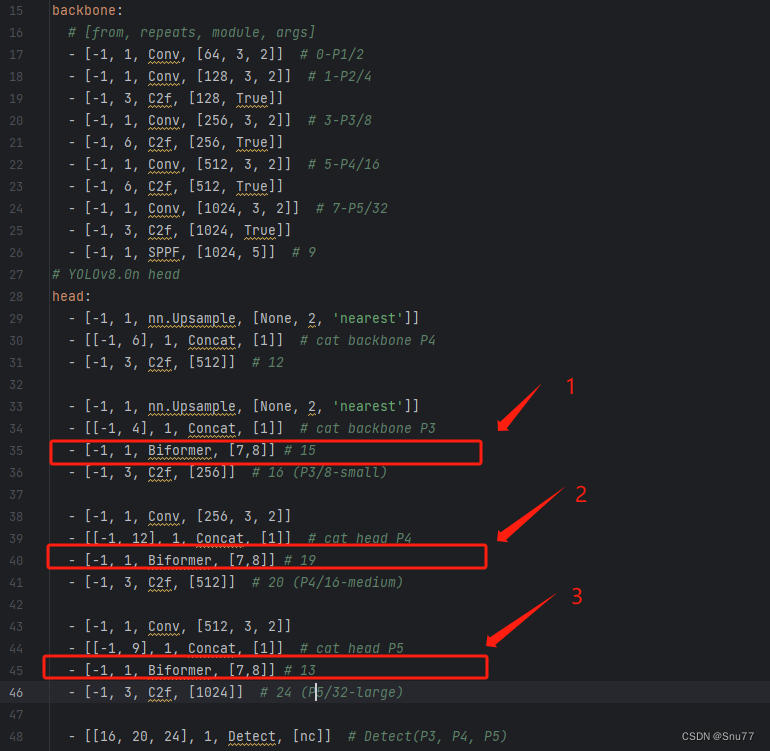
OK到此我们就添加了注意力机制到我们的模型里面了,下面我来讲一下添加的注意力机制中的参数是如何来的,
- 首先-1这里我们不用管, 它代表上一个层的输入输入-1就是让模型自动帮我们算输入的大小!
- 数字1代表这里我们的Biformer注意力机制执行一次
- Biformer代表我们的注意力机制名字,本来类的名字不是这个我在前面导入的时候给他另命名了前面有讲到
- [7,8]这里是根据Biformer定义的时候来的,你只需要输入前两个即可(需要注意的是无参数的注意力机制这里什么都不用填写可以看看你的无参数注意力机制需要什么那种超参数你给予赋值即可,不用从模型中获取任何的其它参数)。

当然这两个参数你可以换,调成其它的试试效果。
五、Neck部分
持续更新~
六、检测头
持续更新~
七、损失函数
持续更新~

-
相关阅读:
关于硬盘质量大数据分析的思考
弘辽科技:拼多多没出单改销量吗?拼多多如何提高销量?
运行vue,浏览器出错
算法分析至栈与队列
图像检索常规算法---学习笔记
聚焦“硬核”技术,开放原子开源大赛苏州站圆满落幕
修复Windows上“发生意外错误”问题的5种方法,总有一种适合你
CVPR 2018 基于累积注意力的视觉定位 Visual Grounding via Accumulated Attention 详解
律师事务所站
Due to a bug fix in https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/28687
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/java1314777/article/details/134432710
