-
Flex布局---看一篇就够了
1. flex布局是什么?
flex是flexible Box的缩写,用来为盒装模型提供的最大的灵活性,任何一个容器都可以指定为flex布局。Flex布局称为flex容器,所有的子元素为容器成员Flex项目(flex item);
当为父盒子设为flex布局以后,子元素的float、vertical-align,clear数据将失效。
flex布局伸缩布局 = 弹性布局 = 伸缩盒布局 = 弹性盒布局
方法: 通过给父盒子添加flex属性,来控制子盒子的位置和排列方式。
2. 传统的布局 VS Flex布局
传统布局:兼容性好,布局繁琐,有布局性,不能在移动端很好的布局
Flex布局:操作方便,布局简单;移动端应用广泛
总结:PC端页面中布局,推荐使用传统布局,移动端布局或者不考虑兼容性问题的话PC端页面布局,还是使用Flex弹性布局更加实用。
需要在最大的盒子中(box)加入display: flex;【使用flex布局,否则功能无法实现】
实例代码【可自行看效果】
- html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
- <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
- <title>Documenttitle>
- <style>
- * {
- margin: 0;
- padding: 0;
- }
- .box {
- height: 300px;
- margin: auto;
- border: 1px solid #000;
- }
- .box div {
- width: 100px;
- height: 100px;
- background-color: pink;
- }
- style>
- head>
- <body>
- <div class="box">
- <div>1div>
- <div>2div>
- <div>3div>
- div>
- body>
- html>
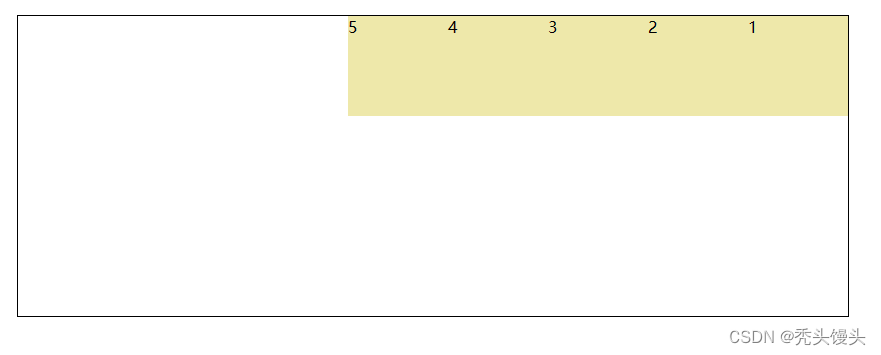
3. flex-direction设置主轴方向
flex-direction 是属性决定主轴的方向,就是项目的排列方向
flex-direction一共有四个方法

①row :是主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。(默认值)
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}展示效果如下:

②row-reverse:是主轴为水平方向,起点在右端。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}展示效果如下:
③column:是主轴为垂直方向,起点在上端。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}展示效果如下:

④column-reverse:是主轴为垂直方向,起点在下端。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column-reverse;
}展示效果如下:

4. justify-content
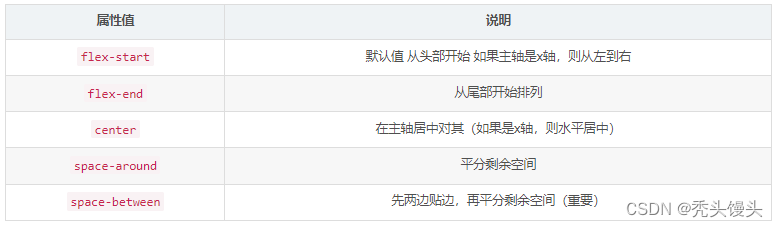
justify-content 设置主轴上的子元素排列方式,属性定义了项目在主轴上的对齐方式
注意:使用这个属性之前一定要确定好主轴是哪个
/* 对齐方式 */
justify-content: center; /* 居中排列 */
justify-content: start; /* 从行首开始排列 */
justify-content: end; /* 从行尾开始排列 */
justify-content: flex-start; /* 从行首起始位置开始排列 */
justify-content: flex-end; /* 从行尾位置开始排列 */
justify-content: left; /* 一个挨一个在对齐容器得左边缘 */
justify-content: right; /* 元素以容器右边缘为基准,一个挨着一个对齐, */
/* 分配弹性元素方式 *//* 均匀排列每个元素首个元素放置于起点,末尾元素放置于终点 */
justify-content: space-between;
/* 均匀排列每个元素 每个元素周围分配相同的空间 */
justify-content: space-around;/* 均匀排列每个元素每个元素之间的间隔相等 */
justify-content: space-evenly;
/* 均匀排列每个元素'auto'-sized 的元素会被拉伸以适应容器的大小 */
justify-content: stretch;
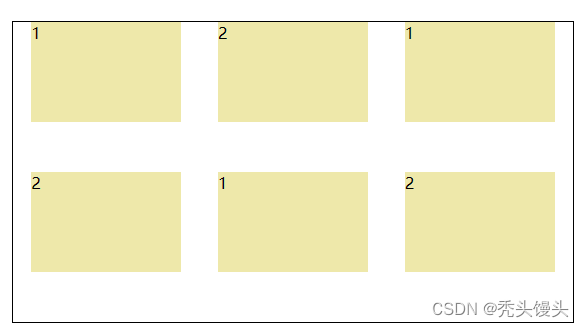
居中分布
- display: flex;
- justify-content: space-around;
- flex-direction: row;
- flex-wrap: wrap;【flex-flow: column wrap;】
效果展示:
两端对齐
- .box {
- display: flex;
- justify-content: space-between;
- }

其他方式
左对齐 右对齐 居中对齐 .box {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-start;
}.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}5. flex-wrap属性
flex-wrap属性定义,如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行。
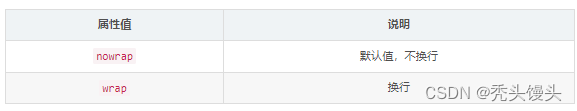
①nowarp:是不换行(默认值)。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
}②warp:是换行,第一行在上方。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}③wrap-reverse:是换行,但是第一行是在下面。
.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;
}6. align-items
是控制子项在侧轴(默认y轴)上的排列方式,在子项为单项的时候使用。
align-items属性定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐,设置侧轴上的对齐方式。
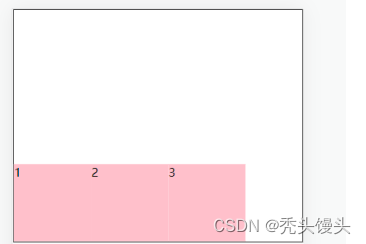
① flex-start:是交叉轴的起点对齐
.box {
display: flex;
align-items: flex-start;
}
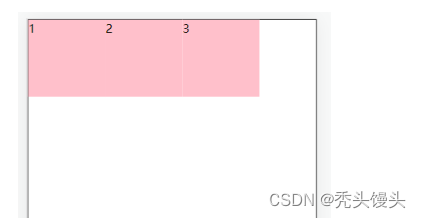
② flex-end 交叉轴的终点对齐
.box {
display: flex;
align-items: flex-end;
}
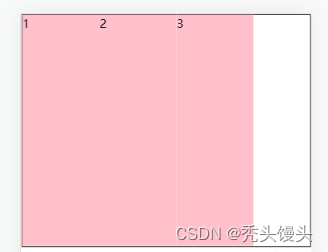
③center:是垂直居中。
.box {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}

④stretch这个代码的意思是如果项目未设置高度或设为auto,将占满整个容器的高度,也就是拉伸的意思,默认值(现有状态,测试的时候去掉子级的高度或者设置为auto)
.box {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch;
}
7. align-content
设置子项在侧轴上的排列方式,并且只能用于子项出现换行的情况(多行)
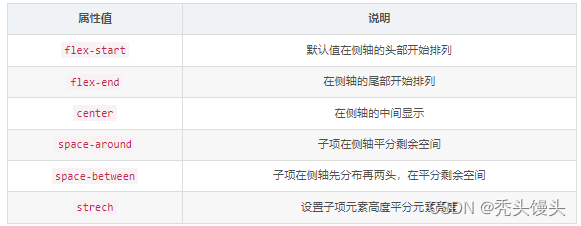
注意:align-content VS align-items(竖向排列)
align-items适用于单行情况下,只有上对齐、下对齐、居中和拉伸
align-content适应于换行(多行)情况下(单行情况下无效),可以设置上对齐、下对齐、居中、拉升以及平均分配剩余空间等属性值。8. flex-flow
flex-flow 属性是flex-direction和flex-wrap 属性的复合属性。
补充内容:
-
相关阅读:
【web-攻击后端组件】(7.2)操作文件路径、注入XML解释器、注入后端HTTP请求、注入电子邮件
base系列编码
python用PyPDF2函数库方法对pdf文件切割
Vue+element-ui的el-cascader实现动态添加删除级联地点输入框
Spring解决循环依赖
Docker基本原理
Centos - SSH 服务搭建
潇洒郎: 小白一次性成功——小米红米手机解BL锁+ ROOT-刷面具
C++ —— 继承
程序员的下一个风口
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_54721820/article/details/134444526
