-
[PyTorch][chapter 62][强化学习-基本概念]
前言:
目录:
- 强化学习概念
- 马尔科夫决策
- Bellman 方程
- 格子世界例子
一 强化学习
强化学习 必须在尝试之后,才能发现哪些行为会导致奖励的最大化。
当前的行为可能不仅仅会影响即时奖赏,还有影响下一步奖赏和所有奖赏强化学习五要素如下:

1.2 强化学习流程

1: 产生轨迹(trajectory)
2: 策略评估(policy-evaluate)
3: 策略提升(policy-improve)
这里重点讲一下 产生轨迹:
当前处于某个state 下面,
按照策略选择 action =

根据新的state 给出 reward:

最后产生了轨迹链

二 马尔科夫决策
2.1 马尔科夫决策要求:
1: 能够检测到理想的状态
2: 可以多次尝试
3: 系统的下个状态只与当前信息有关,与更早的状态无关。
决策过程中还可和当前采取的动作有关.
2.2 马尔科夫决策五要素
S: 状态集合 states
A: 动作集合 actions
P: 状态转移概率
R: 奖励函数(reward function) ,agent 采取某个动作后的及时奖励
r: 折扣系数意味当下的reward 比未来反馈更重要
![r \in (0,1]](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084522793.png)
2.3 主要流程
1: Agent 处于状态
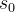
2: 按照策略 选择动作

3:执行该动作后,有一定的概率转移到新的状态


2.4 价值函数

当前时刻处于状态s,未来获得期望的累积奖赏
分为两种: state 价值函数 state-action 价值函数
最优价值函数:
不同策略下, 累积奖赏最大的

2.5 策略 policy
当前状态s 下,按照策略,要采用的动作

三 Bellman 方程
4.1 状态值函数为:
![V_{T}^{\pi}(x)=E_{\pi}[\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=1}^Tr_t|x_0=x]](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084521452.png) : T 步累积奖赏
: T 步累积奖赏![V_{\gamma}^{T}(x)=E_{\pi}[\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=0}^T \gamma^tr_{t+1}|x_0=x]](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084521170.png) :
: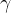 折扣累积奖赏,
折扣累积奖赏,![\gamma \in (0,1]](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084522305.png)
4.2 Bellman 方程


证明:
![V_{T}^{\pi}(x)=E_{\pi}[\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=1}^T r_t|x_0=x]](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084521452.png)
![=E_{\pi}[\frac{1}{T}r_1+\frac{T-1}{T}\frac{1}{T-1}\sum_{t=2}^T r_t|x_0=x]](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084521922.png)
![=\sum_{a \in A} \pi(x,a) \sum _{x^{'} \in X}P_{x\rightarrow x^{'}}^a (\frac{1}{T}R_{x\rightarrow x^{'}}^{a}+\frac{T-1}{T}E_{\pi}[\frac{1}{T-1}\sum_{t=1}^{T-1}r_t|x_0=x^{'}])](https://1000bd.com/contentImg/2023/11/16/084523249.png)

r折扣奖赏bellman 方程

四 格子世界例子
在某个格子,执行上下左右步骤,其中步骤最短的
为最优路径

5.1:gridword.py
- import numpy as np
- #手动输入格子的大小
- WORLD_SIZE = 4
- START_POS = [0,0]
- END_POS = [WORLD_SIZE-1, WORLD_SIZE-1]
- prob = 1.0
- #折扣因子
- DISCOUNT = 0.9
- # 动作集={上,下,左,右}
- ACTIONS = [np.array([0, -1]), #left
- np.array([-1, 0]), # up
- np.array([0, 1]), # right
- np.array([1, 0])] # down
- class GridwordEnv():
- def action_name(self, action):
- if action ==0:
- name = "左"
- elif action ==1:
- name = "上"
- elif action ==2:
- name = "右"
- else:
- name = "上"
- return name
- def __init__(self):
- self.nA = 4 #action:上下左右
- self.nS = 16 #state: 16个状态
- self.S = []
- for i in range(WORLD_SIZE):
- for j in range(WORLD_SIZE):
- state =[i,j]
- self.S.append(state)
- def step(self, s, a):
- action = ACTIONS[a]
- state = self.S[s]
- done = False
- reward = 0.0
- next_state = (np.array(state) + action).tolist()
- if (next_state == START_POS) or (state == START_POS):
- next_state = START_POS
- done = True
- elif (next_state == END_POS) or (state == START_POS):
- next_state = END_POS
- done = True
- else:
- x, y = next_state
- # 判断是否出界
- if x < 0 or x >= WORLD_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= WORLD_SIZE:
- reward = -1.0
- next_state = state
- else:
- reward = -1.0
- return prob, next_state, reward,done
5.2 main.py
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- Created on Mon Nov 13 09:39:37 2023
- @author: chengxf2
- """
- import numpy as np
- def init_state(WORLD_SIZE):
- S =[]
- for i in range(WORLD_SIZE):
- for j in range(WORLD_SIZE):
- state =[i,j]
- S.append(state)
- print(S)
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- Created on Fri Nov 10 16:48:16 2023
- @author: chengxf2
- """
- import numpy as np
- import sys
- from gym.envs.toy_text import discrete #环境
- from enum import Enum
- from gridworld import GridwordEnv
- class Agent():
- def __init__(self,env):
- self.discount_factor = 1.0 #折扣率
- self.theta = 1e-3 #最大偏差
- self.S = []
- self.env = env
- #当前处于的位置,V 累积奖赏
- def one_step_lookahead(self,s, v):
- R = np.zeros((env.nA)) #不同action的累积奖赏
- for action in range(env.nA):
- prob, next_state,reward, done = env.step(s, action) #只有一个
- next_state_index = self.env.S.index(next_state)
- #print("\n state",s ,"\t action ",action, "\t new_state ", next_state,"\t next_state_index ", next_state_index,"\t r: ",reward)
- r= prob*(reward + self.discount_factor*v[next_state_index])
- R[action] +=r
- #print("\n state ",s, "\t",R)
- return R
- def value_iteration(self, env, theta= 1e-3, discount_factor =1.0):
- v = np.zeros((env.nS)) #不同状态下面的累积奖赏,16个状态
- iterNum = 0
- while True:
- delta = 0.0
- for s in range(env.nS):
- R = self.one_step_lookahead(s,v)#在4个方向上面得到的累积奖赏
- best_action_value = np.max(R)
- #print("\n state ",s, "\t R ",R, "\t best_action_value ",best_action_value)
- bias = max(delta, np.abs(best_action_value-v[s]))
- v[s] =best_action_value
- #if (s+1)%4 == 0:
- #print("\n -----s ------------",s)
- iterNum +=1
- if bias<theta:
- break
- print("\n 迭代次数 ",iterNum)
- return v
- def learn(self):
- policy = np.zeros((env.nS,env.nA))
- v = self.value_iteration(self.env, self.theta, self.discount_factor)
- for s in range(env.nS):
- R = self.one_step_lookahead(s,v)
- best_action= np.argmax(R)
- #print(s,best_action_value )
- policy[s,best_action] = 1.0
- return policy,v
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- env = GridwordEnv()
- agent =Agent(env)
- policy ,v = agent.learn()
- for s in range(env.nS):
- action = np.argmax(policy[s])
- act_name = env.action_name(action)
- print("\n state ",s, "\t action ",act_name, "\t 累积奖赏 ",v[s])
参考:
【强化学习玩游戏】1小时竟然就学会了强化学习dqn算法原理及实战(人工智能自动驾驶/深度强化学习/强化学习算法/强化学习入门/多智能体强化学习)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
-
相关阅读:
Docker实战之Redis主从集群搭建实战
如何将原生微信小程序页面改成原生VUE框架的H5页面
一款IM即时通讯聊天系统源码,包含app和后台源码
设置Oracle环境变量
SpringBoot 框架 2022-8-1
窗口函数OVER(PARTITION BY)详细用法——语法+函数+开窗范围ROWS和RANGE
android 后台运行service实现和后台的持续交互
卡数据兼容性要求-consumer设备架构
tensorflow中的slim函数集合
礼物道具投票系统源码 可以无限多开 吸粉神器 附带完整的搭建教程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/chengxf2/article/details/134332675
