-
Netty Review - 核心组件扫盲
文章目录

Pre
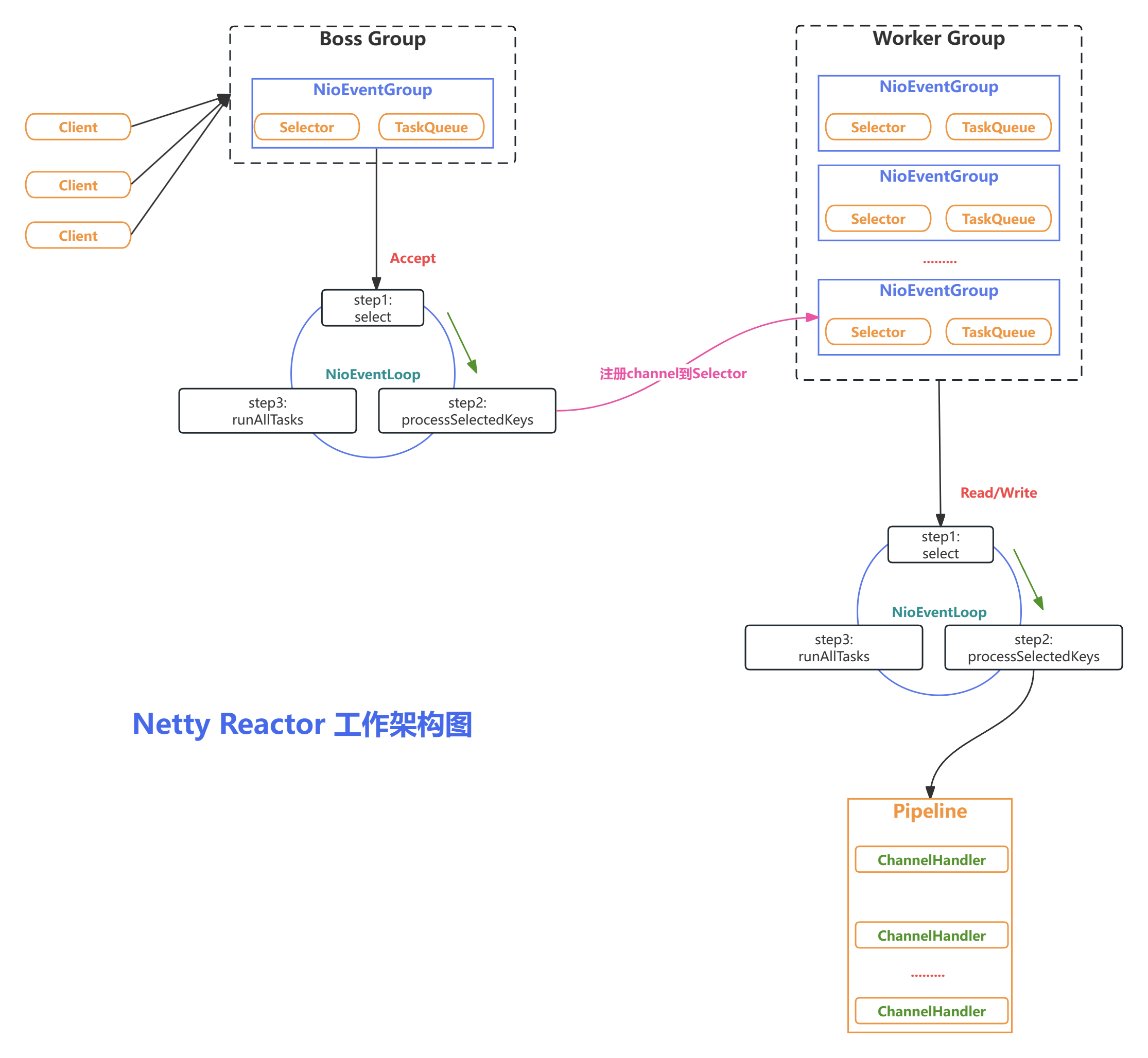
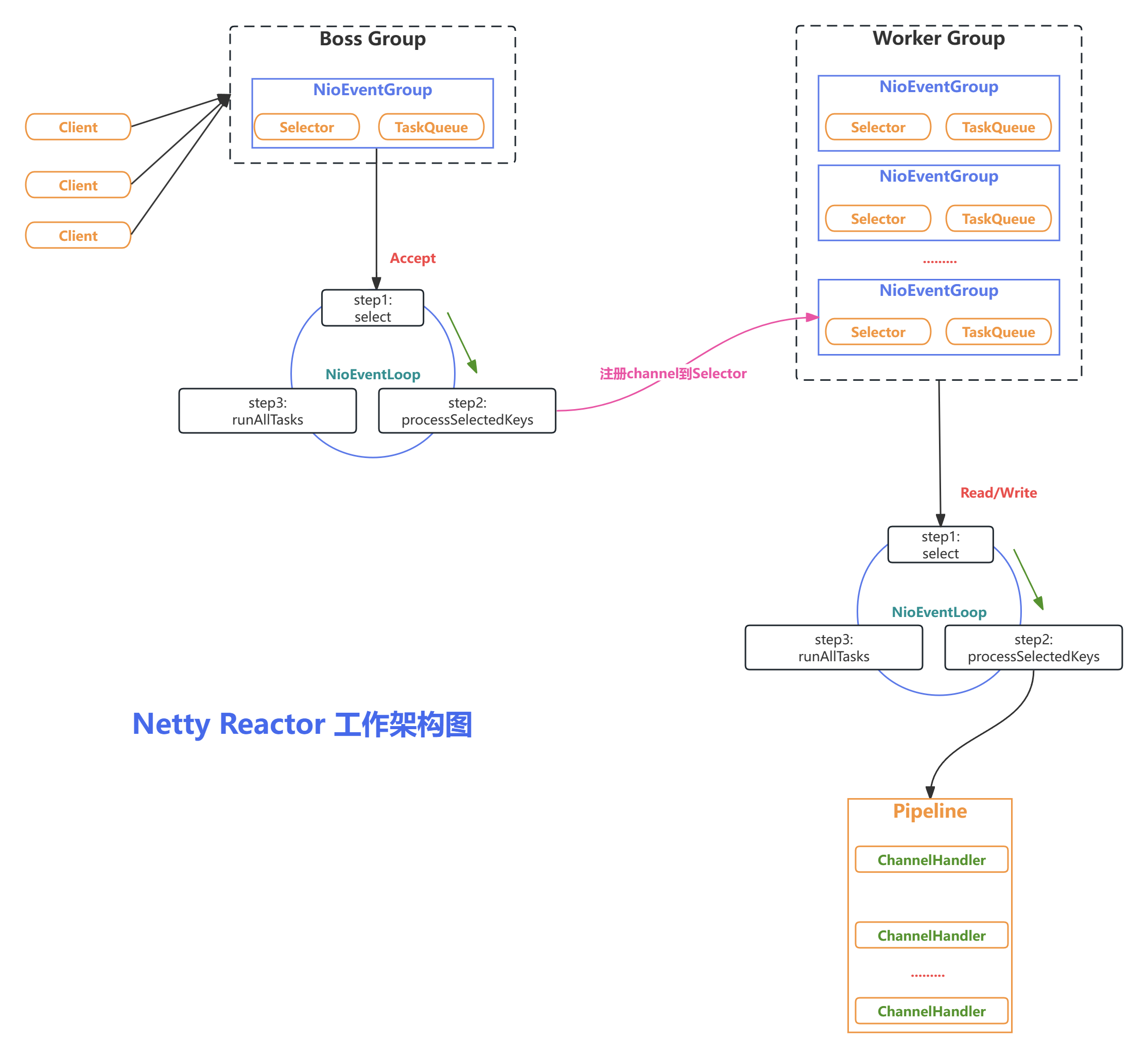
Netty Reactor 的工作架构图
Code
POM
<dependency> <groupId>io.nettygroupId> <artifactId>netty-allartifactId> <version>4.1.94.Finalversion> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Server
【Handler 】
package com.artisan.netty4.server; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; /** * @author 小工匠 * @version 1.0 * @description: 自定义的Handler需要继承Netty规定好的HandlerAdapter才能被Netty框架所关联 * @mark: show me the code , change the world */ @ChannelHandler.Sharable public class ArtisanServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { //获取客户端发送过来的消息 ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("收到客户端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "发送的消息:" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //发送消息给客户端 ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(">>>>>>msg sent from server 2 client.....", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { //发生异常,关闭通道 ctx.close(); } } ``` 【启动类 】 ```java package com.artisan.netty4.server; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; /** * @author 小工匠 * @version 1.0 * @description: 服务端启动类 * @mark: show me the code , change the world */ public class ArtisanServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 创建两个线程组 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { // 创建服务端的启动对象,设置参数 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); // 设置两个线程组 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) // 设置服务端通道类型实现 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 设置bossGroup线程队列的连接个数 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 设置workerGroup保持活动连接状态 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 使用匿名内部类的形式初始化通道对象 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { // 给pipeline管道设置处理器 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ArtisanServerHandler()); } });// 给workerGroup的EventLoop对应的管道设置处理器 System.out.println("服务端已经准备就绪..."); // 绑定端口,启动服务 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync(); // 对关闭通道进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
Client
【Handler 】
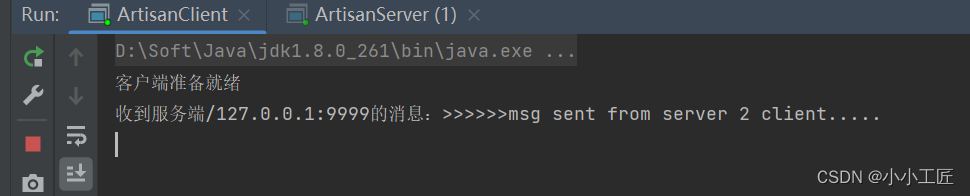
package com.artisan.netty4.client; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; /** * @author 小工匠 * @version 1.0 * @description: 通用handler,处理I/O事件 * @mark: show me the code , change the world */ @ChannelHandler.Sharable public class ArtisanClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //发送消息到服务端 ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("msg send from client 2 server ~~~", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { //接收服务端发送过来的消息 ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("收到服务端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "的消息:" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
【启动类 】
package com.artisan.netty4.client; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; /** * @author 小工匠 * @version 1.0 * @description: 客户端启动程序 * @mark: show me the code , change the world */ public class ArtisanClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { NioEventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { //创建bootstrap对象,配置参数 Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); //设置线程组 bootstrap.group(eventExecutors) //设置客户端的通道实现类型 .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) //使用匿名内部类初始化通道 .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { //添加客户端通道的处理器 ch.pipeline().addLast(new ArtisanClientHandler()); } }); System.out.println("客户端准备就绪"); //连接服务端 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 9999).sync(); //对通道关闭进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { //关闭线程组 eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
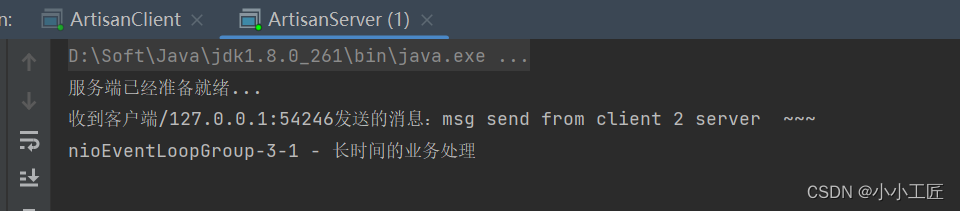
先启动服务端,再启动客户端
Netty 重要组件
taskQueue任务队列
如果Handler处理器有一些长时间的业务处理,可以交给taskQueue异步处理。
我们在
ArtisanServerHandler#channelRead中添加如下代码@Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { //获取客户端发送过来的消息 ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("收到客户端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "发送的消息:" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); //获取到线程池eventLoop,添加线程,执行 ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(() -> { //长时间操作,不至于长时间的业务操作导致Handler阻塞 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - 长时间的业务处理"); }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
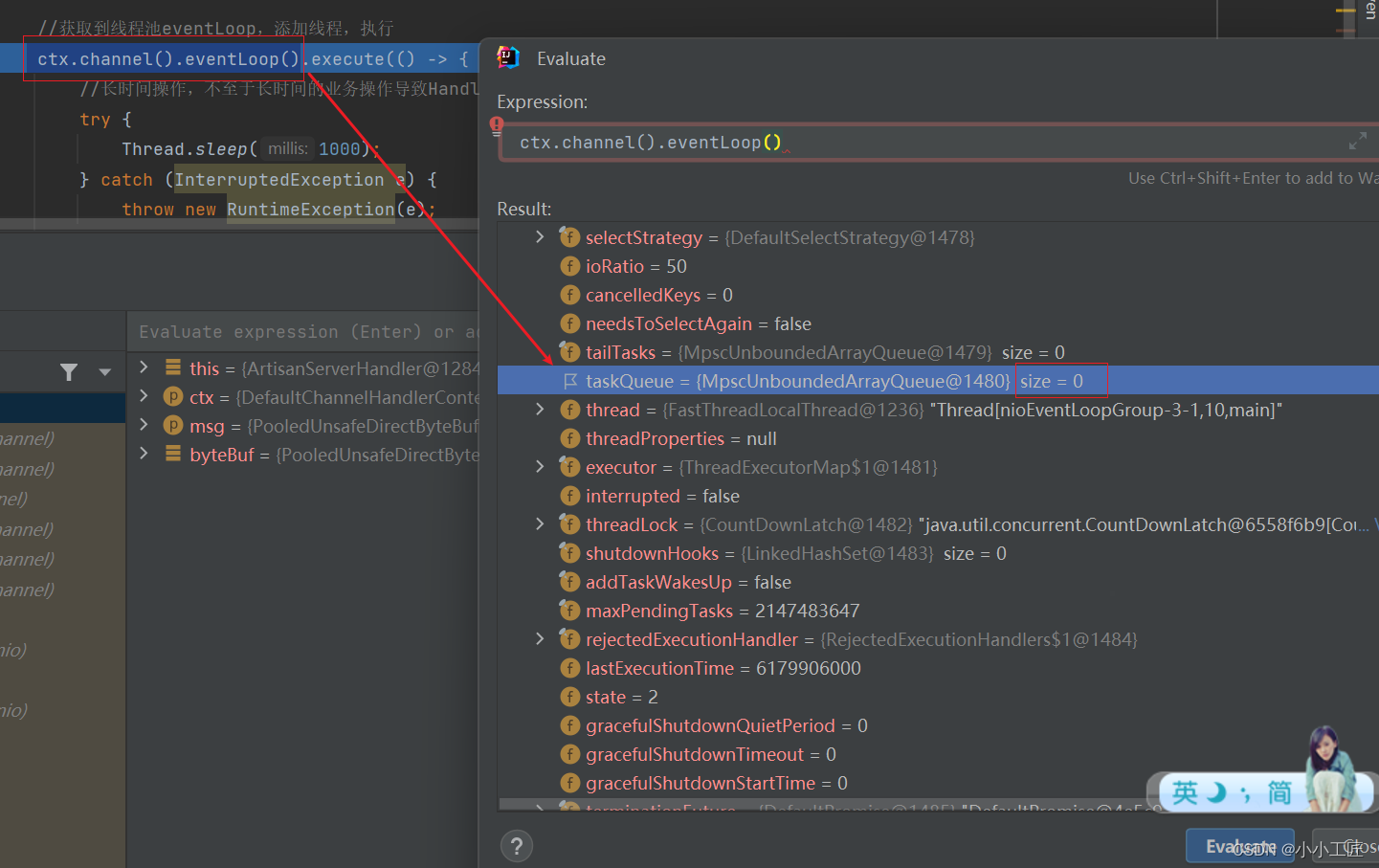
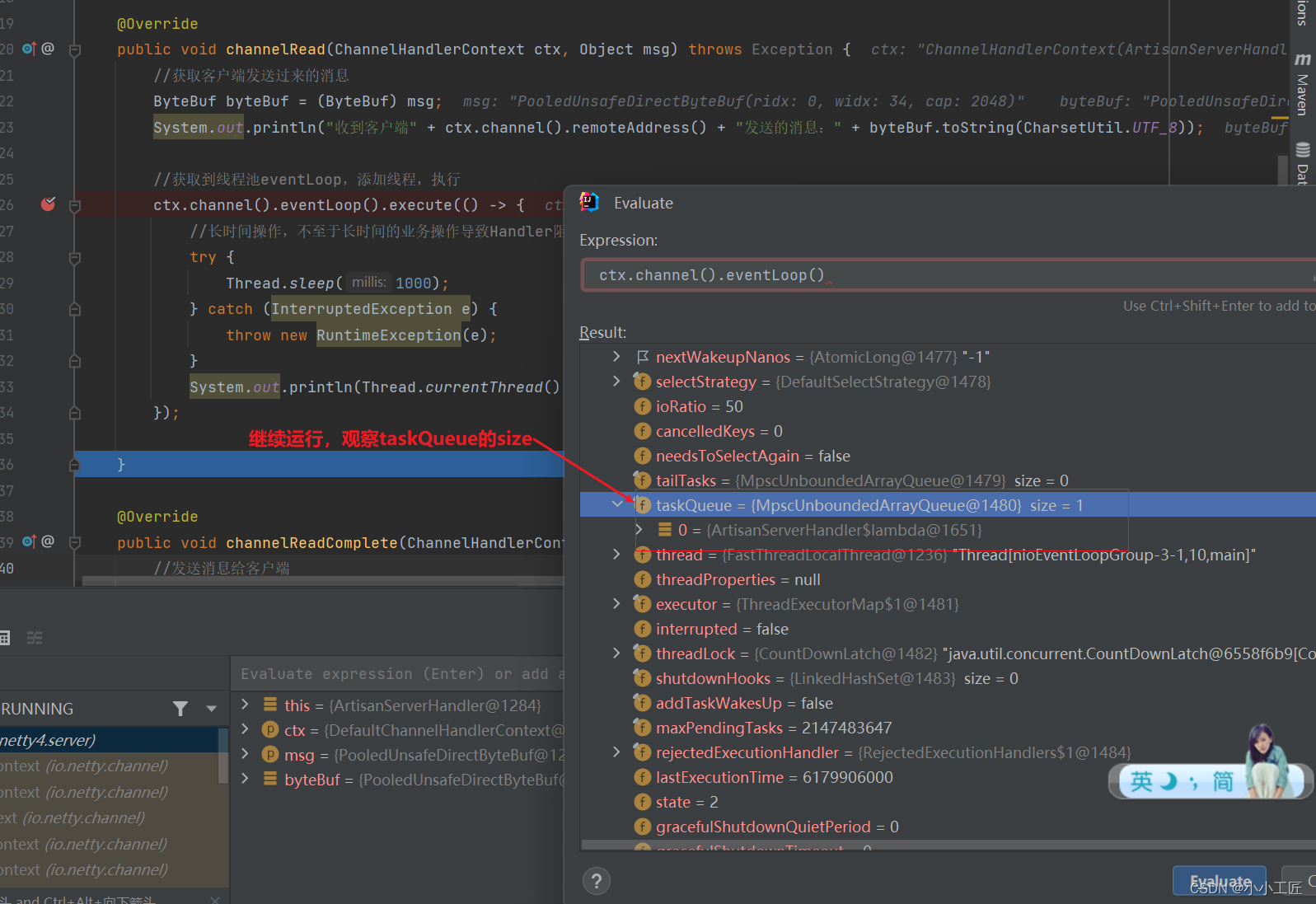
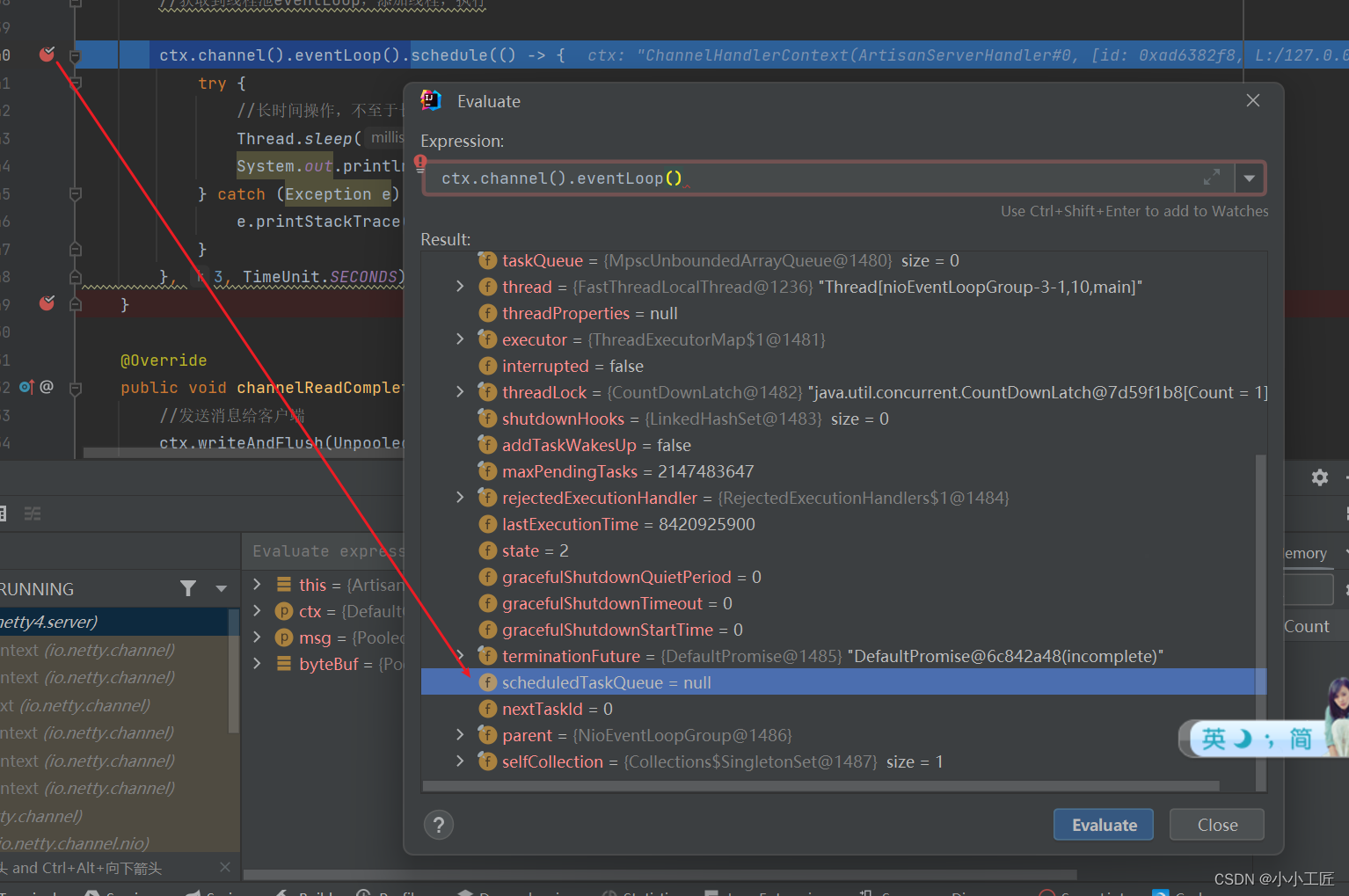
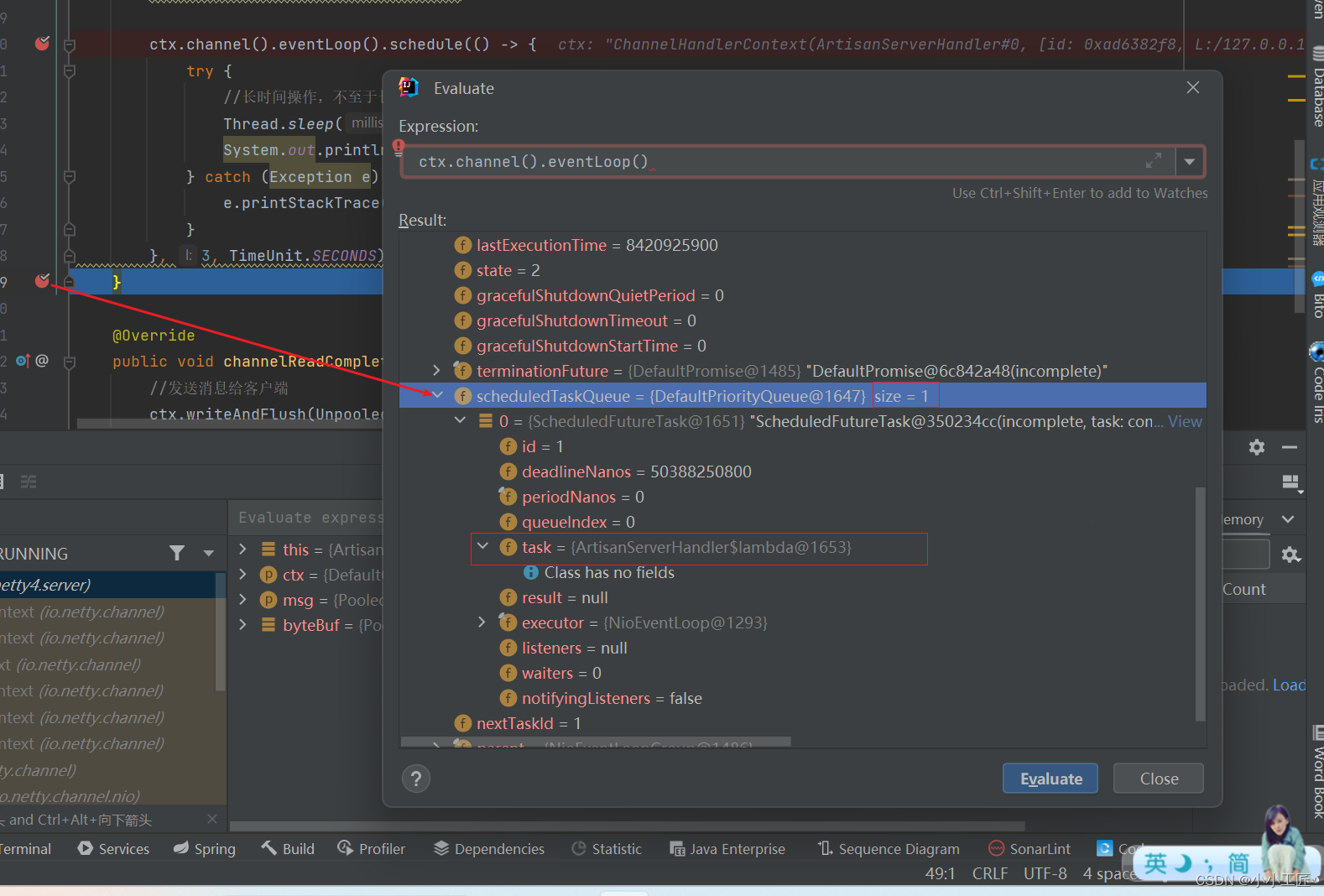
scheduleTaskQueue延时任务队列
Future异步机制
// 绑定端口,启动服务 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync();- 1
- 2
这个ChannelFuture对象是用来做什么的呢?
ChannelFuture提供操作完成时一种异步通知的方式。一般在Socket编程中,等待响应结果都是同步阻塞的,而Netty则不会造成阻塞,因为ChannelFuture是采取类似观察者模式的形式进行获取结果。
请看一段代码演示:
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception { if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("连接成功"); } else { System.out.println("连接失败"); } } });- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Bootstrap与ServerBootStrap
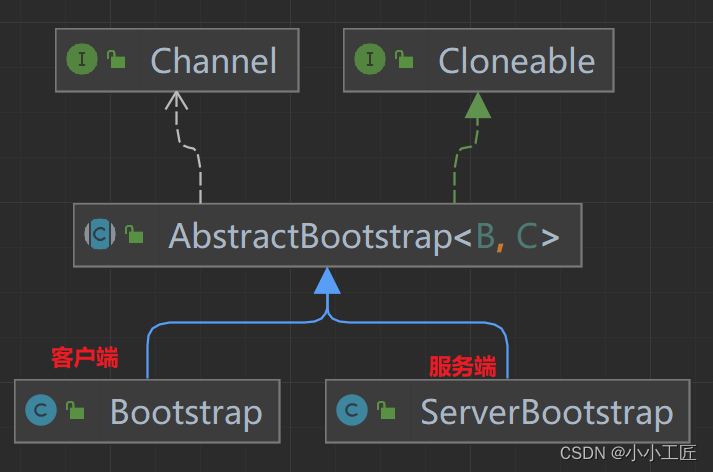
都是继承于
AbstractBootStrap抽象类,所以大致上的配置方法都相同。一般来说,使用Bootstrap创建启动器的步骤可分为以下几步:
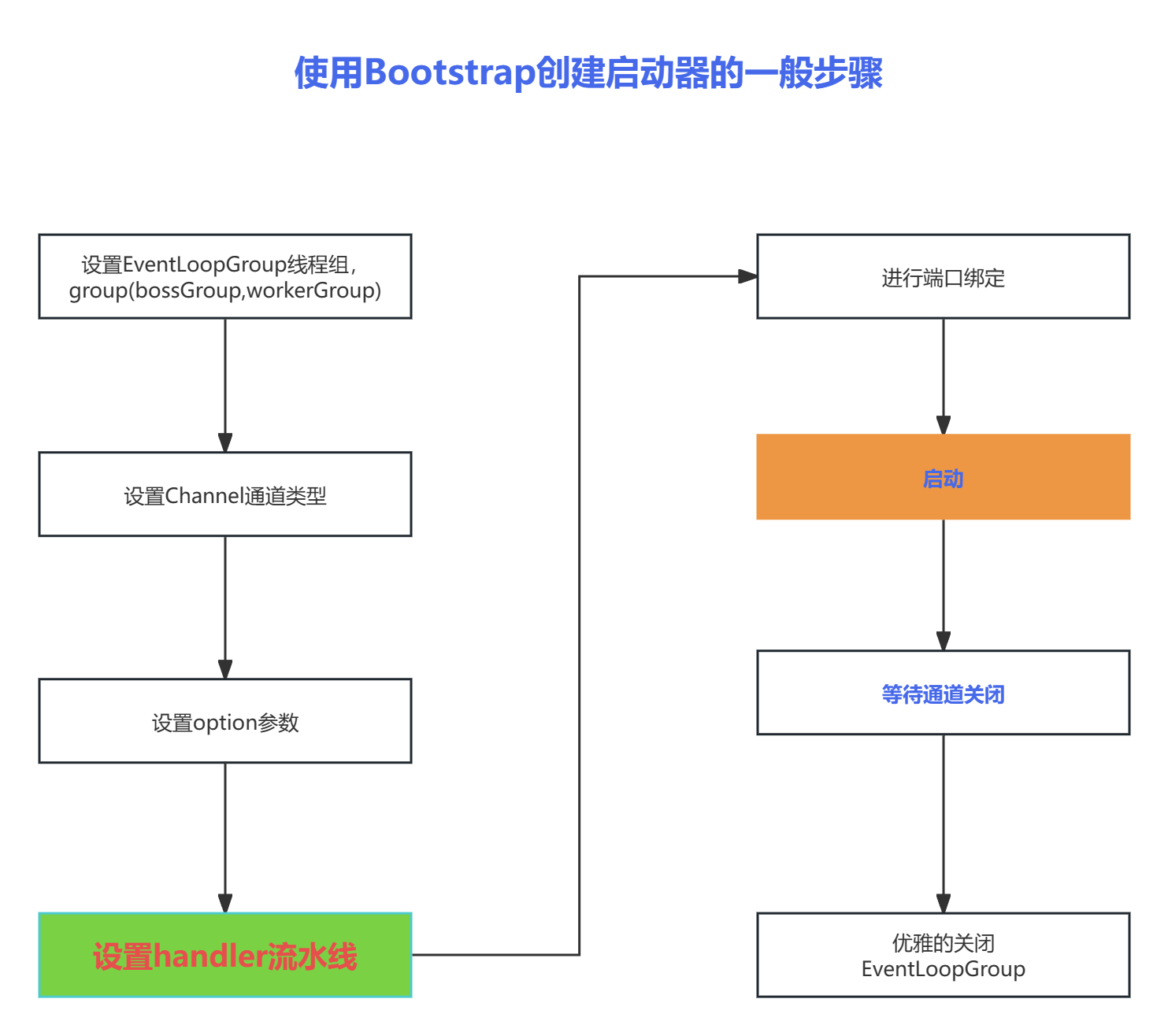
group()
// 创建两个线程组 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 创建服务端的启动对象,设置参数 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); // 设置两个线程组 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) ... ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- bossGroup 用于监听客户端连接,专门负责与客户端创建连接,并把连接注册到workerGroup的Selector中。
- workerGroup用于处理每一个连接发生的读写事件
一般创建线程组直接new:
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();- 1
- 2
默认线程数cpu核数的两倍 。 在
MultithreadEventLoopGroup定义NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS; static { DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt( "io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2)); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
通过源码可以看到,默认的线程数是cpu核数的两倍。假设想自定义线程数,可以使用有参构造器:
//设置bossGroup线程数为1 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); //设置workerGroup线程数为16 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
channel()
这个方法用于设置通道类型,当建立连接后,会根据这个设置创建对应的Channel实例。
-
NioSocketChannel: 异步非阻塞的客户端 TCP Socket 连接。 -
NioServerSocketChannel: 异步非阻塞的服务器端 TCP Socket 连接。
常用的就是这两个通道类型,因为是异步非阻塞的。所以是首选。
-
OioSocketChannel: 同步阻塞的客户端 TCP Socket 连接 (已废弃)。 -
OioServerSocketChannel: 同步阻塞的服务器端 TCP Socket 连接 (已废弃) 。
//server端代码,跟上面几乎一样,只需改三个地方 //这个地方使用的是OioEventLoopGroup EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new OioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); bootstrap.group(bossGroup)//只需要设置一个线程组boosGroup .channel(OioServerSocketChannel.class)//设置服务端通道实现类型 //client端代码,只需改两个地方 //使用的是OioEventLoopGroup EventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new OioEventLoopGroup(); //通道类型设置为OioSocketChannel bootstrap.group(eventExecutors)//设置线程组 .channel(OioSocketChannel.class)//设置客户端的通道实现类型- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
-
NioSctpChannel: 异步的客户端 Sctp(Stream Control Transmission Protocol,流控制传输协议)连接。 -
NioSctpServerChannel: 异步的 Sctp 服务器端连接。只能在linux环境下才可以启动
option()与childOption()
-
option()设置的是服务端用于接收进来的连接,也就是boosGroup线程。 -
childOption()是提供给父管道接收到的连接,也就是workerGroup线程。
列举一下常用的参数
SocketChannel参数,也就是childOption()常用的参数:- SO_RCVBUF Socket参数,TCP数据接收缓冲区大小。
- TCP_NODELAY TCP参数,立即发送数据,默认值为Ture。
- SO_KEEPALIVE Socket参数,连接保活,默认值为False。启用该功能时,TCP会主动探测空闲连接的有效性。
ServerSocketChannel参数,也就是option()常用参数:- SO_BACKLOG Socket参数,服务端接受连接的队列长度,如果队列已满,客户端连接将被拒绝。默认值,Windows为200,其他为128。
ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline是Netty处理请求的责任链,ChannelHandler则是具体处理请求的处理器。实际上每一个channel都有一个处理器的流水线在Bootstrap中childHandler()方法需要初始化通道,实例化一个ChannelInitializer,这时候需要重写initChannel()初始化通道的方法,装配流水线就是在这个地方进行。
代码演示如下:
//使用匿名内部类的形式初始化通道对象 bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { //给pipeline管道设置自定义的处理器 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new MyServerHandler()); } });- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
处理器Handler主要分为两种:
-
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(入站处理器): 入站指的是数据从底层java NIO Channel到Netty的Channel。 -
ChannelOutboundHandler(出站处理器) :出站指的是通过Netty的Channel来操作底层的java NIO Channel
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter处理器常用的事件有:- 注册事件
fireChannelRegistered。 - 连接建立事件
fireChannelActive。 - 读事件和读完成事件
fireChannelRead、fireChannelReadComplete。 - 异常通知事件
fireExceptionCaught。 - 用户自定义事件
fireUserEventTriggered。 - Channel 可写状态变化事件
fireChannelWritabilityChanged。 - 连接关闭事件
fireChannelInactive。
ChannelOutboundHandler处理器常用的事件有:- 端口绑定
bind。 - 连接服务端
connect。 - 写事件
write。 - 刷新时间
flush。 - 读事件
read。 - 主动断开连接
disconnect。 - 关闭 channel 事件
close - 还有一个类似的
handler(),主要用于装配parent通道,也就是bossGroup线程。一般情况下,都用不上这个方法
bind()
提供用于服务端或者客户端绑定服务器地址和端口号,默认是异步启动。如果加上sync()方法则是同步。
有五个同名的重载方法,作用都是用于绑定地址端口号。
优雅地关闭EventLoopGroup
//释放掉所有的资源,包括创建的线程 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();- 1
- 2
- 3
会关闭所有的child Channel。关闭之后,释放掉底层的资源。
Channle
Channel是什么
A nexus to a network socket or a component which is capable of I/O operations such as read, write, connect, and bind- 1
翻译大意:一种连接到网络套接字或能进行读、写、连接和绑定等I/O操作的组件。
A channel provides a user: the current state of the channel (e.g. is it open? is it connected?), the configuration parameters of the channel (e.g. receive buffer size), the I/O operations that the channel supports (e.g. read, write, connect, and bind), and the ChannelPipeline which handles all I/O events and requests associated with the channel.- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
channel为用户提供:
- 通道当前的状态(例如它是打开?还是已连接?)
- channel的配置参数(例如接收缓冲区的大小)
- channel支持的IO操作(例如读、写、连接和绑定),以及处理与channel相关联的所有IO事件和请求的ChannelPipeline。
获取channel的状态
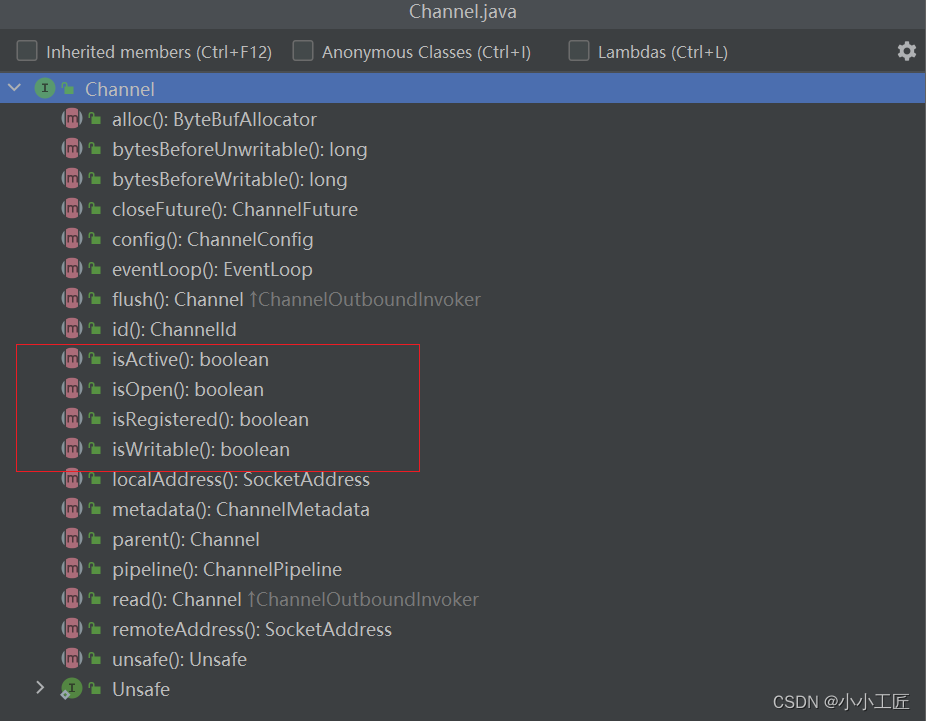
boolean isOpen(); //如果通道打开,则返回true boolean isRegistered();//如果通道注册到EventLoop,则返回true boolean isActive();//如果通道处于活动状态并且已连接,则返回true boolean isWritable();//当且仅当I/O线程将立即执行请求的写入操作时,返回true。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
以上就是获取channel的四种状态的方法。
获取channel的配置参数
获取单条配置信息,使用getOption(), :
// 获取单个配置信息 Integer option = channelFuture.channel().config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG); System.out.println(option);- 1
- 2
- 3
获取多条配置信息,使用getOptions() :
// 获取多条配置信息 Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = channelFuture.channel().config().getOptions(); for (Map.Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> entry : options.entrySet()) { System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
输出
Key = ALLOCATOR, Value = PooledByteBufAllocator(directByDefault: true) Key = AUTO_READ, Value = true Key = RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR, Value = io.netty.channel.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator@724af044 Key = WRITE_BUFFER_HIGH_WATER_MARK, Value = 65536 Key = SO_REUSEADDR, Value = false Key = WRITE_SPIN_COUNT, Value = 16 Key = SO_RCVBUF, Value = 65536 Key = WRITE_BUFFER_WATER_MARK, Value = WriteBufferWaterMark(low: 32768, high: 65536) Key = SO_RCVBUF, Value = 65536 Key = WRITE_BUFFER_LOW_WATER_MARK, Value = 32768 Key = SO_REUSEADDR, Value = false Key = SO_BACKLOG, Value = 128 Key = MESSAGE_SIZE_ESTIMATOR, Value = io.netty.channel.DefaultMessageSizeEstimator@4678c730 Key = MAX_MESSAGES_PER_READ, Value = 16 Key = AUTO_CLOSE, Value = true Key = SINGLE_EVENTEXECUTOR_PER_GROUP, Value = true Key = CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, Value = 30000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
完整代码如下
package com.artisan.netty4.server; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.oio.OioServerSocketChannel; import java.util.Map; /** * @author 小工匠 * @version 1.0 * @description: 服务端启动类 * @mark: show me the code , change the world */ public class ArtisanServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 创建两个线程组 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { // 创建服务端的启动对象,设置参数 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); // 设置两个线程组 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) // 设置服务端通道类型实现 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 设置bossGroup线程队列的连接个数 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 设置workerGroup保持活动连接状态 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 使用匿名内部类的形式初始化通道对象 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { // 给pipeline管道设置处理器 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ArtisanServerHandler()); } });// 给workerGroup的EventLoop对应的管道设置处理器 System.out.println("服务端已经准备就绪..."); // 绑定端口,启动服务 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync(); channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception { if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("连接成功"); } else { System.out.println("连接失败"); } } }); // 获取单个配置信息 Integer option = channelFuture.channel().config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG); System.out.println(option); // 获取多条配置信息 Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = channelFuture.channel().config().getOptions(); for (Map.Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> entry : options.entrySet()) { System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue()); } // 对关闭通道进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
channel支持的IO操作
写操作
这里演示从服务端写消息发送到客户端
@Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //发送消息给客户端 ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(">>>>>>msg sent from server 2 client.....", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
连接操作
ChannelFuture connect = channelFuture.channel().connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666));//一般使用启动器,这种方式不常用- 1
- 2
通过channel获取ChannelPipeline,并做相关的处理:
//获取ChannelPipeline对象 ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.channel().pipeline(); //往pipeline中添加ChannelHandler处理器,装配流水线 pipeline.addLast(new ArtisanServerHandler());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Selector
Netty中的Selector也和NIO的Selector是一样的,就是用于监听事件,管理注册到Selector中的channel,实现多路复用器。
PiPeline与ChannelPipeline
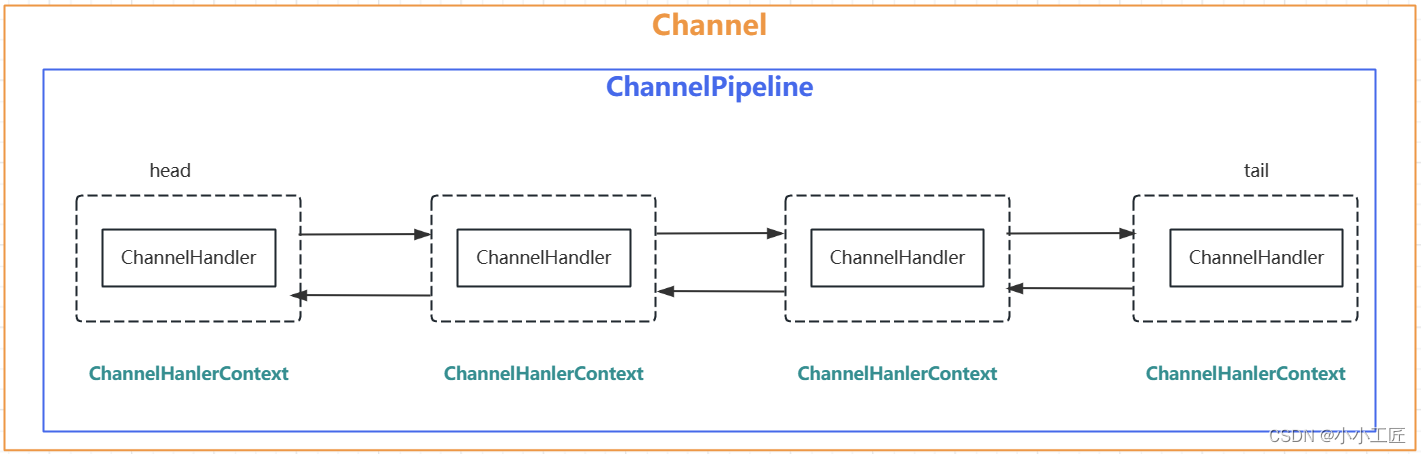
我们知道可以在channel中装配ChannelHandler流水线处理器,那一个channel不可能只有一个channelHandler处理器,肯定是有很多的,既然是很多channelHandler在一个流水线工作,肯定是有顺序的。
于是pipeline就出现了,pipeline相当于处理器的容器。初始化channel时,把channelHandler按顺序装在pipeline中,就可以实现按序执行channelHandler了。
在一个Channel中,只有一个ChannelPipeline。该pipeline在Channel被创建的时候创建。ChannelPipeline包含了一个ChannelHander形成的列表,且所有ChannelHandler都会注册到ChannelPipeline中。
ChannelHandlerContext
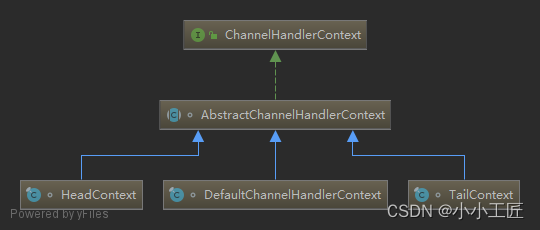
在Netty中,Handler处理器是由我们定义的,上面讲过通过集成入站处理器或者出站处理器实现。这时如果我们想在Handler中获取pipeline对象,或者channel对象,怎么获取呢。于是Netty设计了这个ChannelHandlerContext上下文对象,就可以拿到channel、pipeline等对象,就可以进行读写等操作。
通过类图,ChannelHandlerContext是一个接口,下面有三个实现类。
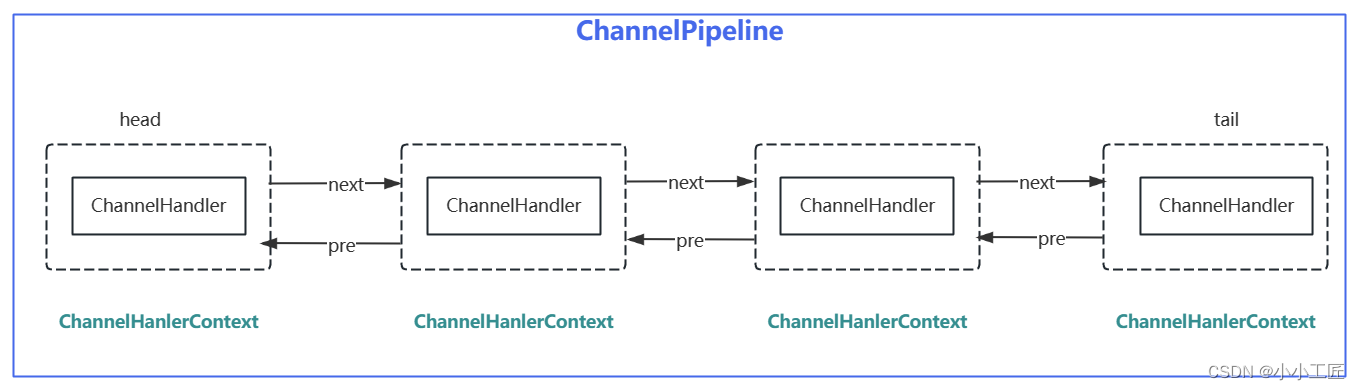
实际上ChannelHandlerContext在pipeline中是一个链表的形式
//ChannelPipeline实现类DefaultChannelPipeline的构造器方法 protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) { this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel"); succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null); voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true); //设置头结点head,尾结点tail tail = new TailContext(this); head = new HeadContext(this); head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
EventLoopGroup
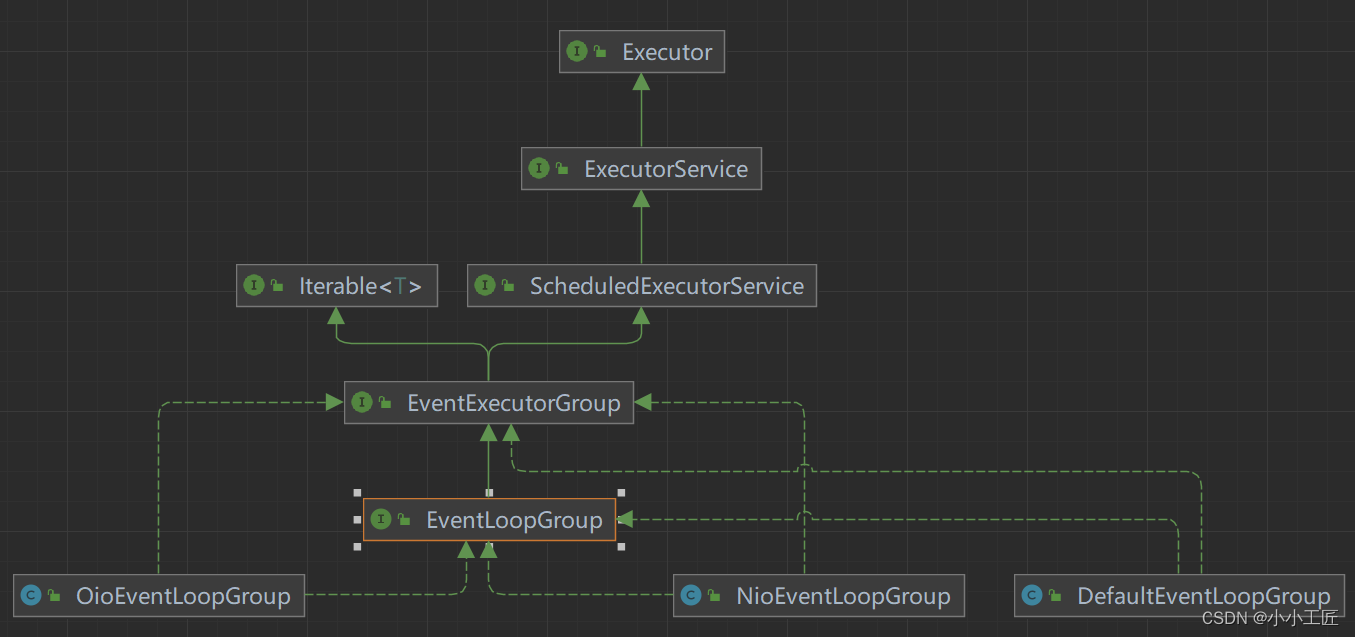
其中包括了常用的实现类NioEventLoopGroup。
从Netty的架构图中,可以知道服务器是需要两个线程组进行配合工作的,而这个线程组的接口就是EventLoopGroup。
每个EventLoopGroup里包括一个或多个EventLoop,每个EventLoop中维护一个Selector实例

-
相关阅读:
归并排序和非比较排序
【Leetcode打卡冲冲冲】
vivado查看报告和消息4
Linux线上环境问题排查命令
NLP-D58-nlp比赛D27&刷题D14&读论文&mathtype
clickhouse出现数据重复问题
基于stm3210系列的简单DMA通信
关于将预留单中增强字段带入物料凭证和会计凭证中
IDEA Plugin插件开发相关踩坑
c语言之二级指针
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yangshangwei/article/details/134378716