-
Python数据结构: 列表(List)详解

在Python中,列表(
List)是一种有序、可变的数据类型,被广泛用于存储和处理多个元素。列表是一种容器,可以包含任意数据类型的元素,包括数字、字符串、列表、字典等。本文将深入讨论列表的各个方面,包括基本语法、常见操作,以及实际应用场景。将覆盖列表的创建、访问、修改、列表推导式和嵌套列表推导式等关键内容。1.创建列表
列表的创建可以通过多种方式创建,可以根据使用场景去选择
# 空列表 empty_list = [] # 包含元素的列表 int_list = [2,4,5,6,8] float_list = [3.0,3.14,100.1,99.999] colors = ['RED','GREEN','BLUE','YELLOW'] bools = [True,False,True,True,False] # 包含其他数据结构类型的数据 list1 = [[2,3],[4,6]] list2 = [(3,4,2)] list3 = [{'name':'Alice'},{'age':18},{'性别':'女'}] # 包含不同数据类型的元素 mixed_list = [11,3.14,'hello',True,[3,'python'],('a','b','c'),{'fruits':'banana'}] # 使用内置函数list()创建 numbers = list(range(2,8))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2.访问列表元素或修改元素
通过索引可以访问和修改列表元素,索引从
0开始,同时支持负索引从列表末尾访问列表中的元素。mixed_list = [11,3.14,'hello',True,[3,'python'],('a','b','c'),{'fruits':'banana'}] # 通过切片的方式访问列表中的元素 print(mixed_list[0]) # 访问第一元素,输出结果: 11 print(mixed_list[-1]) # 访问末尾的元素,输出结果: {'fruits': 'banana'} print(mixed_list[2:5]) # 输出结果: ['hello', True, [3, 'python']] # 通过索引还可以修改列表 mixed_list[1] = 'modify' print(mixed_list) # 列表中第2个元素值已修改- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.列表方法
列表支持很多方法:
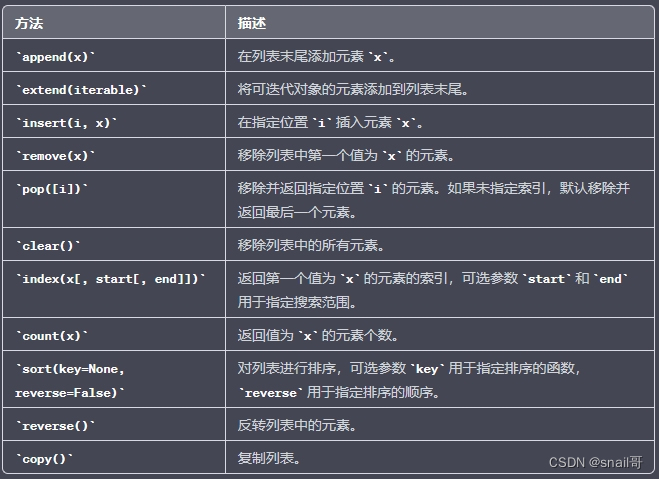
3.1 list.append(x)
在列表末尾添加一个元素,相当于
a[len(a):] = [x]fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] fruits.append('pear') print(fruits) # 输出: ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'pear']- 1
- 2
- 3
3.2 list.extend(iterable)
用可迭代对象的元素扩展列表。相当于
a[len(a):] = iterable。fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] more_fruits = ['pear','cherries'] fruits.extend(more_fruits) print(fruits) # 输出 ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'pear', 'cherries']- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.3 list.insert(i, x)
在指定位置插入元素。第一个参数是插入元素的索引,因此,
a.insert(0, x)在列表开头插入元素,a.insert(len(a), x)等同于a.append(x)fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] fruits.insert(0,'pear') # 在开头插入 fruits.insert(len(fruits),'cherries')# 在末尾插入 print(fruits)# 输出 ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'pear', 'cherries']- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.4 list.remove(x)
从列表中删除第一个值为
x的元素。未找到指定元素时,触发ValueError异常。fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] fruits.remove('orange') print(fruits) # 输出 ['apple', 'banana'] fruits.remove('pear') #未找到指定元素时,触发 ValueError 异常 print(fruits)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:

3.5 list.pop([i])
删除列表中指定位置的元素,并返回被删除的元素。未指定位置时,
a.pop()删除并返回列表的最后一个元素。(方法签名中 i 两边的方括号表示该参数是可选的,不是要求输入方括号。)fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange','pear'] remove_fruit = fruits.pop(2) print(remove_fruit)# 输出 orange print(fruits)# 输出 ['apple', 'banana', 'pear']- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.6 list.clear()
删除列表里的所有元素,相当于
del a[:]。fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange','pear'] fruits.clear() print(fruits)# 输出 []- 1
- 2
- 3
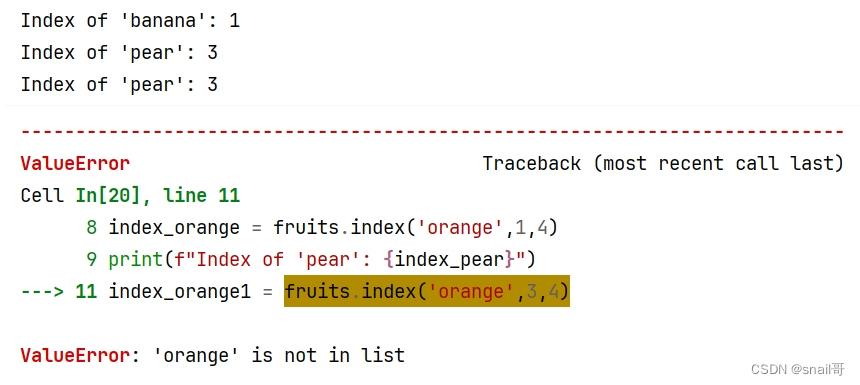
3.7 list.index(x[, start[, end]])
返回列表中第一个值为
x的元素的零基索引。未找到指定元素时,触发ValueError异常。
可选参数start和end是切片符号,用于将搜索限制为列表的特定子序列。返回的索引是相对于整个序列的开始计算的,而不是start参数。fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange','pear','cherries','grape'] index_banana = fruits.index('banana') # print(f"Index of 'banana': {index_banana}") index_pear = fruits.index('pear',2) # 从索引2开始查找 print(f"Index of 'pear': {index_pear}") index_orange = fruits.index('orange',1,4) # 在索引1到4之间查找 print(f"Index of 'pear': {index_pear}") index_orange1 = fruits.index('orange',3,4) # 错误索引查找- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
运行结果:
3.8 list.count(x)
返回列表中元素
x出现的次数。fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange','pear','cherries','grape','apple','apple'] count_apple = fruits.count('apple') print(f'苹果在列表中出现了{count_apple}次')- 1
- 2
- 3
3.9 list.sort(*, key=None, reverse=False)
就地排序列表中的元素
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange','pear','cherries','grape','apple','apple'] fruits.sort()# 按照字母顺序排序 print(fruits) # 输出 ['apple', 'apple', 'apple', 'banana', 'cherries', 'grape', 'orange', 'pear'] numbers = [4, 2, 1, 3, 5] numbers.sort() print(numbers) # 输出: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
3.10 list.reverse()
翻转列表中的元素。
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange','pear'] fruits.reverse() print(fruits)# 输出 ['pear', 'orange', 'banana', 'apple']- 1
- 2
- 3
3.11 list.copy()
返回列表的浅拷贝。相当于
a[:]。fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] fruits_copy = fruits.copy() print(fruits_copy) # 输出: ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']- 1
- 2
- 3
4.列表推导式
4.1 语法
new_list= [expression for item in iterable if condition]
expression是对每个元素进行操作的表达式。
item是来自可迭代对象(如列表、字符串等)的元素。
condition是可选的条件,用于过滤元素。4.2 示例
1) 基本列表推导式
# 生成平方数列表 squares = [x**2 for x in range(5)] print(squares) # 输出: [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]- 1
- 2
- 3
2) 带条件的列表推导式
# 生成偶数平方数列表 even_squares = [x**2 for x in range(10) if x % 2 == 0] print(even_squares) # 输出: [0, 4, 16, 36, 64]- 1
- 2
- 3
3) 字符串操作列表推导式
# 提取字符串中的数字 string = "Hello 123 Python 456" numbers = [int(x) for x in string if x.isdigit()] print(numbers) # 输出: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4) 嵌套列表推导式
# 生成九九乘法表 multiplication_table = [[i * j for j in range(1, 10)] for i in range(1, 10)] for l_table in multiplication_table: print(l_table) # 输出: 一个包含九个列表的列表,每个列表表示乘法表的一行- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:

5)带条件的嵌套列表推导式
# 生成过滤偶数的九九乘法表 filtered_table = [[i * j for j in range(1, 10) if (i * j) % 2 == 0] for i in range(1, 10)] for l_table in filtered_table: print(l_table) # 输出: 一个包含九个列表的列表,每个列表包含符合条件的乘法表元素- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:

-
相关阅读:
k8s-pod控制器
Vue3: 获取元素DOM的方法
泊松抠图论文复现
电路电子技术3 电位的计算&受控源在电路分析中的作用
[附源码]java毕业设计-室内田径馆预约管理系统
【JavaWeb】01_Tomcat、Servlet、Thymeleaf
第12章 软件测试基础 12.1-软件测试 12.2-验证与确认 12.3-软件缺陷
通讯录管理系统
day03_基础语法
Sophos Firewall OS (SFOS) 18.5 MR4
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Snailandfish/article/details/134339737
