-
19.13 Boost Asio 发送TCP流数据
Boost框架中默认就提供了针对TCP流传输的支持,该功能可以用来进行基于文本协议的通信,也可以用来实现自定义的协议。一般
tcp::iostream会阻塞当前线程,直到IO操作完成。首先来看服务端代码,如下所示在代码中首先通过
GetFileSize读取文件行数,当有了行数我们就可以使用循环的方式依次调用acceptor.accept(*tcp_stream.rdbuf())接收客户端的相应请求,并使用<<符号向建立了链接的文件内追加字符串数据。#include#include #include using namespace std; using namespace boost; using namespace boost::asio; // 利用流获取文件大小 long GetFileSize(std::string filename) { long ref_kb; std::ifstream ptr(filename, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary); if (ptr.is_open() == true) { ptr.seekg(0, std::ios::end); // 移动到末尾 ref_kb = ptr.tellg(); // 获取字节数 ptr.close(); return ref_kb; } return 0; } // 一次性读入,并循环输出 void ReadAllFile(std::string filename) { char *buffer; long size; std::ifstream ptr(filename, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate); size = ptr.tellg(); std::cout << "总大小: " << size << std::endl; ptr.seekg(0, std::ios::beg); buffer = new char[size]; ptr.read(buffer, size); ptr.close(); // 循环输出逐字节输出 for (int x = 0; x < size; x++) { if (buffer[x] != '\0') { std::cout << buffer[x]; } } delete[] buffer; } // 每次读入一行,并输出 void ReadLineFileA(std::string filename) { std::ifstream ptr(filename); std::string string; while (std::getline(ptr, string)) { std::cout << string.c_str() << std::endl; } } void ReadLineFileB(std::string filename) { char buffer[1024]; std::fstream ptr; ptr.open(filename, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary); if (ptr.is_open() == true) { while (!ptr.eof()) { // 该行长度到达1024或者遇到\n则结束 ptr.getline(buffer, 1024, '\n'); std::cout << buffer << std::endl; } } } // 获取文本总行数 int GetFileLine(std::string filename) { char buffer[1024]; std::fstream ptr; int line_count = 0; ptr.open(filename, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary); if (ptr.is_open() == true) { while (!ptr.eof()) { ptr.getline(buffer, 1024, '\n'); line_count = line_count + 1; } } return line_count; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { std::string file_path = "d://lyshark.txt"; // 获取行号 int count = GetFileLine(file_path); std::cout << "行数: " << count << std::endl; // 发送数据流 io_service io; ip::tcp::endpoint ep(ip::tcp::v4(), 6666); ip::tcp::acceptor acceptor(io, ep); std::ifstream ptr(file_path); std::string get_string; while (std::getline(ptr, get_string)) { ip::tcp::iostream tcp_stream; acceptor.accept(*tcp_stream.rdbuf()); tcp_stream << get_string.c_str(); } std::system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
与服务端相比,客户端的代码则显得非常简单,在代码中我们只需要通过
ip::tcp::iostream tcp_stream链接到服务端,并通过调用getline即可每次在流中获取一行数据,由于我们循环了3次,所有也就是只读取前三行。#include#include using namespace std; using namespace boost::asio; using namespace boost::system; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { // 循环从流中读入,前三行 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { ip::tcp::iostream tcp_stream("127.0.0.1", "6666"); string str; getline(tcp_stream, str); cout << str << endl; } std::system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
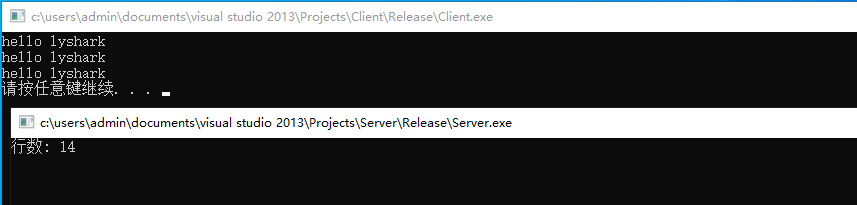
读者可自行编译并运行上述代码片段,则可看到如下图所示的输出信息;
-
相关阅读:
渗透测试-Python安全工具编程进阶
springMVC执行流程详解
docker如何查看对外暴露接口
mybatisplus 自定义mapper加多表联查结合分页插件查询时出现缺失数据的问题
yolov7--制作自己的数据集(VOC转YOLO)
NSS [SWPUCTF 2021 新生赛]sql
Unity WIFI 无线打包至手机
Docker专题(二)之 操作Docker容器
快速抽取resnet_v2_152中间的特征层
CSP-J/S信息学奥赛-算法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lyshark_csdn/article/details/134287279
