-
Java对象的拷贝与克隆
Java对象的拷贝与克隆
在日常开发中,我们经常需要给对象进行赋值,通常会调用其 set/get 方法,有些时候,为了简化代码,我们会采用第三方工具类进行属性拷贝。但是面对如此多的拷贝工具和方法,其性能差异如何不得而知,下面我就对几种属性拷贝工具和方法进行性能分析。
比如我们经常在代码中会对一个数据结构封装成 DO、SDO、DTO、VO 等,而 这些 Bean 中的大部分属性都是一样的,所以使用属性拷贝类工具可以帮助我们节省 大量的 set 和 get 操作。
属性拷贝
我所知道的属性拷贝方法大致分为三种:1.原生get/set方法 2.属性拷贝工具类 3. 序列化再反序列化
-
set/get方法这里就不做介绍了。
-
属性拷贝工具类。
目前使用比较广泛的属性拷贝工具类有:
-
Spring BeanUtils
-
Apache BeanUtils
还有其他属性拷贝的工具类这里就不再赘述了,原理都差不多。只不过实现的功能有所差异。性能对比:
首先定义两个类:
@Data public static class Student { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private Date birthday; } @Data public static class StudentDTO { private String name; private Integer age; private Date birthday; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
进行拷贝测试性能:
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setName("独孤求败"); student.setAge(18); student.setBirthday(new Date()); StopWatch watch = new StopWatch(); watch.start(); int size = 1000000; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { StudentDTO dto = new StudentDTO(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(student, dto); } watch.stop(); System.out.println(watch.prettyPrint()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
结果如下:
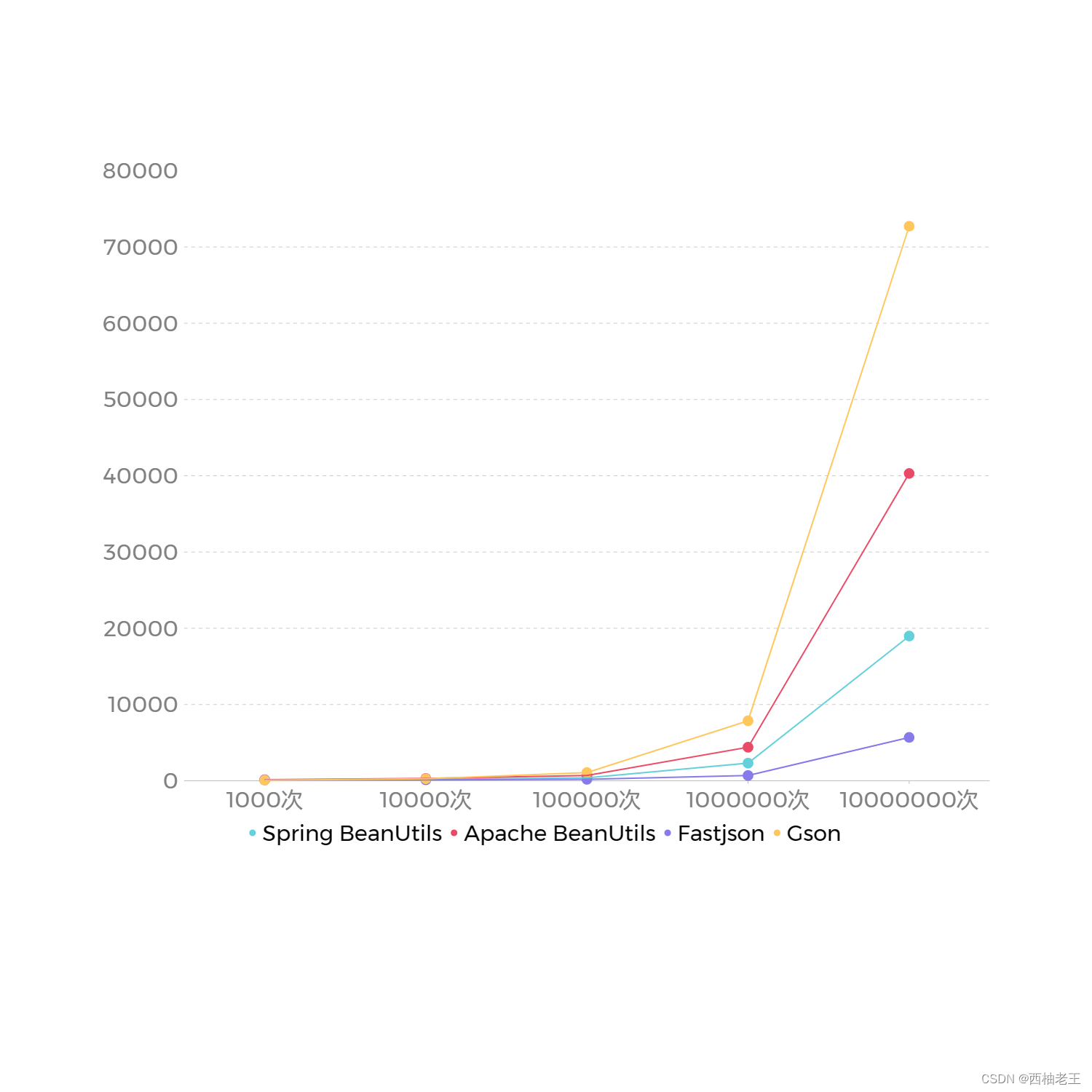
工具类 执行1000次耗时 执行10000次耗时 执行100000次耗时 执行1000000次耗时 执行10000000次耗时 Spring BeanUtils 132ms 178ms 386ms 2315ms 18976ms Apache BeanUtils 140ms 314ms 699ms 4399ms 40302ms 结论:
由此可见,Sping的属性拷贝工具类是最快的,因为
Apache BeanUtils力求做得完美 , 在代码中增加了非常多的校验、兼容、日志打印等代码,过度的包装导致性能下降严重。如果是追求性能的话建议不要使用Apache BeanUtils。
-
-
JSON序列化再反序列化实现拷贝
序列化和反序列化也能实现拷贝和克隆的功能,常见的JSON序列化方式有:
-
阿里的
Fastjson -
Google的
Gson进行拷贝功能测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setName("独孤求败"); student.setAge(18); student.setBirthday(new Date()); StopWatch watch = new StopWatch(); Gson gson = new Gson(); watch.start(); int size = 1000; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { StudentDTO dto = JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(student), StudentDTO.class); // StudentDTO dto = gson.fromJson(gson.toJson(student), StudentDTO.class); } watch.stop(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
结果如下:
序列化工具 执行1000次耗时 执行10000次耗时 执行100000次耗时 执行1000000次耗时 执行10000000次耗时 Fastjson 94ms 121ms 195ms 691ms 5684ms Gson 81ms 251ms 1073ms 7867ms 72722ms 结论:
可以看出,阿里的Fastjson表现还是不错的,当数据量非常大时,Fastjson与Gson的效率有非常明显的差别。但是,Fastjson漏洞频发,导致使用Fastjson的公司不得不经常加班修复漏洞,希望后面Fastjson漏洞能少一点吧。
最后从整体上看一下两类属性拷贝的性能差距
工具类 执行1000次耗时 执行10000次耗时 执行100000次耗时 执行1000000次耗时 执行10000000次耗时 Spring BeanUtils 132ms 178ms 386ms 2315ms 18976ms Apache BeanUtils 140ms 314ms 699ms 4399ms 40302ms Fastjson 94ms 121ms 195ms 691ms 5684ms Gson 81ms 251ms 1073ms 7867ms 72722ms 从下图中能更加直观的看出几种属性拷贝的执行效率差别。不过,最高效的还是直接调用get/set方法,所谓的大道至简应该就是这个道理吧。
-
对象克隆(拷贝)
在Java语言中,拷贝一个对象时,有浅拷贝与深拷贝两种。
浅拷贝:只拷贝源对象的地址,所以新对象与老对象共用一个地址,当该地址变化时,两个对象也会随之改变。
深拷贝:拷贝对象的所有值,即使源对象发生任何改变,拷贝的值也不会变化。
浅拷贝这里就不介绍了,主要介绍一下几种深拷贝方式。常用的深拷贝方式有几种:
- 重写
Object中的clone()方法 Apache Commons Lang序列化JSON序列化
重写clone
调用重写的
Object中的clone()方法,实际上是调用C++的本地函数进行拷贝,所以其拷贝效率非常高。但是有几点需要注意。-
拷贝对象需要实现
Cloneable接口,并重写clone()方法。 -
拷贝对象的属性如果是对象乐行,拷贝的仍然是原属性对象。
比如:
@Data public static class Student implements Serializable, Cloneable { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private Date birthday; @Override public Student clone() { try { Student clone = (Student) super.clone(); // TODO: copy mutable state here, so the clone can't change the internals of the original return clone; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new AssertionError(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
拷贝之后,新的对象中的属性对象仍然是原对象中的属性对象。所以对象属性需要特殊处理。但是,有些对象不用处理,比如String和基本类型的包装类,因为他们都是不可变类,每次进行运算时都会指向新的对象,所以不用担心修改后会影响克隆对象的属性值。
Apache Commons Lang序列化
Apache Commons Lang序列化主要使用
org.apache.commons.lang3包下SerializationUtils.clone()方法进行序列化克隆。序列化克隆后生成的属性对象都是新的,与原对象没有关系。此种方法也有几点需要注意:-
克隆对象需要实现
Serializable接口。 -
序列化效率比较低。
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setName("独孤求败"); student.setAge(18); student.setBirthday(new Date()); Student student1 = SerializationUtils.clone(student); System.out.println(student1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
JSON序列化
JSON序列化通过把对象序列化为json字符串,再把json字符串反序列化成对象实现。上面属性拷贝的时候已经讲过了,主流的
JSON工具有阿里的FastJson和Google的Gson,这里就不再赘述。下面通过简单的测试验证几种克隆的效率:
public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setName("独孤求败"); student.setAge(18); student.setBirthday(new Date()); StopWatch watch = new StopWatch(); Gson gson = new Gson(); watch.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { Student student1 = student.clone(); // Student student1 = SerializationUtils.clone(student); // Student student1 = gson.fromJson(gson.toJson(student), Student.class); // Student student1 = JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(student), Student.class); } watch.stop(); System.out.println(watch.getTotalTimeMillis() + "ms"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
测试结果:
拷贝方法 执行1000次 执行10000次 执行100000次 执行1000000次 执行10000000次 原生clone 0ms 0ms 4ms 14ms 75ms Apache SerializationUtils 96ms 320ms 1148ms 7880ms 76159ms Gson 111ms 315ms 1069ms 7345ms 70489ms FastJson 113ms 121ms 203ms 514ms 3552ms 
综上所述,原生clone和FastJson序列化方式进行拷贝比较好,如果对象属性是基本类型或者String和基本类型的包装类这种不可变类,就可以用原生clone方法进行克隆,否则则可以用FastJson序列化再反序列化进行克隆。当然,上面讲到的属性拷贝也可以用,但是性能却没有那么好。
-
-
相关阅读:
Spark Optimizer 规则详解和示例
echarts 实现tooltip提示框样式自定义
前端css实现水平居中、垂直居中、水平垂直居中【木鱼精简】
Serverless入门
当一名阿里P9是什么样的体验?
JCR一区级 | Matlab实现TCN-LSTM-MATT时间卷积长短期记忆神经网络多特征分类预测
洛谷算法记录-P1013
WPF 截图控件之绘制方框与椭圆(四) 「仿微信」
《 前端挑战与未来:如何看待“前端已死”》
AR人脸道具SDK,打造极致用户体验
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/pig_boss/article/details/134265032
