-
【Redis】Redis整合SSM&&Redis注解式缓存&&Redis中的缓存穿透、雪崩、击穿的原因以及解决方案(详解)

目录:
目录
三,Redis中的缓存穿透、雪崩、击穿的原因以及解决方案(附图)
一,SSM整合redis
1.原因:
整合SSM和Redis可以提升系统的性能、可伸缩性和可靠性,在分布式环境下更好地支持会话管理、消息队列和分布式锁等功能。
2.步骤:可以参考SSM整合mysql
导入pom依赖在Maven中添加Redis的依赖
- <redis.version>2.9.0</redis.version>
- <redis.spring.version>1.7.1.RELEASE</redis.spring.version>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
- <artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
- <version>${redis.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
- <version>${redis.spring.version}</version>
- </dependency>
2.2.spring-redis.xml的相关配置
redis.properties
- redis.hostName=127.0.0.1
- redis.port=6379
- redis.password=123456
- redis.timeout=10000
- redis.maxIdle=300
- redis.maxTotal=1000
- redis.maxWaitMillis=1000
- redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
- redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun=1024
- redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000
- redis.testOnBorrow=true
- redis.testWhileIdle=true
- redis.expiration=3600
spring-redis.xml
- "1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
- <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
- <property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}"/>
- <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/>
- <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"/>
- <property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}"/>
- <property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}"/>
- <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}"/>
- <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"/>
- <property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}"/>
- bean>
- <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"
- destroy-method="destroy">
- <property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/>
- <property name="hostName" value="${redis.hostName}"/>
- <property name="port" value="${redis.port}"/>
- <property name="password" value="${redis.password}"/>
- <property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"/>
- bean>
- <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
- <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"/>
- <property name="keySerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
- property>
- <property name="valueSerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
- property>
- <property name="hashKeySerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
- property>
- <property name="hashValueSerializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
- property>
- <property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/>
- bean>
- <bean id="redisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager">
- <constructor-arg name="redisOperations" ref="redisTemplate"/>
- <property name="defaultExpiration" value="${redis.expiration}"/>
- <property name="usePrefix" value="true"/>
- <property name="cachePrefix">
- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCachePrefix">
- <constructor-arg index="0" value="-cache-"/>
- bean>
- property>
- bean>
- <bean id="cacheKeyGenerator" class="com.zking.ssm.redis.CacheKeyGenerator">bean>
- <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="redisCacheManager" key-generator="cacheKeyGenerator"/>
- beans>
2.3.修改applicationContext.xml
如果spring配置文件中需要配置两个及以上的properties文件则需要在applicationContext.xml中进行配置处理,否则会出现覆盖的情况。
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
- xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
- <!--1. 引入外部多文件方式 -->
- <bean id="propertyConfigurer"
- class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
- <property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" />
- <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" />
- <property name="locations">
- <list>
- <value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
- <value>classpath:redis.properties</value>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
- <!-- 随着后续学习,框架会越学越多,不能将所有的框架配置,放到同一个配制间,否者不便于管理 -->
- <import resource="applicationContext-mybatis.xml"></import>
- <import resource="spring-redis.xml"></import>
- <import resource="applicationContext-shiro.xml"></import>
- </beans>
2.4.配置redis的key生成策略
CacheKeyGenerator.java
- package com.zking.ssm.redis;
- import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
- import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
- import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
- import java.lang.reflect.Array;
- import java.lang.reflect.Method;
- @Slf4j
- public class CacheKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
- // custom cache key
- public static final int NO_PARAM_KEY = 0;
- public static final int NULL_PARAM_KEY = 53;
- @Override
- public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
- StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder();
- key.append(target.getClass().getSimpleName()).append(".").append(method.getName()).append(":");
- if (params.length == 0) {
- key.append(NO_PARAM_KEY);
- } else {
- int count = 0;
- for (Object param : params) {
- if (0 != count) {//参数之间用,进行分隔
- key.append(',');
- }
- if (param == null) {
- key.append(NULL_PARAM_KEY);
- } else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveArray(param.getClass())) {
- int length = Array.getLength(param);
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- key.append(Array.get(param, i));
- key.append(',');
- }
- } else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(param.getClass()) || param instanceof String) {
- key.append(param);
- } else {//Java一定要重写hashCode和eqauls
- key.append(param.hashCode());
- }
- count++;
- }
- }
- String finalKey = key.toString();
- // IEDA要安装lombok插件
- log.debug("using cache key={}", finalKey);
- return finalKey;
- }
- }
二,redis注解式缓存
关于什么是Redis注解式:
注解式缓存是一种通过在方法上添加特定的注解来实现自动缓存的机制。在Java开发中,我们可以使用Spring框架提供的
@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict等注解来实现对Redis的缓存操作。-
@Cacheable注解:- 作用:标记方法的返回值可以被缓存,并且在下次调用该方法时,会直接从缓存中获取结果,而不会执行方法体内的逻辑。使用该注解会将查询结果放入Redis中下一次同样的查询就不会走数据库,而是走Redis.
- 示例代码:
- @Cacheable(value = "myCache", key = "#id")
- public User getUserById(String id) {
- // 从数据库或其他数据源获取用户信息的逻辑
- return user;
- }
解释:以上代码表示将方法的返回值以键值对的形式缓存在,减少了数据访问对MySQL数据库的压力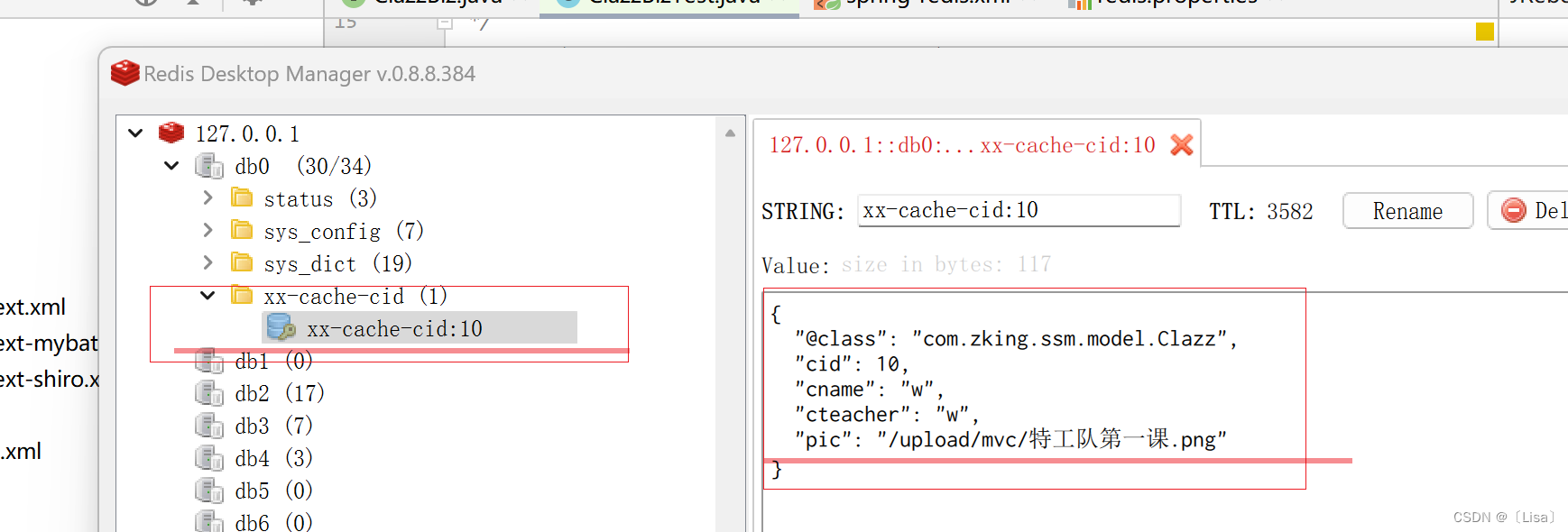
-
@CachePut注解:- 作用:标记方法的返回值需要更新缓存,即每次调用方法都会执行方法体内的逻辑,并将返回值存入缓存。
- 示例代码:
- @CachePut(value = "myCache", key = "#user.id")
- public User updateUser(User user) {
- // 更新用户信息的逻辑
- return user;
- }
-
@CacheEvict注解:- 作用:标记方法会清除缓存中的指定数据。
- 示例代码:
- @CacheEvict(value = "myCache", key = "#id")
- public void deleteUser(String id) {
- // 删除用户信息的逻辑
- }
解释:以上代码表示调用该方法时会从名为"myCache"的缓存中移除key为参数"id"对应的缓存数据。
-
CachePut和Cacheable的区别:
Cacheable和CachePut都是Spring框架中用于缓存的注解,它们的主要区别是:Cacheable用于获取缓存中的数据,如果缓存不存在,就会执行方法并将返回值放入缓存中;而CachePut用于更新缓存中的数据,它每次都会执行方法,并将返回值放入缓存中。
Cacheable和CachePut的key生成方式不同,Cacheable默认使用方法的参数作为key,可以通过key属性指定key的生成方式或使用SpEL表达式自定义key的生成方式;而CachePut默认使用Cacheable的默认key生成方式,也可以通过key属性指定key的生成方式。
Cacheable和CachePut的Sync属性也不同,Cacheable默认为false,即异步处理;而CachePut默认为true,即同步处理。
通过使用这些注解,我们可以更加方便地实现对Redis的缓存操作,减少了手动管理缓存的复杂性。但需要注意的是,使用注解式缓存时,需要确保被缓存的方法的输入参数和返回值类型是可序列化的,以便在Redis中进行存储和读取。
此外,还可以通过配置Spring框架的缓存管理器、缓存策略等来进一步优化和配置缓存行为。具体的配置和使用细节可以参考Spring框架的文档和教程。
三,Redis中的缓存穿透、雪崩、击穿的原因以及解决方案(附图)
-
缓存穿透(Cache Penetration):
- 原因:当请求查询一个不存在于缓存和数据库中的数据时,每次查询都会直接访问数据库,导致对数据库的频繁访问,增加数据库负载。情景:客户端发送大量的不可响应的请求:比如发送一个id为-999的用户
- 解决方案:
- 布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter):用于判断请求的数据是否存在于缓存或数据库中。使用布隆过滤器可以快速过滤掉一部分不存在的数据,避免对数据库的无效查询。
- 空值缓存(Null Object Caching):将不存在的数据也缓存起来,但设置一个较短的过期时间,以便下次查询时可以从缓存中获取。
注意事项:
使用空值作为缓存的时候,key设置的过期时间不能太长,防止占用太多redis资源
对空值缓存是一种被动的防御方式,当遇到黑客暴力请求很多不存在的数据就需要写入大量的null值到Redis中,可能导致Redis内存占用不足的情况
使用布隆过滤器,可以在用户访问的时候判断该资源是否存在,不存在则直接拒绝访问
布隆过滤器是有一定的误差,所以一般需要配合一些接口流量的限制(规定用户在一段时间内访问的频率)、权限校验、黑名单等来解决缓存穿透的问题
-
缓存雪崩(Cache Avalanche):
- 原因:当缓存中的大量数据同时过期或失效时,所有请求都会直接访问数据库,导致数据库压力骤增,甚至导致数据库宕机。
- 解决方案:
- 随机过期时间(Randomized Expiration):为缓存中的数据设置随机的过期时间,以避免大量数据同时过期。
- 并发控制(Concurrency Control):使用分布式锁或互斥机制,确保只有一个线程可以重新加载缓存数据,避免重复查询。
-
缓存击穿(Cache Miss):
- 原因:当某个热点数据过期或失效时,大量请求同时涌入,导致并发查询数据库,增加数据库压力。
- 解决方案:
- 互斥锁(Mutex Lock):在缓存失效的情况下,使用互斥锁来确保只有一个请求可以查询数据库,并将查询结果进行缓存,其他请求等待缓存更新后再获取数据。
- 提前加载(Preloading):提前加载热点数据到缓存中,并设置较长的过期时间,以避免热点数据过期后被击穿。
-
相关阅读:
贝锐蒲公英异地组网:降低建筑工地远程视频监控成本、简化运维
eval()方法字符串转对象; 分别取对象属性名和属性的方法
Java Web程序设计基础二(服务器交互篇——四大属性作用域)
【数据结构初阶】三、 线性表里的链表(无头+单向+非循环链表)
【LinkedHashMap】146. LRU 缓存
ESP8266-Arduino编程实例-LED点阵驱动(基于Max7219)
创邻科技Galaxybase图技术如何在网络攻击中为你保驾护航
如何设置代理ip服务器地址
实景三维渐成测绘大趋势,数据存储迎来新风口
CARLA和LGSVL坐标系差异
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73647713/article/details/134254036
