-
Technology strategy Pattern 学习笔记1-Context: Architecture and Strategy
Context: Architecture and Strategy
1 Architect and Strategist
1.1 three primary concerns of the architect
1.1.1 Contain entropy(熵-混乱程度,不确定性,惊奇程度,不可预测性,信息量等等)
- The architect who is containing entropy is stating a vision around
which to rally; showing a path in a roadmap; garnering support for
that vision through communication of guidelines and standards; and
creating clarity to ensure efficiency of execution and that you’re
doing the right things and doing things right - One cannot be successful as an architect without thinking of not only what to do, but how to get it done within an organization, which requires knowing why it should matter to someone who isn’t a technologist.
- a critical first step to being not only useful but powerful as an architect and strategist.
1.1.2 Specify the nonfunctional requirements.
1.1.3 Determine (权衡) trade-offs
The role of the architect is to see where those challenges may lurk(隐伏), seek to make them explicit, and make value judgments about how to balance the solutions and the new problems they occasion, under the guidance of the broader business strategy1.2 business strategy
1.2.1 business strategies will concern themselves with the following
- The goals of the organization
- The operating model: processes and how your company conducts its business
- Culture: the mores and value system, the modes of communication
- Talent strategy: how you source and retain talent, how you train them
- Facilities strategy: where you do business, relevant local laws,
and cost concerns
1.2.2 the strategist asks these questions - Are resources devoted to the right areas, to the most important
customers? - Are we creating products and services that can thrive in a market in different time horizons?
- Where should we spend money? Where should we cut costs?
- Where do skills need to be added or strengthened?
- Where can productivity be improved?
- What culture, attitude, and skills are required?
1.3 the strategist finds herself concerned with some or all of the following:
- Identifying business development opportunities
- Finding, proposing, and validating mergers and acquisition opportunities
- Building strategic capabilities within certain areas of the organization
- Performing research based on data to recommend long-term
directions for the company
战略-文化-及执行关系
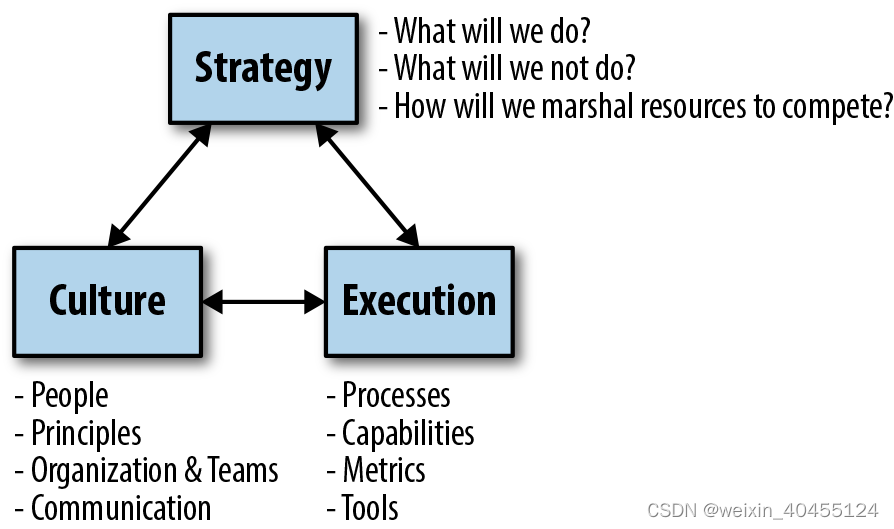
A good first step for doing so is to create two versions of the strategy
1.5.1 可公开的版本及不可公开的事项版本:
- shorter version that communicates only the
changes you’re driving in a way that you can share publicly with teams.
1.5.2 给高管的版本:- one that provides an honest and detailed examination of all three factors to share with the executive team
- In long-range planning there are financial, business transaction, and personnel matters that obviously can’t be disclosed.
Applying the Patterns
2.1 Establish context
- a. Analyze the trends happening in the world outside.
- b. Analyze the forces at work across your industry, your organization,and your department.
- c. Gain a view on your stakeholders.
2.2 Understand your competition, the market, and the technology landscape
2.3 Identify strategic options in your products, services, and technology roadmap.
2.4 Evaluate those options
2.5 Make a compelling recommendation with a coherent, cohesive, comprehensive strategy to gain approval and resources to execute your plans. - The architect who is containing entropy is stating a vision around
-
相关阅读:
第八部分:JSP
代码随想录 动态规划Ⅸ
有什么可替代问卷星的好用的问卷工具?
java连接数据库SQL注入问题的解决
【web课程设计网页规划与设计】基于HTML+CSS+JavaScript火车票网上预订系统网站(4个页面)
计算机毕业论文java毕业设计选题基于springboot的社区服务管理包运行成功]
漫谈测试成长之探索——缺陷分析
【操作系统】磁盘管理高级
uniapp上传二进制图片
LeetCode二叉树系列——102.二叉树的层序遍历
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40455124/article/details/134221745