-
Steger算法实现结构光光条中心提取(python版本)
Steger算法原理
对结构光进行光条中心提取时,Steger算法是以Hessian矩阵为基础的。它的基础步骤如下所示:
- 从Hessian矩阵中求出线激光条纹的法线方向
- 在光条纹法线方向上将其灰度分布按照泰勒多项式展开,求取的极大值即为光条在该法线方向上的亚像素坐标。对于二维离散图像
 来说,Hessian矩阵可以表示为:
来说,Hessian矩阵可以表示为:

这里面的u,v表示的就是像素的行坐标和列坐标,
 代表像素
代表像素 的灰度也可以称之为灰度分布函数。而
的灰度也可以称之为灰度分布函数。而 ,
, 和
和 都可以通过
都可以通过 与二维高斯函数
与二维高斯函数 卷积运算得到。
卷积运算得到。

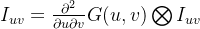

在这里,二维高斯函数,其主要作用是为了让光条灰度分布特性更加明显,在G(u,v)表达式中,
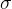 是标准差,一般取
是标准差,一般取 ,W代表光条宽度。在像素(u,v)处的Hessian矩阵有两个特征向量,其中一个绝对值较大,为该像素处的法线方向向量,而另外一个则是切向方向向量。因此可以通过求取Hessian矩阵的特征向量来计算出法线方向。某一像素点
,W代表光条宽度。在像素(u,v)处的Hessian矩阵有两个特征向量,其中一个绝对值较大,为该像素处的法线方向向量,而另外一个则是切向方向向量。因此可以通过求取Hessian矩阵的特征向量来计算出法线方向。某一像素点 ,在二阶泰勒展开式Hessian矩阵为:
,在二阶泰勒展开式Hessian矩阵为:H(u0,v0)=[IuuIuvIuvIvv]
由该点的Hessian矩阵所求出的特征值和特征向量分别与该点的法线方向和该方向的二阶方向导数相对应。其中法线方向的单位向量为:e=[eu,ev],并且在光条纹法线方向上的像素点(u0+t⋅eu,v0+t⋅ev),并且在光条纹法线方向上的像素点I=(u0+t⋅eu,v0+t⋅ev)可以由像素(u0,v0)的灰度I(u0,v0)和二阶泰勒展开多项式表示为:
I(u0+t⋅eu,v0+t⋅ev)=I(u0,v0)+t⋅e[Iu,Iv]T+t⋅e⋅H(u,v)⋅eT
t=−eu⋅Iu+ev⋅Ive2u⋅Iuu+2⋅eu⋅ev⋅Iuv+e2v⋅Ivv
再将t(即泰勒展开式)代入其中即可求出光条纹中心的亚像素坐标。
Steger算法Python实现
这一部分,我在网上找到了许多C++版本的Steger算法实现,本人参考了现有的C++版本Steger算法实现,在此基础上进行了改进,用Python重新去实现该算法。
计算图像的一阶导数和二阶导数
这里我采用了三种方法,分别是自定义卷积、Scharr 滤波器、Sobel 滤波器来计算图像的导数和二阶导数。
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- def _derivation_with_Filter(Gaussimg):
- dx = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1], [0], [-1]]))
- dy = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1, 0, -1]]))
- dxx = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1], [-2], [1]]))
- dyy = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1, -2, 1]]))
- dxy = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1, -1], [-1, 1]]))
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def _derivation_with_Scharr(Gaussimg):
- dx = cv2.Scharr(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0)
- dy = cv2.Scharr(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1)
- dxx = cv2.Scharr(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0)
- dxy = cv2.Scharr(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1)
- dyy = cv2.Scharr(dy, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1)
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def _derivation_with_Sobel(Gaussimg):
- dx = cv2.Sobel(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
- dy = cv2.Sobel(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
- dxx = cv2.Sobel(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
- dxy = cv2.Sobel(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
- dyy = cv2.Sobel(dy, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- if __name__=="__main__":
- from pyzjr.dlearn import Runcodes
- sigmaX, sigmaY = 1.1, 1.1
- img = cv2.imread(r"D:\PythonProject\net\line\linedata\Image_1.jpg")
- gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- Gaussimg = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_img, ksize=(0, 0), sigmaX=sigmaX, sigmaY=sigmaY)
- with Runcodes("Filter"):
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = _derivation_with_Filter(Gaussimg)
- print(type(dx[0][0]))
- with Runcodes("Scharr"):
- dx1, dy1, dxx1, dyy1, dxy1 = _derivation_with_Scharr(Gaussimg)
- print(type(dx1[0][0]))
- with Runcodes("Sobel"):
- dx2, dy2, dxx2, dyy2, dxy2 = _derivation_with_Sobel(Gaussimg)
- print(type(dx2[0][0]))
在控制台中输出为:
Filter: 0.00602 sec
Scharr: 0.00770 sec
Sobel: 0.01025 sec从运算时间上来看,自定义的Filter速度最快,scharr滤波器居中,sobel滤波器最慢;从元素类型上来看,第一种为uint8,另外两种为float32类型。
通过选择计算方法可以去创建Hessian矩阵。
- def Magnitudefield(dxx, dyy):
- """计算幅度和相位"""
- dxx = dxx.astype(float)
- dyy = dyy.astype(float)
- mag = cv2.magnitude(dxx, dyy)
- phase = mag*180./np.pi
- return mag, phase
- def derivation(gray_img, sigmaX, sigmaY, method="Scharr", nonmax=False):
- """
- 计算图像的一阶导数 dx 和 dy,以及二阶导数 dxx、dyy 和 dxy
- :param gray_img: 灰度图
- :param sigmaX: 在水平方向的高斯核标准差,用于激光线提取建议取1-2
- :param sigmaY: 在垂直方向上的高斯核标准差,用于激光线提取建议取1-2
- :param method:"Scharr" or "Filter" or "Sobel"
- 选择什么方式获取dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy,提供了卷积与Scharr和Sobel滤波器三种方式计算,
- Scharr滤波器通常会产生更平滑和准确的结果,所以这里默认使用"Scharr"方法,虽然
- "Sobel"运行比另外两种要慢,但在使用的时候,建议自己试试
- :return: dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- """
- Gaussimg = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_img, ksize=(0, 0), sigmaX=sigmaX, sigmaY=sigmaY)
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = _derivation_with_Scharr(Gaussimg)
- if method == "Filter":
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = _derivation_with_Filter(Gaussimg)
- elif method == "Sobel":
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy =_derivation_with_Sobel(Gaussimg)
- if nonmax:
- normal, phase = Magnitudefield(dxx, dyy)
- dxy = nonMaxSuppression(normal, phase)
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def nonMaxSuppression(det, phase):
- """非最大值抑制"""
- gmax = np.zeros(det.shape)
- # thin-out evry edge for angle = [0, 45, 90, 135]
- for i in range(gmax.shape[0]):
- for j in range(gmax.shape[1]):
- if phase[i][j] < 0:
- phase[i][j] += 360
- if ((j+1) < gmax.shape[1]) and ((j-1) >= 0) and ((i+1) < gmax.shape[0]) and ((i-1) >= 0):
- # 0 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 337.5 or phase[i][j] < 22.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 157.5 and phase[i][j] < 202.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i][j + 1] and det[i][j] >= det[i][j - 1]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- # 45 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 22.5 and phase[i][j] < 67.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 202.5 and phase[i][j] < 247.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i - 1][j + 1] and det[i][j] >= det[i + 1][j - 1]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- # 90 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 67.5 and phase[i][j] < 112.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 247.5 and phase[i][j] < 292.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i - 1][j] and det[i][j] >= det[i + 1][j]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- # 135 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 112.5 and phase[i][j] < 157.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 292.5 and phase[i][j] < 337.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i - 1][j - 1] and det[i][j] >= det[i + 1][j + 1]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- return gmax
Magnitudefield(dxx, dyy)函数计算梯度的幅度和相位,使用给定的 x 和 y 导数 (dxx 和 dyy)。幅度代表梯度的强度,相位代表梯度的方向;nonMaxSuppression(det, phase)函数根据梯度的相位 (phase) 对梯度幅度 (det) 执行非最大值抑制。它有助于在梯度方向上仅保留局部最大值,从而细化检测到的边缘;然后应用于derivation函数中去调控。
二阶泰勒展开式Hessian矩阵
- def HessianMatrix(self, dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy, threshold=0.5):
- """
- HessianMatrix = [dxx dxy]
- [dxy dyy]
- compute hessian:
- [dxx dxy] [00 01]
- ====>
- [dxy dyy] [10 11]
- """
- point=[]
- direction=[]
- value=[]
- for x in range(0, self.col):
- for y in range(0, self.row):
- if dxy[y,x] > 0:
- hessian = np.zeros((2,2))
- hessian[0,0] = dxx[y,x]
- hessian[0,1] = dxy[y,x]
- hessian[1,0] = dxy[y,x]
- hessian[1,1] = dyy[y,x]
- # 计算矩阵的特征值和特征向量
- _, eigenvalues, eigenvectors = cv2.eigen(hessian)
- if np.abs(eigenvalues[0,0]) >= np.abs(eigenvalues[1,0]):
- nx = eigenvectors[0,0]
- ny = eigenvectors[0,1]
- else:
- nx = eigenvectors[1,0]
- ny = eigenvectors[1,1]
- # Taylor展开式分子分母部分,需要避免为0的情况
- Taylor_numer = (dx[y, x] * nx + dy[y, x] * ny)
- Taylor_denom = dxx[y,x]*nx*nx + dyy[y,x]*ny*ny + 2*dxy[y,x]*nx*ny
- if Taylor_denom != 0:
- T = -(Taylor_numer/Taylor_denom)
- # Hessian矩阵最大特征值对应的特征向量对应于光条的法线方向
- if np.abs(T*nx) <= threshold and np.abs(T*ny) <= threshold:
- point.append((x,y))
- direction.append((nx,ny))
- value.append(np.abs(dxy[y,x]+dxy[y,x]))
- return point, direction, value
这一部分我定义在steger类下了
绘制中心线在背景与原图中
- def centerline(self,img, sigmaX, sigmaY, method="Scharr", usenonmax=True, color=(0, 0, 255)):
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = derivation(self.gray_image, sigmaX, sigmaY, method=method, nonmax=usenonmax)
- point, direction, value = self.HessianMatrix(dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy)
- for point in point:
- self.newimage[point[1], point[0]] = 255
- img[point[1], point[0], :] = color
- return img, self.newimage
代码以及效果展示
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- def _derivation_with_Filter(Gaussimg):
- dx = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1], [0], [-1]]))
- dy = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1, 0, -1]]))
- dxx = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1], [-2], [1]]))
- dyy = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1, -2, 1]]))
- dxy = cv2.filter2D(Gaussimg,-1, kernel=np.array([[1, -1], [-1, 1]]))
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def _derivation_with_Scharr(Gaussimg):
- dx = cv2.Scharr(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0)
- dy = cv2.Scharr(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1)
- dxx = cv2.Scharr(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0)
- dxy = cv2.Scharr(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1)
- dyy = cv2.Scharr(dy, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1)
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def _derivation_with_Sobel(Gaussimg):
- dx = cv2.Sobel(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
- dy = cv2.Sobel(Gaussimg, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
- dxx = cv2.Sobel(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
- dxy = cv2.Sobel(dx, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
- dyy = cv2.Sobel(dy, cv2.CV_32F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def Magnitudefield(dxx, dyy):
- """计算幅度和相位"""
- dxx = dxx.astype(float)
- dyy = dyy.astype(float)
- mag = cv2.magnitude(dxx, dyy)
- phase = mag*180./np.pi
- return mag, phase
- def derivation(gray_img, sigmaX, sigmaY, method="Scharr", nonmax=False):
- """
- 计算图像的一阶导数 dx 和 dy,以及二阶导数 dxx、dyy 和 dxy
- :param gray_img: 灰度图
- :param sigmaX: 在水平方向的高斯核标准差,用于激光线提取建议取1-2
- :param sigmaY: 在垂直方向上的高斯核标准差,用于激光线提取建议取1-2
- :param method:"Scharr" or "Filter" or "Sobel"
- 选择什么方式获取dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy,提供了卷积与Scharr和Sobel滤波器三种方式计算,
- Scharr滤波器通常会产生更平滑和准确的结果,所以这里默认使用"Scharr"方法,虽然
- "Sobel"运行比另外两种要慢,但在使用的时候,建议自己试试
- :return: dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- """
- Gaussimg = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_img, ksize=(0, 0), sigmaX=sigmaX, sigmaY=sigmaY)
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = _derivation_with_Scharr(Gaussimg)
- if method == "Filter":
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = _derivation_with_Filter(Gaussimg)
- elif method == "Sobel":
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy =_derivation_with_Sobel(Gaussimg)
- if nonmax:
- normal, phase = Magnitudefield(dxx, dyy)
- dxy = nonMaxSuppression(normal, phase)
- return dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy
- def nonMaxSuppression(det, phase):
- """非最大值抑制"""
- gmax = np.zeros(det.shape)
- # thin-out evry edge for angle = [0, 45, 90, 135]
- for i in range(gmax.shape[0]):
- for j in range(gmax.shape[1]):
- if phase[i][j] < 0:
- phase[i][j] += 360
- if ((j+1) < gmax.shape[1]) and ((j-1) >= 0) and ((i+1) < gmax.shape[0]) and ((i-1) >= 0):
- # 0 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 337.5 or phase[i][j] < 22.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 157.5 and phase[i][j] < 202.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i][j + 1] and det[i][j] >= det[i][j - 1]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- # 45 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 22.5 and phase[i][j] < 67.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 202.5 and phase[i][j] < 247.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i - 1][j + 1] and det[i][j] >= det[i + 1][j - 1]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- # 90 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 67.5 and phase[i][j] < 112.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 247.5 and phase[i][j] < 292.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i - 1][j] and det[i][j] >= det[i + 1][j]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- # 135 degrees
- if (phase[i][j] >= 112.5 and phase[i][j] < 157.5) or (phase[i][j] >= 292.5 and phase[i][j] < 337.5):
- if det[i][j] >= det[i - 1][j - 1] and det[i][j] >= det[i + 1][j + 1]:
- gmax[i][j] = det[i][j]
- return gmax
- class Steger():
- def __init__(self, gray_image):
- self.gray_image = gray_image
- self.row, self.col = self.gray_image.shape[:2]
- self.newimage = np.zeros((self.row, self.col), np.uint8)
- def centerline(self,img, sigmaX, sigmaY, method="Scharr", usenonmax=True, color=(0, 0, 255)):
- dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy = derivation(self.gray_image, sigmaX, sigmaY, method=method, nonmax=usenonmax)
- point, direction, value = self.HessianMatrix(dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy)
- for point in point:
- self.newimage[point[1], point[0]] = 255
- img[point[1], point[0], :] = color
- return img, self.newimage
- def HessianMatrix(self, dx, dy, dxx, dyy, dxy, threshold=0.5):
- """
- HessianMatrix = [dxx dxy]
- [dxy dyy]
- compute hessian:
- [dxx dxy] [00 01]
- ====>
- [dxy dyy] [10 11]
- """
- point=[]
- direction=[]
- value=[]
- for x in range(0, self.col):
- for y in range(0, self.row):
- if dxy[y,x] > 0:
- hessian = np.zeros((2,2))
- hessian[0,0] = dxx[y,x]
- hessian[0,1] = dxy[y,x]
- hessian[1,0] = dxy[y,x]
- hessian[1,1] = dyy[y,x]
- # 计算矩阵的特征值和特征向量
- _, eigenvalues, eigenvectors = cv2.eigen(hessian)
- if np.abs(eigenvalues[0,0]) >= np.abs(eigenvalues[1,0]):
- nx = eigenvectors[0,0]
- ny = eigenvectors[0,1]
- else:
- nx = eigenvectors[1,0]
- ny = eigenvectors[1,1]
- # Taylor展开式分子分母部分,需要避免为0的情况
- Taylor_numer = (dx[y, x] * nx + dy[y, x] * ny)
- Taylor_denom = dxx[y,x]*nx*nx + dyy[y,x]*ny*ny + 2*dxy[y,x]*nx*ny
- if Taylor_denom != 0:
- T = -(Taylor_numer/Taylor_denom)
- # Hessian矩阵最大特征值对应的特征向量对应于光条的法线方向
- if np.abs(T*nx) <= threshold and np.abs(T*ny) <= threshold:
- point.append((x,y))
- direction.append((nx,ny))
- value.append(np.abs(dxy[y,x]+dxy[y,x]))
- return point, direction, value
- def threshold(mask, std=127.5):
- """阈值法"""
- mask[mask > std] = 255
- mask[mask < std] = 0
- return mask.astype("uint8")
- def Bessel(xi: list):
- """贝塞尔公式"""
- xi_array = np.array(xi)
- x_average = np.mean(xi_array)
- squared_diff = (xi_array - x_average) ** 2
- variance = squared_diff / (len(xi)-1)
- bessel = np.sqrt(variance)
- return bessel
- def test_Steger():
- img = cv2.imread(r"D:\PythonProject\net\line\data\Image_20230215160728679.jpg")
- gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- gray_img = threshold(gray_img)
- steger = Steger(gray_img)
- img,newimage=steger.centerline(img,sigmaX=1.1,sigmaY=1.1,method="Sobel")
- # point, direction, value = HessianMatrix(gray_img, 1.1, 1.1, usenonmax=True)
- cv2.imwrite("result/main3.png", newimage)
- cv2.imwrite("result/main3_img.png", img)
- def test_derivation_methods_time():
- from pyzjr.dlearn import Runcodes
- img = cv2.imread(r"D:\PythonProject\net\line\data\Image_20230215160728411.jpg")
- img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
- gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- with Runcodes(description="Filter"):
- print(derivation(gray_img,1.1,1.1,"Filter"))
- # Filter: 0.01344 sec
- with Runcodes(description="Scharr"):
- print(derivation(gray_img, 1.1, 1.1))
- # Scharr: 0.00959 sec
- with Runcodes(description="Sobel"):
- print(derivation(gray_img, 1.1, 1.1,"Sobel"))
- # Sobel: 0.01820 sec
- if __name__=="__main__":
- # test_derivation_methods_time()
- test_Steger()


我目前也没有弄明白为什么会出现三条线,似乎是中心线和轮廓,后续如果有改进会再次的更新
-
相关阅读:
simulink基础学习笔记
Cadence23学习笔记(三)
模型训练中的常见超参数解析
【探索C语言中VS调试技巧】:提高效率和准确性
python求多叉树任意两点之间的距离
led台灯哪个牌子最好?2022最新的台灯牌子排名
计算机毕业设计之java+ssm家校通网站
角速度变化时四元数和旋转矩阵微分方程的证明
与创新者同行!Apache Doris 首届线下峰会即将开启,最新议程公开!|即刻预约
ubuntu14.04改静态ip
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62919535/article/details/133245716
