-
【C++面向对象】9. 重载
【 1. 基本原理 】
- C++ 允许在同一作用域中对某个函数和运算符指定多个定义,分别称为 函数重载 和 运算符重载。即 同名的函数或者运算符。
- 重载声明是指一个与之前已经在该作用域内声明过的函数或方法具有 相同名称的声明,但是它们的 参数列表和定义(实现)不相同 。
- 当我们调用一个重载函数或重载运算符时,编译器通过把使用的参数类型与定义中的参数类型进行比较,决定选用最合适的定义。这个选择最合适的重载函数或重载运算符的过程,称为 重载决策 。
【 2. 函数重载 】
- 在同一个作用域内,可以声明几个功能类似的同名函数,但是这些 同名函数的形式参数(指参数的个数、类型或者顺序)至少有1个必须不同。我们不能仅通过返回类型的不同来重载函数。
- 实例
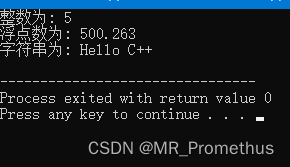
调用相同函数名但形参不同的类的成员函数,实现不同的输出功能。
#includeusing namespace std; class printData { public: void print(int i) { cout << "整数为: " << i << endl; } void print(double f) { cout << "浮点数为: " << f << endl; } void print(char c[]) { cout << "字符串为: " << c << endl; } }; int main(void) { printData pd; pd.print(5); // 输出整数 pd.print(500.263);// 输出浮点数 char c[] = "Hello C++"; pd.print(c);// 输出字符串 return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
【 3. 运算符重载 】
- 通过重定义或重载大部分 C++ 内置的运算符。我们就能使用 自定义类型的运算符。
- 重载的运算符是带有特殊名称的函数,大多数的重载运算符可被定义为普通的非成员函数(外部函数)或者被定义为 类的成员函数。
- 函数名是由 关键字 operator 和其后要重载的运算符符号构成的。与其他函数一样,重载运算符有一个返回类型和一个参数列表 。如下所示:KeywordType 是重载运算符的返回类型。
KeywordType operator++ (); // 一元前缀运算符的重载 KeywordType operator++ (int); // 一元后缀运算符的重载 KeywordType operator+ (const Box&); // 二元运算符的重载- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.1 可重载运算符 / 不可重载运算符
- 可重载的运算符列表
类型 名称 双目/二元 算术运算符 + 加
- 减
* 乘
/ 除
% 取模关系运算符 == 等于
!= 不等于
< 小于
> 大于
<= 小于等于
>= 大于等于逻辑运算符 || 逻辑或
&& 逻辑与
! 逻辑非单目/一元 运算符 + 正
- 负
* 指针
& 取地址自增自减运算符 ++ 自增
- - 自减位运算符 || 按位或
& 按位与
~ 按位取反
^ 按位异或
<< 左移
>> 右移赋值运算符 =
+=
-=
*=
/=
% =
&=
|=
^=
<<=
>>=空间申请与释放 new
delete
new[ ]
delete[ ]其他运算符 () 函数调用
-> 成员访问
, 逗号
[ ] 下标- 不可重载的运算符列表
名称 符号 成员访问运算符 . 成员指针访问运算符 .
->域运算符 :: 长度运算符 sizeof 条件运算符 ?: 预处理符号 # 3.2 一元负运算符 - 重载
- 实例
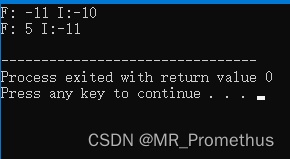
重载一元负运算符-,对对象的成员数据进行取反操作。
#includeusing namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; int inches; public: Distance() //构造函数-赋默认值 { feet = 0; inches = 0; } Distance(int f, int i) // 构造函数-赋自定义值 { feet = f; inches = i; } void displayDistance() // 成员函数-输出距离 { cout << "F: " << feet << " I:" << inches <<endl; } Distance operator- () // 重载负运算符- { feet = -feet; inches = -inches; return Distance(feet, inches); } }; int main() { Distance D1(11, 10), D2(-5, 11); -D1; // 取相反数 D1.displayDistance(); // 距离 D1 -D2; // 取相反数 D2.displayDistance(); // 距离 D2 return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
3.3 二元加运算符 + 重载
- 实例
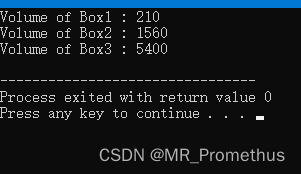
重载二元加运算符+,实现量对象的相加。使用类的成员函数演示运算符+重载的概念,对象作为参数进行传递,对象的属性使用 this 运算符进行访问。
#includeusing namespace std; class Box { private: double length; // 长度 double breadth; // 宽度 double height; // 高度 public: double getVolume(void) // 成员函数,获取体积 { return length * breadth * height; } void setLength( double len ) // 成员函数:设置长度 { length = len; } void setBreadth( double bre )// 成员函数:设置宽度 { breadth = bre; } void setHeight( double hei ) // 成员函数:设置高度 { height = hei; } Box operator+(const Box& b) // 重载 + 运算符,用于把两个 Box 对象相加 { Box box; box.length = this->length + b.length; box.breadth = this->breadth + b.breadth; box.height = this->height + b.height; return box; } }; int main( ) { Box Box1; // 定义对象 Box1 Box Box2; // 定义对象 Box2 Box Box3; // 定义对象 Box3 double volume = 0.0; // 把体积存储在该变量中 // Box1 赋值 Box1.setLength(6.0); Box1.setBreadth(7.0); Box1.setHeight(5.0); // Box2 赋值 Box2.setLength(12.0); Box2.setBreadth(13.0); Box2.setHeight(10.0); // Box1 的体积 volume = Box1.getVolume(); cout << "Volume of Box1 : " << volume <<endl; // Box2 的体积 volume = Box2.getVolume(); cout << "Volume of Box2 : " << volume <<endl; // 把两个对象相加,得到 Box3 Box3 = Box1 + Box2; // Box3 的体积 volume = Box3.getVolume(); cout << "Volume of Box3 : " << volume <<endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
3.4 小于运算符 < 重载
- 实例
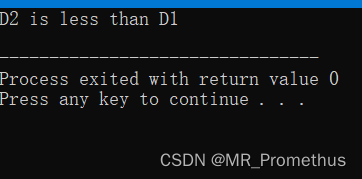
重载小于运算符 <,实现两对象成员数据的 比较。
#includeusing namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; int inches; public: Distance() // 构造函数-赋默认值 { feet = 0; inches = 0; } Distance(int f, int i) // 构造函数-赋自定义值 { feet = f; inches = i; } void displayDistance() // 成员函数-输出距离 { cout << "F: " << feet << " I:" << inches <<endl; } Distance operator- () // 重载负运算符- { feet = -feet; inches = -inches; return Distance(feet, inches); } bool operator <(const Distance& d) // 重载小于运算符< { if(feet < d.feet) { return true; } if(feet == d.feet && inches < d.inches) { return true; } return false; } }; int main() { Distance D1(11, 10), D2(5, 11); if( D1 < D2 ) { cout << "D1 is less than D2 " << endl; } else { cout << "D2 is less than D1 " << endl; } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
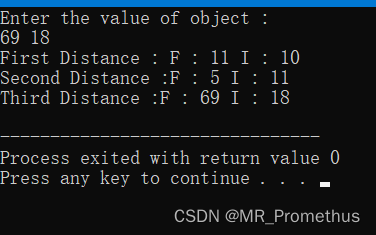
3.5 输入运算符>>和输出运算符<< 重载
- 实例
重载输入运算符>>和输出运算符<<,实现自定义的输入输出效果。
#includeusing namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; int inches; public: Distance() // 构造函数-赋默认值 { feet = 0; inches = 0; } Distance(int f, int i) // 构造函数-赋自定义值 { feet = f; inches = i; } friend ostream &operator<<( ostream &output, const Distance &D ) { output << "F : " << D.feet << " I : " << D.inches; return output; } friend istream &operator>>( istream &input, Distance &D ) { input >> D.feet >> D.inches; return input; } }; int main() { Distance D1(11, 10), D2(5, 11), D3; cout << "Enter the value of object : " << endl; cin >> D3; cout << "First Distance : " << D1 << endl; cout << "Second Distance :" << D2 << endl; cout << "Third Distance :" << D3 << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
3.6 自加运算符 ++ 重载
- 如下所示, 括号中插入int表示是后缀运算符 。
Time operator++ () // 重载前缀自加运算符 ++ Time operator++( int ) // 重载后缀自加运算符 ++- 1
- 2
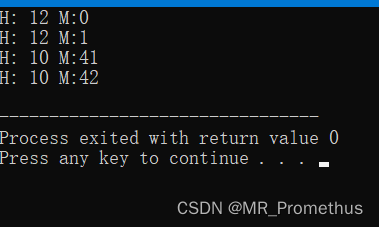
- 实例
对对象所包含的小时和时间进行前缀自加运算以及后缀自加运算。
#includeusing namespace std; class Time { private: int hours; int minutes; public: Time() // 构造函数-赋默认值 { hours = 0; minutes = 0; } Time(int h, int m) // 构造函数-赋自定义值 { hours = h; minutes = m; } void displayTime() // 成员函数-输出时间 { cout << "H: " << hours << " M:" << minutes <<endl; } Time operator++ () // 重载前缀自加运算符 ++ { // 返回运算后的值 ++minutes; if(minutes >= 60) { ++hours; minutes -= 60; } return Time(hours, minutes); // 返回运算后的对象 } Time operator++( int ) // 重载后缀自加运算符 ++ ,【括号中插入int表示后缀】 { // 返回运算前的原值 Time T(hours, minutes);// 将运算前的值保存在对象T ++minutes; if(minutes >= 60) { ++hours; minutes -= 60; } return T; // 返回运算前的对象 T } }; int main() { Time T1(11, 59), T2(10,40); ++T1; // T1 加 1 T1.displayTime(); // 显示 T1 ++T1; // T1 再加 1 T1.displayTime(); // 显示 T1 T2++; // T2 加 1 T2.displayTime(); // 显示 T2 T2++; // T2 再加 1 T2.displayTime(); // 显示 T2 return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
3.7 赋值运算符 = 重载
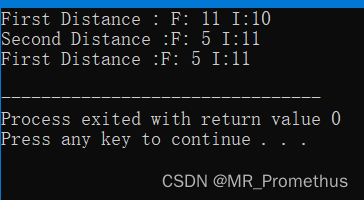
- 实例
重载赋值运算符 = ,将类的一个对象赋值给另一个对象。
#includeusing namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; int inches; public: Distance() // 构造函数-赋默认值 { feet = 0; inches = 0; } Distance(int f, int i) // 构造函数-赋自定义值 { feet = f; inches = i; } void displayDistance() //成员函数-输出距离 { cout << "F: " << feet << " I:" << inches << endl; } void operator=(const Distance &D ) // 重载赋值运算符 = { feet = D.feet; inches = D.inches; } }; int main() { Distance D1(11, 10), D2(5, 11); cout << "First Distance : "; D1.displayDistance(); cout << "Second Distance :"; D2.displayDistance(); D1 = D2; // 使用赋值运算符 cout << "First Distance :"; D1.displayDistance(); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
3.8 函数调用运算符 () 重载
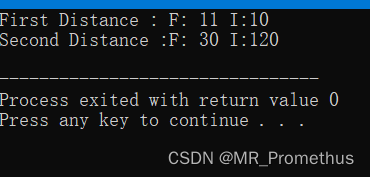
- 实例
重载函数调用运算符 (),实现对象成员数据的赋值。
#includeusing namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; int inches; public: Distance() // 构造函数-赋默认值 { feet = 0; inches = 0; } Distance(int f, int i) // 构造函数-赋自定义值 { feet = f; inches = i; } void displayDistance() //成员函数-输出距离 { cout << "F: " << feet << " I:" << inches << endl; } Distance operator()(int a, int b, int c) // 重载函数调用运算符() { Distance D; D.feet = a + c + 10; D.inches = b + c + 100 ; return D; } }; int main() { Distance D1(11, 10), D2; cout << "First Distance : "; D1.displayDistance(); D2 = D1(10, 10, 10); // 重载运算符 () cout << "Second Distance :"; D2.displayDistance(); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
3.9 下标运算符 [ ] 重载
- 实例
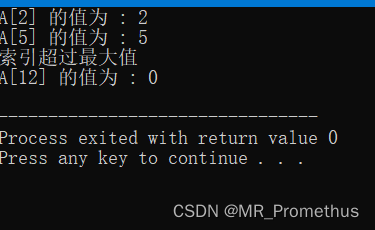
重载下标运算符 [ ],当下标 [ ] 中的索引超过范围时,返回第一个元素的值。
#includeusing namespace std; const int SIZE = 10; class safearay { private: int arr[SIZE]; public: safearay() // 构造函数-赋默认值 { register int i; for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { arr[i] = i; } } int& operator[](int i) // 重载下标运算符[] { if( i > SIZE ) { cout << "索引超过最大值" <<endl; return arr[0];// 返回第一个元素 } return arr[i]; } }; int main() { safearay A; cout << "A[2] 的值为 : " << A[2] <<endl; cout << "A[5] 的值为 : " << A[5] <<endl; cout << "A[12] 的值为 : " << A[12]<<endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
3.10 类成员访问运算符 -> 重载
- 类成员访问运算符( -> )可以被重载,但它较为麻烦。它被定义用于为一个类赋予"指针"行为。 运算符 -> 必须是一个成员函数。如果使用了 -> 运算符, 返回类型必须是指针或者是类的对象。
- 运算符 -> 通常与指针引用运算符 * 结合使用,用于实现"智能指针"的功能。这些指针是行为与正常指针相似的对象,唯一不同的是,当我们通过指针访问对象时,它们会执行其他的任务。比如,当指针销毁时,或者当指针指向另一个对象时,会自动删除对象。
- 间接引用运算符 -> 可被定义为一个一元后缀运算符。也就是说,给出一个类:
class Ptr { //... X * operator->(); };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
类 Ptr 的对象可用于访问类 X 的成员,使用方式与指针的用法十分相似。例如:
void f(Ptr p ) { p->m = 10 ; // (p.operator->())->m = 10 ,语句 p->m 被解释为 (p.operator->())->m。 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 实例
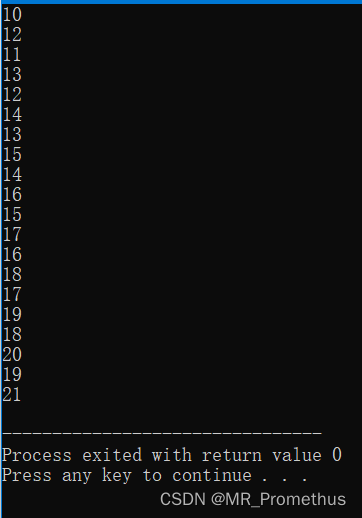
重载类成员访问运算符 ->
// 演示如何 #include#include using namespace std; // 假设一个实际的类 class Obj { static int i, j; public: void f() const { cout << i++ << endl; } void g() const { cout << j++ << endl; } }; // 静态成员定义 int Obj::i = 10; int Obj::j = 12; // 为上面的类实现一个容器 class ObjContainer { vector<Obj*> a; public: void add(Obj* obj) { a.push_back(obj); // 调用向量的标准方法 } friend class SmartPointer; }; // 实现智能指针,用于访问类 Obj 的成员 class SmartPointer { ObjContainer oc; int index; public: SmartPointer(ObjContainer& objc) { oc = objc; index = 0; } // 返回值表示列表结束 bool operator++() // 前缀版本 { if(index >= oc.a.size() - 1) return false; if(oc.a[++index] == 0) return false; return true; } bool operator++(int) // 后缀版本 { return operator++(); } Obj* operator->() const // 重载运算符 -> { if(!oc.a[index]) { cout << "Zero value"; return (Obj*)0; } return oc.a[index]; } }; int main() { const int sz = 10; Obj o[sz]; ObjContainer oc; for(int i = 0; i < sz; i++) { oc.add(&o[i]); } SmartPointer sp(oc); // 创建一个迭代器 do { sp->f(); // 智能指针调用 sp->g(); } while(sp++); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
3.11 实例
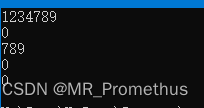
- 外部函数重载运算符、类的成员函数重载运算符。
//Str.h #pragma once #includeusing namespace std; class Str { char* data; public: Str() { data = new char[1],*data='\0';} //构造函数:默认值 Str(const char*); //构造函数:给定值 ~Str() { delete[] data; }; //析构函数 bool operator < (const Str&) const; // 类的成员函数重载运算符 < Str& operator = (const Str&); // 类的成员函数重载运算符 < Str& operator += (const Str&); // 类的成员函数重载运算符 < friend ostream& operator << ( ostream& a, const Str& b); // 类的友元函数重载运算符 << }; bool operator > (const Str& a, const Str& b); // 外部函数重载运算符 > bool operator == (const Str& a, const Str& b); // 外部函数重载运算符 == - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
//Str.cpp #include "Str.h" #include//构造函数:用户给定值 Str::Str(const char* a) { data = new char[strlen(a) + 1]; strcpy_s(data,strlen(a)+1,a); } //成员函数重载运算符:< bool Str::operator<(const Str& a)const { return strcmp(data,a.data) < 0; } //成员函数重载运算符:= Str& Str:: operator = (const Str& a) { if (this != &a) { delete[] data; data = new char[strlen(a.data) + 1]; strcpy_s(data,strlen(a.data)+1,a.data); } return *this; } //成员函数重载运算符:+= Str& Str:: operator += (const Str& a) { char* temp = new char[strlen(data) + strlen(a.data) + 1]; strcpy_s(temp,strlen(data)+1,data); strcat_s(temp, strlen(temp) + strlen(a.data)+1, a.data); delete[] data; data = temp; return *this; } //外部函数重载运算符:> bool operator >(const Str& a, const Str& b) { return (b<a); } //外部函数重载运算符:== bool operator ==(const Str& a, const Str& b) { return !(b < a) && !( a< b); } //外部函数重载运算符:<< std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& a, const Str& b) { a << b.data; return a; }; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
//Main.cpp #include"Str.h" #includeusing namespace std; bool operator > (const Str& a, const Str& b); bool operator == (const Str& a, const Str& b); int main(void) { Str a("1234"), b("789"); cout << (a += b) <<endl; cout << (a == b) << endl; cout << (a = b) << endl; cout << (a < b) << endl; cout << (a > b) << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
-
相关阅读:
Linux系统中如何使用tslib库实现触摸功能
2024最新群智能优化算法:人工原生动物优化器(Artificial Protozoa Optimizer ,APO))求解23个函数,MATLAB代码
LDAP服务器如何重启
vue 与 swiper结合使用时,swiper效果失效
[李宏毅深度学习作业] 作业1:ML2021Spring-hw1 COVID-19 Cases Prediction【以时间线为记录】
电脑重装系统后usbcleaner怎么格式化u盘
Tomcat服务器和Web开发介绍
RT-Thread UART设备
头歌平台云计算实验
NodeJs 实践之他说
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44431690/article/details/134048500
