-
二、W5100S/W5500+RP2040树莓派Pico<DHCP>
1 前言
随着云计算的推广和普及,越来越多的网络设备和服务需要连接到网络,这意味着需要更多的IP地址和其他网络配置信息。DHCP服务器可以动态地分配IP地址和其他配置信息,简化了网络配置管理,提高了网络设备的可用性和效率。
W5100S/W5500是一款集成全硬件 TCP/IP 协议栈的嵌入式以太网控制器,同时也是一颗工业级以太网控制芯片。本教程将介绍W5100S/W5500以太网DHCP应用的基本原理、使用步骤、应用实例以及注意事项,帮助读者更好地掌握这一技术。
2 简介
2 .1 什么是DHCP?
DHCP是指动态主机配置协议,是一种网络管理协议,用于将网际协议地址动态分配给网络上的任何设备或节点,以便它们可以使用IP进行通信。DHCP自动化并集中管理这些配置,而不是要求网络管理员手动为所有网络设备分配IP地址。DHCP可以在小型本地网络以及大型企业网络上实现。
2.2 为什么要使用DHCP?
在IP网络中,每个连接Internet的设备都需要分配唯一的IP地址。DHCP使网络管理员能从中心结点监控和分配IP地址。当某台计算机移到网络中的其它位置时,能自动收到新的IP地址。DHCP实现的自动化分配IP地址不仅降低了配置和部署设备的时间,同时也降低了发生配置错误的可能性。另外DHCP服务器可以管理多个网段的配置信息,当某个网段的配置发生变化时,管理员只需要更新DHCP服务器上的相关配置即可,实现了集中化管理。
总体来看,DHCP相比设置静态IP地址带来了如下优势:
- 准确的IP配置:IP地址配置参数必须准确,并且在处理“ 192.168.XXX.XXX”之类的输入时,很容易出错。另外印刷错误通常很难解决,使用DHCP服务器可以最大程度地降低这种风险。
- 减少IP地址冲突:每个连接的设备都必须有一个IP地址。但是,每个地址只能使用一次,重复的地址将导致无法连接一个或两个设备的冲突。当手动分配地址时,尤其是在存在大量仅定期连接的端点(例如移动设备)时,可能会发生这种情况。DHCP的使用可确保每个地址仅使用一次。
- IP地址管理的自动化:如果没有DHCP,网络管理员将需要手动分配和撤消地址。跟踪哪个设备具有什么地址可能是徒劳的,因为几乎无法理解设备何时需要访问网络以及何时需要离开网络。DHCP允许将其自动化和集中化,因此网络专业人员可以从一个位置管理所有位置。
- 高效的变更管理:DHCP的使用使更改地址,范围或端点变得非常简单。例如,组织可能希望将其IP寻址方案从一个范围更改为另一个范围。DHCP服务器配置有新信息,该信息将传播到新端点。同样,如果升级并更换了网络设备,则不需要网络配置。
2.3 DHCP工作原理
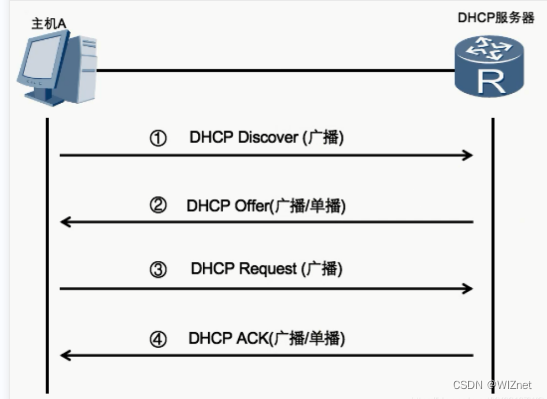
一般步骤:
- DHCP Client以广播的方式发出DHCP Discover报文,请求IP地址。
- DHCP Server向DHCP Client发送一个DHCP Offer报文,提供IP地址和其它网络设置。
- DHCP Client会向DHCP Server发出一个广播的DHCP Request报文,其中包含选中的 DHCP Server的IP地址和需要的IP地址。
- DHCP Server向DHCP Client响应一个DHCP ACK报文,正式下发IP地址及其它网络设置。此时,DHCP Client就可以使用这个IP地址了。
2.4 DHCP应用场景
DHCP的应用场景通常集中在需要动态分配IP地址的局域网环境中。例如,在大型的办公环境或者学校中,由于有大量的网络设备需要连接到网络,手动为每个设备分配和管理IP地址会非常麻烦,而且容易出错。使用DHCP可以集中管理IP地址的分配,提高网络管理员的工作效率,减少错误的发生。
3 WIZnet以太网芯片
WIZnet 主流硬件协议栈以太网芯片参数对比
Model Embedded Core Host I/F TX/RX Buffer HW Socket Network Performance W5100S TCP/IPv4, MAC & PHY 8bit BUS, SPI 16KB 4 Max.25Mbps W6100 TCP/IPv4/IPv6, MAC & PHY 8bit BUS, Fast SPI 32KB 8 Max.25Mbps W5500 TCP/IPv4, MAC & PHY Fast SPI 32KB 8 Max 15Mbps - W5100S/W6100 支持 8bit数据总线接口,网络传输速度会优于W5500。
- W6100 支持IPV6,与W5100S 硬件兼容,若已使用W5100S的用户需要支持IPv6,可以Pin to Pin兼容。
- W5500 拥有比 W5100S更多的 Socket数量以及发送与接收缓存。
4 DHCP网络设置示例概述以及使用
4.1 流程图
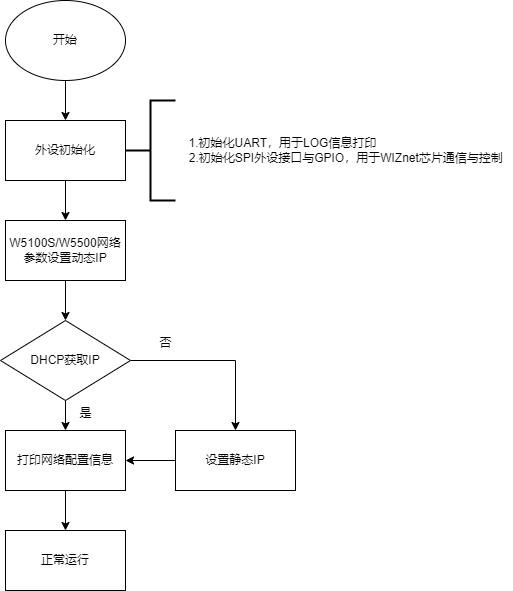
程序的运行框图如下所示:
4.2 准备工作核心
软件
- Visual Studio Code
- WIZnet UartTool
硬件
- W5100SIO模块 + RP2040 树莓派Pico开发板 或者 WIZnet W5100S-EVB-Pico开发板
- Micro USB 接口的数据线
- TTL 转 USB
- 网线
4.3 连接方式
-
通过数据线连接PC的USB口(主要用于烧录程序,也可以虚拟出串口使用)
-
通过TTL串口转USB,连接UART0 的默认引脚:
- RP2040 GPIO0(UART0 TX) <----> USB_TTL_RX
- RP2040 GPIO1(UART0 RX) <----> USB_TTL_TX
-
使用模块连接RP2040 进行接线时
- RP2040 GPIO16 <----> W5100S MISO
- RP2040 GPIO17 <----> W5100S CS
- RP2040 GPIO18 <----> W5100S SCK
- RP2040 GPIO19 <----> W5100S MOSI
- RP2040 GPIO20 <----> W5100S RST
-
通过PC和设备都通过网线连接路由器LAN口
4.4 主要代码概述
我们使用的是WIZnet官方的ioLibrary_Driver库。该库支持的协议丰富,操作简单,芯片在硬件上集成了TCP/IP协议栈,该库又封装好了TCP/IP层之上的协议,我们只需简单调用相应函数即可完成协议的应用。
第一步:dhcp_client.c文件中加入对应的.h文件。
第二步:定义DHCP配置需要的宏。
第三步:网络信息的配置,开启DHCP模式。
第四步:编写定时器回调处理函数,用于 DHCP 1s滴答定时器处理函数。
第五步:主函数先是对串口和SPI的初始化,然后写入W5100S的网络配置参数,初始化DHCP后主循环开始DHCP获取IP,获取到就打印获取到的IP,获取次数超过最大获取次数时就使用静态IP。
#include#include "pico/stdlib.h" #include "pico/binary_info.h" #include "hardware/spi.h" #include "wizchip_conf.h" #include "bsp_spi.h" #include "dhcp.h" #define ETHERNET_BUF_MAX_SIZE (1024 * 2) #define SOCKET_DHCP 0 #define DHCP_RETRY_COUNT 5 wiz_NetInfo net_info = { .mac = {0x00, 0x08, 0xdc, 0x16, 0xed, 0x2e}, // Define MAC variables .ip = {192, 168, 1, 10}, // Define IP variables .sn = {255, 255, 255, 0}, // Define subnet variables .gw = {192, 168, 1, 1}, // Define gateway variables .dns = {8, 8, 8, 8}, // Define DNS variables .dhcp = NETINFO_DHCP}; // Define the DNCP mode static uint8_t dhcp_get_ip_flag = 0; // Define the DHCP acquisition flag static uint8_t ethernet_buf[ETHERNET_BUF_MAX_SIZE] = { 0, }; /* @brief Callback processing after triggering the timer. @param Timer struct. @return True. */ bool repeating_timer_callback(struct repeating_timer *t); int main() { wiz_NetInfo get_info; int dhcp_state = 0; int count = 0; struct repeating_timer timer; // Define the timer structure /*mcu init*/ stdio_init_all(); // Initialize the main control peripheral wizchip_initialize(); // spi initialization /*wiznet chip init*/ wizchip_setnetinfo(&net_info); // Write configuration information /*dhcp init*/ add_repeating_timer_ms(1000, repeating_timer_callback, NULL, &timer); // Add DHCP 1s Tick Timer handler DHCP_init(SOCKET_DHCP, ethernet_buf); // DHCP initialization printf("wiznet chip dhcp example start.\r\n"); while (true) { dhcp_state = DHCP_run(); // Do the DHCP client switch (dhcp_state) { case DHCP_IP_LEASED: // DHCP resolves the domain name successfully if (dhcp_get_ip_flag == 0) { dhcp_get_ip_flag = 1; getSHAR(get_info.mac); getIPfromDHCP(get_info.ip); getGWfromDHCP(get_info.gw); getSNfromDHCP(get_info.sn); getDNSfromDHCP(get_info.dns); get_info.dhcp = NETINFO_DHCP; /* Network initialize */ network_initialize(get_info); // apply from DHCP print_network_information(&get_info); // Read back the configuration information and print it printf(" DHCP leased time : %ld seconds\n", getDHCPLeasetime()); } break; case DHCP_FAILED: count++; if (count <= DHCP_RETRY_COUNT) // If the number of times is less than or equal to the maximum number of times, try again { printf(" DHCP timeout occurred and retry %d \r\n", count); } else if (count > DHCP_RETRY_COUNT) // If the number of times is greater than DHCP fails { printf(" DHCP failed \r\n"); DHCP_stop(); // Stop processing DHCP protocol net_info.dhcp = NETINFO_STATIC; wizchip_setnetinfo(&net_info); // Write configuration information print_network_information(&get_info); // Read back the configuration information and print it } } } } bool repeating_timer_callback(struct repeating_timer *t) { DHCP_time_handler(); // DHCP 1s Tick Timer handler return true; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
4.5 结果演示
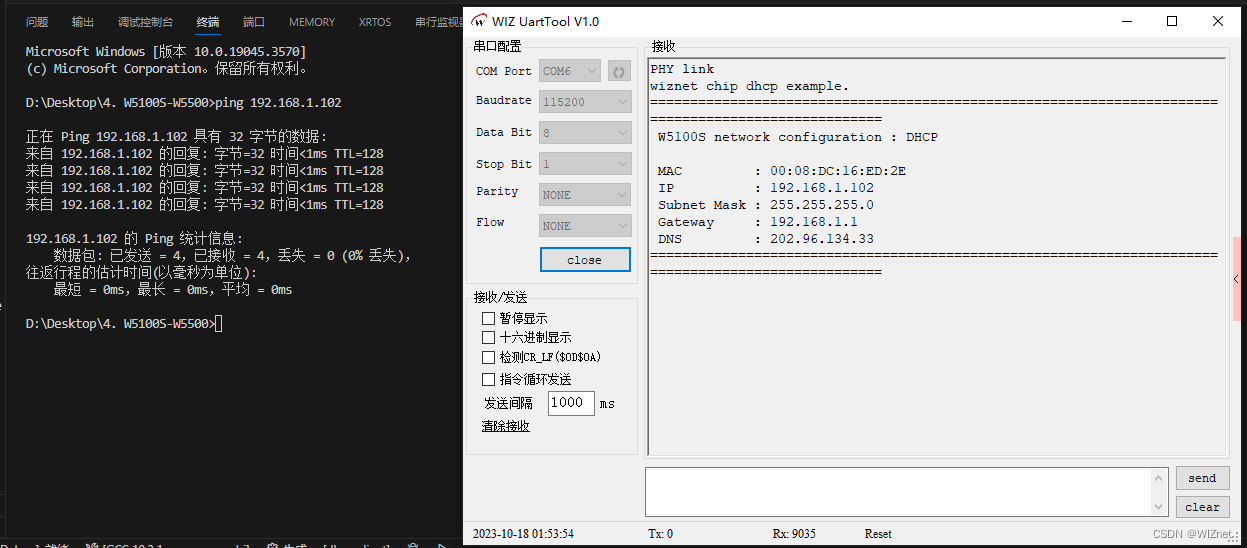
1.打开WIZ UartTool,填入参数:选择串口对应的COM Port,波特率115200,8位数据位,1位停止位,无校验位,无流控,填完参数后点击open打开。
2.打开串口后,按下复位键可以看到串口打印DHCP获取到的信息,其中IP为192.168.1.138。
3.通过PC终端PING获取到的IP,发现可以PING通,所以DHCP成功。
5 注意事项
- 要获取到动态IP,必需将网络结构体配置中dhcp的值改为 NETINFO_DHCP,这样才能跑DHCP模式。
- 如果想用WIZnet的W5500来实现本章的示例,我们只需修改两个地方即可:
(1)在library/ioLibrary_Driver/Ethernet/下找到wizchip_conf.h这个头文件,将_WIZCHIP_ 宏定义修改为W5500。
(2)在library下找到CMakeLists.txt文件,将COMPILE_SEL设置为ON即可,OFF为W5100S,ON为W5500。
6 相关链接
想了解更多,评论留言哦!
-
相关阅读:
第五篇 《随机点名答题系统》——抽点答题详解(类抽奖系统、在线答题系统、线上答题系统、在线点名系统、线上点名系统、在线考试系统、线上考试系统)
CentOS 7上生成HTTPS证书
jmeter测试场景设计
我的十年编程路 2015年篇
服务器硬件监控解决方案,提升服务器稳定性
Pytest简介及jenkins集成
PyTorch DataLoader整理函数详解【collate_fn】
LeetCode每日一题(1937. Maximum Number of Points with Cost)
本地部署 Qwen-14B-Chat
使用C#开发163邮件发送功能
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/WIZnet2012/article/details/134043644
