-
51单片机KeyWard
eg1: 单片机键盘的分类
- 键盘分为编码键盘和非编码键盘,键盘上闭合键的识别由专用的硬件编码器实现,并产生键编码号或键值得称为编码键盘,如计算机键盘,而靠软件来识别的称为非编码键盘,在单片机组成的各种系统中使用最多的就是非编码键盘,也有使用到编码键盘的,非编码键盘又称为独立式和矩阵式键盘。
单片机键盘根据按键的结构和工作原理的不同,可以分为以下几类:
- 矩阵键盘(Matrix Keyboard):
- 矩阵键盘是最常见的单片机键盘之一。
- 它使用一种矩阵排列的按键结构,通过行和列的交叉点来确定按下的按键。
- 一般通过行列扫描的方式来检测按键的按下和释放。
- 独立按键(Individual Key):
- 独立按键是指每一个按键都有独立的引脚连接到单片机。
- 每个按键都使用一个独立的IO引脚,通过读取引脚的电平状态来检测按键的按下和释放。
- 独立按键一般用于需要较少按键的应用场景。
- 脉冲编码开关(Encoder Switch):
- 脉冲编码开关也被称为旋转编码开关,用于检测旋转操作。
- 它通常由两个触点组成,通过检测两个触点的状态变化来确定旋转方向和步数。
- 脉冲编码开关常用于旋转编码器、音量调节器等应用场景。
- 矩阵键盘和独立按键结合:
- 在某些情况下,矩阵键盘和独立按键可能会结合使用。
- 例如,一些常用的功能按键使用独立按键,而数字键盘使用矩阵键盘的方式来连接到单片机。
单片机键盘电路设计图
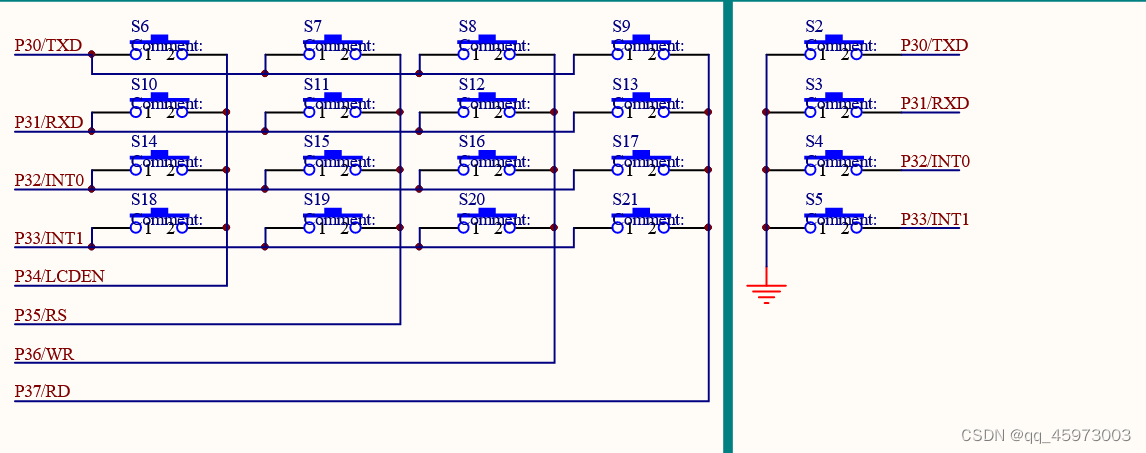 test1:点击第一个按钮时点亮第一个led管
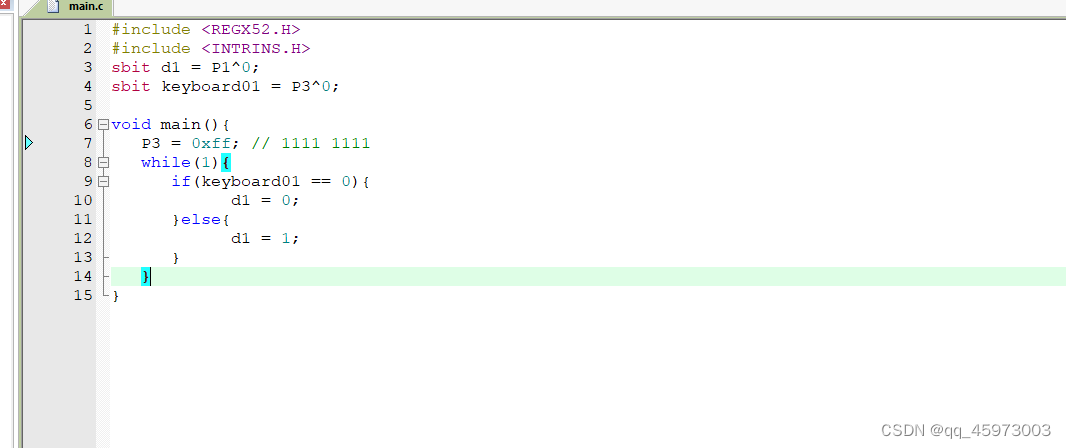
test1:点击第一个按钮时点亮第一个led管#include#include sbit d1 = P1^0; sbit keyboard01 = P3^0; void main(){ P3 = 0xff; // 1111 1111 while(1){ if(keyboard01 == 0){ d1 = 0; }else{ d1 = 1; } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
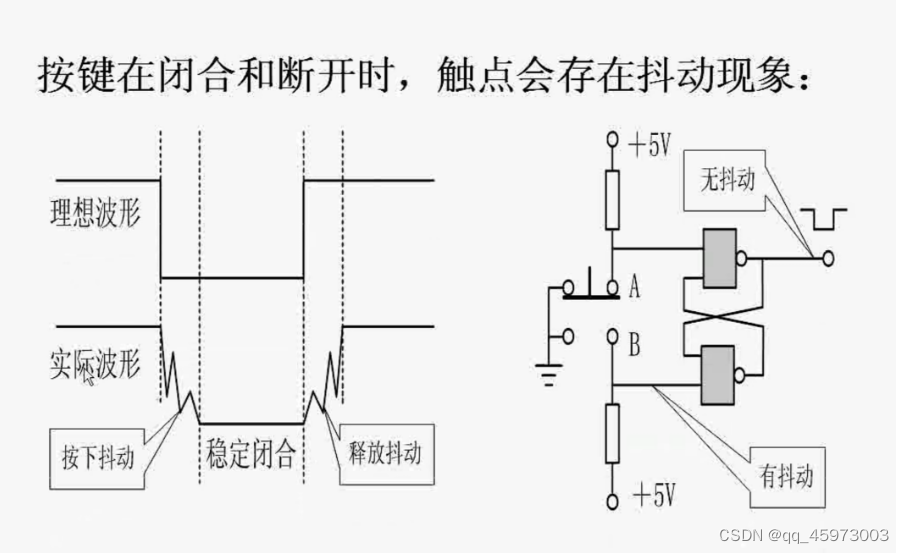
 单片机的按键在闭合和断开时,触点会出现抖动现象
单片机的按键在闭合和断开时,触点会出现抖动现象
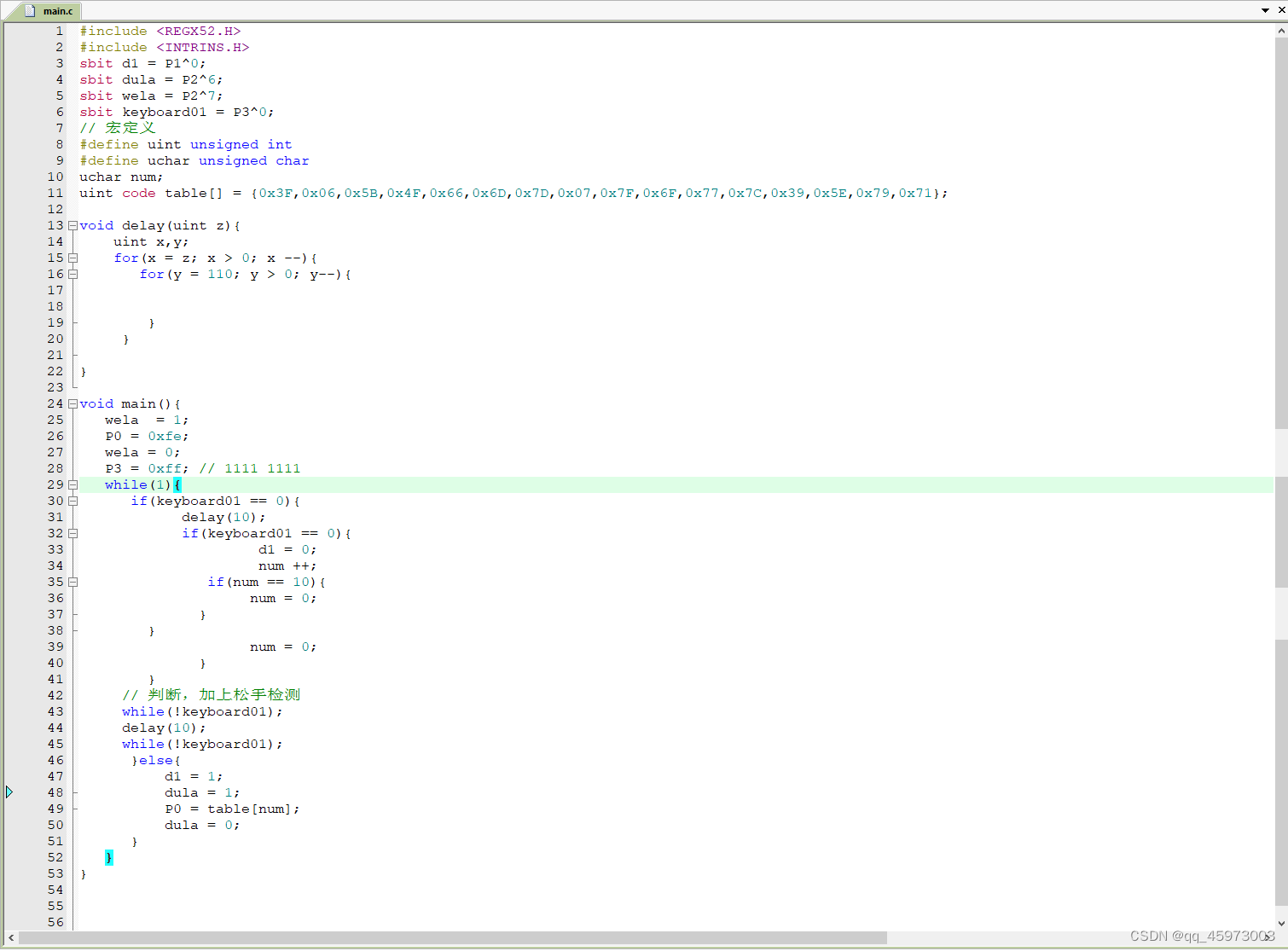
 独立键盘的检测与消抖
独立键盘的检测与消抖- eg2: 点击独立按键的同时led亮灭同时晶体管统计次数当数字为9时归0
#include#include sbit d1 = P1^0; sbit dula = P2^6; sbit wela = P2^7; sbit keyboard01 = P3^0; // 宏定义 #define uint unsigned int #define uchar unsigned char uchar num; uint code table[] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7C,0x39,0x5E,0x79,0x71}; void delay(uint z){ uint x,y; for(x = z; x > 0; x --){ for(y = 110; y > 0; y--){ } } } void main(){ wela = 1; P0 = 0xfe; wela = 0; P3 = 0xff; // 1111 1111 while(1){ if(keyboard01 == 0){ delay(10); if(keyboard01 == 0){ d1 = 0; num ++; if(num == 10){ num = 0; } } // 判断,加上松手检测 while(!keyboard01); delay(10); while(!keyboard01); }else{ d1 = 1; dula = 1; P0 = table[num]; dula = 0; } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
 eg3:矩阵键盘
eg3:矩阵键盘
 以下的矩阵表示第二行的第一个按键按下去其它的16进制依次类推
以下的矩阵表示第二行的第一个按键按下去其它的16进制依次类推
10110111 − − − − > 11101101 = = 0 x e d 10110111 ----> 1110 1101 == 0xed 10110111−−−−>11101101==0xed eg4:51片机矩阵代码实现每按一个按键就会显示一个不同的数
eg4:51片机矩阵代码实现每按一个按键就会显示一个不同的数#include#include sbit d1 = P1^0; sbit dula = P2^6; sbit wela = P2^7; sbit keyboard01 = P3^0; // 宏定义 #define uint unsigned int #define uchar unsigned char uchar num,temp,num1; uint code table[] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7C,0x39,0x5E,0x79,0x71}; // 函数声明 uchar keyboardScan(); void delay(uint z){ uint x,y; for(x = z; x > 0; x --){ for(y = 110; y > 0; y--){ } } } void main(){ // 让所有的数码管都显示 num = 17; dula = 1; P0 = 0; dula = 0; wela = 1; P0 = 0xc0; wela = 0; //0xfe 的值是0111 1111 ---> 1111 1110 while(1){ num1 = keyboardScan(); dula = 1; P0 = table[num1-1]; dula = 0; } } // 键盘扫描函数 uchar keyboardScan(){ // 检测键盘 P3 = 0xfe; temp = P3; // 1111 1110 & 1111 0000 == 1111 0000 // 0xf0 表示的值是0000 1111---> 1111 0000 temp = temp&0xf0; // c语言中的switchcase语句 while(temp != 0xf0){ delay(5); temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; switch(temp){ case 0xee: // 0111 --> 1110 num = 1; break; case 0xde: //1011 --> 1101 num = 2; break; case 0xbe: // 1011 num = 3; break; case 0x7e: // 0111 num = 4; break; } while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; } // 函数的参数可以作为子函数进行调用 /* dula = 1; 0 = table[num -1]; dula = 0; */ } } // 检测第二行------------------------------------------------------ // 检测键盘 P3 = 0xfd; temp = P3; // 1111 1110 & 1111 0000 == 1111 0000 // 0xf0 表示的值是0000 1111---> 1111 0000 temp = temp&0xf0; // c语言中的switchcase语句 while(temp != 0xf0){ delay(5); temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; switch(temp){ case 0xed: // 0111 --> 1110 num = 5; break; case 0xdd: //1011 --> 1101 num = 6; break; case 0xbd: // 1011 num = 7; break; case 0x7d: // 0111 num = 8; break; } while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; } // 函数的参数可以作为子函数进行调用 /* dula = 1; 0 = table[num -1]; dula = 0; */ } } // 检测第三行-------------------------------------------|---------------|-----------------|----------------| // 检测键盘 P3 = 0xfb; temp = P3; // 1111 1110 & 1111 0000 == 1111 0000 // 0xf0 表示的值是0000 1111---> 1111 0000 temp = temp&0xf0; // c语言中的switchcase语句 while(temp != 0xf0){ delay(5); temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; switch(temp){ case 0xeb: // 0111 --> 1110 num = 9; break; case 0xdb: //1011 --> 1101 num = 10; break; case 0xbb: // 1011 num = 11; break; case 0x7b: // 0111 num = 12; break; } while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; } // 函数的参数可以作为子函数进行调用 /* dula = 1; 0 = table[num -1]; dula = 0; */ } } // 检测第四行--------|---------------|--------------------|---------------------------|-----------------------|------------- // 检测键盘 P3 = 0xf7; temp = P3; // 1111 1110 & 1111 0000 == 1111 0000 // 0xf0 表示的值是0000 1111---> 1111 0000 temp = temp&0xf0; // c语言中的switchcase语句 while(temp != 0xf0){ delay(5); temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; switch(temp){ case 0xe7: // 0111 --> 1110 num = 13; break; case 0xd7: //1011 --> 1101 num = 14; break; case 0xb7: // 1011 num = 15; break; case 0x77: // 0111 num = 16; break; } // 松手检测代码 while(temp != 0xf0){ temp = P3; temp = temp&0xf0; } // 函数的参数可以作为子函数进行调用 /* dula = 1; 0 = table[num -1]; dula = 0; */ } } return num; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
代码的截图----------->需要后期优化
 51单片机点击某个keyboard后的显示结果
51单片机点击某个keyboard后的显示结果

-
相关阅读:
非零基础自学Golang 2 开发环境 2.2 配置GOPATH
卡尔曼滤波与融合算法
【深度学习实验】注意力机制(四):点积注意力与缩放点积注意力之比较
国学---佛系算吉凶~
【第八期】Apache DolphinScheduler 每周 FAQ 集锦
前端网页开发实例入门
JSP 人力资源管理系统myeclipse开发mysql数据库BS模式java编程网页设计
雷达传感器感应模块,人体存在感控方案,助力产品智能化触发联动
【IT行业就业前景广阔:探讨热门方向与就业机会】
三位数中哪些是水仙花数(基础作业
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45973003/article/details/133979027
