-
LVGL_文件系统FS
LVGL_文件系统FS
前言:
LVG 内置支持以下文件系统:
1、FATFS
2、STDIO (Linux 和 Windows 都可以使用的 C 标准函数接口,比如:fopen, fread…)
3、POSIX (Linux 和 Windows 都可以使用的 POSIX 函数接口,比如:open, read…)
4、WIN32 (Windows 使用 Win32 API 函数接口比如:CreateFileA, ReadFile…)1、在lv_conf.h中配置
/*--------------------- * 3rd party libraries *--------------------*/ /*File system interfaces for common APIs */ /*API for fopen, fread, etc*/ #define LV_USE_FS_STDIO 0 #if LV_USE_FS_STDIO #define LV_FS_STDIO_LETTER '\0' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/ #define LV_FS_STDIO_PATH "" /*Set the working directory. File/directory paths will be appended to it.*/ #define LV_FS_STDIO_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/ #endif /*API for open, read, etc*/ #define LV_USE_FS_POSIX 0 #if LV_USE_FS_POSIX #define LV_FS_POSIX_LETTER '\0' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/ #define LV_FS_POSIX_PATH "" /*Set the working directory. File/directory paths will be appended to it.*/ #define LV_FS_POSIX_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/ #endif /*API for CreateFile, ReadFile, etc*/ #define LV_USE_FS_WIN32 1 #if LV_USE_FS_WIN32 #define LV_FS_WIN32_LETTER 'E' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/ #define LV_FS_WIN32_PATH "" /*Set the working directory. File/directory paths will be appended to it.*/ #define LV_FS_WIN32_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/ #endif /*API for FATFS (needs to be added separately). Uses f_open, f_read, etc*/ #define LV_USE_FS_FATFS 0 #if LV_USE_FS_FATFS #define LV_FS_FATFS_LETTER '\0' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/ #define LV_FS_FATFS_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/ #endif- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
2、使用示例
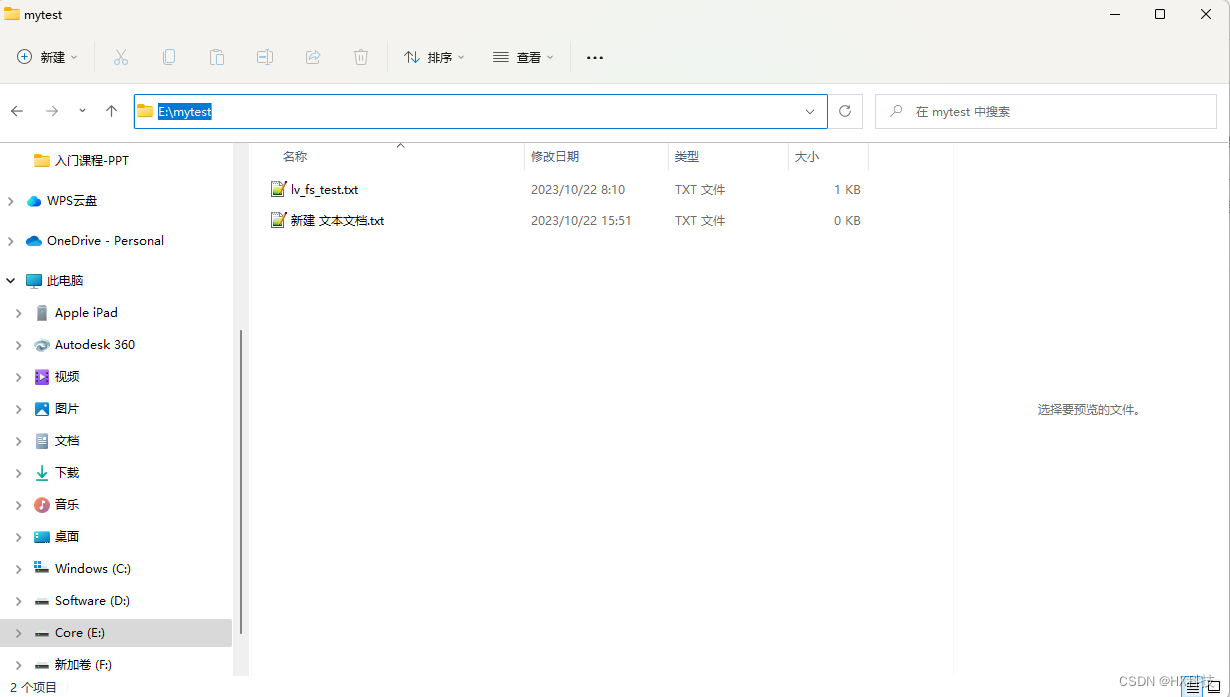
在电脑的E盘中新建测试文件
// 要打开的文件 #define FILE_NAME "E:/mytest/lv_fs_test.txt" // 要读取的目录 #define DIR_PATH "E:/mytest/" /* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取文件 */ static void lv_fs_read_dir(char * fn); /* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取目录内容 */ static void lv_fs_read_file(char * path); void lv_100ask_demo_course_6_1_1(void) { // 读取文件 lv_fs_read_file(FILE_NAME); // 读取目录内容 lv_fs_read_dir(DIR_PATH); } /* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取文件 */ static void lv_fs_read_file(char * fn) { lv_fs_file_t f; lv_fs_res_t res; // 打开文件有两个模式: LV_FS_MODE_RD(只读) 和 LV_FS_MODE_WR(写) res = lv_fs_open(&f, fn, LV_FS_MODE_RD); // 如果一切正常会返回 LV_FS_RES_OK ,其他错误代码请看 lv_fs.h 中的 lv_fs_res_t 定义 if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK) { LV_LOG_USER("Open error! Error code: %d", res); return; } /* 每次实际读取到的数据大小(byte) */ uint32_t read_num; /* 数据缓冲区 */ uint8_t buf[8]; /* 读取整个文件并打印内容 */ while (1) { res = lv_fs_read(&f, buf, 8, &read_num); if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK) { LV_LOG_USER("Read error! Error code: %d", res); break; } /* 将读取到数据打印出来 */ printf("%s", buf); if (read_num != 8) break; } lv_fs_close(&f); } /* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取目录内容 */ static void lv_fs_read_dir(char * path) { lv_fs_dir_t dir; lv_fs_res_t res; res = lv_fs_dir_open(&dir, path); if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK){ LV_LOG_USER("Open DIR error! Error code: %d", res); return; } char fn[256]; // 缓冲区 while(1) { res = lv_fs_dir_read(&dir, fn); if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK) { LV_LOG_USER("Read DIR error! Error code: %d", res); break; } /* 如果没有更多文件可以读取时 fn 就为空 */ if(strlen(fn) == 0) { LV_LOG_USER("Fn is empty, if not more files to read."); break; } printf("%s\n", fn); } lv_fs_dir_close(&dir); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
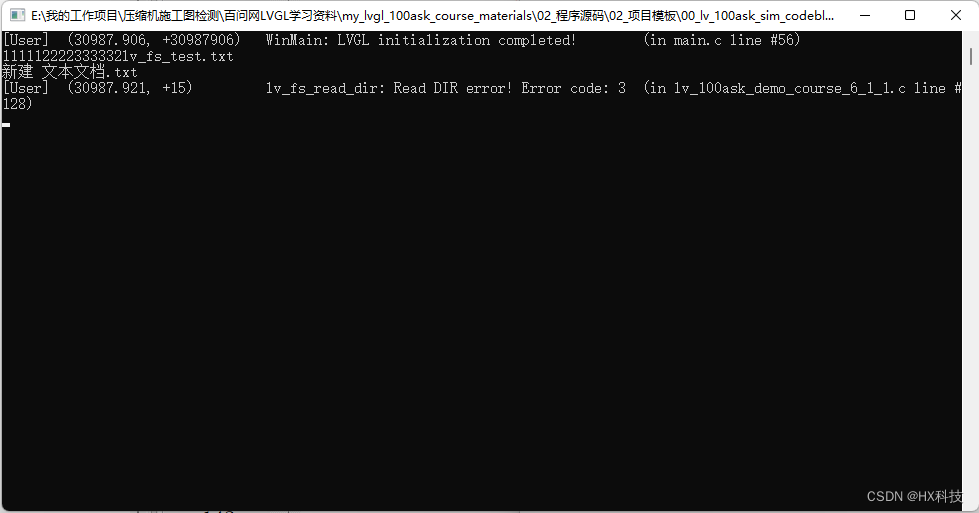
运行上述代码结果如下(打印出文件内容,文件夹的内容)
-
相关阅读:
16. Thymeleaf教程(10分钟入门)
【java毕业设计】 基于Spring Boot+mysql的社区团购系统设计与实现(程序源码)-社区团购系统
逆功率保护装置
基于Python+Nodejs+MONGODB的电影推荐网站
【JavaEE基础与高级 第61章】Java中的注解和元注解的介紹使用、注解解析
docker常用命令大全
C++Prime Plus(7)
WebService总结
Windows下使用MySQL二进制包安装MySQL5.7
【在线编程-Python篇】Python入门 04 列表(上)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_50183638/article/details/133969124