-
订单30分钟自动关闭的五种解决方案
1 前言
在开发中,往往会遇到一些关于延时任务的需求。例如
- 生成订单30分钟未支付,则自动取消
- 生成订单60秒后,给用户发短信
对上述的任务,我们给一个专业的名字来形容,那就是延时任务 。那么这里就会产生一个问题,这个延时任务 和定时任务 的区别究竟在哪里呢?一共有如下几点区别
- 定时任务有明确的触发时间,延时任务没有
- 定时任务有执行周期,而延时任务在某事件触发后一段时间内执行,没有执行周期
- 定时任务一般执行的是批处理操作是多个任务,而延时任务一般是单个任务
下面,我们以判断订单是否超时为例,进行方案分析
2 方案一:数据库轮询
2.1 思路
该方案通常是在小型项目中使用,即通过一个线程定时的去扫描数据库,通过订单时间来判断是否有超时的订单,然后进行update或delete等操作
2.2 实现
博主当年早期是用quartz来实现的,简单介绍一下 maven项目引入一个依赖如下所示
<dependency> <groupId>org.quartz-schedulergroupId> <artifactId>quartzartifactId> <version>2.2.2version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
调用Demo类MyJob如下所示
package com.rjzheng.delay1; import org.quartz.JobBuilder; import org.quartz.JobDetail; import org.quartz.Scheduler; import org.quartz.SchedulerException; import org.quartz.SchedulerFactory; import org.quartz.SimpleScheduleBuilder; import org.quartz.Trigger; import org.quartz.TriggerBuilder; import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory; import org.quartz.Job; import org.quartz.JobExecutionContext; import org.quartz.JobExecutionException; public class MyJob implements Job { public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException { System.out.println("要去数据库扫描啦。。。"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建任务 JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(MyJob.class) .withIdentity("job1", "group1").build(); // 创建触发器 每3秒钟执行一次 Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder .newTrigger() .withIdentity("trigger1", "group3") .withSchedule( SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule() .withIntervalInSeconds(3).repeatForever()) .build(); Scheduler scheduler = new StdSchedulerFactory().getScheduler(); // 将任务及其触发器放入调度器 scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail, trigger); // 调度器开始调度任务 scheduler.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
运行代码,可发现每隔3秒,输出如下
要去数据库扫描啦。。。- 1
2.3 优缺点
优点:
- 简单易行,支持集群操作
缺点:
- 对服务器内存消耗大
- 存在延迟,比如你每隔3分钟扫描一次,那最坏的延迟时间就是3分钟
- 假设你的订单有几千万条,每隔几分钟这样扫描一次,数据库损耗极大
3 方案二:JDK的延迟队列
3.1 思路
该方案是利用JDK自带的DelayQueue来实现,这是一个无界阻塞队列,该队列只有在延迟期满的时候才能从中获取元素,放入DelayQueue中的对象,是必须实现Delayed接口的。
DelayedQueue实现工作流程如下图所示
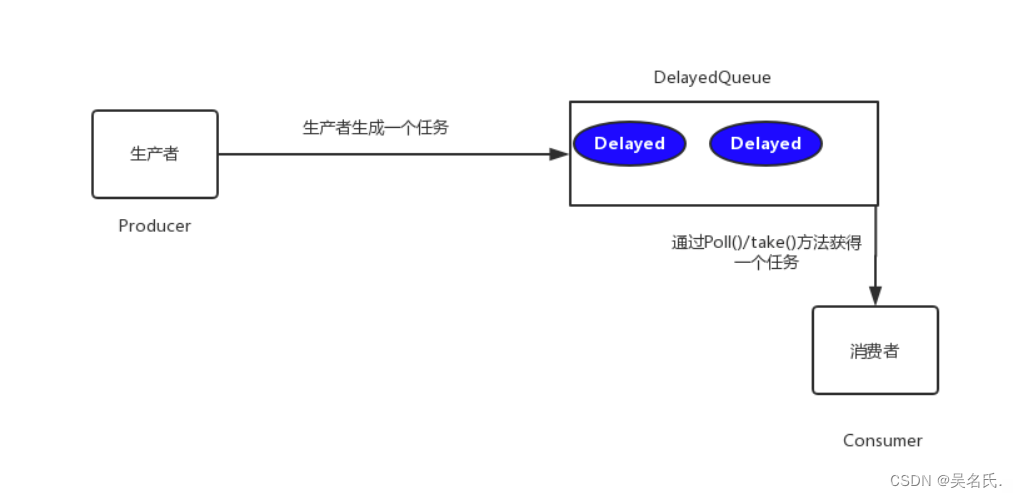
其中- poll():获取并移除队列的超时元素,没有则返回空
- take():获取并移除队列的超时元素,如果没有则wait当前线程,直到有元素满足超时条件,返回结果。
3.2 实现
定义一个类OrderDelay实现Delayed,代码如下
package com.rjzheng.delay2; import java.util.concurrent.Delayed; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class OrderDelay implements Delayed { private String orderId; private long timeout; OrderDelay(String orderId, long timeout) { this.orderId = orderId; this.timeout = timeout + System.nanoTime(); } public int compareTo(Delayed other) { if (other == this) return 0; OrderDelay t = (OrderDelay) other; long d = (getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) - t .getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)); return (d == 0) ? 0 : ((d < 0) ? -1 : 1); } // 返回距离你自定义的超时时间还有多少 public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { return unit.convert(timeout - System.nanoTime(), TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS); } void print() { System.out.println(orderId+"编号的订单要删除啦。。。。"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
运行的测试Demo为,我们设定延迟时间为3秒
package com.rjzheng.delay2; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class DelayQueueDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("00000001"); list.add("00000002"); list.add("00000003"); list.add("00000004"); list.add("00000005"); DelayQueue<OrderDelay> queue = new DelayQueue<OrderDelay>(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0;i<5;i++){ //延迟三秒取出 queue.put(new OrderDelay(list.get(i), TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.convert(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS))); try { queue.take().print(); System.out.println("After " + (System.currentTimeMillis()-start) + " MilliSeconds"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
输出如下
00000001编号的订单要删除啦。。。。 After 3003 MilliSeconds 00000002编号的订单要删除啦。。。。 After 6006 MilliSeconds 00000003编号的订单要删除啦。。。。 After 9006 MilliSeconds 00000004编号的订单要删除啦。。。。 After 12008 MilliSeconds 00000005编号的订单要删除啦。。。。 After 15009 MilliSeconds- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
可以看到都是延迟3秒,订单被删除
3.3 优缺点
优点:
- 效率高,任务触发时间延迟低。
缺点:
- 服务器重启后,数据全部消失,怕宕机
- 集群扩展相当麻烦
- 因为内存条件限制的原因,比如下单未付款的订单数太多,那么很容易就出现OOM异常
- 代码复杂度较高
4 方案三:时间轮算法
4.1 思路
先上一张时间轮的图(这图到处都是啦)
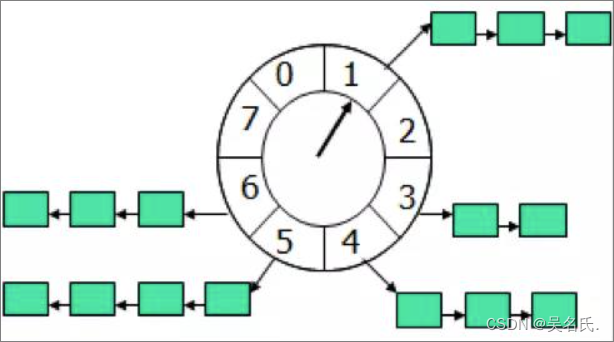
时间轮算法可以类比于时钟,如上图箭头(指针)按某一个方向按固定频率轮动,每一次跳动称为一个 tick。这样可以看出定时轮由个3个重要的属性参数,ticksPerWheel(一轮的tick数),tickDuration(一个tick的持续时间)以及 timeUnit(时间单位),例如当ticksPerWheel=60,tickDuration=1,timeUnit=秒,这就和现实中的始终的秒针走动完全类似了。如果当前指针指在1上面,我有一个任务需要4秒以后执行,那么这个执行的线程回调或者消息将会被放在5上。那如果需要在20秒之后执行怎么办,由于这个环形结构槽数只到8,如果要20秒,指针需要多转2圈。位置是在2圈之后的5上面(20 % 8 + 1)
4.2 实现
我们用Netty的HashedWheelTimer来实现 给Pom加上下面的依赖
<dependency> <groupId>io.nettygroupId> <artifactId>netty-allartifactId> <version>4.1.24.Finalversion> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
测试代码HashedWheelTimerTest如下所示
package com.rjzheng.delay3; import io.netty.util.HashedWheelTimer; import io.netty.util.Timeout; import io.netty.util.Timer; import io.netty.util.TimerTask; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class HashedWheelTimerTest { static class MyTimerTask implements TimerTask{ boolean flag; public MyTimerTask(boolean flag){ this.flag = flag; } public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("要去数据库删除订单了。。。。"); this.flag =false; } } public static void main(String[] argv) { MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask(true); Timer timer = new HashedWheelTimer(); timer.newTimeout(timerTask, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); int i = 1; while(timerTask.flag){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(i+"秒过去了"); i++; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
输出如下
1秒过去了 2秒过去了 3秒过去了 4秒过去了 5秒过去了 要去数据库删除订单了。。。。 6秒过去了- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
4.3 优缺点
优点:
- 效率高,任务触发时间延迟时间比delayQueue低,代码复杂度比delayQueue低。
缺点:
- 服务器重启后,数据全部消失,怕宕机
- 集群扩展相当麻烦
- 因为内存条件限制的原因,比如下单未付款的订单数太多,那么很容易就出现OOM异常
5 方案四:redis缓存
5.1 实现一
利用redis的zset,zset是一个有序集合,每一个元素(member)都关联了一个score,通过score排序来取集合中的值
zset常用命令
-
添加元素:ZADD key score member [[score member] [score member] …]
-
按顺序查询元素:ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
-
查询元素score:ZSCORE key member
-
移除元素:ZREM key member [member …]
测试如下
> 基于 Spring Cloud Alibaba + Gateway + Nacos + RocketMQ + Vue & Element 实现的后台管理系统 + 用户小程序,支持 RBAC 动态权限、多租户、数据权限、工作流、三方登录、支付、短信、商城等功能 > > * 项目地址:<https://github.com/YunaiV/yudao-cloud> > * 视频教程:<https://doc.iocoder.cn/video/> # 添加单个元素 redis> ZADD page_rank 10 google.com (integer) 1 # 添加多个元素 redis> ZADD page_rank 9 baidu.com 8 bing.com (integer) 2 redis> ZRANGE page_rank 0 -1 WITHSCORES 1) "bing.com" 2) "8" 3) "baidu.com" 4) "9" 5) "google.com" 6) "10" # 查询元素的score值 redis> ZSCORE page_rank bing.com "8" # 移除单个元素 redis> ZREM page_rank google.com (integer) 1 redis> ZRANGE page_rank 0 -1 WITHSCORES 1) "bing.com" 2) "8" 3) "baidu.com" 4) "9"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
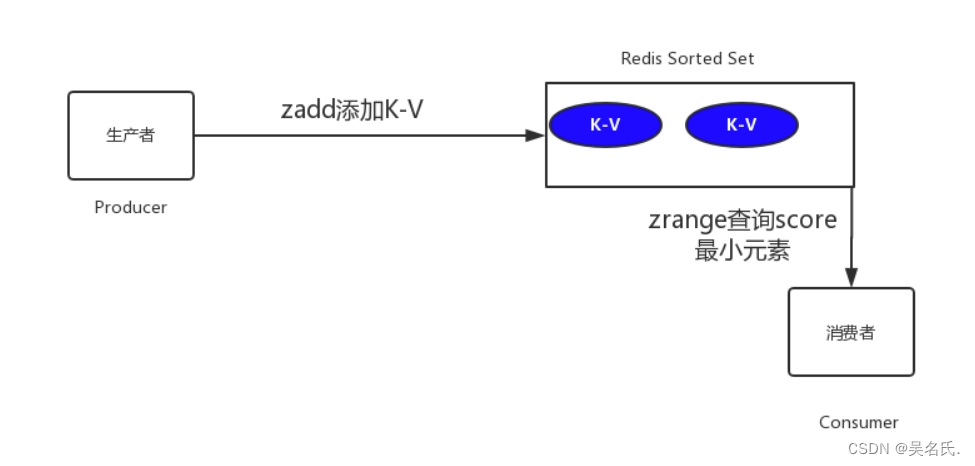
那么如何实现呢?我们将订单超时时间戳与订单号分别设置为score和member,系统扫描第一个元素判断是否超时,具体如下图所示
5.2 实现一
package com.rjzheng.delay4; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Set; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool; import redis.clients.jedis.Tuple; public class AppTest { private static final String ADDR = "127.0.0.1"; private static final int PORT = 6379; private static JedisPool jedisPool = new JedisPool(ADDR, PORT); public static Jedis getJedis() { return jedisPool.getResource(); } //生产者,生成5个订单放进去 public void productionDelayMessage(){ for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ //延迟3秒 Calendar cal1 = Calendar.getInstance(); cal1.add(Calendar.SECOND, 3); int second3later = (int) (cal1.getTimeInMillis() / 1000); AppTest.getJedis().zadd("OrderId", second3later,"OID0000001"+i); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为"+"OID0000001"+i); } } //消费者,取订单 public void consumerDelayMessage(){ Jedis jedis = AppTest.getJedis(); while(true){ Set<Tuple> items = jedis.zrangeWithScores("OrderId", 0, 1); if(items == null || items.isEmpty()){ System.out.println("当前没有等待的任务"); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } continue; } int score = (int) ((Tuple)items.toArray()[0]).getScore(); Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); int nowSecond = (int) (cal.getTimeInMillis() / 1000); if(nowSecond >= score){ String orderId = ((Tuple)items.toArray()[0]).getElement(); jedis.zrem("OrderId", orderId); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() +"ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为"+orderId); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { AppTest appTest =new AppTest(); appTest.productionDelayMessage(); appTest.consumerDelayMessage(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
此时对应输出如下
1525086085261ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000010 1525086085263ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000011 1525086085266ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000012 1525086085268ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000013 1525086085270ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000014 1525086088000ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000010 1525086088001ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000011 1525086088002ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000012 1525086088003ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000013 1525086088004ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000014 当前没有等待的任务 当前没有等待的任务 当前没有等待的任务- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
可以看到,几乎都是3秒之后,消费订单。
然而,这一版存在一个致命的硬伤,在高并发条件下,多消费者会取到同一个订单号,我们上测试代码ThreadTest
package com.rjzheng.delay4; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; public class ThreadTest { private static final int threadNum = 10; private static CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(threadNum); static class DelayMessage implements Runnable{ public void run() { try { cdl.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } AppTest appTest =new AppTest(); appTest.consumerDelayMessage(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AppTest appTest =new AppTest(); appTest.productionDelayMessage(); for(int i=0;i<threadNum;i++){ new Thread(new DelayMessage()).start(); cdl.countDown(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
输出如下所示
1525087157727ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000010 1525087157734ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000011 1525087157738ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000012 1525087157747ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000013 1525087157753ms:redis生成了一个订单任务:订单ID为OID00000014 1525087160009ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000010 1525087160011ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000010 1525087160012ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000010 1525087160022ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000011 1525087160023ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000011 1525087160029ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000011 1525087160038ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000012 1525087160045ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000012 1525087160048ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000012 1525087160053ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000013 1525087160064ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000013 1525087160065ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000014 1525087160069ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为OID00000014 当前没有等待的任务 当前没有等待的任务 当前没有等待的任务 当前没有等待的任务- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
显然,出现了多个线程消费同一个资源的情况。
5.3 解决方案
- 用分布式锁,但是用分布式锁,性能下降了,该方案不细说。
- 对ZREM的返回值进行判断,只有大于0的时候,才消费数据,于是将consumerDelayMessage()方法里的
if(nowSecond >= score){ String orderId = ((Tuple)items.toArray()[0]).getElement(); jedis.zrem("OrderId", orderId); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为"+orderId); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
修改为
if(nowSecond >= score){ String orderId = ((Tuple)items.toArray()[0]).getElement(); Long num = jedis.zrem("OrderId", orderId); if( num != null && num>0){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"ms:redis消费了一个任务:消费的订单OrderId为"+orderId); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
在这种修改后,重新运行ThreadTest类,发现输出正常了
5.4 思路二
该方案使用redis的Keyspace Notifications,中文翻译就是键空间机制,就是利用该机制可以在key失效之后,提供一个回调,实际上是redis会给客户端发送一个消息。是需要redis版本2.8以上。
5.5 实现二
在redis.conf中,加入一条配置
notify-keyspace-events Ex- 1
运行代码如下
package com.rjzheng.delay5; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPubSub; public class RedisTest { private static final String ADDR = "127.0.0.1"; private static final int PORT = 6379; private static JedisPool jedis = new JedisPool(ADDR, PORT); private static RedisSub sub = new RedisSub(); public static void init() { new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { jedis.getResource().subscribe(sub, "__keyevent@0__:expired"); } }).start(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { init(); for(int i =0;i<10;i++){ String orderId = "OID000000"+i; jedis.getResource().setex(orderId, 3, orderId); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"ms:"+orderId+"订单生成"); } } static class RedisSub extends JedisPubSub { @Override public void onMessage(String channel, String message) { System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"ms:"+message+"订单取消"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
输出如下
1525096202813ms:OID0000000订单生成 1525096202818ms:OID0000001订单生成 1525096202824ms:OID0000002订单生成 1525096202826ms:OID0000003订单生成 1525096202830ms:OID0000004订单生成 1525096202834ms:OID0000005订单生成 1525096202839ms:OID0000006订单生成 1525096205819ms:OID0000000订单取消 1525096205920ms:OID0000005订单取消 1525096205920ms:OID0000004订单取消 1525096205920ms:OID0000001订单取消 1525096205920ms:OID0000003订单取消 1525096205920ms:OID0000006订单取消 1525096205920ms:OID0000002订单取消- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
可以明显看到3秒过后,订单取消了
ps:redis的pub/sub 机制存在一个硬伤,官网内容如下
原 :Because Redis Pub/Sub is fire and forget currently there is no way to use this feature if your application demands reliable notification of events, that is, if your Pub/Sub client disconnects, and reconnects later, all the events delivered during the time the client was disconnected are lost.
译 : Redis的发布/订阅目前是即发即弃(fire and forget)模式的,因此无法实现事件的可靠通知。也就是说,如果发布/订阅的客户端断链之后又重连,则在客户端断链期间的所有事件都丢失了。 因此,方案二不是太推荐。当然,如果你对可靠性要求不高,可以使用。
5.6 优缺点
优点:
- 由于使用Redis作为消息通道,消息都存储在Redis中。如果发送程序或者任务处理程序挂了,重启之后,还有重新处理数据的可能性。
- 做集群扩展相当方便
- 时间准确度高
缺点:
- 需要额外进行redis维护
6 方案五:使用消息队列
我们可以采用rabbitMQ的延时队列。RabbitMQ具有以下两个特性,可以实现延迟队列
- RabbitMQ可以针对Queue和Message设置 x-message-tt,来控制消息的生存时间,如果超时,则消息变为dead
letter - lRabbitMQ的Queue可以配置x-dead-letter-exchange
和x-dead-letter-routing-key(可选)两个参数,用来控制队列内出现了deadletter,则按照这两个参数重新路由。
结合以上两个特性,就可以模拟出延迟消息的功能,具体的,我改天再写一篇文章,这里再讲下去,篇幅太长。
6.1 优缺点
优点: 高效,可以利用rabbitmq的分布式特性轻易的进行横向扩展,消息支持持久化增加了可靠性。
缺点:本身的易用度要依赖于rabbitMq的运维.因为要引用rabbitMq,所以复杂度和成本变高
-
相关阅读:
《学术小白学习之路14》主题建模——主题概率分布相似度计算
mybatis中Insert如何返回主键呢?
招投标系统软件源码,招投标全流程在线化管理
好的架构是进化来的,不是设计来的
maven-依赖管理
2.Tensor For Beginner -Tensor Definition
vue echarts条形统计图每个条上部分加数字
ubuntu22.04desktop安装SSH(server)
Java数据结构第二课 —— 泛型(1)
stable diffusion的微调和lora微调代码版本
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37284798/article/details/133942521