-
C++练习:人员信息管理程序计算不同职员的每月工资。
要求编写一个简单的人员信息管理程序,具体要求如下:
- 程序涉及到五个类,分别是employee,technician,salesman,manager,salsemanager。
这五个类的关系为:employee是顶层父类;technician,salesman,manager是employee的子类;salesmanager是salesman,manager的子类。 - employee具有员工号,姓名,收入等属性,有设置姓名,获取姓名,获取员工号,获取收入等函数。
- technician的收入计算方法为工作小时数*时薪,另外具有设置工作小时数,时薪的函数,具有工作小时数和时薪的属性。
- salesman的收入计算方法为销售额*提成比例,另外具有设置销售额,提成比例的函数,具有销售额和提成比例的属性。
- manager的收入计算方法为固定月薪,另外具有设置固定月薪的函数,具有固定月薪的属性。
- salsemanager收入计算方法为销售额*提成比例+固定月薪。
- 要求利用employee类型的指针列表,包含8个子类对象(technician,salesman,manager,salsemanager每个类2个),通过相应方法输出这些对象的姓名(姓名的初始化通过键盘录入),员工号,收入。
employee.h
#pragma once #include#include using namespace std; class Employee { public: Employee(); virtual ~Employee() { cout << "基类Employee" << endl; }; //观察析构函数调用顺序 void SetName(string name = ""); string GetName(); void SetStaffID(string id = ""); string GetStaffID(); virtual void CalSalary() = 0; void SetSalary(float s); float GetSalary(); private: string m_sStaffID; string m_sName; float m_nSalary; }; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
employee.cpp
#include "employee.h" #includeusing namespace std; Employee::Employee() { m_nSalary = 0.0f; } void Employee::SetName(string name) { if (name == "") { printf("请输入该员工的姓名:"); cin >> name; } m_sName = name; } string Employee::GetName() { return m_sName; } void Employee::SetStaffID(string id) { if (id == "") { printf("请输入该员工的工号:"); cin >> id; } m_sStaffID = id; } string Employee::GetStaffID() { return m_sStaffID; } void Employee::SetSalary(float s) { m_nSalary = s; } float Employee::GetSalary() { return m_nSalary; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
technician.h
#pragma once #include "employee.h" class Technician : public Employee { public: Technician(); virtual ~Technician() { cout << "子类Technician"<<endl; }; void Initialize(); void SetWorkHour(float h) { m_nWorkHour = h; }; float GetWorkHour() { return m_nWorkHour; }; void SetHourFee(float fee) { m_nHourFee = fee; }; float GetHourFee() { return m_nHourFee; } void CalSalary(); private: float m_nWorkHour; float m_nHourFee; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
technician.cpp
#include#include "technician.h" #include using namespace std; Technician::Technician() { m_nWorkHour = 0.0f; m_nHourFee = 0.0f; } void Technician::Initialize() { SetName(); SetStaffID(); string name = GetName(); string staffid; float workhour; printf("请输入%s的工作时长数:", name.c_str()); cin >> workhour; SetWorkHour(workhour); float hourfee; printf("请输入%s的时薪:", name.c_str()); cin >> hourfee; SetHourFee(hourfee); } void Technician::CalSalary() { SetSalary(m_nWorkHour * m_nHourFee); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
salesman.h
#pragma once #include "employee.h" class Salesman : virtual public Employee { public: Salesman(); virtual ~Salesman() { cout << "子类Salesman"<<endl; }; void Initialize(); void SetSales(float sales) { m_nSales = sales; }; float GetSales() { return m_nSales; }; void SetPercent(float per) { m_nPercent = per; }; float GetPercent() { return m_nPercent; }; void CalSalary(); private: float m_nSales; float m_nPercent; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
salesman.cpp
#include "salesman.h" #includeusing namespace std; Salesman::Salesman() { m_nSales = 0.0f; m_nPercent = 0.0f; } void Salesman::Initialize() { SetName(); SetStaffID(); string name = GetName(); string staffid; float sales; printf("请输入%s的销售额:", name.c_str()); cin >> sales; SetSales(sales); float percent; printf("请输入%s的提成比例:", name.c_str()); cin >> percent; SetPercent(percent); } void Salesman::CalSalary() { SetSalary(m_nSales*m_nPercent / 100); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
manager.h
#pragma once #include "employee.h" class Manager : virtual public Employee { public: Manager(); virtual ~Manager() { cout << "子类Manager"<<endl; }; void Initialize(); void SetFixedSalary(float salary) { m_nFixedSalary = salary; }; float GetFixedSalary() { return m_nFixedSalary; }; void CalSalary() { SetSalary(m_nFixedSalary); }; private: float m_nFixedSalary; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
manager.cpp
#include "manager.h" #includeusing namespace std; Manager::Manager() { m_nFixedSalary = 0.0f; } void Manager::Initialize() { SetName(); SetStaffID(); string name = GetName(); string staffid; float fixedsalary; printf("请输入%s的固定工资:", name.c_str()); cin >> fixedsalary; SetFixedSalary(fixedsalary); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
salesmanager.h
#pragma once #include "salesman.h" #include "manager.h" class Salsemanager : public Salesman, public Manager { public: Salsemanager() {}; virtual ~Salsemanager() { cout << "子类Salsemanager"<<endl; }; void Initialize(); void CalSalary(); };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
salesmanager.cpp
#include "salsemanager.h" #includeusing namespace std; void Salsemanager::Initialize() { SetName(); SetStaffID(); string name = GetName(); string staffid; float sales; printf("请输入%s的销售额:", name.c_str()); cin >> sales; SetSales(sales); float percent; printf("请输入%s的提成比例:", name.c_str()); cin >> percent; SetPercent(percent); float fixedsalary; printf("请输入%s的固定工资:", name.c_str()); cin >> fixedsalary; SetFixedSalary(fixedsalary); } void Salsemanager::CalSalary() { float sales = GetSales(); float percent = GetPercent(); float fixedsalary = GetFixedSalary(); Employee::SetSalary(sales * percent / 100 + fixedsalary); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
main.cpp
#include "employee.h" #include "manager.h" #include "salesman.h" #include "salsemanager.h" #include "technician.h" #include#include #include using namespace std; int main() { list<shared_ptr<Employee>> lEmployee; cout << "**************开始输入开发人员的相关信息***************" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { cout << "-------------------------------------------" << endl; shared_ptr<Technician> tec = make_shared<Technician>(); tec->Initialize(); tec->CalSalary(); lEmployee.push_back(tec); } cout << "**************开始输入销售人员的相关信息***************" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { cout << "-------------------------------------------" << endl; shared_ptr<Salesman> sale = make_shared<Salesman>(); sale->Initialize(); sale->CalSalary(); lEmployee.push_back(sale); } cout << "**************开始输入经理的相关信息***************" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { cout << "-------------------------------------------" << endl; shared_ptr<Manager> man = make_shared<Manager>(); man->Initialize(); man->CalSalary(); lEmployee.push_back(man); } cout << "**************开始输入销售经理的相关信息***************" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { cout << "-------------------------------------------" << endl; shared_ptr<Salsemanager> saleman = make_shared<Salsemanager>(); saleman->Initialize(); saleman->CalSalary(); lEmployee.push_back(saleman); } for (auto iter = lEmployee.begin(); iter != lEmployee.end(); ++iter) { printf("工号为 %s 的员工 %s 的本月薪资为:%f \n", (*iter)->GetStaffID().c_str(), (*iter)->GetName().c_str(), (*iter)->GetSalary()); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
虚继承
本题在Employee、Salesman、Manager、Salesmanager类之间存在多重继承,使用一般的继承方式容易出现内存占用和二义性问题,需要采用 虚继承 的方式来解决这个问题。
继承有 普通继承 和 虚继承 两种机制,默认继承方式是普通继承,如果要使用多重继承时,需要在继承方式里加上关键字virtual,即虚继承。
在C++中,多重继承可以让一个类同时继承于多个基类,从而实现更加灵活和复杂的面向对象编程。然而多重继承也会导致 同一个基类在派生类中出现多次,导致内存占用的增加以及代码调用二义性问题。
如下图所示,Salesmanager 类分别从 Sales 类和 Manager 类中继承了 Employee 类,这就会导致 Employee 类在 Salesmanager 类中出现两次。如果 Sales 类和 Manager 类中都有 Employee 类的成员变量或成员函数,那么在 Salesmanager 类中就会存在两份相同的 Employee 类成员,这就增加了内存占用,并且调用这些成员时,也会出现二义性问题。
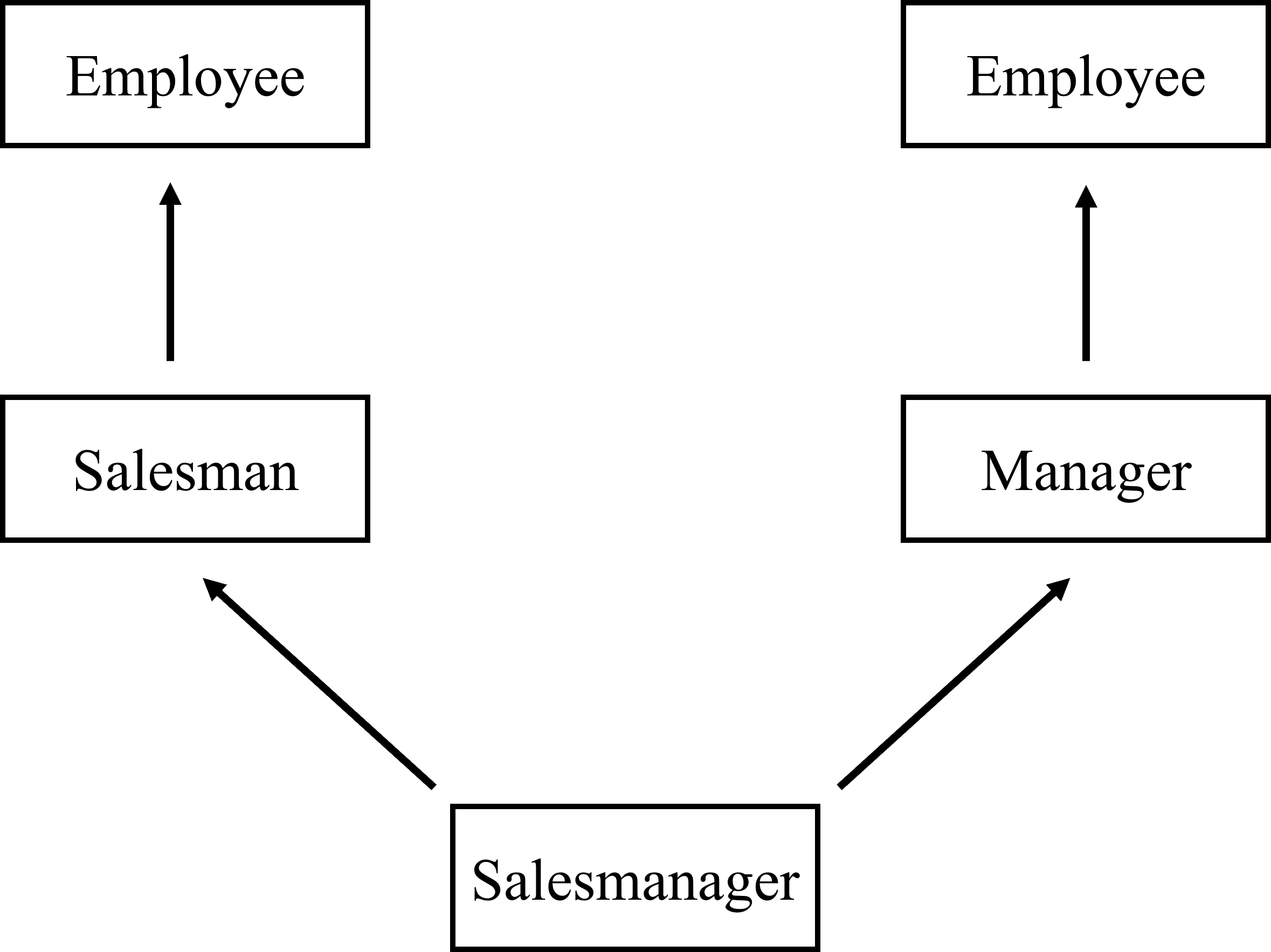
虚继承就是为了解决这个问题而出现的。虚继承允许一个类以虚继承方式继承一个基类,这样基类的成员变量和成员函数只在最终派生类中保留一份,而不是每个派生类都保留一份,这样就避免了菱形继承的问题,减少了内存占用和二义性问题。
虚继承会增加一些开销,它需要在派生类中维护虚基类的地址偏移量,以及查找基类成员的位置。
虚继承的用法
class Employee { public: int a; }; class Sales : virtual public Employee { public: int b; }; class Manager : virtual public Employee { public: int c; }; class Salesmanager : public Manager , public Sales { public: int d; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
当采用虚继承后,类结构图如下所示,Salesmanager 中只有一份 Employee 类,当调用 Employee 类数据时,并不会发生冗余。

虚继承原理
在虚继承中,父类数据并不存放在虚继承的子类中,在虚继承的类中,会定义一个虚基表指针vbptr,指向虚基表。则虚基表中会存在偏移量,这个量就是表的地址到父类数据地址的距离。
智能指针
本次练习题中采用shared_ptr智能指针,不用考虑指针的释放问题。
析构函数
本次练习题中析构函数声明为虚函数,也可以防止基类指针操作子类成员后出现内存泄漏的情况。在析构函数中输出相关信息方便观察指针释放时析构函数的调用次序。
- 程序涉及到五个类,分别是employee,technician,salesman,manager,salsemanager。
-
相关阅读:
Java_Validation分组校验
网络通信错误代码列表 HTTP 、FTP
SpringBoot根据配置注入接口的不同实现类
避坑指南:小红书品牌投放易入的“七大坑”
【力客热题HOT100】-【038】96 不同的二叉搜索树
【观察】华为陈帮华:学习“都江堰模式”,构筑强健分销体系
国内crm解决方案的主要提供商有哪些?对比7家
[Vue 配置] Vite + Vue3 项目配置 Tailwind CSS
c 按位运算
Pyhon-每日一练(1)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33021529/article/details/133953018
