-
Datawhale-新能源时间序列赛事学习笔记(1)
1.赛题描述
在电动汽车充电站运营管理中,准确预测充电站的电量需求对于提高充电站运营服务水平和优化区域电网供给能力非常关键。本次赛题旨在建立站点充电量预测模型,根据充电站的相关信息和历史电量数据,准确预测未来某段时间内充电站的充电量需求。赛题数据中提供了电动汽车充电站的场站编号、位置信息、历史电量等基本信息。参赛者需要基于这些数据,利用人工智能相关技术,建立预测模型来预测未来一段时间内的需求电量,帮助管理者提高充电站的运营效益和服务水平,促进电动汽车行业的整体发展。
2.赛题任务
根据赛题提供的电动汽车充电站多维度脱敏数据,构造合理特征及算法模型,预估站点未来一周每日的充电量。(以天为单位)
3.赛题数据集
本赛题提供的数据集包含三张数据表。其中,power_forecast_history.csv 为站点运营数据,power.csv为站点充电量数据,stub_info.csv为站点静态数据,训练集为历史一年的数据,测试集为未来一周的数据。
数据集清单与格式说明:

注:
(1)h3编码是一种用于分层地理编码的系统,可以将地球划分为不同的六边形网格。选手可以尝试使用 h3 编码来构造与地理位置相关的额外特征。
(2)脱敏字段,不提供字段业务描述,供选手自由探索。
4.评估指标-RMSE

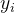 为第个数据的真实值,
为第个数据的真实值,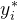 为第个数据的预测值,
为第个数据的预测值,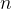 为样本总数。
为样本总数。5.Baseline
5.1 导入库
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- import lightgbm as lgb
- import xgboost as xgb
- from catboost import CatBoostRegressor
- from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold, KFold, GroupKFold
- from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import tqdm
- import sys
- import os
- import gc
- import argparse
- import warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
5.2 数据准备与探索
- # 读取数据
- train_power_forecast_history = pd.read_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\训练集\power_forecast_history.csv')
- train_power = pd.read_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\训练集\power.csv')
- train_stub_info = pd.read_csv('F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\训练集\stub_info.csv')
- test_power_forecast_history = pd.read_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\测试集\power_forecast_history.csv')
- test_stub_info = pd.read_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\测试集\stub_info.csv')
- # 聚合数据(按日期+场站编码分组后取每一组第一条数据)
- train_df = train_power_forecast_history.groupby(['id_encode','ds']).head(1)
- del train_df['hour']
- test_df = test_power_forecast_history.groupby(['id_encode','ds']).head(1)
- del test_df['hour']
- tmp_df = train_power.groupby(['id_encode','ds'])['power'].sum()
- tmp_df.columns = ['id_encode','ds','power']
- # 合并充电量数据
- train_df = train_df.merge(tmp_df, on=['id_encode','ds'], how='left')
- ### 合并数据
- train_df = train_df.merge(train_stub_info, on='id_encode', how='left')
- test_df = test_df.merge(test_stub_info, on='id_encode', how='left')
- # 定义要绘制的列
- cols = ['power']
- # 遍历id_encode的五个值
- for ie in [0,1,2,3,4]:
- # 获取train_df中id_encode为当前值ie的所有行,并重置索引
- tmp_df = train_df[train_df['id_encode']==ie].reset_index(drop=True)
- # 再次重置索引,并为新索引添加一个名为'index'的列
- tmp_df = tmp_df.reset_index(drop=True).reset_index()
- # 遍历要绘制的列
- for num, col in enumerate(cols):
- # 设置图的大小
- plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
- # 创建子图,总共有4行1列,当前为第num+1个子图
- plt.subplot(4,1,num+1)
- # 绘制图形:x轴为'index',y轴为当前列的值
- plt.plot(tmp_df['index'],tmp_df[col])
- # 为当前子图设置标题,标题为当前列的名称
- plt.title(col)
- # 显示图形
- plt.show()
- # 创建一个新的图,大小为20x5
- plt.figure(figsize=(20,5))

5.3 特征工程
- train_df['flag'] = train_df['flag'].map({'A':0,'B':1})
- test_df['flag'] = test_df['flag'].map({'A':0,'B':1})
- def get_time_feature(df, col):
- df_copy = df.copy()
- prefix = col + "_"
- df_copy['new_'+col] = df_copy[col].astype(str)
- col = 'new_'+col
- df_copy[col] = pd.to_datetime(df_copy[col], format='%Y%m%d')
- df_copy[prefix + 'year'] = df_copy[col].dt.year
- df_copy[prefix + 'month'] = df_copy[col].dt.month
- df_copy[prefix + 'day'] = df_copy[col].dt.day
- # df_copy[prefix + 'weekofyear'] = df_copy[col].dt.weekofyear
- df_copy[prefix + 'dayofweek'] = df_copy[col].dt.dayofweek
- df_copy[prefix + 'is_wknd'] = df_copy[col].dt.dayofweek // 6
- df_copy[prefix + 'quarter'] = df_copy[col].dt.quarter
- df_copy[prefix + 'is_month_start'] = df_copy[col].dt.is_month_start.astype(int)
- df_copy[prefix + 'is_month_end'] = df_copy[col].dt.is_month_end.astype(int)
- del df_copy[col]
- return df_copy
- train_df = get_time_feature(train_df, 'ds')
- test_df = get_time_feature(test_df, 'ds')
- cols = [f for f in test_df.columns if f not in ['ds','power','h3']]
5.4 模型训练与验证
- def cv_model(clf, train_x, train_y, test_x, clf_name, seed = 2023):
- '''
- clf:调用模型
- train_x:训练数据
- train_y:训练数据对应标签
- test_x:测试数据
- clf_name:选择使用模型名
- seed:随机种子
- '''
- folds = 5
- kf = KFold(n_splits=folds, shuffle=True, random_state=seed)
- oof = np.zeros(train_x.shape[0])
- test_predict = np.zeros(test_x.shape[0])
- cv_scores = []
- for i, (train_index, valid_index) in enumerate(kf.split(train_x, train_y)):
- print('************************************ {} ************************************'.format(str(i+1)))
- trn_x, trn_y, val_x, val_y = train_x.iloc[train_index], train_y[train_index], train_x.iloc[valid_index], train_y[valid_index]
- if clf_name == "lgb":
- train_matrix = clf.Dataset(trn_x, label=trn_y)
- valid_matrix = clf.Dataset(val_x, label=val_y)
- params = {
- 'boosting_type': 'gbdt',
- 'objective': 'regression',
- 'metric': 'mae',
- 'min_child_weight': 6,
- 'num_leaves': 2 ** 6,
- 'lambda_l2': 10,
- 'feature_fraction': 0.8,
- 'bagging_fraction': 0.8,
- 'bagging_freq': 4,
- 'learning_rate': 0.1,
- 'seed': 2023,
- 'nthread' : 16,
- 'verbose' : -1,
- }
- model = clf.train(params, train_matrix, 2000, valid_sets=[train_matrix, valid_matrix],
- categorical_feature=[], verbose_eval=200, early_stopping_rounds=100)
- val_pred = model.predict(val_x, num_iteration=model.best_iteration)
- test_pred = model.predict(test_x, num_iteration=model.best_iteration)
- if clf_name == "xgb":
- xgb_params = {
- 'booster': 'gbtree',
- 'objective': 'reg:squarederror',
- 'eval_metric': 'mae',
- 'max_depth': 5,
- 'lambda': 10,
- 'subsample': 0.7,
- 'colsample_bytree': 0.7,
- 'colsample_bylevel': 0.7,
- 'eta': 0.1,
- 'tree_method': 'hist',
- 'seed': 520,
- 'nthread': 16
- }
- train_matrix = clf.DMatrix(trn_x , label=trn_y)
- valid_matrix = clf.DMatrix(val_x , label=val_y)
- test_matrix = clf.DMatrix(test_x)
- watchlist = [(train_matrix, 'train'),(valid_matrix, 'eval')]
- model = clf.train(xgb_params, train_matrix, num_boost_round=2000, evals=watchlist, verbose_eval=200, early_stopping_rounds=100)
- val_pred = model.predict(valid_matrix)
- test_pred = model.predict(test_matrix)
- if clf_name == "cat":
- params = {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'depth': 5, 'bootstrap_type':'Bernoulli','random_seed':2023,
- 'od_type': 'Iter', 'od_wait': 100, 'random_seed': 11, 'allow_writing_files': False}
- model = clf(iterations=2000, **params)
- model.fit(trn_x, trn_y, eval_set=(val_x, val_y),
- metric_period=200,
- use_best_model=True,
- cat_features=[],
- verbose=1)
- val_pred = model.predict(val_x)
- test_pred = model.predict(test_x)
- oof[valid_index] = val_pred
- test_predict += test_pred / kf.n_splits
- score = mean_absolute_error(val_y, val_pred)
- cv_scores.append(score)
- print(cv_scores)
- return oof, test_predict
◒LightGBM
- lgb_oof, lgb_test = cv_model(lgb, train_df[cols], train_df['power'], test_df[cols])
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- #交叉验证分数
- [266.7260370569527, 269.9232639345857, 265.154677843001, 265.21192193943574, 266.49163591068003]
- test_df['power'] = lgb_test
- test_df['power'] = test_df['power'].apply(lambda x: 0 if x<0 else x)
- test_df[['id_encode','ds','power']].to_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\result.csv', index=False)
线上分数:240.51261765759443
◒XGBoost
- xgb_oof, xgb_test = cv_model(xgb, train_df[cols], train_df['power'], test_df[cols], 'xgb')
- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- #交叉验证分数
- [188.14222230685203, 189.79883333942658, 189.98780480651146, 188.90711501159402, 189.63885769696023]
- test_df['power'] = xgb_test
- test_df['power'] = test_df['power'].apply(lambda x: 0 if x<0 else x)
- test_df[['id_encode','ds','power']].to_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\xgb_result.csv', index=False)
线上分数:269.1201702406025
◒CatBoost
- cat_oof, cat_test = cv_model(CatBoostRegressor, train_df[cols], train_df['power'], test_df[cols], 'cat')
- ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- #交叉验证分数
- [217.60469992799398, 221.48162281844884, 221.30109254841568, 220.89774625184162, 219.70713010328046]
- test_df['power'] = cat_test
- test_df['power'] = test_df['power'].apply(lambda x: 0 if x<0 else x)
- test_df[['id_encode','ds','power']].to_csv(r'F:\Jupyter Files\比赛\新能源赛道初赛数据集\初赛1008\cat_result.csv', index=False)
线上分数:302.69904271933
6.总结
从线下结果来看,XGBoost>CatBoost>LightGBM,即XGBoost的效果最优;而从线上结果来看,LightGBM>XGBoost>CatBoost,即LightGBM的效果最优。因为不同模型结果相差较大,所以没有考虑对这三模型进行融合。接下来会更侧重对LightGBM和XGBoost进行调参,并做特征工程,争取有更好的效果。
-
相关阅读:
ubuntu修改IP地址
2022年“科学探索奖”获奖者90%具有海外经历
Java学习笔记3.8.1 内部类 - 成员内部类
vmware centos7虚拟机出现 Generating /run/initramfs/rdsosreport.txt 问题?
基于Go语言的xmind读写库,我主要用来把有道云笔记思维导图转为xmind
LESS vs. SCSS:选择何种CSS预处理器?
精英VS普通测试开发程序员?截然不同......
Python-对象与json互转-json读写-文件读写
Office技巧(持续更新)(Word、Excel、PPT、PowerPoint、连续引用、标题、模板、论文)
如何在 Net6.0 中对 WebAPI 进行 JWT 认证和授权
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60200880/article/details/133916030
