-
【常用图像增强技术,Python-opencv】
常用图像增强技术
图像增强技术是常用于数据增强的方法,可以帮助增加数据集中图像的多样性,提高深度学习模型的性能和泛化能力。
调整大小(Resize):
调整图像的尺寸,通常用于将图像缩放到模型输入的期望尺寸。
灰度变换(Grayscale Transformation):
将彩色图像转换为灰度图像,降低图像的复杂度,常用于处理黑白图像。
标准化(Normalization):
对图像的像素值进行标准化处理,将像素值缩放到一个特定的范围,例如[0, 1]或[-1, 1],有助于加速模型的训练。
随机旋转(Random Rotation):
在一定角度范围内对图像进行随机旋转,增加模型对旋转变换的鲁棒性。
中心裁剪(Center Crop):
将图像从中心位置裁剪到指定的尺寸,常用于处理物体识别任务。
随机裁剪(Random Crop):
在图像的随机位置进行裁剪,增加模型对位置变换的适应性。
高斯模糊(Gaussian Blur):
对图像进行高斯模糊操作,模糊图像,降低图像中的噪声,有助于模型学习更鲁棒的特征。
亮度、对比度调节(Brightness and Contrast Adjustment):
调整图像的亮度和对比度,增加图像的光照变化,提高模型的鲁棒性。
水平翻转(Horizontal Flip):
将图像水平翻转,增加模型对图像翻转的适应性。
垂直翻转(Vertical Flip):
将图像垂直翻转,增加模型对图像垂直翻转的适应性。
高斯噪声(Gaussian Noise):
向图像中添加高斯噪声,增加图像的复杂性,提高模型的鲁棒性。
随机块(Random Patch):
将图像的随机区域替换为随机像素值或者另外一幅图像的随机区域,增加图像的多样性。
中心区域裁剪(Center Area Crop):
与中心裁剪类似,但是不仅仅是将图像的中心裁剪出来,还可以选择图像的其他区域进行裁剪,增加多样性。这些技术可以单独应用,也可以组合使用,根据具体任务和数据集的特点选择合适的增强方法,以增加数据的多样性,提高模型的性能和泛化能力。
调整大小
在开始图像大小的调整之前我们需要导入数据(图像以眼底图像为例)。
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('image/000001.tif')) torch.manual_seed(0) # 设置 CPU 生成随机数的 种子 ,方便下次复现实验结果 print(np.asarray(orig_img).shape) #(800, 800, 3) #图像大小的调整 resized_imgs = [T.Resize(size=size)(orig_img) for size in [128,256]] # plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(131) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(132) ax2.set_title('resize:128*128') ax2.imshow(resized_imgs[0]) ax3 = plt.subplot(133) ax3.set_title('resize:256*256') ax3.imshow(resized_imgs[1]) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
首先导入了必要的Python库,包括PIL(Python Imaging Library,也叫Pillow,用于图像处理)、Pathlib(用于操作文件路径)、Matplotlib(用于绘制图表)以及NumPy和PyTorch(用于数学计算和深度学习任务的库)。
接着,通过Image.open(Path(‘image/000001.tif’))语句,从指定路径读取了一张tif格式的原始图像,并将其存储在orig_img变量中。
然后,通过torch.manual_seed(0)设置了PyTorch的随机数种子,确保在每次运行代码时生成的随机数相同,以便实验结果能够被复现。
接下来,代码使用了PIL库中的Image类和torchvision.transforms模块中的T.Resize方法,对原始图像进行了尺寸调整。具体地说,它将原始图像分别调整为128x128和256x256两种不同大小的图像,并将处理后的图像分别存储在resized_imgs列表的两个元素中。
最后,使用Matplotlib库,代码创建了一个包含三个子图(subplot)的图表。第一个子图(ax1)显示了原始图像,第二个子图(ax2)显示了调整大小后的128x128图像,第三个子图(ax3)显示了调整大小后的256x256图像。每个子图的标题用中文标注,通过ax1.set_title(‘original’)、ax2.set_title(‘resize:128128’)和ax3.set_title('resize:256256’)语句分别设置。
最后,通过plt.show()语句,将这三个子图显示在屏幕上。
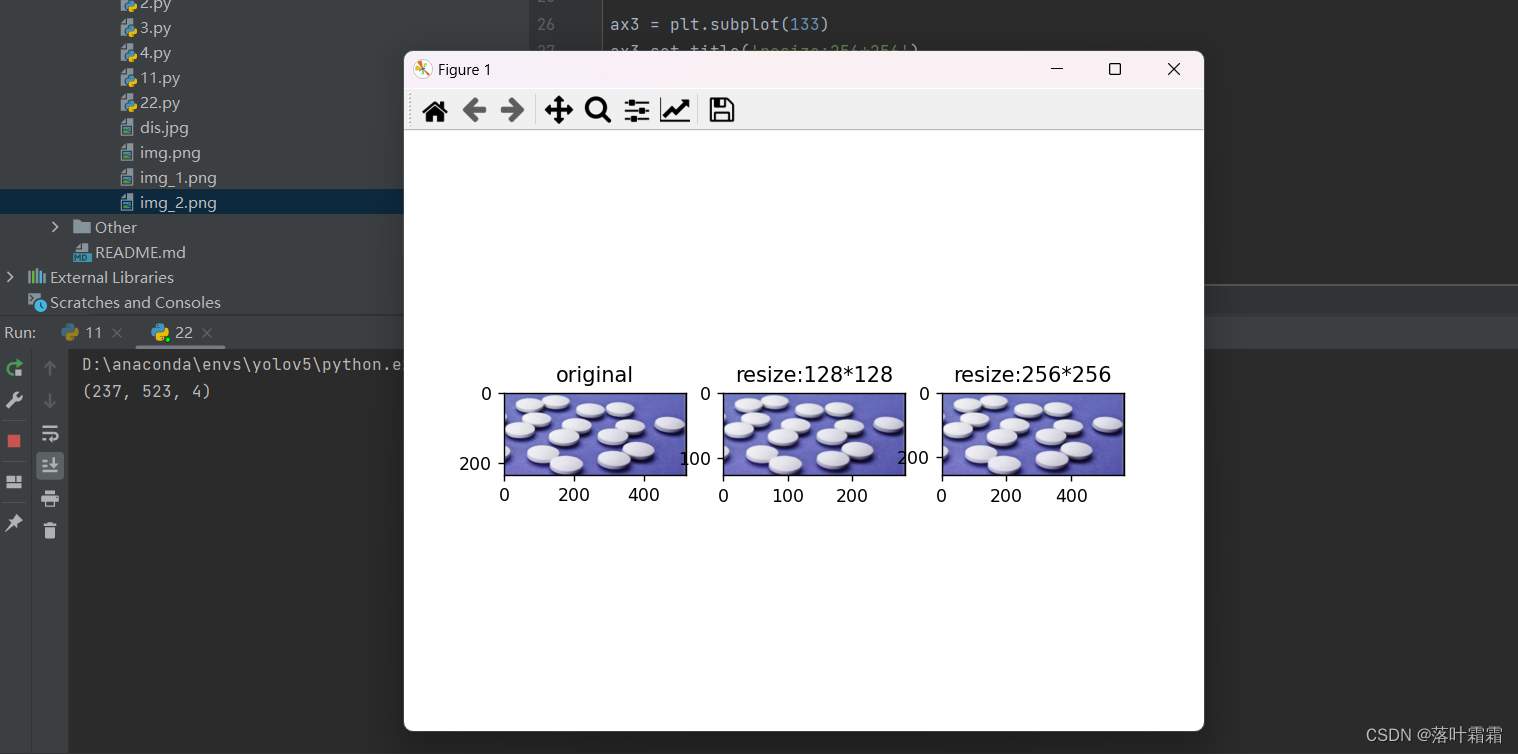
灰度变换
此操作将RGB图像转化为灰度图像。
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import torch import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) torch.manual_seed(0) # 设置 CPU 生成随机数的 种子 ,方便下次复现实验结果 print(np.asarray(orig_img).shape) #(800, 800, 3) gray_img = T.Grayscale()(orig_img) # 将灰度图像转换为NumPy数组,并确保数据类型为np.uint8 gray_array = np.array(gray_img, dtype=np.uint8) # 显示灰度图像 plt.imshow(gray_array, cmap='gray') plt.title('Grayscale Image') plt.axis('off') # 隐藏坐标轴 plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
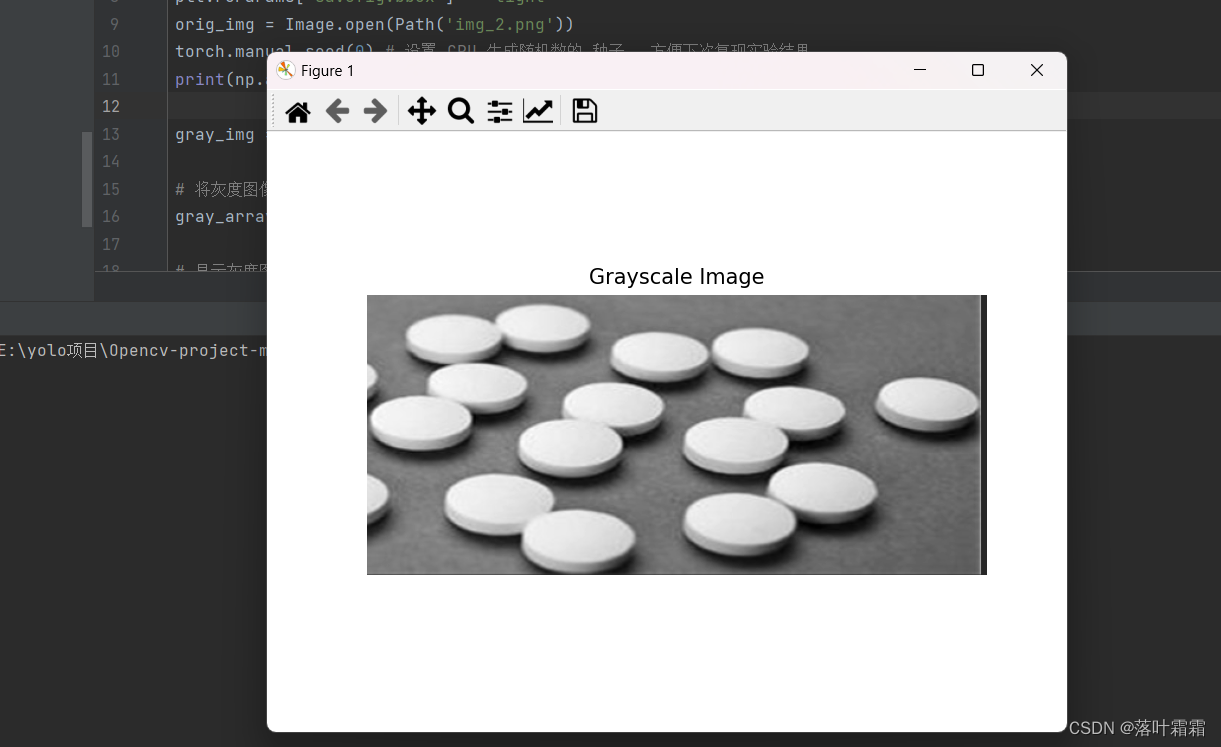
标准化
标准化可以加快基于神经网络结构的模型的计算速度,加快学习速度。
从每个输入通道中减去通道平均值
将其除以通道标准差。from PIL import Image import torch import torchvision.transforms as T # 打开并转换图像为RGB模式 orig_img = Image.open('img_2.png').convert('RGB') # 使用torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()将PIL图像转换为PyTorch张量 tensor_img = T.ToTensor()(orig_img) # 对图像进行归一化 normalized_img = T.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))(tensor_img) normalized_img = [T.ToPILImage()(normalized_img)] # 以下是您的绘图和显示代码 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('normalize') ax2.imshow(normalized_img[0]) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
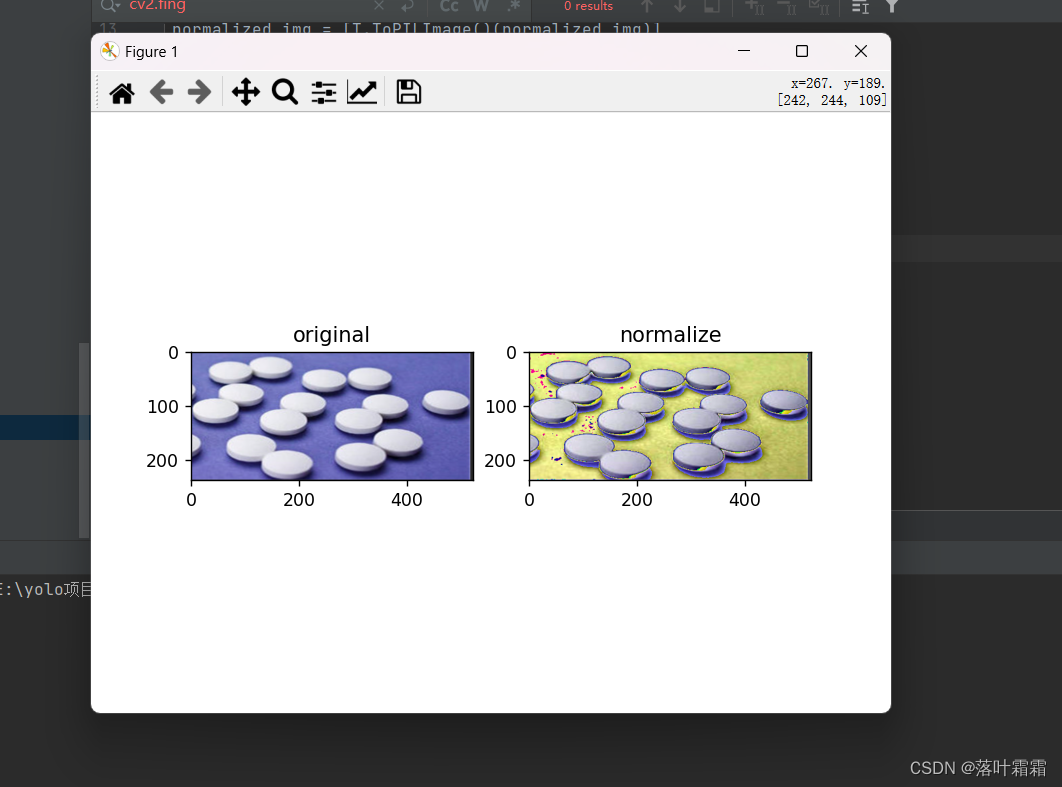
随机旋转
设计角度旋转图像
from PIL import Image import torch import torchvision.transforms as T # 打开并转换图像为RGB模式 orig_img = Image.open('img_2.png').convert('RGB') # 随机旋转角度范围为±30度 random_rotation = T.RandomRotation(degrees=30) # 使用torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()将PIL图像转换为PyTorch张量 tensor_img = T.ToTensor()(orig_img) # 对图像进行随机旋转和归一化 transform = T.Compose([ random_rotation, T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) ]) transformed_img = transform(orig_img) transformed_img_pil = T.ToPILImage()(transformed_img) # 以下是您的绘图和显示代码 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('transformed') ax2.imshow(transformed_img_pil) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
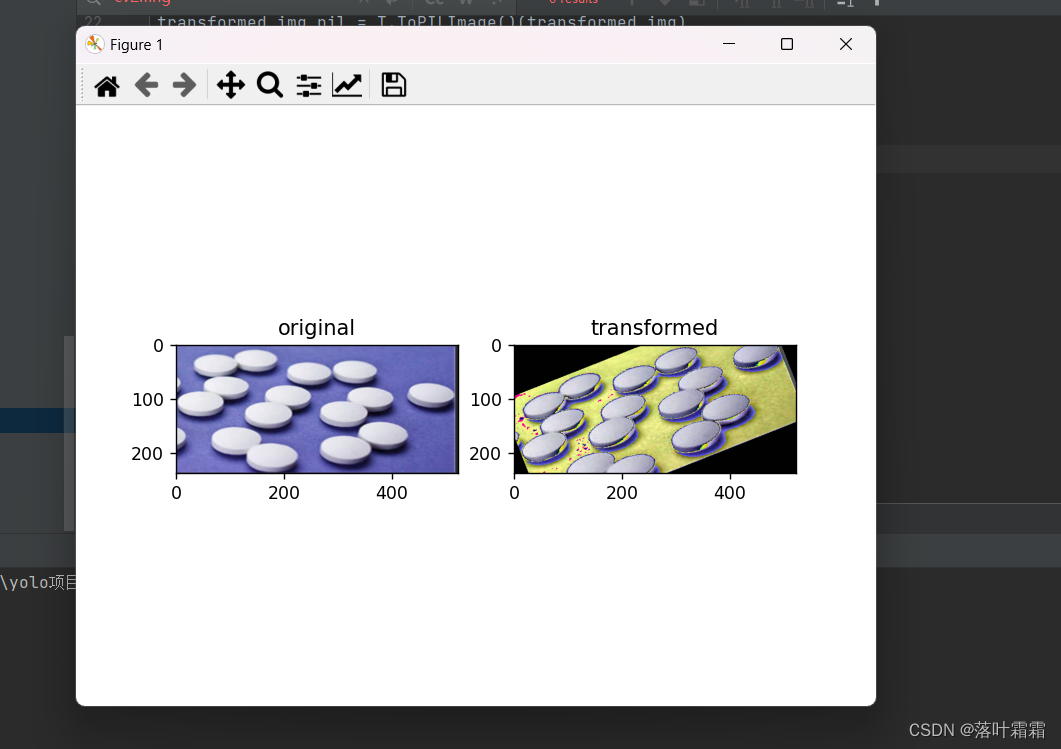
中心剪切
剪切图像的中心区域
from PIL import Image import torch import torchvision.transforms as T # 打开并转换图像为RGB模式 orig_img = Image.open('img_2.png').convert('RGB') # 定义中心剪切的目标尺寸 crop_size = (200, 200) # 随机旋转角度范围为±30度 random_rotation = T.RandomRotation(degrees=30) # 中心剪切 center_crop = T.CenterCrop(crop_size) # 使用torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()将PIL图像转换为PyTorch张量 tensor_img = T.ToTensor()(orig_img) # 对图像进行随机旋转、中心剪切和归一化 transform = T.Compose([ random_rotation, center_crop, T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) ]) transformed_img = transform(orig_img) transformed_img_pil = T.ToPILImage()(transformed_img) # 以下是您的绘图和显示代码 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('transformed') ax2.imshow(transformed_img_pil) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
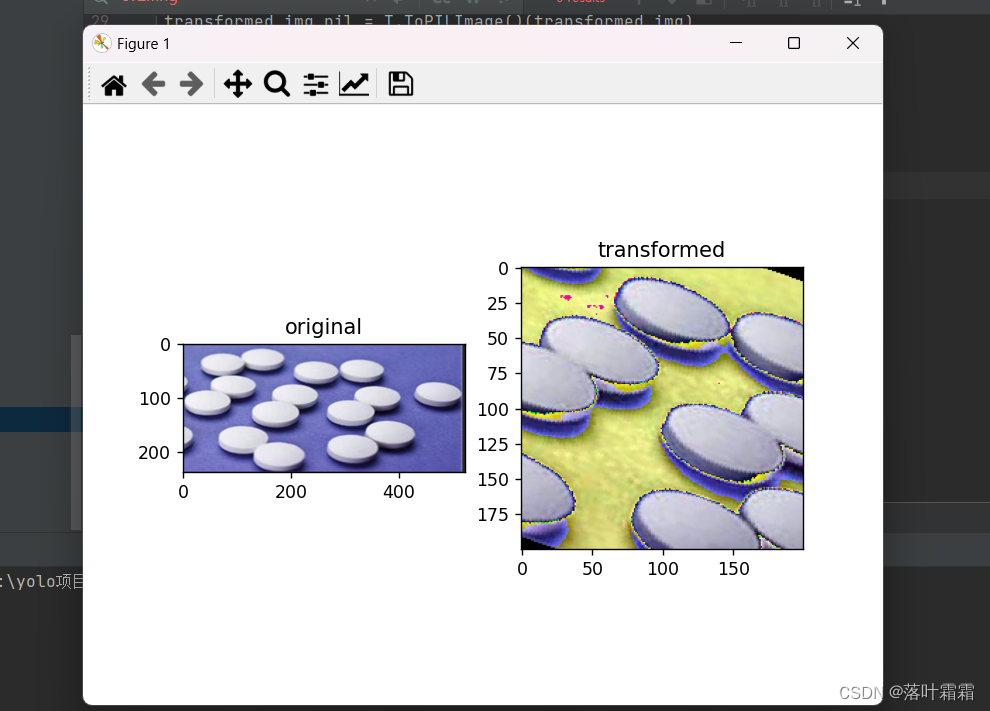
随机裁剪
随机剪切图像的某一部分
from PIL import Image import torch import torchvision.transforms as T # 打开并转换图像为RGB模式 orig_img = Image.open('img_2.png').convert('RGB') # 定义随机剪切的目标尺寸 crop_size = (200, 200) # 随机剪切和随机旋转的组合 random_crop = T.RandomResizedCrop(crop_size, scale=(0.8, 1.0)) random_rotation = T.RandomRotation(degrees=30) # 使用torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()将PIL图像转换为PyTorch张量 tensor_img = T.ToTensor()(orig_img) # 对图像进行随机剪切、随机旋转和归一化 transform = T.Compose([ random_crop, random_rotation, T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) ]) transformed_img = transform(orig_img) transformed_img_pil = T.ToPILImage()(transformed_img) # 以下是您的绘图和显示代码 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('transformed') ax2.imshow(transformed_img_pil) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
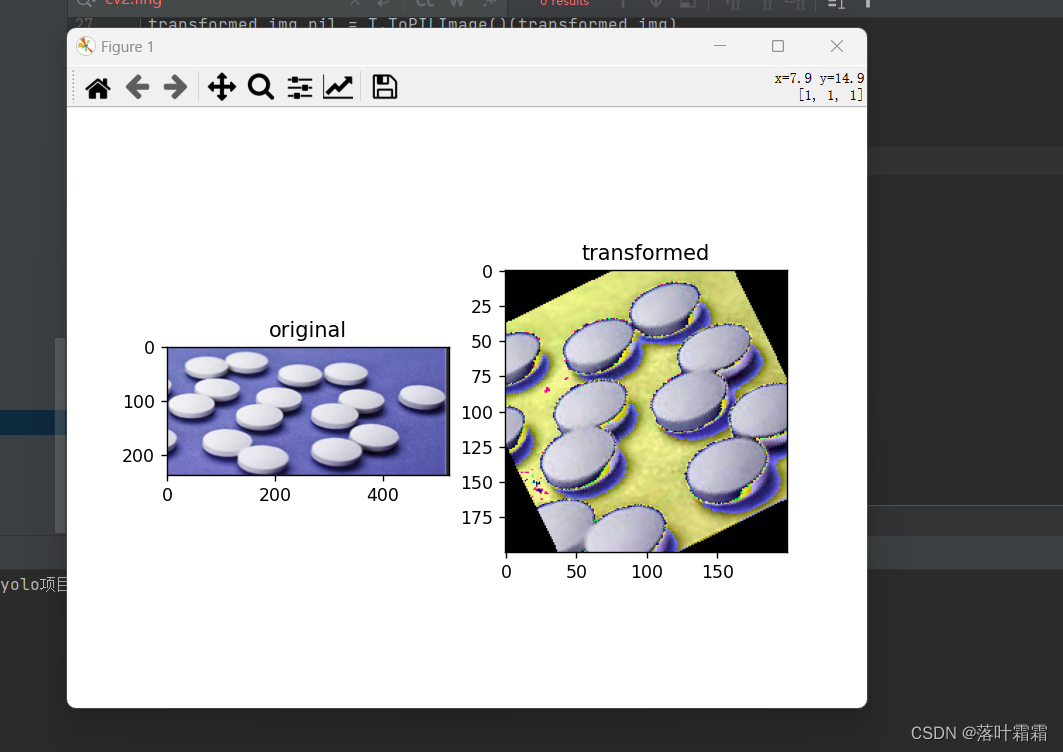
高斯模糊
使用高斯核对图像进行模糊变换
from PIL import Image import torch import torchvision.transforms as T # 打开并转换图像为RGB模式 orig_img = Image.open('img_2.png').convert('RGB') # 定义高斯模糊的卷积核大小 blur_radius = 5 # 高斯模糊和随机剪切的组合 gaussian_blur = T.GaussianBlur(blur_radius) random_crop = T.RandomResizedCrop((200, 200), scale=(0.8, 1.0)) # 使用torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()将PIL图像转换为PyTorch张量 tensor_img = T.ToTensor()(orig_img) # 对图像进行高斯模糊、随机剪切和归一化 transform = T.Compose([ gaussian_blur, random_crop, T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) ]) transformed_img = transform(orig_img) transformed_img_pil = T.ToPILImage()(transformed_img) # 以下是您的绘图和显示代码 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('transformed') ax2.imshow(transformed_img_pil) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43

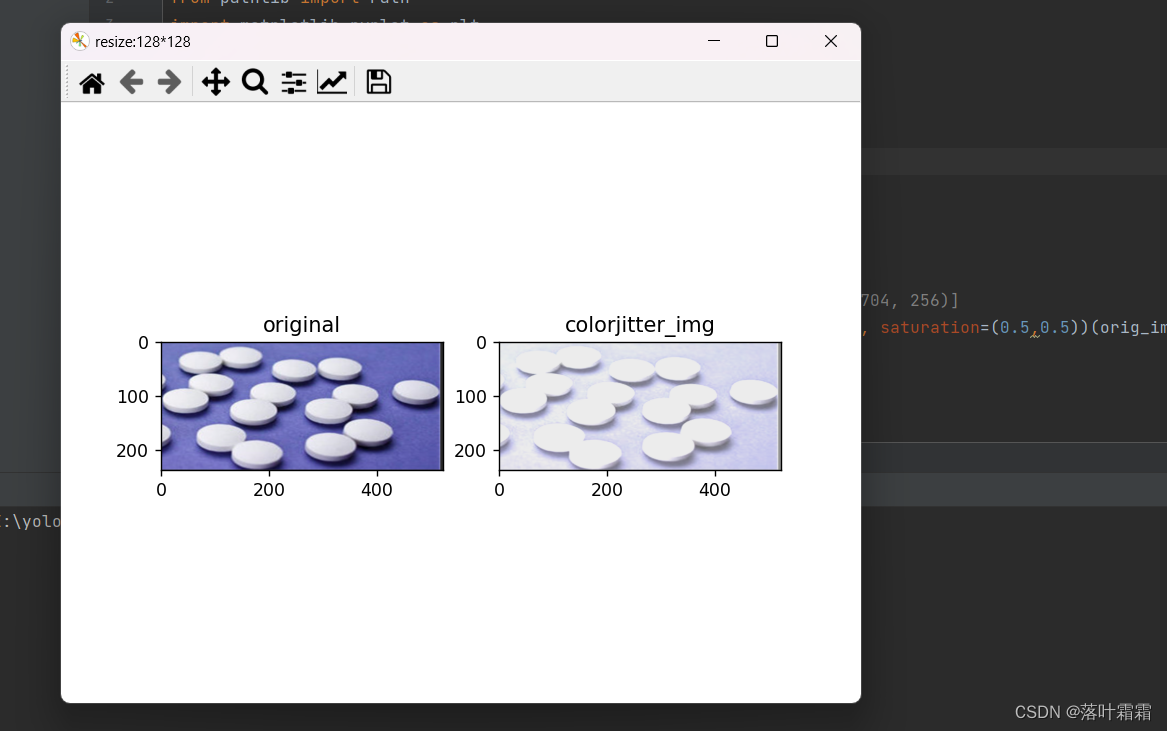
亮度、对比度和饱和度调节
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) # random_crops = [T.RandomCrop(size=size)(orig_img) for size in (832,704, 256)] colorjitter_img = [T.ColorJitter(brightness=(2,2), contrast=(0.5,0.5), saturation=(0.5,0.5))(orig_img)] plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('colorjitter_img') ax2.imshow(np.array(colorjitter_img[0])) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
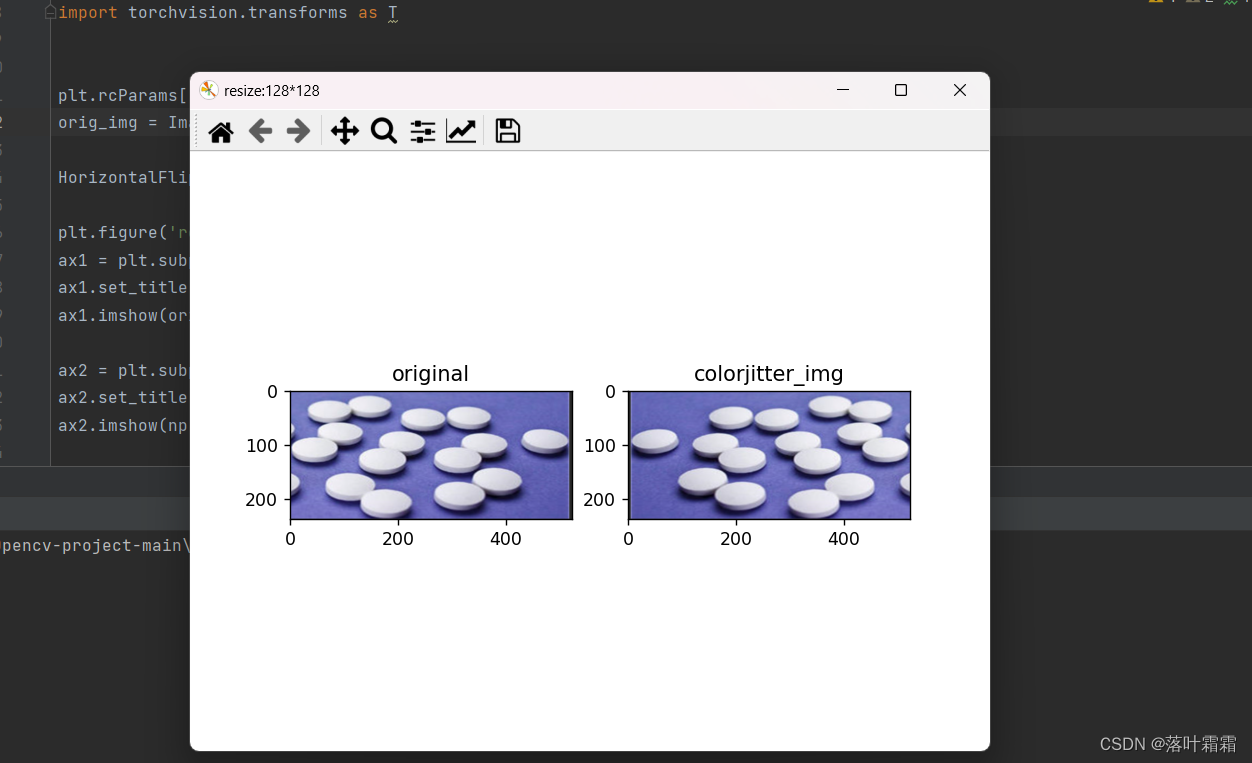
水平翻转
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) HorizontalFlip_img = [T.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=1)(orig_img)] plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('colorjitter_img') ax2.imshow(np.array(HorizontalFlip_img[0])) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
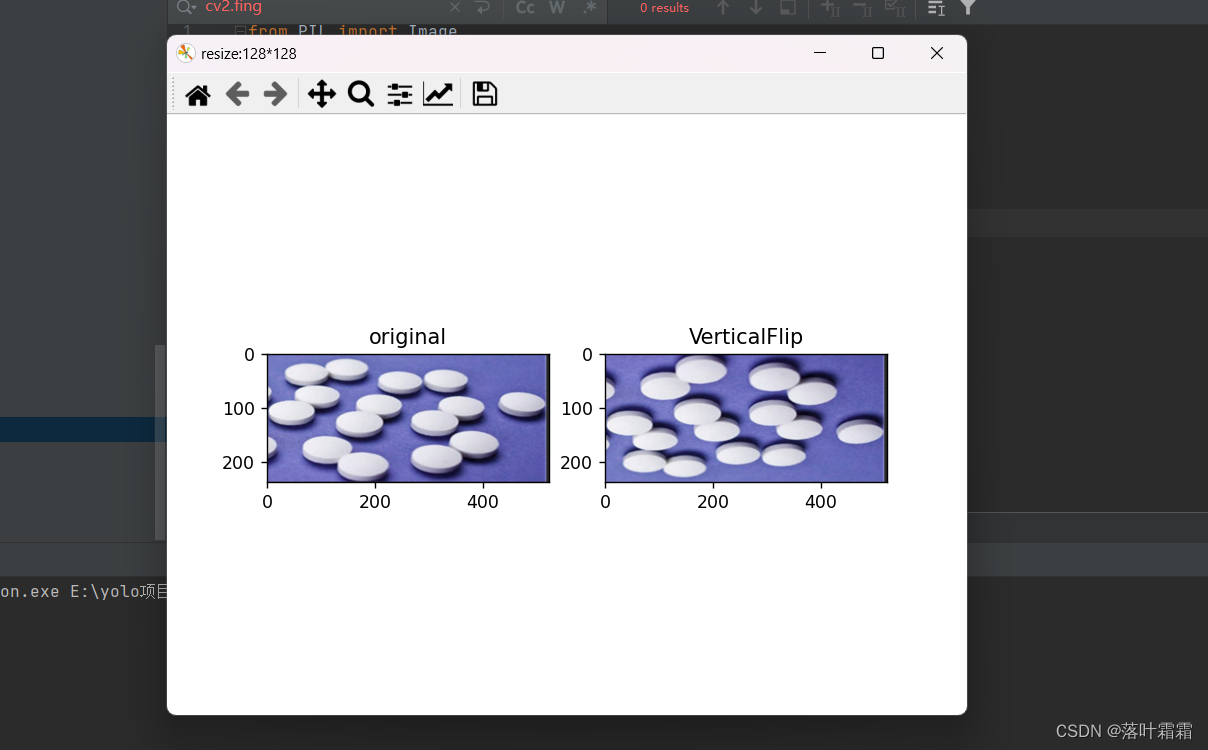
垂直翻转
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) VerticalFlip_img = [T.RandomVerticalFlip(p=1)(orig_img)] plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.set_title('VerticalFlip') ax2.imshow(np.array(VerticalFlip_img[0])) # ax3 = plt.subplot(133) # ax3.set_title('sigma=7') # ax3.imshow(np.array(blurred_imgs[1])) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
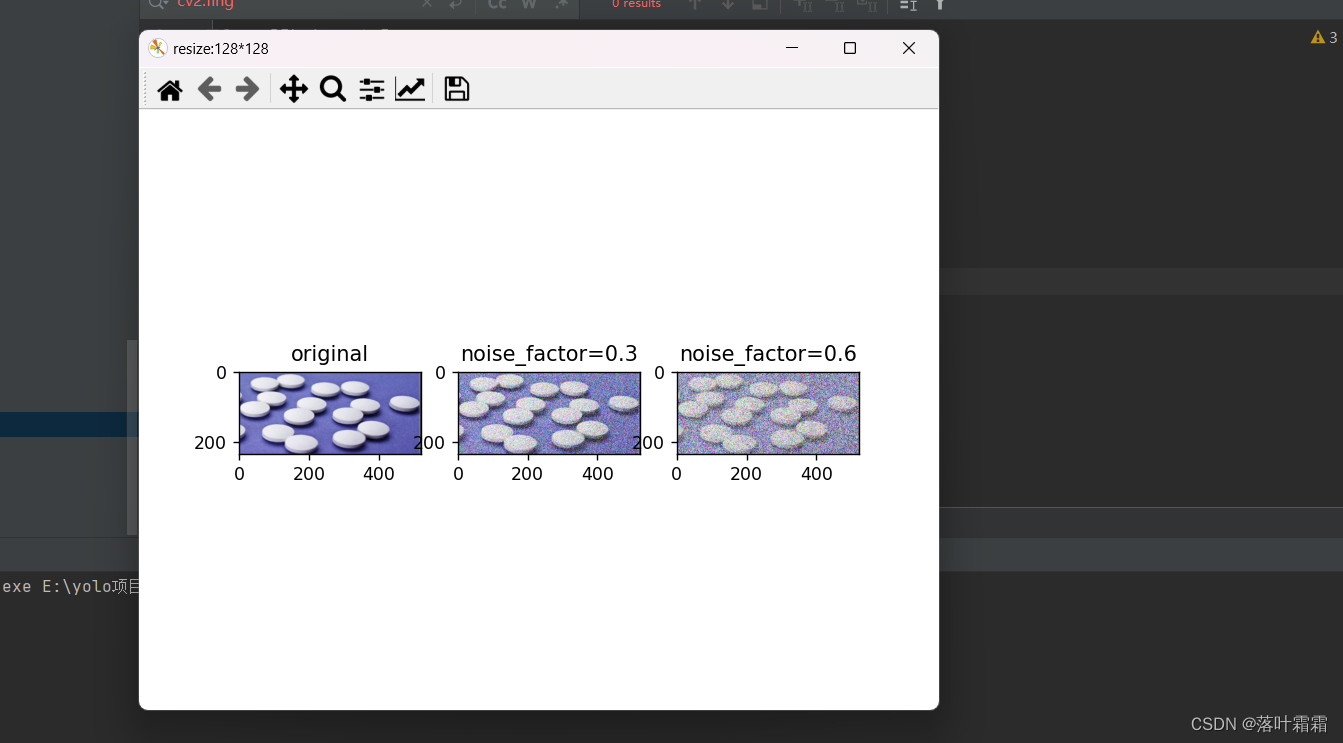
高斯噪声
向图像中加入高斯噪声。通过设置噪声因子,噪声因子越高,图像的噪声越大
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) def add_noise(inputs, noise_factor=0.3): noisy = inputs + torch.randn_like(inputs) * noise_factor noisy = torch.clip(noisy, 0., 1.) return noisy noise_imgs = [add_noise(T.ToTensor()(orig_img), noise_factor) for noise_factor in (0.3, 0.6)] noise_imgs = [T.ToPILImage()(noise_img) for noise_img in noise_imgs] plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(131) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(132) ax2.set_title('noise_factor=0.3') ax2.imshow(np.array(noise_imgs[0])) ax3 = plt.subplot(133) ax3.set_title('noise_factor=0.6') ax3.imshow(np.array(noise_imgs[1])) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
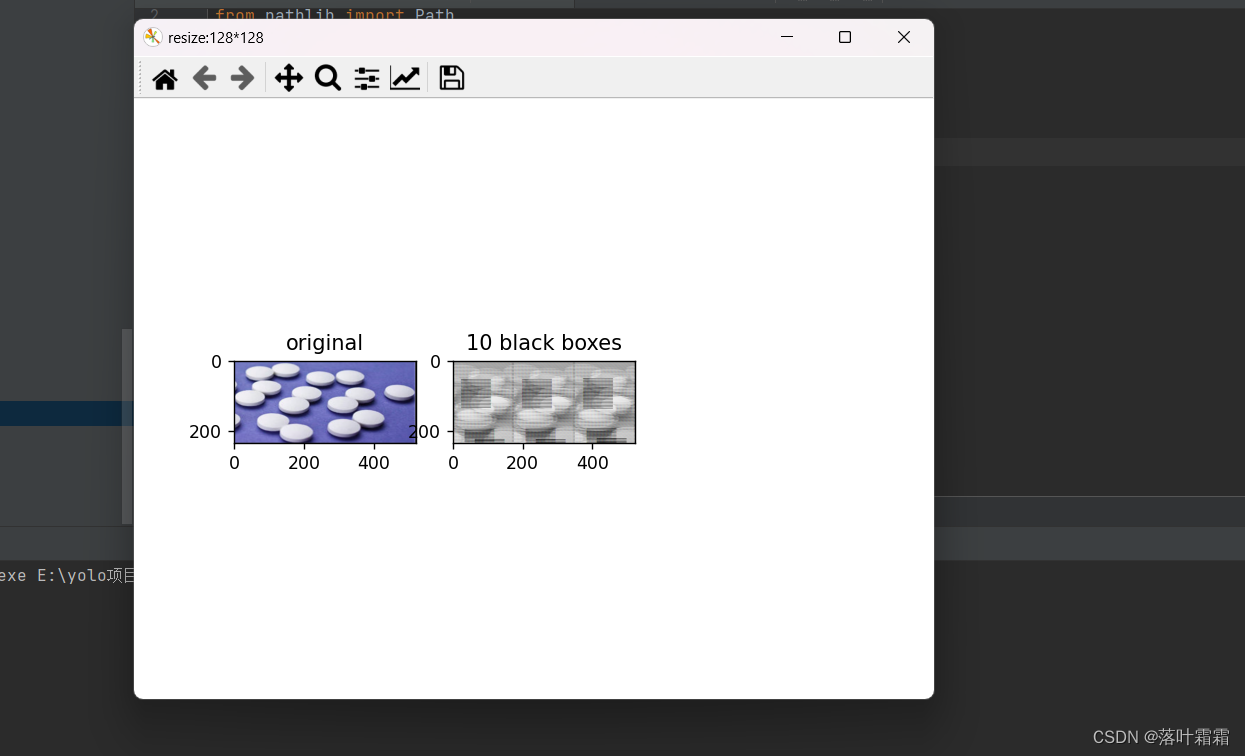
随机块
正方形补丁随机应用在图像中。这些补丁的数量越多,神经网络解决问题的难度就越大
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) def add_random_boxes(img,n_k,size=64): h,w = size,size img = np.asarray(img).copy() img_size = img.shape[1] boxes = [] for k in range(n_k): y,x = np.random.randint(0,img_size-w,(2,)) img[y:y+h,x:x+w] = 0 boxes.append((x,y,h,w)) img = Image.fromarray(img.astype('uint8'), 'RGB') return img blocks_imgs = [add_random_boxes(orig_img,n_k=10)] plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(131) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(132) ax2.set_title('10 black boxes') ax2.imshow(np.array(blocks_imgs[0])) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
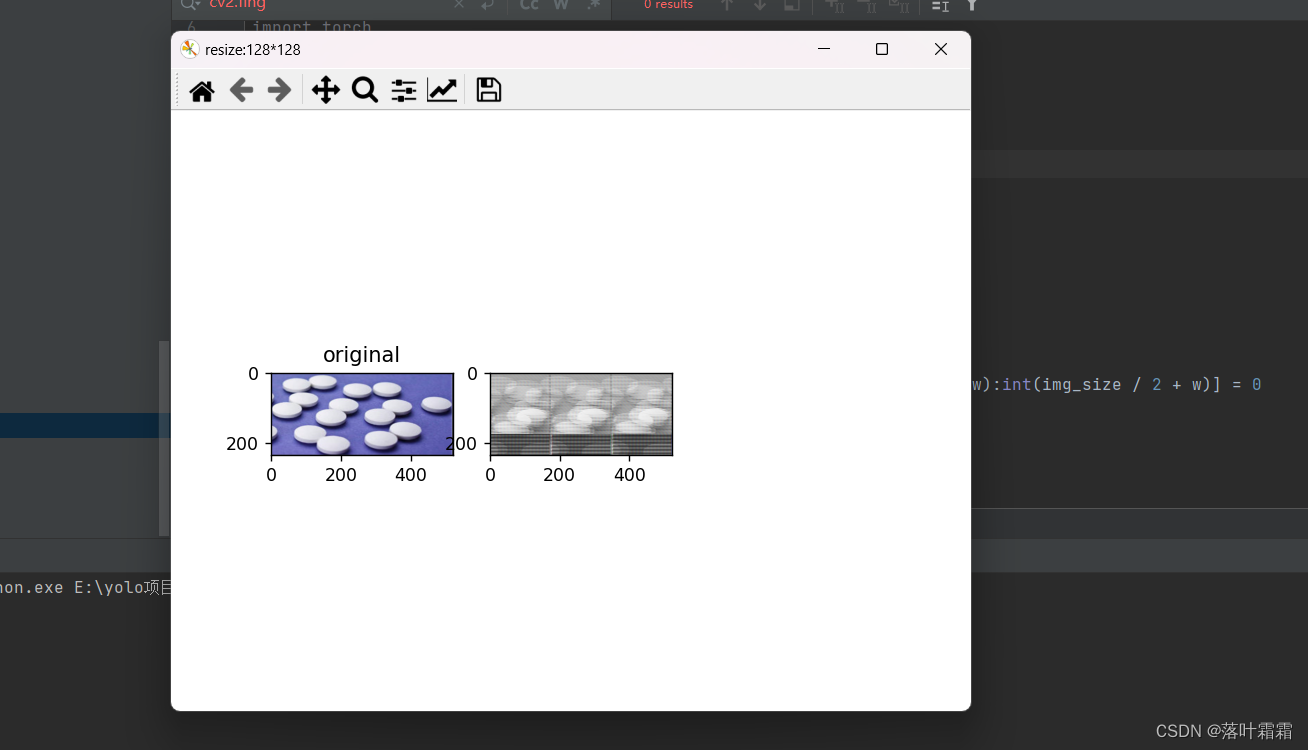
中心区域
和随机块类似,只不过在图像的中心加入补丁。
from PIL import Image from pathlib import Path import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys import torch import numpy as np import torchvision.transforms as T plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight' orig_img = Image.open(Path('img_2.png')) def add_central_region(img, size=32): h, w = size, size img = np.asarray(img).copy() img_size = img.shape[1] img[int(img_size / 2 - h):int(img_size / 2 + h), int(img_size / 2 - w):int(img_size / 2 + w)] = 0 img = Image.fromarray(img.astype('uint8'), 'RGB') return img central_imgs = [add_central_region(orig_img, size=128)] plt.figure('resize:128*128') ax1 = plt.subplot(131) ax1.set_title('original') ax1.imshow(orig_img) ax2 = plt.subplot(132) ax2.set_title('') ax2.imshow(np.array(central_imgs[0])) # # ax3 = plt.subplot(133) # ax3.set_title('20 black boxes') # ax3.imshow(np.array(blocks_imgs[1])) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
-
相关阅读:
《21天精通TypeScript-3》-安装搭建TypeScript开发环境.md
【Redis】springboot整合redis(模拟短信注册)
Java从入门到精通
binutils 2.40 Linker (ld) 官方文档下载
【日积月累】后端刷题日志
版本控制Git
【Docker】redis分片集群搭建:3主3从,容错迁移,扩缩容
使用Navicat将SQL server数据库导入mysql数据库
python数据容器
Redis缓存Key过期原理和内存淘汰策略
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47869094/article/details/133915010