-
计算机竞赛 : 题目:基于深度学习的水果识别 设计 开题 技术
1 前言
Hi,大家好,这里是丹成学长,今天做一个 基于深度学习的水果识别demo
这是一个较为新颖的竞赛课题方向,学长非常推荐!
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
2 开发简介
深度学习作为机器学习领域内新兴并且蓬勃发展的一门学科, 它不仅改变着传统的机器学习方法, 也影响着我们对人类感知的理解,
已经在图像识别和语音识别等领域取得广泛的应用。 因此, 本文在深入研究深度学习理论的基础上, 将深度学习应用到水果图像识别中,
以此来提高了水果图像的识别性能。3 识别原理
3.1 传统图像识别原理
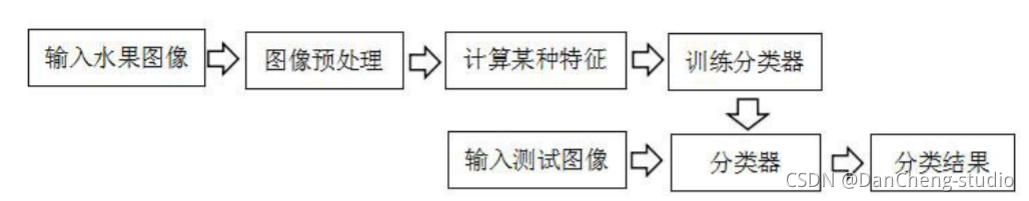
传统的水果图像识别系统的一般过程如下图所示,主要工作集中在图像预处理和特征提取阶段。
在大多数的识别任务中, 实验所用图像往往是在严格限定的环境中采集的, 消除了外界环境对图像的影响。 但是实际环境中图像易受到光照变化、 水果反光、
遮挡等因素的影响, 这在不同程度上影响着水果图像的识别准确率。在传统的水果图像识别系统中, 通常是对水果的纹理、 颜色、 形状等特征进行提取和识别。
3.2 深度学习水果识别
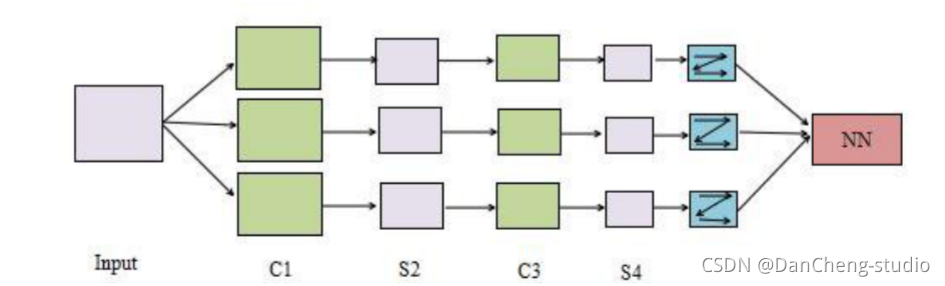
CNN 是一种专门为识别二维特征而设计的多层神经网络, 它的结构如下图所示,这种结构对平移、 缩放、 旋转等变形具有高度的不变性。
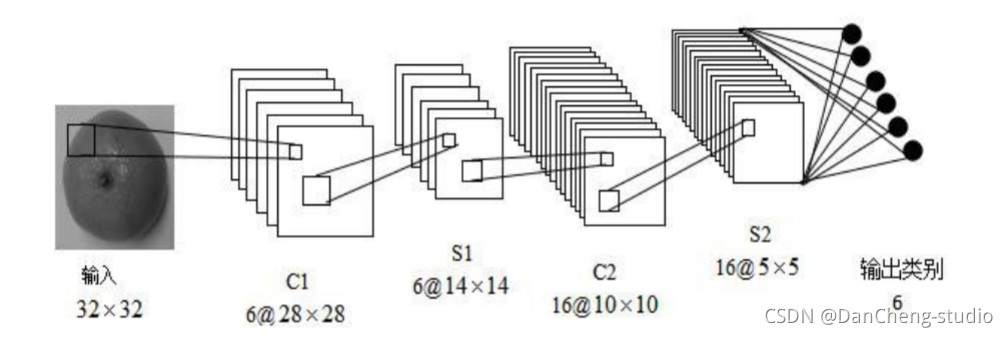
学长本次采用的 CNN 架构如图:
4 数据集
-
数据库分为训练集(train)和测试集(test)两部分
-
训练集包含四类apple,orange,banana,mixed(多种水果混合)四类237张图片;测试集包含每类图片各两张。图片集如下图所示。
-
图片类别可由图片名称中提取。
训练集图片预览
测试集预览

数据集目录结构
5 部分关键代码
5.1 处理训练集的数据结构
import os import pandas as pd train_dir = './Training/' test_dir = './Test/' fruits = [] fruits_image = [] for i in os.listdir(train_dir): for image_filename in os.listdir(train_dir + i): fruits.append(i) # name of the fruit fruits_image.append(i + '/' + image_filename) train_fruits = pd.DataFrame(fruits, columns=["Fruits"]) train_fruits["Fruits Image"] = fruits_image print(train_fruits)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
5.2 模型网络结构
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, img_to_array, load_img from glob import glob from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Activation, Dropout, Flatten, Dense img = load_img(train_dir + "Cantaloupe 1/r_234_100.jpg") plt.imshow(img) plt.axis("off") plt.show() array_image = img_to_array(img) # shape (100,100) print("Image Shape --> ", array_image.shape) # 131个类目 fruitCountUnique = glob(train_dir + '/*' ) numberOfClass = len(fruitCountUnique) print("How many different fruits are there --> ",numberOfClass) # 构建模型 model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(32,(3,3),input_shape = array_image.shape)) model.add(Activation("relu")) model.add(MaxPooling2D()) model.add(Conv2D(32,(3,3))) model.add(Activation("relu")) model.add(MaxPooling2D()) model.add(Conv2D(64,(3,3))) model.add(Activation("relu")) model.add(MaxPooling2D()) model.add(Flatten()) model.add(Dense(1024)) model.add(Activation("relu")) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) # 区分131类 model.add(Dense(numberOfClass)) # output model.add(Activation("softmax")) model.compile(loss = "categorical_crossentropy", optimizer = "rmsprop", metrics = ["accuracy"]) print("Target Size --> ", array_image.shape[:2]) ##- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
5.3 训练模型
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale= 1./255, shear_range = 0.3, horizontal_flip=True, zoom_range = 0.3) test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale= 1./255) epochs = 100 batch_size = 32 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( train_dir, target_size= array_image.shape[:2], batch_size = batch_size, color_mode= "rgb", class_mode= "categorical") test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory( test_dir, target_size= array_image.shape[:2], batch_size = batch_size, color_mode= "rgb", class_mode= "categorical") for data_batch, labels_batch in train_generator: print("data_batch shape --> ",data_batch.shape) print("labels_batch shape --> ",labels_batch.shape) break hist = model.fit_generator( generator = train_generator, steps_per_epoch = 1600 // batch_size, epochs=epochs, validation_data = test_generator, validation_steps = 800 // batch_size) #保存模型 model_fruits.h5 model.save('model_fruits.h5')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
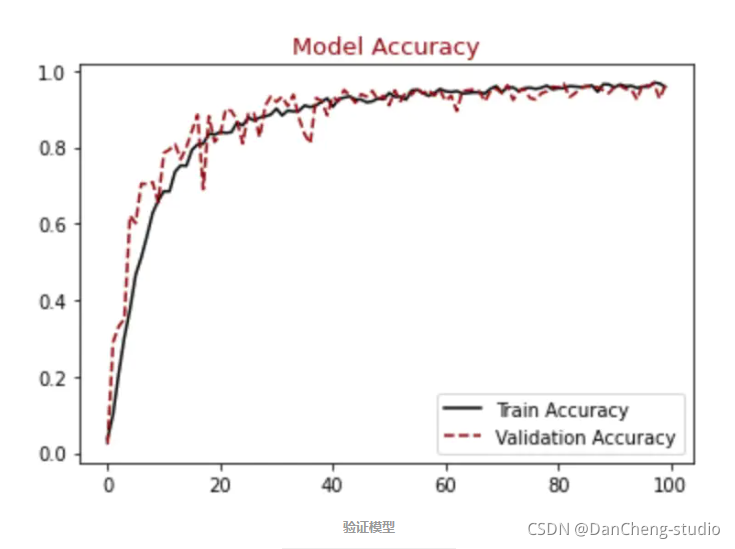
顺便输出训练曲线
#展示损失模型结果 plt.figure() plt.plot(hist.history["loss"],label = "Train Loss", color = "black") plt.plot(hist.history["val_loss"],label = "Validation Loss", color = "darkred", linestyle="dashed",markeredgecolor = "purple", markeredgewidth = 2) plt.title("Model Loss", color = "darkred", size = 13) plt.legend() plt.show() #展示精确模型结果 plt.figure() plt.plot(hist.history["accuracy"],label = "Train Accuracy", color = "black") plt.plot(hist.history["val_accuracy"],label = "Validation Accuracy", color = "darkred", linestyle="dashed",markeredgecolor = "purple", markeredgewidth = 2) plt.title("Model Accuracy", color = "darkred", size = 13) plt.legend() plt.show() 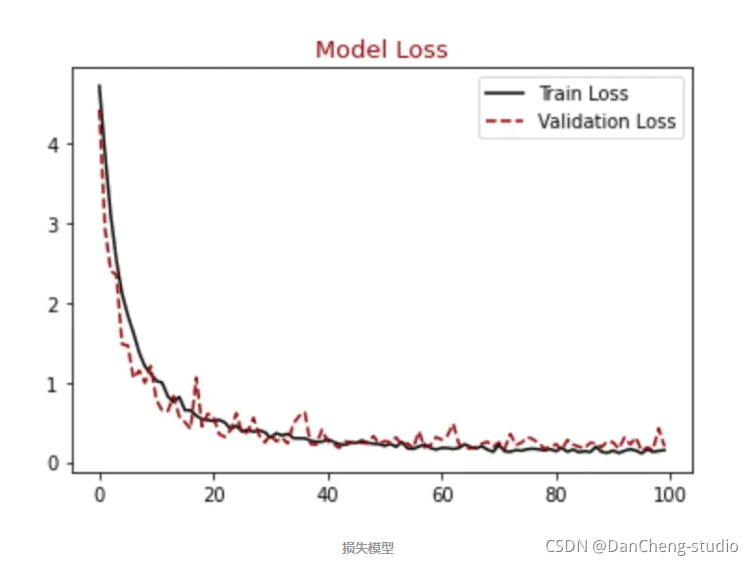- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
6 识别效果
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model import os import pandas as pd from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator,img_to_array, load_img import cv2,matplotlib.pyplot as plt,numpy as np from keras.preprocessing import image train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale= 1./255, shear_range = 0.3, horizontal_flip=True, zoom_range = 0.3) model = load_model('model_fruits.h5') batch_size = 32 img = load_img("./Test/Apricot/3_100.jpg",target_size=(100,100)) plt.imshow(img) plt.show() array_image = img_to_array(img) array_image = array_image * 1./255 x = np.expand_dims(array_image, axis=0) images = np.vstack([x]) classes = model.predict_classes(images, batch_size=10) print(classes) train_dir = './Training/' train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( train_dir, target_size= array_image.shape[:2], batch_size = batch_size, color_mode= "rgb", class_mode= "categorical”) print(train_generator.class_indices)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33

fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 16)) axes = [] files = [] predictions = [] true_labels = [] rows = 5 cols = 2 # 随机选择几个图片 def getRandomImage(path, img_width, img_height): """function loads a random image from a random folder in our test path""" folders = list(filter(lambda x: os.path.isdir(os.path.join(path, x)), os.listdir(path))) random_directory = np.random.randint(0, len(folders)) path_class = folders[random_directory] file_path = os.path.join(path, path_class) file_names = [f for f in os.listdir(file_path) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(file_path, f))] random_file_index = np.random.randint(0, len(file_names)) image_name = file_names[random_file_index] final_path = os.path.join(file_path, image_name) return image.load_img(final_path, target_size = (img_width, img_height)), final_path, path_class def draw_test(name, pred, im, true_label): BLACK = [0, 0, 0] expanded_image = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, 160, 0, 0, 300, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=BLACK) cv2.putText(expanded_image, "predicted: " + pred, (20, 60), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.85, (255, 0, 0), 2) cv2.putText(expanded_image, "true: " + true_label, (20, 120), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.85, (0, 255, 0), 2) return expanded_image IMG_ROWS, IMG_COLS = 100, 100 # predicting images for i in range(0, 10): path = "./Test" img, final_path, true_label = getRandomImage(path, IMG_ROWS, IMG_COLS) files.append(final_path) true_labels.append(true_label) x = image.img_to_array(img) x = x * 1./255 x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0) images = np.vstack([x]) classes = model.predict_classes(images, batch_size=10) predictions.append(classes) class_labels = train_generator.class_indices class_labels = {v: k for k, v in class_labels.items()} class_list = list(class_labels.values()) for i in range(0, len(files)): image = cv2.imread(files[i]) image = draw_test("Prediction", class_labels[predictions[i][0]], image, true_labels[i]) axes.append(fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i+1)) plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) plt.grid(False) plt.axis('off') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55

7 最后
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
-
-
相关阅读:
python编程难在哪里?
Servlet
关于Springboot的@Profile的写法以及多个profile的写法排坑(“!profile1 && !profile2“ 的写法)
JVM关闭与关闭钩子 Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook() 作用以及相关注意事项
KEGG通路图绘制 | ggpathway包
《论文阅读》Generating Responses with a Specific Emotion in Dialog
吴恩达机器学习课程笔记二
Linux下用rm误删除文件的三种恢复方法
学习Java的第二十一天。。。(接口)
基于java的滑雪场学具租赁管理系统计算机毕业设计源码+系统+lw文档+mysql数据库+调试部署
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_43533/article/details/133701299
