-
Spring的AOP开发-AOP简介
目录
AOP简介
AOP概念
- AOP,Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程,是对面向对象编程OOP的生化,OOP是纵向对一个事务的抽象,一个对象包括静态的信息属性,包括动态的方法信息等。而AOP是横向对不同事务的抽象,属性与属性(多个对象的属性进行抽取)、方法与方法(多个对象的方法进行抽取)、对象与对象(多个对象进行抽取)都可成为一个切面,而用这种思维去设计编程的方法叫做面向切面编程。
AOP思想的实现方案
- 动态代理技术(Proxy),在运行期间,对目标对象的方法进行增强,代理对象同名方法内可以执行原有逻辑的同时嵌入执行其它增强逻辑或其它对象的方法,关于proxy代理的文章,可参考:Java高级-代理(proxy)-CSDN博客
模拟AOP的基础代码
- 在Spring框架中对于bean对象的增强主要是通过后处理器使用AOP思想来进行实现的,在后处理器中使用代理对象对目标对象进行增强,然后将增强后的代理对象放入单例池中。
- 具体的示例代码如下
-
- package com.example.Processor;
- import com.example.advice.MyAdvice;
- import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
- import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
- import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
- import java.lang.reflect.Method;
- import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
- @Component
- public class MockAopBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
- private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
- @Override
- public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
- // 目的:对UserServiceImpl中的show1和show2方法进行增强,增强的方法存在于MyAdvice中
- // 问题:设定增强范围(判断语句)、如何获取MyAdvice(从Spring容器中获取)
- if (bean.getClass().getPackage().getName().equals("com.example.Service.ServiceImpl")) {
- // 生成当前Bean的Proxy对象
- Object beanProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
- bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
- bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
- (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) -> {
- // 执行增强对象的before方法
- MyAdvice myAdvice = applicationContext.getBean(MyAdvice.class);
- myAdvice.beforeAdvice();
- // 执行目标对象的目标方法
- Object result = method.invoke(bean, args);
- // 执行增强对象的after方法
- myAdvice.afterAdvice();
- return result;
- }
- );
- return beanProxy;
- }
- return bean;
- }
- @Override
- public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
- this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
- }
- }
上述代码是实现bean对象增强的核心过程,指定了需要增强bean对象的范围,以及具体的增强逻辑。实现的两个接口作用具体参照文章:SpringBean的生命周期-CSDN博客
- 目标对象
-
- package com.example.Service.ServiceImpl;
- import com.example.Service.UserService;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
- @Service
- public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
- @Override
- public void show1() {
- System.out.println("show1.....");
- }
- @Override
- public void show2() {
- System.out.println("show2.....");
- }
- }
-
-
通知类
-
- package com.example.advice;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
- // 自定义增强类,内部提供增强方法
- @Component("myAdvice")
- public class MyAdvice {
- public void beforeAdvice() {
- System.out.println("前置增强");
- }
- public void afterAdvice() {
- System.out.println("后置增强");
- }
- }
-
-
测试类
-
- package com.example.Test;
- import com.example.Service.UserService;
- import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
- import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
- public class TestMyAOP {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
- UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
- userService.show1();
- }
- }
-
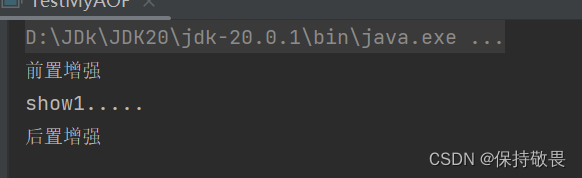
- 运行结果
-
ps:在上述举例代码中,我是在Spring框架下使用注解的的方式进行bean对象的注册,同时需要在配置文件中设置组件扫描的范围,以此让注解进行生效
 当然你也可以使用xml配置文件的方式,将对应类的bean对象交给Spring容器管理,具体如何实现可以参考我的往期Spring注解开发、基于Xml方式配置Bean的相关文章
当然你也可以使用xml配置文件的方式,将对应类的bean对象交给Spring容器管理,具体如何实现可以参考我的往期Spring注解开发、基于Xml方式配置Bean的相关文章AOP相关概念
-
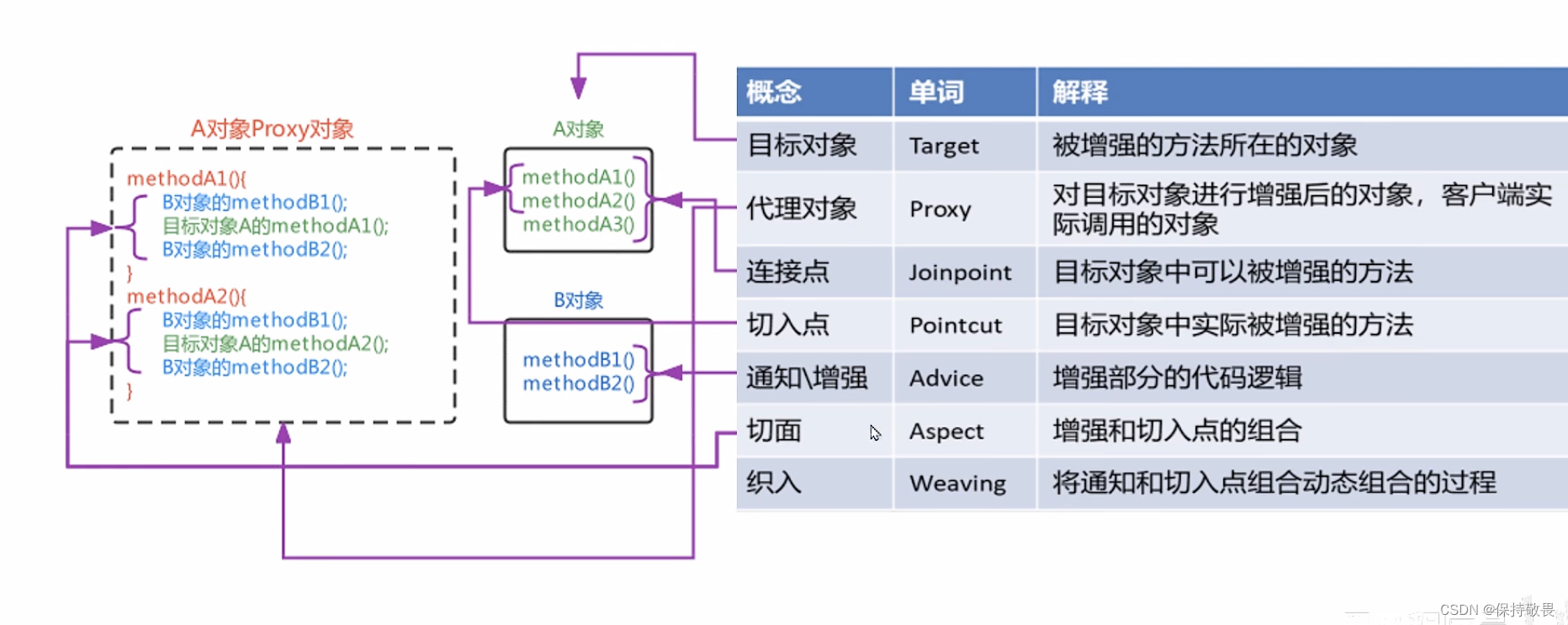
概念 描述 切面(Aspect) 增强和切入点的代码组合 连接点(Joinpoint) 目标对象可以被增强的方法 通知/增强(Advice) 增强部分的代码逻辑 切点(切入点)(Pointcut) 目标对象中实际被增强的方法,连接点包括切点。 引入(Introduction) 在不修改类代码的前提下,引入新的接口和功能。 织入(Weaving) 把切面(增强和切入点代码的组合)应用到目标对象并创建新的代理对象的过程。 目标对象(Target Object) 被增强的方法所在的对象 代理对象(Proxy) 对目标对象增强后的对象,客户端实际调用的对象
-
相关阅读:
架构漫谈 - 如何设计高性能、高可用、高扩展架构
每日三题 11.01
【论文粗读】(NeurIPS 2020) SwAV:对比聚类结果的无监督视觉特征学习
Angular 依赖注入介绍及使用(五)
【C++指针】函数返回指针类型 与 函数返回英语类型(关于获取局部变量的操作)
我的周刊(第045期)
Mybatis入门实战
【译】我为 .NET 开发人员准备的 2023 年 Visual Studio 10 大新功能
Android 10.0 11.0 12.0 启动模拟器教程
会员一卡通是什么?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64939936/article/details/133525856