-
[C++随想录] 优先级队列的模拟实现
底层结构
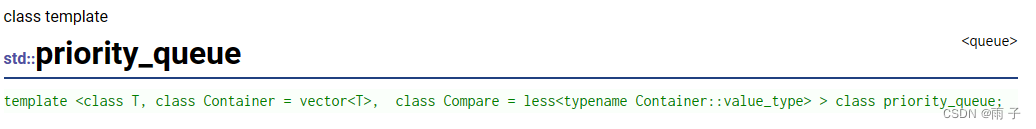
namespace muyu { template <class T, class Continer = std::vector<T>, class Compare = less<T> > class priority_queue { private: Continer _con; // 底层维护的容器 }; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
在库中, priority_queue是有三个模版参数的,
T — — 控制数据类型
Container — — 容器适配器
Compare — — 仿函数, 控制大小堆的那么有两个问题:
- Container 为啥默认是vector, 而不是 deque呢?
通过前面数据结构的学习, 我们知道堆是支持随机访问的, 即支持下标访问, []会用的很频繁的
list不用说了, 不支持下标访问
deque虽然支持下标访问, 但[] 不够极致 ⇐ 需要计算在哪个buff中, 还要计算在该buff数组中的哪个位置上
而反观vector,它的[] 就很极致 ⇐ 连续的空间 - 仿函数是啥?
其实, 前面讲sort时, 提过一下仿函数.
仿函数就是仿函数通过重载(), 从而达到类的对象可以像函数一样使用👇👇👇
template<class T> class Com { public: bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) { return x > y; } }; int main() { Com<int> com; // 类对象 int a = 5, b = 3; bool res = com(a, b); cout << res << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
运行结果:
1- 1

👇👇👇class Date { public: Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1) : _year(year) , _month(month) , _day(day) {} bool operator<(const Date& d)const { return (_year < d._year) || (_year == d._year && _month < d._month) || (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day); } bool operator>(const Date& d)const { return (_year > d._year) || (_year == d._year && _month > d._month) || (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day); } friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d) { _cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day; return _cout; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; template<class T> class Com { public: bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) { return x > y; } }; int main() { Com<Date> com; // 类对象 Date d1(2023, 7, 20); Date d2(2023, 7, 26); bool res = com(d1, d2); cout << res << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
运行结果:
0- 1
当然
仿函数作为泛型编程, 在后面模版的特化中还有很多意想不到的妙用!!
🗨️ 如果上面的传的是Date*, 那该怎么办?void test() { muyu::priority_queue<Date*> pq; pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 27)); pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 28)); pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 29)); pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 1)); while (!pq.empty()) { cout << *pq.top() << " "; pq.pop(); } cout << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行结果:
2023-9-1 2023-9-28 2023-9-27 2023-9-29- 1
- 如果传的的是
Date*, 编译器的less会按照地址的大小去比较, 这并不是我们想要的结果
我们想要的是日期之间的比较
由于是内置类型, 我们又重载不了!!!
那该怎么办?
模版的特化就大显身手了👇👇👇
// 普通的按照T来进行比较 template <class T> class Less { public: bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) { return x < y; } }; // 偏特化 -- 对类型做进一步的限制 template <class T> class Less<T*> { public: bool operator()(const T* x, const T* y) { return *x < *y; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
特化, 特化, 就是
对此模版做进一步的特殊化处理
如上面的代码, 我们就针对了指针做了特殊处理 – -->按照指针指向的对象来进行比较
初始化
默认初始化咱就不说了,
底层的容器 vector 是自定义类型, 它本身的初始化就够用了
下面, 我们重点讲讲迭代区间初始化priority_queue() { } template<class InputIterator> priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) { // 一股脑地倒进来 while (first != last) { _con.push_back(*first); ++first; } // 建堆 for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AjustDown(i); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
注意几个点:
- 区间是左闭右开的
- 向下调整算法的前提条件是
左右子树都是大(小)堆⇒从第一个非叶子节点开始
向下调整 && 向上调整
private: void AjustUp(int child) { Compare com; int parent = (child - 1) / 2; while (child > 0) { if( com(_con[parent], _con[child]) ) { std::swap(_con[child], _con[parent]); // 在内部更新child 和 parent child = parent; parent = (child - 1) / 2; } else { break; } } } void AjustDown(int parent) { Compare com; int child = 2 * parent + 1; while (child < _con.size()) { // 找到孩子中大的那一个 if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]) ) { child++; } if ( com(_con[parent], _con[child])) { std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]); // 在内部更新parent 和 child parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 默认是
大堆, 即less,<

push && pop
- push
void push(const T& val = T()) { _con.push_back(val); AjustUp(_con.size() - 1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
堆的整体结构并没有发生变化, 即
左右子树都是大(小)堆⇒ 使用向上调整- pop
(1) 删除头节点 ⇒ 交换头尾节点, 删除尾节点
(2) 头节点的 左右子树的堆结构没有发生变化, 但是头节点有问题 ⇒ 从头节点开始向下调整
void pop() { std::swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]); _con.pop_back(); AjustDown(0); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
top && empty && size
const T& top() const { return _con[0]; } bool empty() const { return _con.size() == 0; } size_t size() const { return _con.size(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
源码
# pragma once #includenamespace muyu { template <class T, class Continer = std::vector<T>, class Compare = less<T> > class priority_queue { private: void AjustUp(int child) { Compare com; int parent = (child - 1) / 2; while (child > 0) { if( com(_con[parent], _con[child]) ) { std::swap(_con[child], _con[parent]); // 在内部更新child 和 parent child = parent; parent = (child - 1) / 2; } else { break; } } } void AjustDown(int parent) { Compare com; int child = 2 * parent + 1; while (child < _con.size()) { // 找到孩子中大的那一个 if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]) ) { child++; } if ( com(_con[parent], _con[child])) { std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } } } public: priority_queue() { } template<class InputIterator> priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) { // 一股脑地倒进来 while (first != last) { _con.push_back(*first); ++first; } // 建堆 for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AjustDown(i); } } void push(const T& val = T()) { _con.push_back(val); AjustUp(_con.size() - 1); } void pop() { std::swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]); _con.pop_back(); AjustDown(0); } const T& top() const { return _con[0]; } bool empty() const { return _con.size() == 0; } size_t size() const { return _con.size(); } private: Continer _con; }; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
夫学贵得之于心。求之于心而非也,虽其言之出于孔子,不敢以为是也,而况其未及孔子者乎?求之于心而是也,虽其言出于庸常,不敢以为非也,而况其出于孔子者乎? — — 王阳明
-
相关阅读:
pytorch深度学习实战lesson17
windows10系统安装nvm切换电脑node版本
系统性详解Redis操作Hash类型数据(带源码分析及测试结果)
运维-技能大杂烩
react-demo项目:支持使用scss(不使用create-react-app脚手架)
.NET异步编程模式(四)-TAP
含文档+PPT+源码等]精品springboot的二手车管理系统vue[包运行成功]Java毕业设计SSM项目源码
react-native渲染富文本的几种方案
实战型开发2/3--架构设计
xorm源码学习
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_67549203/article/details/133407022
