-
Python实用技术二:数据分析和可视化(2)
目录
Series是一维表格,每个元素带标签且有下标,兼具列表和字典的访问形式
DataFrame是带行列标签的二维表格,每一列都是一个Series
一,多维数组库numpy
➢多维数组库,创建多维数组很方便,可以替代多维列表
➢速度比多维列表快
➢支持向量和矩阵的各种数学运算
➢所有元素类型必须相同1,操作函数:

- import numpy as np #以后numpy简写为np
- print (np.array([1,2,3]) ) #>>[1 2 3]
- print (np. arange(1,9,2) ) #>>[13 5 7]
- print (np. linspace(1,10,4)) #>>[ 1. 4. 7. 10. ]
- print (np . random. randint (10,20, [2,3]) )
- #>>[[12 19 12]
- #>> [19 13 10 ]]
- print (np . random. randint (10,20,5) ) #>> [12 19 19 10 13]
- a = np. zeros (3)
- print (a)
- #>>[ 0. 0. 0.]
- print(list(a) )
- #>>[0.0,0.0,0.0]
- a = np. zeros((2 ,3) ,dtype=int) #创建- t个2行3列的元素都是整数0的数组
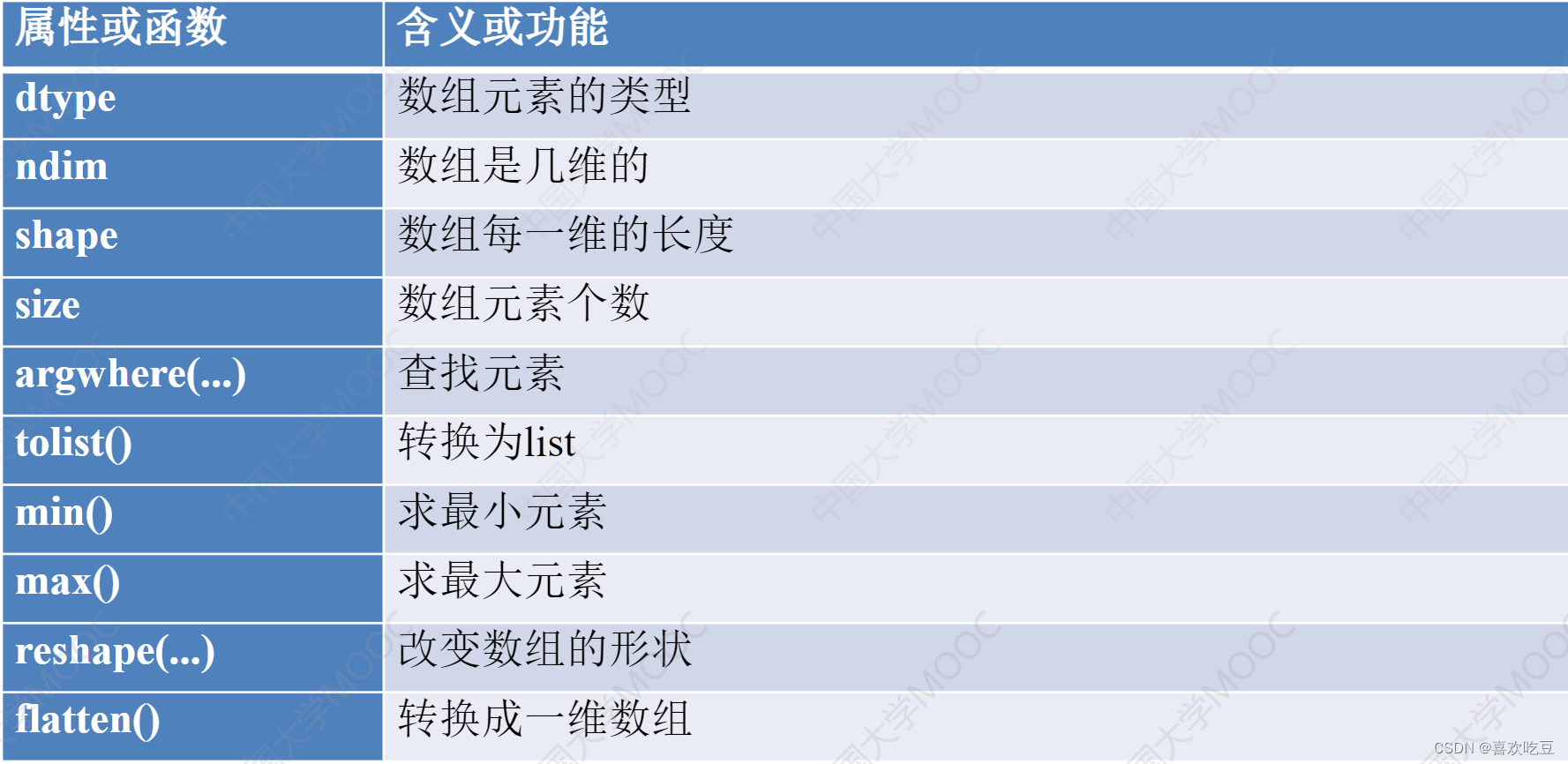
- import numpy as np
- b = np.array([i for i in range (12) ])
- #b是[ 0 1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
- a = b.reshape( (3,4) )
- #转换成3行4列的数组,b不变
- print (len(a) )
- #>>3 a有3行
- print(a. size )
- #>>12 a的元素个数是12
- print (a. ndim)
- #>>2 a是2维的
- print (a. shape)
- #>>(3, 4) a是3行4列
- print (a. dtype)
- #>>int32 a的元素类型 是32位的整数
- L = a.tolist ()
- #转换成列表,a不变
- print (L)
- #>>[[0,1,2,3],[4,5,6,7],[8,9,10,11]]
- b = a. flatten ()
- #转换成一维数组
- print (b)
- #>>[0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
2,numpy数组元素增删
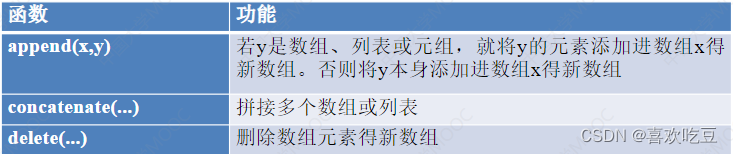
numpy数组一旦生成,元素就不能增删。上面 函数返回一个新的数组。
1)添加数组元素
- import numpy as np
- a = np.array((1,2,3) )
- #a是[123]
- b = np. append(a,10)<
- #a不会发生变化
- print (b)
- #>>[1 2 3 10]
- print (np. append(a, [10,20] ) )
- #>>[1 2 3 10 20]
- C=np. zeros ( (2,3) , dtype=int)
- #c是2行3列的全0数组
- print (np. append(a,c) )
- #>>[1 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0]
- print (np. concatenate( (a, [10,20] ,a)) )
- #>>[1 2 3 10 20 1 2 3]
- print (np. concatenate( (C, np. array([[10 ,20,30]] ) ) ) )
- #c拼接一行[10, 20 ,30]得新数组
- print (np. concatenate( (C, np.array([[1,2], [10,20]])) ,axis=1) )
- #c的第0行拼接了1,2两个元素、第1行拼接了10 , 20两个新元素后得到新数组
2)numpy删除数组元素
- import numpy as np
- a = np.array((1,2,3,4) )
- b = np.delete(a,1) #删除a中下标为1的元素, a不会改变
- print (b)
- #>>[1_ 3 4]
- b = np.array([[1,2,3,4] ,[5,6, 7,8], [9,10,11,121])
- print (np. delete (b,1 ,axis=0) )
- #删除b的第1行得新数组
- #>>[[1 2 3 4]
- #>>[9 10 11 12]]
- print (np. delete (b,1 ,axis=1) )
- #删除b的第1列得新数组
- print (np. delete (b,[1,2] ,axis=0) )
- #删除b的第1行和第2行得新数组
- print (np. delete (b,[1,3] ,axis=1) )
- #删除b的第1列和第3列得新数组
3)在numpy数组中查找元素
- import numpy as np
- a = np.array( (1,2,3,5,3,4) )
- pos = np. argwhere(a==3)
- #pos是[[2] [4] ]
- a = np.array([[1,2,3] , [4,5,2]])
- print(2 in a)
- #>>True
- pos = np. argwhere(a==2)
- #pos是[[0 1] [1 2]]
- b = a[a>2]
- #抽取a中大于2的元素形成一个一维数组
- print (b)
- #>>[3 4 5]
- a[a>2]=-1
- #a变成[[12-1][-1-12]]
4)numpy数组的数学运算
- import numpy as np
- a = np.array( (1,2,3,4) )
- b=a+1
- print (b)
- #>>[2 3 4 5]
- print (a*b)
- #>>[2 6 12 20] a,b对应元素相乘
- print (a+b)
- #>>[3579]a,b对应元素相加
- c = np.sqrt(a*10) #a*10是[10 20 30 40]
- print(c)
- #>>[ 3. 16227766 4. 47213595 5. 47722558 6.32455532]
3,numpy数组的切片
numpy数组的切片是“视图”,是原数组的一部分,而非一部分的拷贝
- import numpy as np
- a=np.arange(8)
- #a是[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
- b = a[3:6]
- #注意,b是a的一部分
- print (b)
- #>>[3 4 5]
- c = np.copy(a[3:6])
- #c是a的一部分的拷贝
- b[0] = 100
- #会修改a
- print(a)
- #>>[ 0 1 2 100 4 6 7]
- print(c)
- #>>[3 4 5] c不受b影响
- a = np.array([[1,2,3,4] ,[5,6,7,8] , [9,10,11,12] , [13,14,15,16]])
- b = a[1:3,1:4]
- #b是>>[[678][101112]]
二,数据分析库pandas
1,DataFrame的构造和访问
➢核心功能是在二维表格上做各种操作,如增删、修改、求- -列数据的和、方差、中位数、平均数等
➢需要numpy支持
➢如果有openpyxI或xIrd或xIwt支持,还可以读写excel文档。
➢最关键的类: DataFrame,表示二维表格
pandas的重要类:Series
Series是一维表格,每个元素带标签且有下标,兼具列表和字典的访问形式
- import pandas as pd
- s = pd. Series (data=[80, 90,100] , index=['语文', '数学', '英语'])
- for x in s:
- #>>80 90 100
- print(x,end=" ")
- print ("")
- print(s['语文'] ,s[1])
- #>>80 90 标签和序号都可以作为下标来访问元
- print(s[0:2] [ '数学'])
- #>>90 s[0:2]是切片
- print(s['数学': '英语'] [1])
- #>>100
- for i in range (len (s. index) ) :
- #>>语文 数学 英语
- print(s. index[i] ,end = " ")
- s['体育'] = 110
- #在尾部添加元素,标签为'体育',值为110
- s. pop('数学')
- #删除标签为'数学’的元素
- s2 = s. append (pd . Series (120, index = [' 政治'])) #不改变s
- print(s2['语文'] ,s2['政治'])
- #>>80 120
- print (1ist(s2) )
- #>>[80,100, 110, 120]
- print(s.sum() ,s.min() ,s .mean() ,s . median() )
- #>>290 80 96. 66666666667 100.0输出和、 最小值、平均值、中位数>
- print (s . idxmax() ,s. argmax () )
- #>>体育 2 输出最大元素的标签和下标
DataFrame是带行列标签的二维表格,每一列都是一个Series
- import pandas as pd
- pd.set_ option( 'display . unicode.east asian width' , True)
- #输出对齐方面的设置
- scores = [['男' ,108 ,115,97] ,['女' ,115,87,105] , ['女' ,100, 60 ,130]
- ['男' ,112,80,50]]
- names = ['刘一哥,'王二姐’,'张三妹',李四弟'] .
- courses = ['性别', '语文', '数学', '英语']
- df = . pd.DataFrame (data=scores ,index = names , columns = courses)
- print (df)
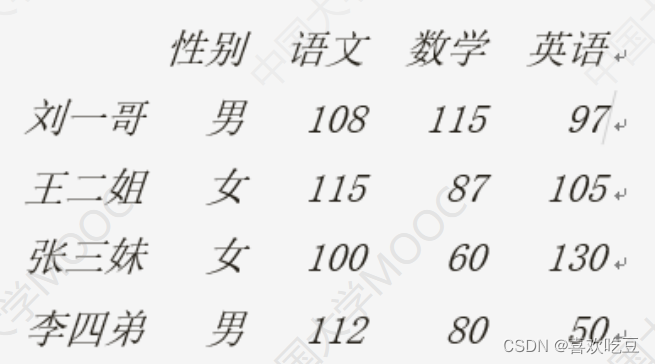
- print (df. values[0] [1] , type (df. values) ) #>>108.
- print (list (df. index) )
- #>>['刘一哥','王二姐','张三妹','李四弟']
- print (list (df. columns) )
- #>>['性别','语文','数学','英语']
- print (df . index[2] ,df . columns[2]) #>>张三妹 数学
- s1 = df['语文']
- #s1是个Series,代表'语文'那一列
- print(s1['刘一哥'] ,s1[0])
- #>>108 108 刘一哥语文成绩
- print(df['语文']['刘一哥'])
- #>>108 列索引先写
- s2 = df.1oc['王二姐']
- #s2也是个Series,代表“王二姐”那一行
- print(s2['性别'] ,s2['语文'] ,s2[2])
- #>>女 115 87 二姐的性别、语文和数学分数
2,DataFrame的切片和统计
- #DataFrame的切片:
- #1loc[行选择器,.列选择器] 用下标做切片
- #Ioc[行选择器,列选择器] 用标签做切片
- #DataFrame的切片是视图
- df2 = df. iloc[1:3] #行切片,是视图,选1 ,2两行
- dt2 = df.1c['王二姐':张三妹'] #和上一行等价
- print (df2)

- df2 = df. i1oc[: ,0:3] #列切片(是视图),选0、1. 2三列
- df2 = df.1oc[:, '性别': '数学'] #和上一行等价
- print (df2)

- df2 = df.i1oc[:2,[1,3]] #行列切片
- df2 = df.1oc[:'王二姐',['语文', '英语']] #和上一行等价
- print (df2)

- df2 = df.i1oc[[1,3] ,2:4] #取第1、3行,第2、3列<
- df2 = df.1oc[['王二姐' , '李四弟'],'数学': '英语'] #和上一行等价
- print (df2)

3,DataFrame的分析统计
- print ("---下面是DataFrame的分析和统计---")
- print (df. T)
- #df . T是df的转置矩阵,即行列互换的矩阵
- print (df . sort_ values ( '语文' , ascending=False)) #按语文成绩降序排列
- print (df.sum() [ '语文'] ,df .mean() ['数学'],df .median() ['英语'])
- #>>435 85.5 101.0语文分数之和、 数学平均分、英语中位数
- print(df .min() ['语文'] ,df .max() ['数学'])
- #>>100 115 语文最低分,数学最高分
- print (df .max(axis = 1)['王二姐'1) #>>115 二姐的最高分科目的分数
- print (df['语文' ] . idxmax() )
- #>>王二姐 语文最高分所在行的标签
- print(df['数学] . argmin())
- #>>2 数学最低分所在行的行号
- print (df.1oc[ (df['语文'] > 100) & (df['数学'] >= 85)])


4,DataFrame的修改增删
- print ("---下面是DataFrame的增删和修改---")
- df.1oc['王二姐', '英语'] = df. iloc[0,1] = 150 #修改王二姐英语和刘一哥语文成绩
- df['物理'] = [80, 70,90,100]
- #为所有人添加物理成绩这-列
- df. insert(1, "体育", [89,77, 76,45])
- #为所有人插入体育成绩到第1列
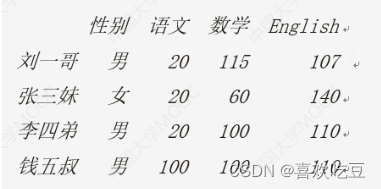
- df.1oc['李四弟'] = ['男' ,100 ,100 ,100 ,100,100] #修改李四弟全部信息
- df.1oc[: , '语文'] = [20,20,20,20]
- #修改所有人语文成绩
- df.1oc[ '钱五叔'] = [ '男' , 100 , 100 ,100, 100 , 100]
- #加一行
- df.1oc[: , '英语'] += 10
- #>>所有人英语加10分
- df. columns = ['性别', '体育', '语文', '数学', 'English', '物理'] #改列标签
- print (df)


- df.drop( ['体育', '物理'] ,axis=1, inplace=True) #删除体育和物理成绩
- df.drop( '王二姐' ,axis = 0,inplace=True)
- #删除王二姐那一行
- print (df)
- df.drop ( [df. index[i] for i in range(1,3) ] ,axis=0 , inplace = True)
- #删除第1,2行
- df .drop( [df . columns[i] for i in range(3) ] ,axis = y 1 , inplace=
- True) #删除第0到2列
5,读写excel和csv文档
➢需要openpyxI(对 .xIsx文件)或xIrd或xIwt支持(老的.xls文件)
➢读取的每张工作表都是一个DataFrame
1)用pandas读excel文档
- import pandas as pd
- pd.set option ( ' display . unicode.east asian width' , True)
- dt = pd. read excel ("'excel sample.xlsx" , sheet name= [ '销售情况' ,1] ,
- index col=0) #读取第0和第1张二工作表
- df =
- dt [ '销售情况']
- #dt是字典,df是DataFrame
- print (df. iloc[0,0] ,df.loc[ 'I睡袋' , '数量'])
- #>>4080 4080
- print (df)

- print (pd. isnu1l (df.1oc['彩盒', '销售额']))
- #>> True
- df . fillna (0 , inplace= =True)
- #将所有NaNa用0替换
- print(df.loc[ '彩盒' , '销售额'] ,df. iloc[2,2] )
- #>>0.0 0.0
df.to excel (filename , sheet_ name="Sheet1" ,na_ rep='',.. ......)
➢将DataFrame对象df中的数据写入exce1文档filename中的"Sheet1"工作表, NaN用' '代替。
➢会覆盖原有的filename文件
➢如果要在一个excel文档中写入多个工作表,需要用ExcelWrite
- # (接.上面程序)
- writer = pd. Exce 1Writer ("new.x1sx")
- #创建ExcelWri ter对象
- df. to exce1 (writer , sheet_ name="S1")
- df.T. to exce1 (writer, sheet_ name="S2")
- #转置矩阵写入
- df.sort_ values( '销售额' , ascending= False) . to exce1 (writer ,
- sheet_ name="S3")
- #按销售额排序的新DataFrame写入工作表s3
- df[ '销售额'] . to excel (writer ,sheet_ name="S4")
- #只写入一列
- writer . save ()
2)用pandas读写csv文件
- df. to_ csv (" result. csv" ,sep=" ," ,na rep= 'NA' ,
- float_ format="号 .2f" , encoding="gbk")
- df = pd. read csv (" result. csv")
三,用matplotlib进行数据展示
1,绘制直方图

- import matp1otlib. pYp1ot as plt #以后plt等价于ma tplotlib . pyplot
- from ma tp1ot1ib import rcParams
- rcParams[ ' font. family'] = rcParams[ ' font. sans-serif'] = ' SimHei '
- #设置中文支持,中文字体为简体黑体
- ax = p1t. figure() .add subp1ot ()
- #建图,获取子图对象ax
- ax.bar(x = (0.2,0.6,0.8,1.2) ,height = (1,2,3,0.5) ,width = 0.1)
- #x表示4个柱子中心横坐标分别是0.2,0.6,0.8,1
- #height表示4个柱子高度分别是1,2,3,0.5
- #width表示柱子宽度0.1
- ax.set_ title ('我的直方图)
- #设置标题
- p1t. show ()
- #显示绘图结果
- 纵向
- ax.bar(x = (0.2,0.6,0.8,1.2) ,height = (1,2,3,0.5) ,width = 0.1)
- 横向
- ax.barh(y = (0.2,0.6,0.8,1.2) ,width = (1,2,3,0.5) ,height = 0.1)

2,绘制堆叠直方图

- import ma tplotlib. pyp1ot as p1t
- ax = plt. figure() . add subp1ot()
- labels = ['Jan' ,'Feb' ,'Mar' ,lApr']
- num1 = [20, 30, 15, 35]
- #Dept1的数据
- num2 = [15, 30,40, 20]
- #Dept2的数据
- cordx = range (len (num1) )
- #x轴刻度位置
- rects1 = ax.bar(x = cordx,height=num1, width=0.5, color=' red' ,
- label="Dept1")
- rects2 = ax.bar(x = cordx, height=num2, width=0 .5,color='green' ,
- label="Dept2",bottom= =num1 )
- ax.set_ y1im(0, 100)
- #y轴坐标范围
- ax. set_ ylabel ("Profit")
- #y轴含义(标签)
- ax. set xticks (cordx )
- #设置x轴刻度位置
- ax. set_ xlabel ("In year 2020")
- #x轴含义(标签)
- ax.set_ title ("My Company")
- ax. legend()
- #在右上角显示图例说明
- p1t. show ()
3,绘制对比直方图(有多组数据)
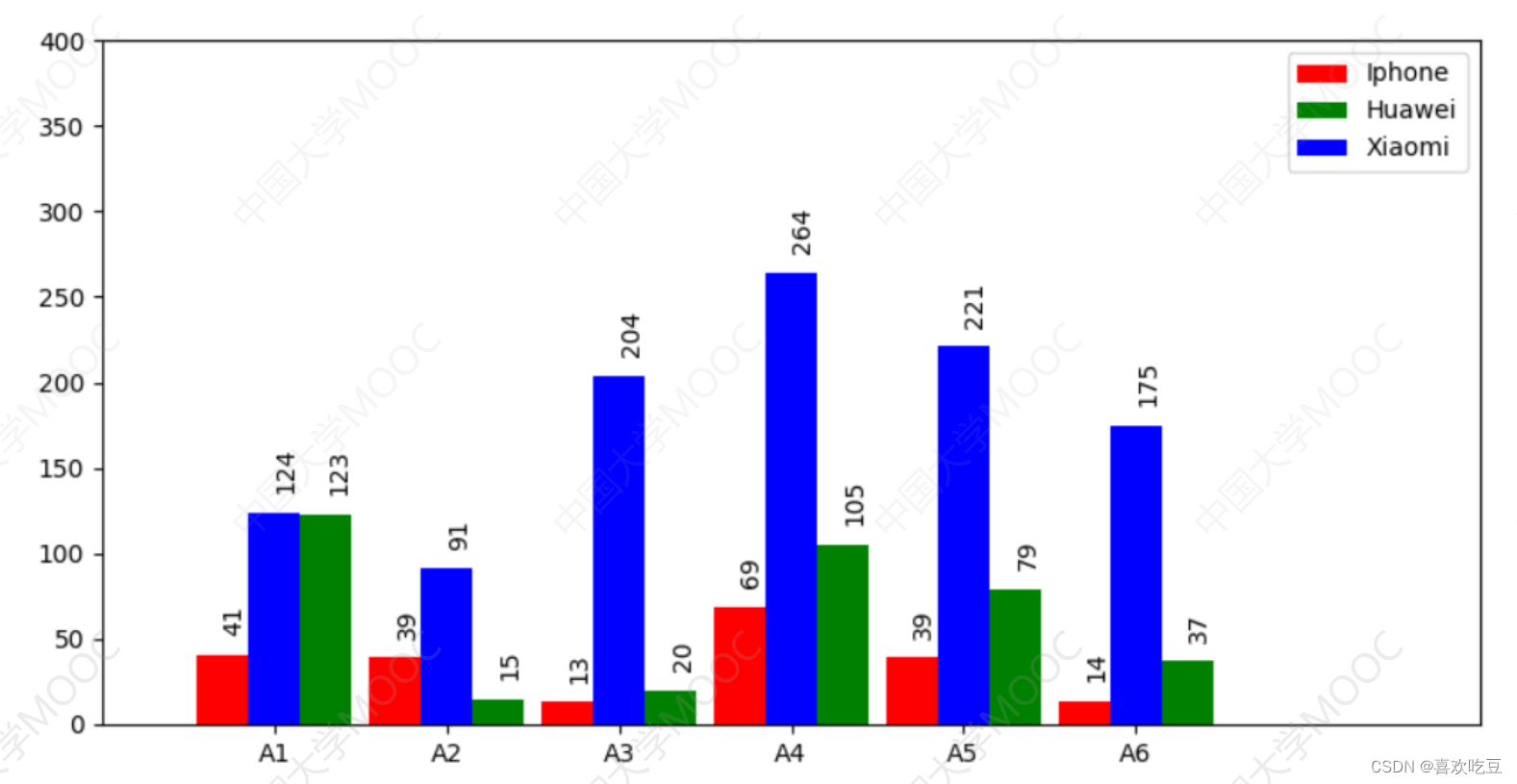
- import matplotlib. pyp1ot as plt
- ax =. plt. figure (figsize= (10,5)) . add_ subplot () #建图,获取子图对象ax
- ax.set ylim(0, 400)
- #指定y轴坐标范围
- ax.set xlim(0, 80)
- #指定x轴坐标范围
- #以下是3组直方图的数据
- x1=[7,17,27,37,47,57]
- #第一-组直方图每个柱子中心点的横坐标
- x2 = [13, 23,33,43, 53,63] #第二组直方图每个柱子中心点的横坐标
- x3 = [10, 20,30,40, 50, 60]
- y1 = [41, 39,13,69,39, 14]
- #第一组直方图每个柱子的高度
- y2 = [123,15, 20,105,79,37] #第二组直方图每个柱子的高度
- y3 = [124,91, 204, 264,221, 175]
- rects1 = ax.bar(x1, y1,facecolor='red' ,width=3, label =_ ' Iphone' )
- rects2 = ax.bar (x2,y2,facecolor='green' ,width=3, label = ' Huawei ' )
- rects3 = ax.bar(x3, y3,facecolor= ='blue',width=3,label = ' Xiaomi )
- ax.set_ xticks (x3)
- #x轴在x3中的各坐标点下面加刻度
- ax. set_ xticklabels( ('A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4' , 'A5', 'A6') )
- #指定x轴上每- -刻度下方的文字
- ax. legend ()
- #显示右.上角三组图的说明
- def 1abe1 (ax , rects) : #在rects的每个柱子顶端标注数值
- for rect in rects :
- height = rect.get_ height()
- ax. text (rect.get_ x() + rect.get_ width() /2,
- height+14, str (height) , rotation=90) #文字旋转90度
- 1abe1 (ax, rects1)
- label (ax , rects2)
- labe1 (ax, rects3)
- p1t. show ()
4,绘制散点,折线图

- import math , random
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- def drawPlot(ax) :
- xs = [i / 100 for i in range (1500)] #1500个 点的横坐标,间隔0 .01
- ys = [10*math.sin(x) for X in xs]
- #对应曲线y=10*sin (x).上的1 500个点的y坐标
- ax.plot (xs,ys, "red" ,label = "Beijing") #画曲线y= =10*sin (x)
- ys = list (range(-18,18) )
- random. shuffle (ys)
- ax. scatter (range(16),ys[:16] ,c = "blue") #画散点
- ax.plot (range(16),ys[:16] ,"blue", label=" Shanghai") #画折线
- ax . legend ()
- #显示右.上角的各条折线说明
- ax.set xticks (range (16) )
- #x轴在坐标0,1.. .15处加刻度
- ax. set_ xticklabels (range (16)) #指定x轴每个刻度 下方显示的文字
- ax = plt. figure (figsize=(10,4) ,dpi=100) .add_ subp1ot() #图像长宽和清晰度
- drawP1ot (ax)
- p1t. show ()
5,绘制饼图

- import matplotlib.pyplot as p1t .
- def drawPie (ax) :
- 1bs = ( 'A','B', 'C',
- 'D' )
- #四个扇区的标签
- sectors = [16, 29.55, 44.45, 10]
- #四个扇区的份额(百分比)
- exp1 = [0, 0.1, 0,0]
- #四个扇区的突出程度
- ax.pie (x=sectors,labels=lbs, exp1ode=exp1,
- autopct=18.2f' , shadow=True, labeldistance=1 .1,
- pctdistance = 0 .6, startangle = 90)
- ax.set_ title ("pie sample")
- #饼图标题
- ax = p1t. figure() .add subp1ot()
- drawPie (ax)
- p1t. show()
6,绘制热力图

- import numpy as np
- from matplotlib import pyp1ot as plt
- data = np. random. randint(0,100, 30) .reshape (5,6)
- #生成一一个5行六列,元素[0, 100]内的随机矩阵
- xlabels = [ 'Beijing', ' Shanghai','Chengdu' ,
- ' Guangzhou',' Hangzhou',
- ' Wuhan' ]
- ylabels=['2016','2017','2018','2019','20201]
- ax = plt. figure (figsize=(10,8)) .add_ subp1ot()
- ax.set yticks (range (len (ylabels))) #y轴在坐标 [0 , len (ylabels))处加刻度
- ax.set_ yticklabels (ylabels) #设置y轴刻度文字
- ax. set_ xticks (range (len (xlabels) ) )
- ax.set xticklabels (xlabels)
- heatMp = ax. imshow (data,cmap=plt. cm.hot, aspect=' auto' ,
- vmin =0,vmax=100)
- for i in range (1en (x1abe1s) ) :
- for j in range (1en (y1abe1s) ) :
- ax. text(i,j ,data[j] [i] ,ha = "center" ,va = "center"
- color =
- "blue" ,size=26)
- p1t. colorbar (heatMp)
- #绘制右边的颜色-数值对照柱
- plt . xticks (rotation=45 , ha=" right") #将x轴刻度文字进行旋转, 且水平方向右对齐
- p1t. title ("Sales Volume (ton) ")
- p1t. show ()
7,绘制雷达图

- import matplotlib. pyplot as plt
- from matplotlib import rcParams
- #处理汉字用
- def drawRadar (ax) :
- pi = 3.1415926
- labels = ['EQ', 'IQ','人缘' , '魅力', '财富' , '体力'] #6个属性的名称
- attrNum = len (labels)
- #attrNum是属性种类数,处等于6
- data = [7 ,6,8,9,8,2]
- #六个属性的值
- angles = [2*pi *i/ attrNum for i in range (attrNum) ]
- #angles是以弧度为单位的6个属性对应的6条半径线的角度
- angles2 = [x * 180/pi for x in angles]
- #angles2是以角度为单位的6个属性对应的半径线的角度
- ax.set ylim(0,10)
- #限定半径线上的坐标范围
- ax. set_ thetagrids (angles2,labels , fontproperties="SimHei" )
- #绘制6个属性对应的6条半径
- ax. fi1l (angles,data, facecolor= ; : 6 'g' ,alpha= =0.25)
- #填充,alpha :透明度
- rcParams[' font. family'] = rcParams[' font. sans-serif'] = ' SimHei '
- #处理汉字
- ax = p1t. figure() . add_ subplot (projection = "polar")
- #生成极坐标形式子图
- drawRadar (ax)
- p1t. show ()
8,绘制多层雷达图

- import matplotlib.pyplot as p1t
- from ma tplot1ib import rcPar ams
- rcParams[ ' font. family'] = rcParams[ ' font. sans-serif'] = ' SimHei !
- pi = 3.1415926
- labels = ['EQ', 'IQ','人缘', '魅力',财富', '体力] #6个属性的名称
- attrNum = len (labels)
- names = (张三',李四'王五
- data = [[0.40,0.32,0.35] ,
- [0.85,0.35,0.30] ,
- [0.40,0.32,0.35],[0.40,0.82,0.75] ,
- [0.14,0.12,0.35] ,
- [0.80,0.92,0.35]]
- #三个人的数据
- angles = [2*pi*i/attrNum for i in range (attrNum) ]
- angles2 = [x * 180/pi for x in ang1es]
- ax = p1t. figure() .add_ subp1ot (projection = "polar")
- ax. set_ the tagrids (angles2 , labels)
- ax.set_ title('三巨头人格分析',y = 1.05) #y指明标题垂直位置
- ax. legend (names , 1oc=(0.95,0.9)) #画出右上角不同人的颜色说明
- plt. show ()
9,多子图绘制

- #程序中的import、汉字处理及drawRadar、 drawPie、 drawPlot函数略, 见前面程序
- fig = plt. figure (figsize=(8,8) )
- ax = fig.add subplot(2,2,1) #窗口分割成2*2,取位于第1个方格的子图
- drawPie (ax)
- ax = fig.add subplot(2 ,2 ,2 ,projection = "polar" )
- drawRadar (ax)
- ax = p1t. subp1ot2grid( (2, 2),(1, 0),colspan=2)
- #或写成: ax = fig.add subplot(2,1,2)
- drawPlot (ax)
- plt. figtext(0.05,0.05, ' subplot sample' )
- #显示左下角的图像标题
- plt. show ()
-
相关阅读:
【Linux】--- 详解Linux软件包管理器yum和编辑器vim
经典BN很NB,精读论文《Batch Normalization》
协议类型(总结为主,非详细)
机试(cs,se)
leetcode 1 两数之和
02_SpingBoot 入门案例
Linux系统下KVM虚拟机的基本管理和操作
基于单片机设计的防煤气泄漏装置
Linux忘记密码
debug技巧之使用arthas调试
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63309778/article/details/133471293
