-
Spring Controller内存马
获取当前上下文运行环境
getCurrentWebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext context = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();在SpringMVC环境下获取到的是一个XmlWebApplicationContext类型的Root WebApplicationContext:
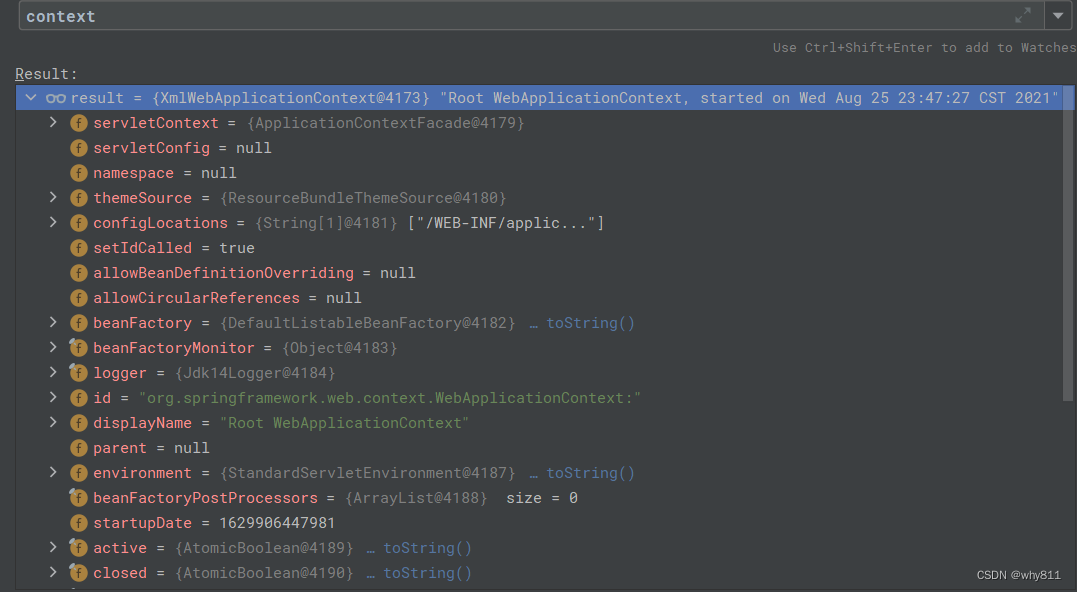
在Spring MVC环境中,由于使用xml文件默认配置了ContextLoaderListener,所以可以获取到Root Context:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 在SpringBoot环境下,默认没有xml文件配置listener,这里获取到的结果会是null。
WebApplicationContextUtils
在Spring环境中可以通过如下代码获取到ApplicationContext(Facade):
- ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
- // attributes.getRequest()获取到的是RequestFacade
- ServletContext servletContext = attributes.getRequest().getServletContext();
- // 最后获取到的servletContext是ApplicationContextFacade
这个servletContext的内部有一个Root Context的attribute:

这个Root Context可以通过WebApplicationContextUtils#getWebApplicationContext方法来获取:

- WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
- // 这里获取到的Root Context是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
值得说明的是,由于在SpringBoot环境中没有使用xml文件进行配置,所以区别与第一种方式获取的XmlWebApplicationContext,这里的Root Context获取到的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。(注解形式配置)
RequestContextUtils
通过ServletRequest类的实例来获取WebApplicationContext:
- ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
- HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
- WebApplicationContext context = RequestContextUtils.findWebApplicationContext(request);
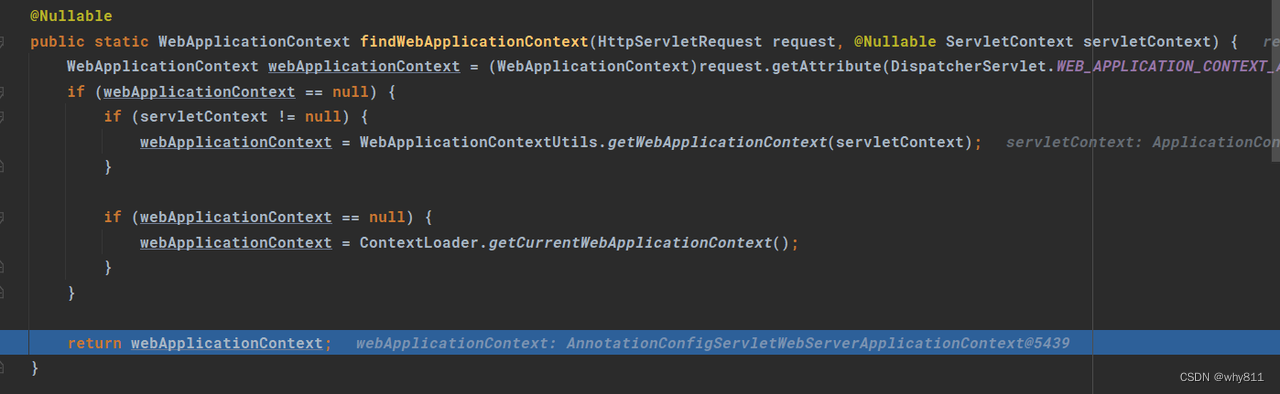
这个context是作为attribute放在request对象中的:
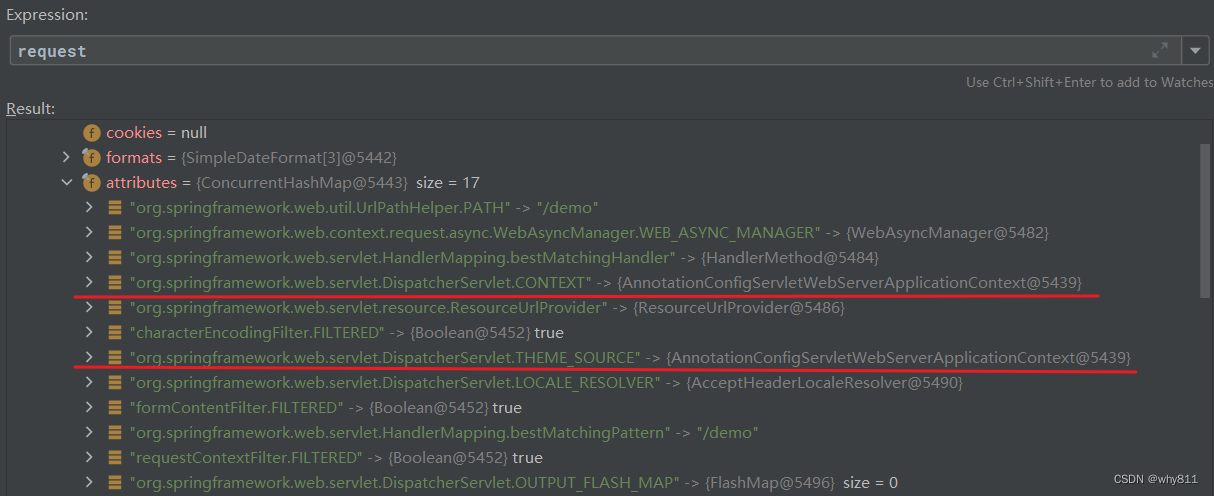
所以引申出了第四种方法,直接通过attribute的名字获取。
getAttribute
- ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
- WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) attributes.getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
attributes是ServletRequestAttributes的实例,其内部就有一个request对象的引用,通过调用getAttribute方法就可以从其内部的request对象里获取属性(0表示从request对象上获取属性,而不是从session对象上获取):

注意事项
前两种方式获取的到的是Root Context,后两种方式获取到的是Child Context,而Root Context无法获取Child Context中的Bean。
在有些MVC的配置中,开启注解扫描(component-scan)配置在
dispatcherServlet-servlet.xml中,导致RequestMappingHandlerMapping的Bean只存在于Child Context中,而使用前两种方式获取到的Root Context是无法拿到对应Bean的,所以推荐使用后两种方式获取上下文环境。手动注册Controller
Controller注册及查找原理
参考:SpringMVC源码之Controller查找原理 - 卧颜沉默 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
Spring2.5 ~ 3.1之间一般使用DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping映射器。
Spring3.1之后使用RequestMappingHandlerMapping映射器来支持对@Controller和@RequestMapping注解。
认识两个类(具体细节可以去看一眼源码):
- RequestMappingInfo类:对@RequestMapping注解的封装,里面包含了Http请求头的信息,如url,method等。
- HandlerMethod类:对Controller处理请求的方法的封装,里面包含了方法所属的bean、方法对应的method,参数等。
Controller注册
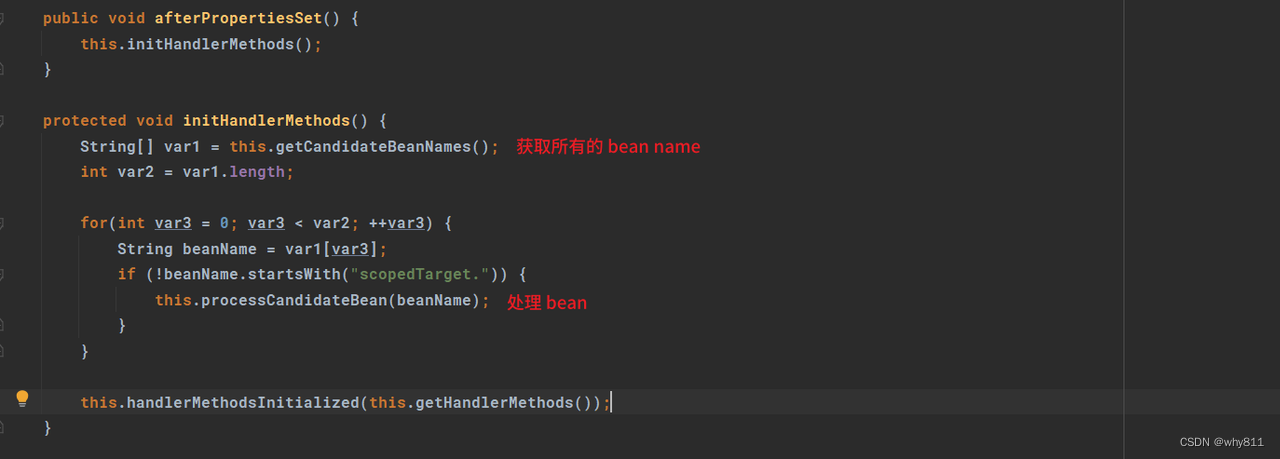
在Spring MVC初始化的时候,会进入RequestMappingHandlerMapping#afterPropertiesSet方法:

来到父类的afterPropertiesSet方法,AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet,这个方法会从context中查找出所有的bean然后进入processCandidateBean方法中处理:
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#processCandidateBean:
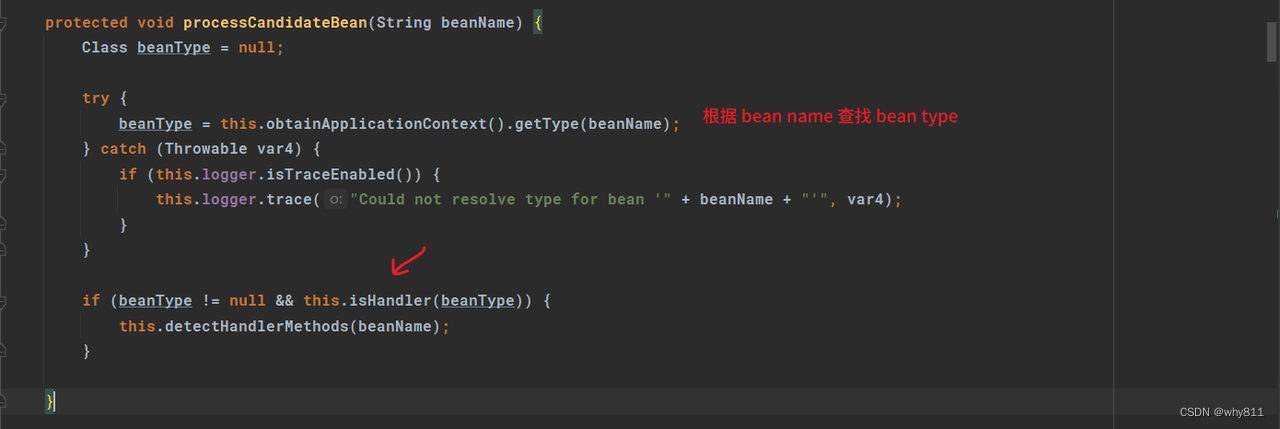
可以注意到isHandler方法,它会判断bean是否含有@Controller和@RequestMapping的注解:

之后来到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods方法,可以结合动调来看:

跟进RequestMappingHandlerMapping#getMappingForMethod方法中先根据method创建RequestMappingInfo实例:
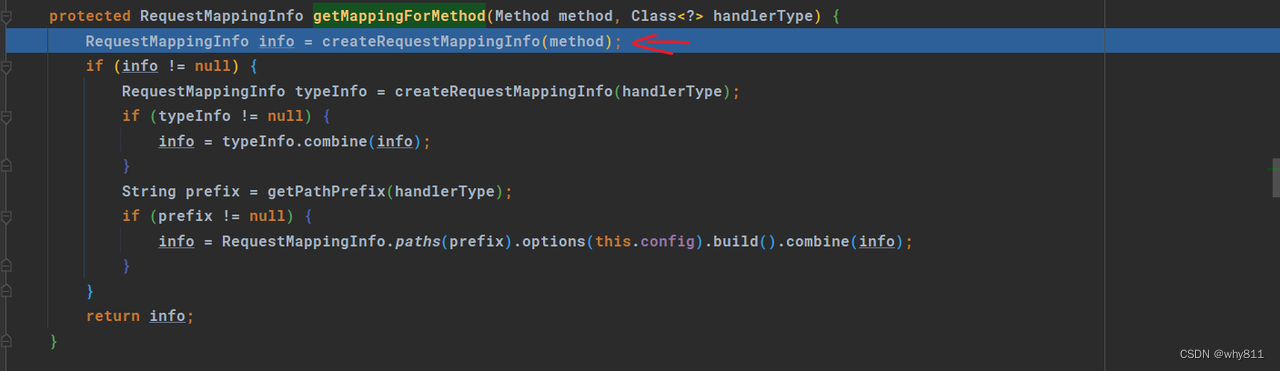
前面提到了这个类是对@RequestMapping注解的封装,跟进createRequestMappingInfo方法中:

再往后来到createRequestMappingInfo方法,它会根据RequestMapping封装的信息来build一个RequestMappingInfo实例然后返回:

处理完根据method寻找handler的逻辑之后,再回到detectHandlerMethods方法,来到了registerHandlerMethod方法来注册handler:

这个方法调用了AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry#register方法:

至此Controller的完成了注册,下面来看一个http请求过来的时候Controller的查找逻辑。
Controller查找
在处理http请求的时候首先会被DispatcherServelt所处理,在DispatcherServlet#doDispatch方法中会根据当前的request对象的请求路径(lookup path)来匹配相应的handler:
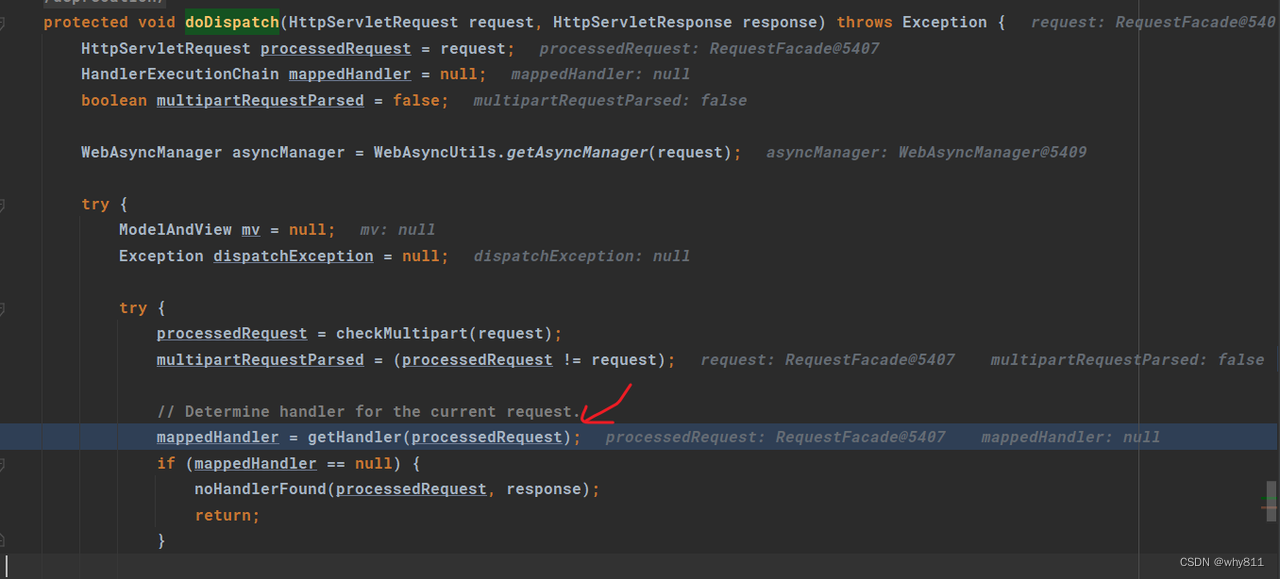
之后经过一系列调用(一直单步跟入就好了)会来到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod方法:

Controller的动态注册
registerMapping
最直接的一种方式,使用RequestMappingHandlerMapping#registerMapping来注册,最后还是调用了MappingRegistry#register方法:

- @RestController
- public class DemoController1 {
- @RequestMapping("/demo")
- public String demo() throws Exception {
- ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
- ServletContext servletContext = attributes.getRequest().getServletContext();
- WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
- // 从IoC容器中获取bean
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping handlerMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
- // 防止重复注册: RequestMappingHandlerMapping#getHandlerMethods 可以获取所有已注册handler的映射关系
- for (RequestMappingInfo info : handlerMapping.getHandlerMethods().keySet()) {
- if (info.toString().contains("/hello")) {
- return "Already injected";
- }
- }
- // 获取method
- Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.springboot.controller.MyController");
- Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethods()[0];
- // 获取mapping (RequestMappingInfo)
- RequestMappingInfo mapping = RequestMappingInfo
- .paths("/hello")
- .customCondition(new RequestMethodsRequestCondition())
- .build();
- // handler就是Controller的一个实例
- Object handler = new MyController();
- handlerMapping.registerMapping(mapping, handler, method);
- return "success";
- }
- }
最后的效果与待注册的Controller中方法的注解有关,如果方法添加了@ResponseBody注解,则会直接返回内容:
- public class MyController {
- @ResponseBody
- public String hello() {
- return "hello";
- }
- }
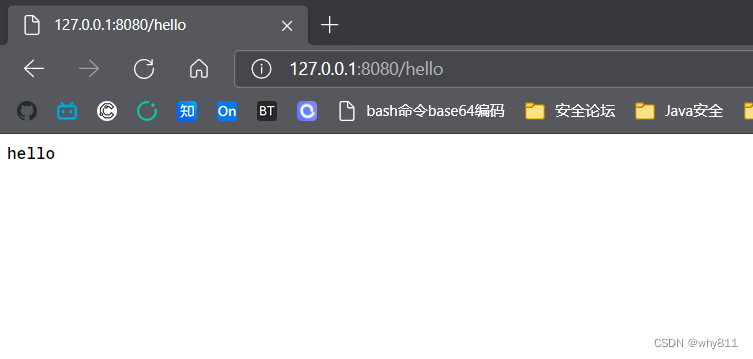
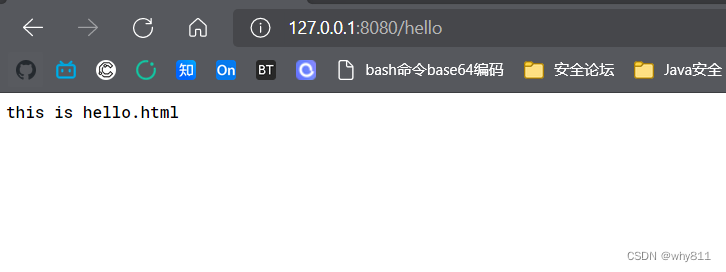
如果没有@ResponseBody注解,则会向view层解析(thymeleaf等模板引擎),这里是hello.html:
- public class MyController {
- public String hello() {
- return "hello";
- }
- }
detectHandlerMethods
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods这个方法在上文中的Controller注册部分提到过:
这里最后会调用registerHandlerMethod方法,之后还是来到了MappingRegistry#register方法:
- ...
- @RequestMapping("/demo2")
- public String demo2() throws Exception {
- ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
- ServletContext servletContext = attributes.getRequest().getServletContext();
- AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext context = (AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext) WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
- // 注册bean
- context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("MyController", new MyController());
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping handlerMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
- Method method = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("detectHandlerMethods", Object.class);
- method.setAccessible(true);
- method.invoke(handlerMapping,"MyController");
- return "demo2";
- }
- ...
这种方式必须在MyController中添加@RequestMapping注解,否则在detectHandlerMethods中无法获取到RequestMappingInfo对象。
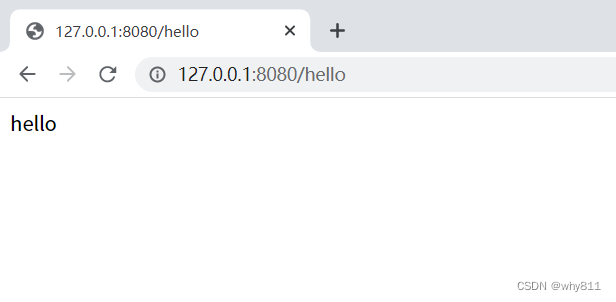
与上面一样,如果有@ResponseBody注解,则会直接返回:
- public class MyController {
- @RequestMapping("/hello")
- @ResponseBody
- public String hello() {
- return "hello";
- }
- }
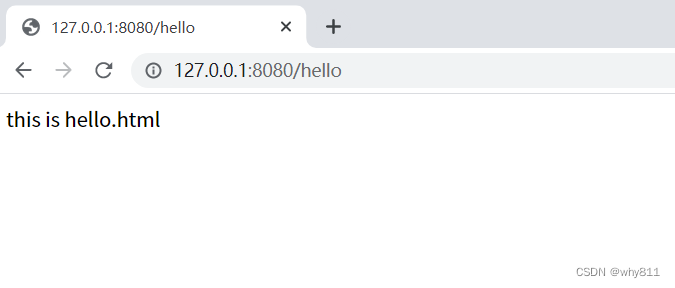
没有@ResponseBody注解,则会向view层解析:
- public class MyController {
- @RequestMapping("/hello")
- public String hello() {
- return "hello";
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
从元宇宙、地产数字化到呼叫中心,华为云携手伙伴共创新价值
GLTF和GLB的区别,各自生成方法
考察进制转化 十进制转为二进制
OpenCV Radon变换探测直线(拉东变换)
芯科蓝牙BG27开发笔记4-SSV5 IDE的使用
MySQL存储过程手册,及创建存储过程:循环为所有表添加字段
KVM虚拟机热扩容
nginx之location的优先级和nginx的重定向
cmdline(一):cmdline是什么?&&cmdline怎么添加?
PCM编码格式
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/why811/article/details/133348187
